BREAKING NEWS
LATEST POSTS
-
Lagoa Multiphysics new simulation solver for Autodesk Softimage
http://features.cgsociety.org/story_custom.php?story_id=5866
FEATURED POSTS
-
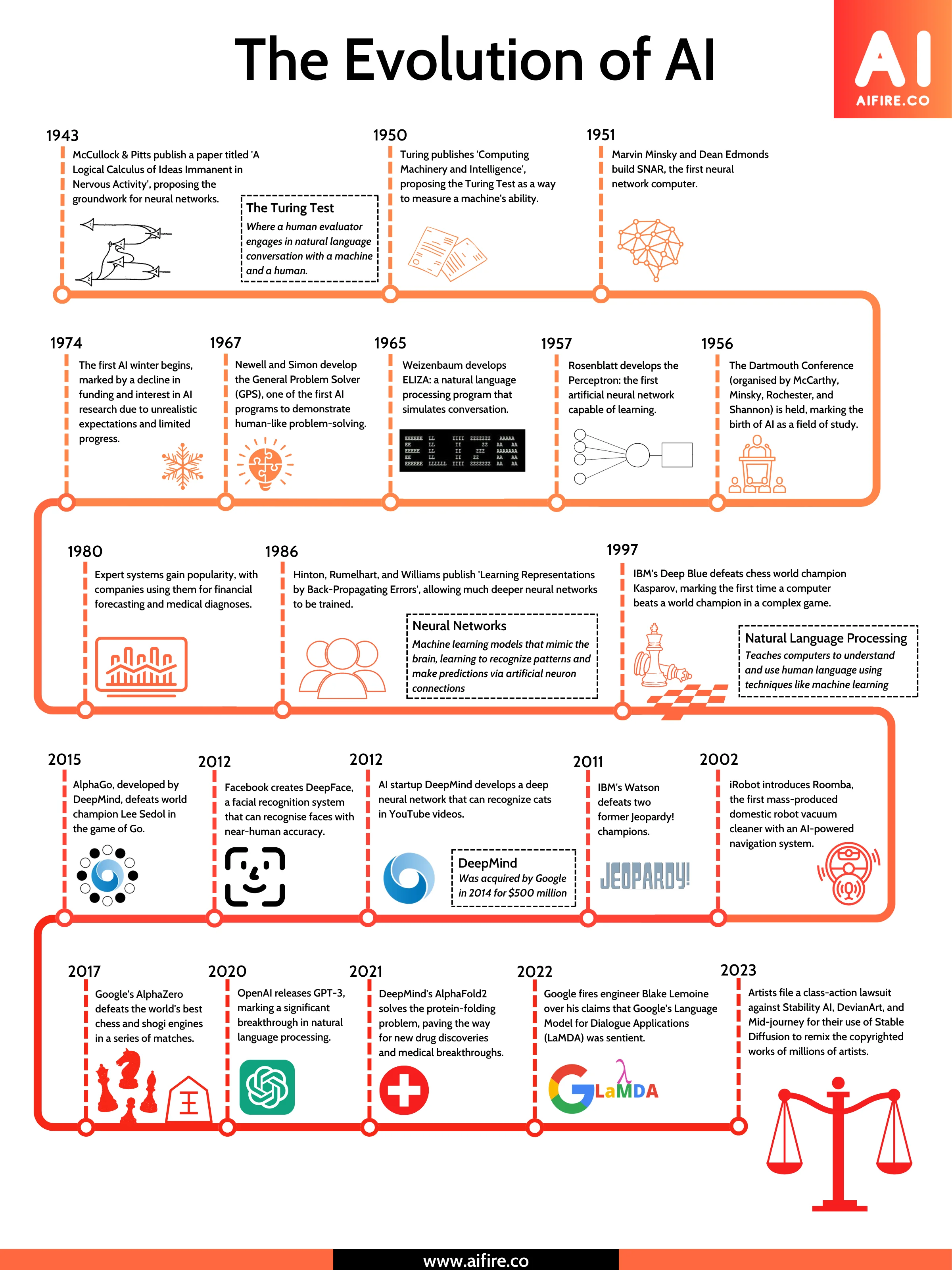
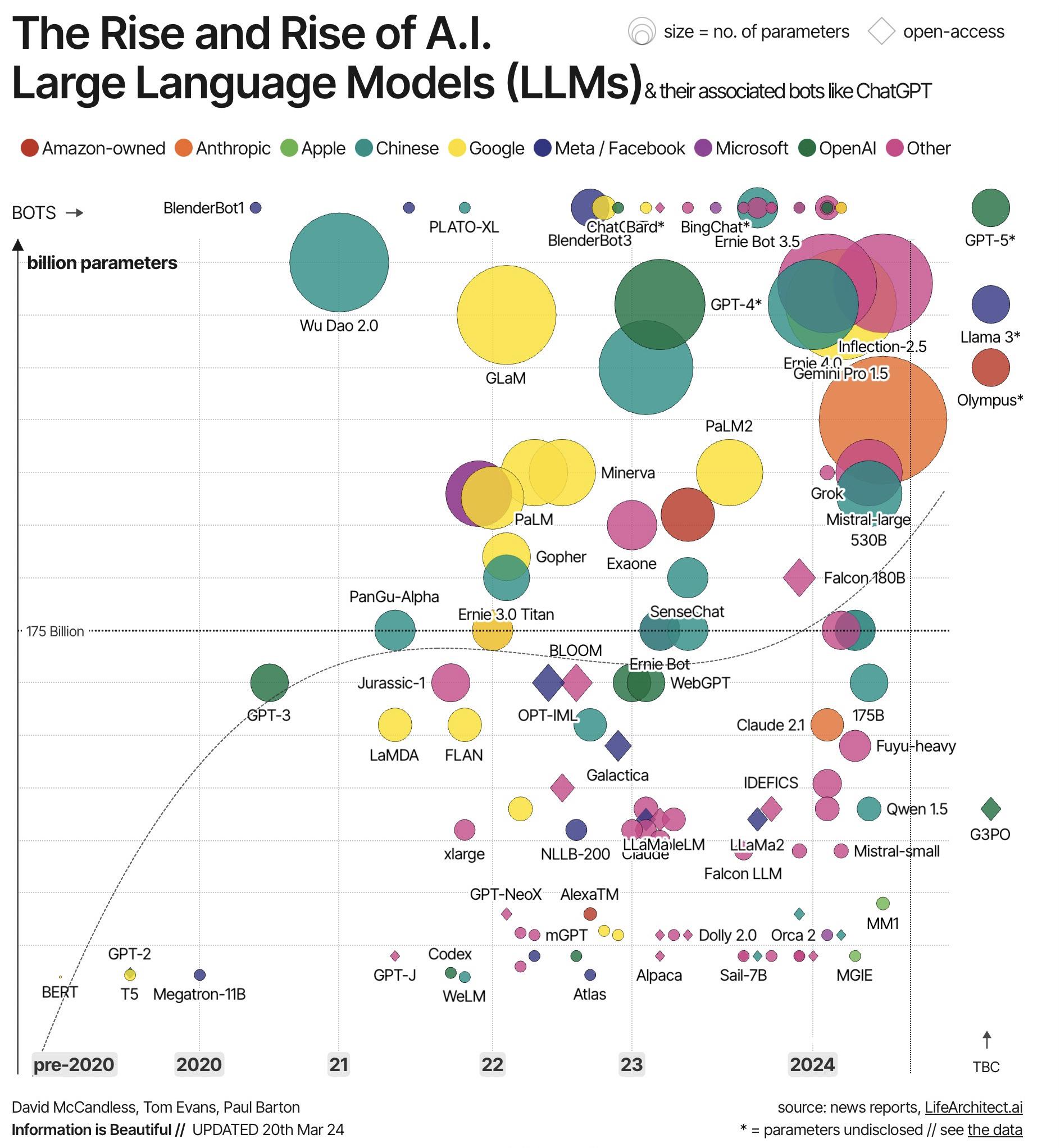
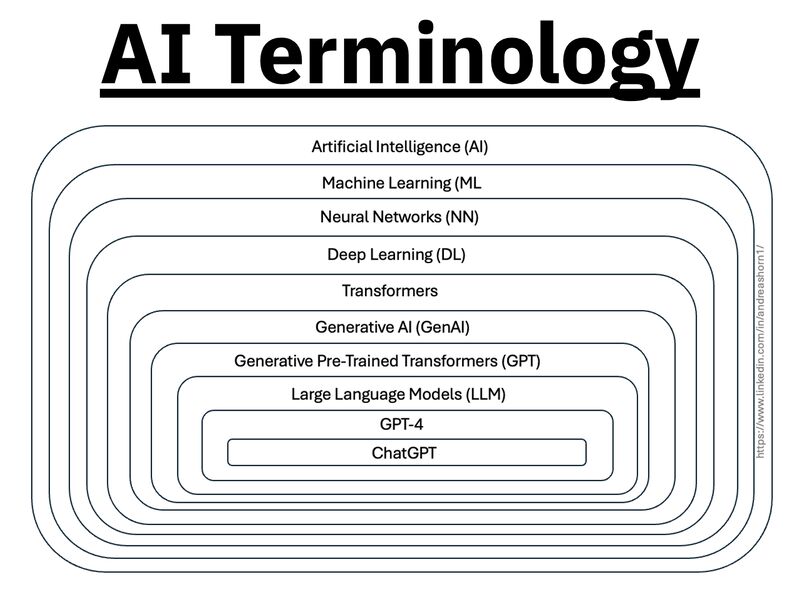
The History, Evolution and Rise of AI
https://medium.com/@lmpo/a-brief-history-of-ai-with-deep-learning-26f7948bc87b
🔹 1943: 𝗠𝗰𝗖𝘂𝗹𝗹𝗼𝗰𝗵 & 𝗣𝗶𝘁𝘁𝘀 create the first artificial neuron.
🔹 1950: 𝗔𝗹𝗮𝗻 𝗧𝘂𝗿𝗶𝗻𝗴 introduces the Turing Test, forever changing the way we view intelligence.
🔹 1956: 𝗝𝗼𝗵𝗻 𝗠𝗰𝗖𝗮𝗿𝘁𝗵𝘆 coins the term “Artificial Intelligence,” marking the official birth of the field.
🔹 1957: 𝗙𝗿𝗮𝗻𝗸 𝗥𝗼𝘀𝗲𝗻𝗯𝗹𝗮𝘁𝘁 invents the Perceptron, one of the first neural networks.
🔹 1959: 𝗕𝗲𝗿𝗻𝗮𝗿𝗱 𝗪𝗶𝗱𝗿𝗼𝘄 and 𝗧𝗲𝗱 𝗛𝗼𝗳𝗳 create ADALINE, a model that would shape neural networks.
🔹 1969: 𝗠𝗶𝗻𝘀𝗸𝘆 & 𝗣𝗮𝗽𝗲𝗿𝘁 solve the XOR problem, but also mark the beginning of the “first AI winter.”
🔹 1980: 𝗞𝘂𝗻𝗶𝗵𝗶𝗸𝗼 𝗙𝘂𝗸𝘂𝘀𝗵𝗶𝗺𝗮 introduces Neocognitron, laying the groundwork for deep learning.
🔹 1986: 𝗚𝗲𝗼𝗳𝗳𝗿𝗲𝘆 𝗛𝗶𝗻𝘁𝗼𝗻 and 𝗗𝗮𝘃𝗶𝗱 𝗥𝘂𝗺𝗲𝗹𝗵𝗮𝗿𝘁 introduce backpropagation, making neural networks viable again.
🔹 1989: 𝗝𝘂𝗱𝗲𝗮 𝗣𝗲𝗮𝗿𝗹 advances UAT (Understanding and Reasoning), building a foundation for AI’s logical abilities.
🔹 1995: 𝗩𝗹𝗮𝗱𝗶𝗺𝗶𝗿 𝗩𝗮𝗽𝗻𝗶𝗸 and 𝗖𝗼𝗿𝗶𝗻𝗻𝗮 𝗖𝗼𝗿𝘁𝗲𝘀 develop Support Vector Machines (SVMs), a breakthrough in machine learning.
🔹 1998: 𝗬𝗮𝗻𝗻 𝗟𝗲𝗖𝘂𝗻 popularizes Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), revolutionizing image recognition.
🔹 2006: 𝗚𝗲𝗼𝗳𝗳𝗿𝗲𝘆 𝗛𝗶𝗻𝘁𝗼𝗻 and 𝗥𝘂𝘀𝗹𝗮𝗻 𝗦𝗮𝗹𝗮𝗸𝗵𝘂𝘁𝗱𝗶𝗻𝗼𝘃 introduce deep belief networks, reigniting interest in deep learning.
🔹 2012: 𝗔𝗹𝗲𝘅 𝗞𝗿𝗶𝘇𝗵𝗲𝘃𝘀𝗸𝘆 and 𝗚𝗲𝗼𝗳𝗳𝗿𝗲𝘆 𝗛𝗶𝗻𝘁𝗼𝗻 launch AlexNet, sparking the modern AI revolution in deep learning.
🔹 2014: 𝗜𝗮𝗻 𝗚𝗼𝗼𝗱𝗳𝗲𝗹𝗹𝗼𝘄 introduces Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), opening new doors for AI creativity.
🔹 2017: 𝗔𝘀𝗵𝗶𝘀𝗵 𝗩𝗮𝘀𝘄𝗮𝗻𝗶 and team introduce Transformers, redefining natural language processing (NLP).
🔹 2020: OpenAI unveils GPT-3, setting a new standard for language models and AI’s capabilities.
🔹 2022: OpenAI releases ChatGPT, democratizing conversational AI and bringing it to the masses.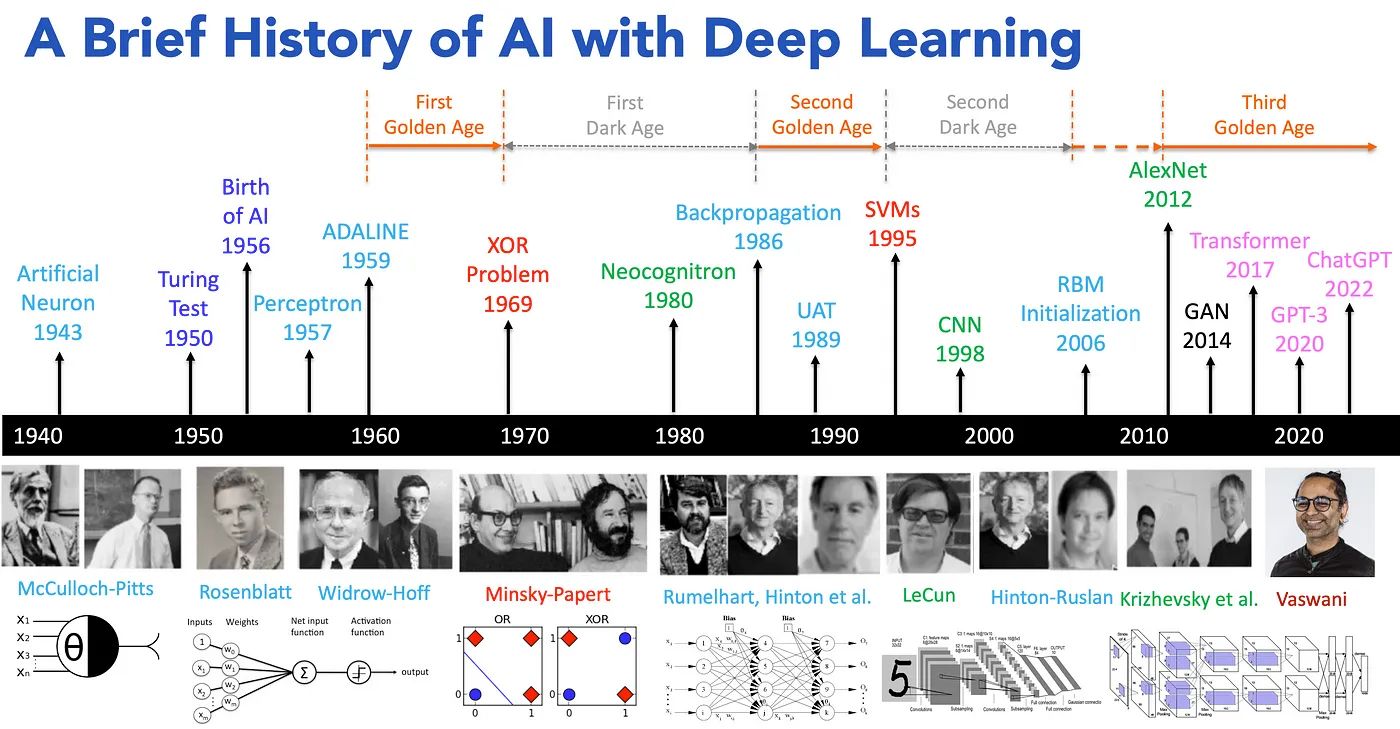
-
Sun cone angle (angular diameter) as perceived by earth viewers
Also see:
https://www.pixelsham.com/2020/08/01/solid-angle-measures/
The cone angle of the sun refers to the angular diameter of the sun as observed from Earth, which is related to the apparent size of the sun in the sky.
The angular diameter of the sun, or the cone angle of the sunlight as perceived from Earth, is approximately 0.53 degrees on average. This value can vary slightly due to the elliptical nature of Earth’s orbit around the sun, but it generally stays within a narrow range.
Here’s a more precise breakdown:
-
- Average Angular Diameter: About 0.53 degrees (31 arcminutes)
- Minimum Angular Diameter: Approximately 0.52 degrees (when Earth is at aphelion, the farthest point from the sun)
- Maximum Angular Diameter: Approximately 0.54 degrees (when Earth is at perihelion, the closest point to the sun)
This angular diameter remains relatively constant throughout the day because the sun’s distance from Earth does not change significantly over a single day.
To summarize, the cone angle of the sun’s light, or its angular diameter, is typically around 0.53 degrees, regardless of the time of day.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Angular_diameter
-




