COMPOSITION
-
Composition – These are the basic lighting techniques you need to know for photography and film
Read more: Composition – These are the basic lighting techniques you need to know for photography and filmhttp://www.diyphotography.net/basic-lighting-techniques-need-know-photography-film/
Amongst the basic techniques, there’s…
1- Side lighting – Literally how it sounds, lighting a subject from the side when they’re faced toward you
2- Rembrandt lighting – Here the light is at around 45 degrees over from the front of the subject, raised and pointing down at 45 degrees
3- Back lighting – Again, how it sounds, lighting a subject from behind. This can help to add drama with silouettes
4- Rim lighting – This produces a light glowing outline around your subject
5- Key light – The main light source, and it’s not necessarily always the brightest light source
6- Fill light – This is used to fill in the shadows and provide detail that would otherwise be blackness
7- Cross lighting – Using two lights placed opposite from each other to light two subjects
-
Photography basics: Camera Aspect Ratio, Sensor Size and Depth of Field – resolutions
Read more: Photography basics: Camera Aspect Ratio, Sensor Size and Depth of Field – resolutionshttp://www.shutterangle.com/2012/cinematic-look-aspect-ratio-sensor-size-depth-of-field/
http://www.shutterangle.com/2012/film-video-aspect-ratio-artistic-choice/
DESIGN
COLOR
-
Light and Matter : The 2018 theory of Physically-Based Rendering and Shading by Allegorithmic
Read more: Light and Matter : The 2018 theory of Physically-Based Rendering and Shading by Allegorithmicacademy.substance3d.com/courses/the-pbr-guide-part-1
academy.substance3d.com/courses/the-pbr-guide-part-2
Local copy:
-
THOMAS MANSENCAL – The Apparent Simplicity of RGB Rendering
Read more: THOMAS MANSENCAL – The Apparent Simplicity of RGB Renderinghttps://thomasmansencal.substack.com/p/the-apparent-simplicity-of-rgb-rendering
The primary goal of physically-based rendering (PBR) is to create a simulation that accurately reproduces the imaging process of electro-magnetic spectrum radiation incident to an observer. This simulation should be indistinguishable from reality for a similar observer.
Because a camera is not sensitive to incident light the same way than a human observer, the images it captures are transformed to be colorimetric. A project might require infrared imaging simulation, a portion of the electro-magnetic spectrum that is invisible to us. Radically different observers might image the same scene but the act of observing does not change the intrinsic properties of the objects being imaged. Consequently, the physical modelling of the virtual scene should be independent of the observer.
-
sRGB vs REC709 – An introduction and FFmpeg implementations
Read more: sRGB vs REC709 – An introduction and FFmpeg implementations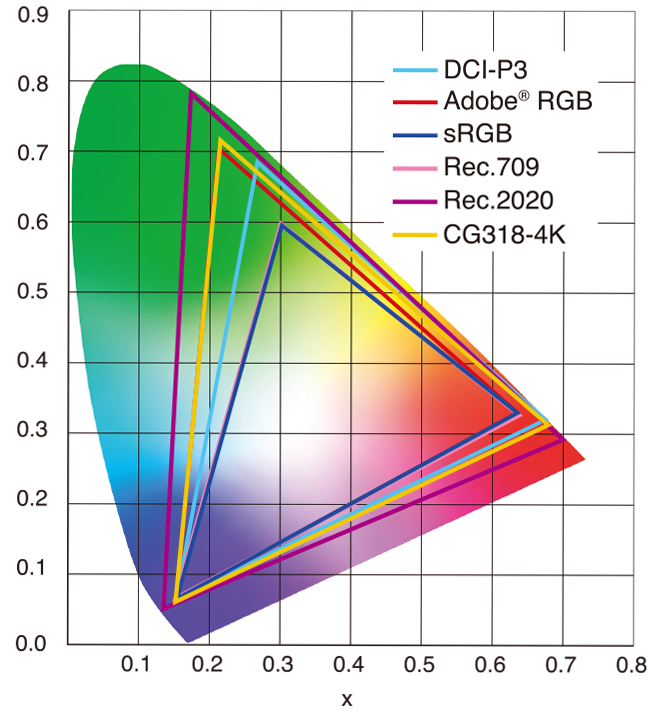
1. Basic Comparison
- What they are
- sRGB: A standard “web”/computer-display RGB color space defined by IEC 61966-2-1. It’s used for most monitors, cameras, printers, and the vast majority of images on the Internet.
- Rec. 709: An HD-video color space defined by ITU-R BT.709. It’s the go-to standard for HDTV broadcasts, Blu-ray discs, and professional video pipelines.
- Why they exist
- sRGB: Ensures consistent colors across different consumer devices (PCs, phones, webcams).
- Rec. 709: Ensures consistent colors across video production and playback chains (cameras → editing → broadcast → TV).
- What you’ll see
- On your desktop or phone, images tagged sRGB will look “right” without extra tweaking.
- On an HDTV or video-editing timeline, footage tagged Rec. 709 will display accurate contrast and hue on broadcast-grade monitors.
2. Digging Deeper
Feature sRGB Rec. 709 White point D65 (6504 K), same for both D65 (6504 K) Primaries (x,y) R: (0.640, 0.330) G: (0.300, 0.600) B: (0.150, 0.060) R: (0.640, 0.330) G: (0.300, 0.600) B: (0.150, 0.060) Gamut size Identical triangle on CIE 1931 chart Identical to sRGB Gamma / transfer Piecewise curve: approximate 2.2 with linear toe Pure power-law γ≈2.4 (often approximated as 2.2 in practice) Matrix coefficients N/A (pure RGB usage) Y = 0.2126 R + 0.7152 G + 0.0722 B (Rec. 709 matrix) Typical bit-depth 8-bit/channel (with 16-bit variants) 8-bit/channel (10-bit for professional video) Usage metadata Tagged as “sRGB” in image files (PNG, JPEG, etc.) Tagged as “bt709” in video containers (MP4, MOV) Color range Full-range RGB (0–255) Studio-range Y′CbCr (Y′ [16–235], Cb/Cr [16–240])
Why the Small Differences Matter
(more…) - What they are
-
mmColorTarget – Nuke Gizmo for color matching a MacBeth chart
Read more: mmColorTarget – Nuke Gizmo for color matching a MacBeth charthttps://www.marcomeyer-vfx.de/posts/2014-04-11-mmcolortarget-nuke-gizmo/
https://www.marcomeyer-vfx.de/posts/mmcolortarget-nuke-gizmo/
https://vimeo.com/9.1652466e+07
https://www.nukepedia.com/gizmos/colour/mmcolortarget
-
Practical Aspects of Spectral Data and LEDs in Digital Content Production and Virtual Production – SIGGRAPH 2022
Read more: Practical Aspects of Spectral Data and LEDs in Digital Content Production and Virtual Production – SIGGRAPH 2022Comparison to the commercial side

https://www.ecolorled.com/blog/detail/what-is-rgb-rgbw-rgbic-strip-lights
RGBW (RGB + White) LED strip uses a 4-in-1 LED chip made up of red, green, blue, and white.
RGBWW (RGB + White + Warm White) LED strip uses either a 5-in-1 LED chip with red, green, blue, white, and warm white for color mixing. The only difference between RGBW and RGBWW is the intensity of the white color. The term RGBCCT consists of RGB and CCT. CCT (Correlated Color Temperature) means that the color temperature of the led strip light can be adjusted to change between warm white and white. Thus, RGBWW strip light is another name of RGBCCT strip.
RGBCW is the acronym for Red, Green, Blue, Cold, and Warm. These 5-in-1 chips are used in supper bright smart LED lighting products
-
Victor Perez – ACES Color Management in DaVinci Resolve
Read more: Victor Perez – ACES Color Management in DaVinci Resolvehttpv://www.youtube.com/watch?v=i–TS88-6xA
-
Polarised vs unpolarized filtering
Read more: Polarised vs unpolarized filteringA light wave that is vibrating in more than one plane is referred to as unpolarized light. …
Polarized light waves are light waves in which the vibrations occur in a single plane. The process of transforming unpolarized light into polarized light is known as polarization.
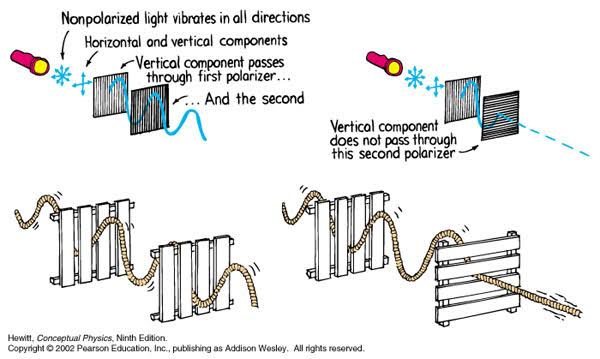
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polarizing_filter_(photography)
The most common use of polarized technology is to reduce lighting complexity on the subject.
(more…)
Details such as glare and hard edges are not removed, but greatly reduced.
LIGHTING
-
What is the Light Field?
Read more: What is the Light Field?http://lightfield-forum.com/what-is-the-lightfield/
The light field consists of the total of all light rays in 3D space, flowing through every point and in every direction.
How to Record a Light Field
- a single, robotically controlled camera
- a rotating arc of cameras
- an array of cameras or camera modules
- a single camera or camera lens fitted with a microlens array
-
Convert between light exposure and intensity
Read more: Convert between light exposure and intensityimport math,sys def Exposure2Intensity(exposure): exp = float(exposure) result = math.pow(2,exp) print(result) Exposure2Intensity(0) def Intensity2Exposure(intensity): inarg = float(intensity) if inarg == 0: print("Exposure of zero intensity is undefined.") return if inarg < 1e-323: inarg = max(inarg, 1e-323) print("Exposure of negative intensities is undefined. Clamping to a very small value instead (1e-323)") result = math.log(inarg, 2) print(result) Intensity2Exposure(0.1)Why Exposure?
Exposure is a stop value that multiplies the intensity by 2 to the power of the stop. Increasing exposure by 1 results in double the amount of light.
Artists think in “stops.” Doubling or halving brightness is easy math and common in grading and look-dev.
Exposure counts doublings in whole stops:- +1 stop = ×2 brightness
- −1 stop = ×0.5 brightness
This gives perceptually even controls across both bright and dark values.
Why Intensity?
Intensity is linear.
It’s what render engines and compositors expect when:- Summing values
- Averaging pixels
- Multiplying or filtering pixel data
Use intensity when you need the actual math on pixel/light data.
Formulas (from your Python)
- Intensity from exposure: intensity = 2**exposure
- Exposure from intensity: exposure = log₂(intensity)
Guardrails:
- Intensity must be > 0 to compute exposure.
- If intensity = 0 → exposure is undefined.
- Clamp tiny values (e.g.
1e−323) before using log₂.
Use Exposure (stops) when…
- You want artist-friendly sliders (−5…+5 stops)
- Adjusting look-dev or grading in even stops
- Matching plates with quick ±1 stop tweaks
- Tweening brightness changes smoothly across ranges
Use Intensity (linear) when…
- Storing raw pixel/light values
- Multiplying textures or lights by a gain
- Performing sums, averages, and filters
- Feeding values to render engines expecting linear data
Examples
- +2 stops → 2**2 = 4.0 (×4)
- +1 stop → 2**1 = 2.0 (×2)
- 0 stop → 2**0 = 1.0 (×1)
- −1 stop → 2**(−1) = 0.5 (×0.5)
- −2 stops → 2**(−2) = 0.25 (×0.25)
- Intensity 0.1 → exposure = log₂(0.1) ≈ −3.32
Rule of thumb
Think in stops (exposure) for controls and matching.
Compute in linear (intensity) for rendering and math. -
Terminators and Iron Men: HDRI, Image-based lighting and physical shading at ILM – Siggraph 2010
Read more: Terminators and Iron Men: HDRI, Image-based lighting and physical shading at ILM – Siggraph 2010
COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
-
HDRI Median Cut plugin
-
Game Development tips
-
What’s the Difference Between Ray Casting, Ray Tracing, Path Tracing and Rasterization? Physical light tracing…
-
Advanced Computer Vision with Python OpenCV and Mediapipe
-
Sensitivity of human eye
-
Daniele Tosti Interview for the magazine InCG, Taiwan, Issue 28, 201609
-
What Is The Resolution and view coverage Of The human Eye. And what distance is TV at best?
-
GretagMacbeth Color Checker Numeric Values and Middle Gray
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.