COMPOSITION
DESIGN
COLOR
-
Practical Aspects of Spectral Data and LEDs in Digital Content Production and Virtual Production – SIGGRAPH 2022
Read more: Practical Aspects of Spectral Data and LEDs in Digital Content Production and Virtual Production – SIGGRAPH 2022Comparison to the commercial side

https://www.ecolorled.com/blog/detail/what-is-rgb-rgbw-rgbic-strip-lights
RGBW (RGB + White) LED strip uses a 4-in-1 LED chip made up of red, green, blue, and white.
RGBWW (RGB + White + Warm White) LED strip uses either a 5-in-1 LED chip with red, green, blue, white, and warm white for color mixing. The only difference between RGBW and RGBWW is the intensity of the white color. The term RGBCCT consists of RGB and CCT. CCT (Correlated Color Temperature) means that the color temperature of the led strip light can be adjusted to change between warm white and white. Thus, RGBWW strip light is another name of RGBCCT strip.
RGBCW is the acronym for Red, Green, Blue, Cold, and Warm. These 5-in-1 chips are used in supper bright smart LED lighting products
-
HDR and Color
Read more: HDR and Colorhttps://www.soundandvision.com/content/nits-and-bits-hdr-and-color
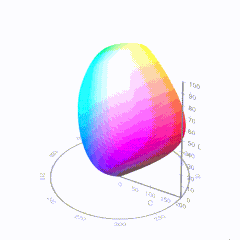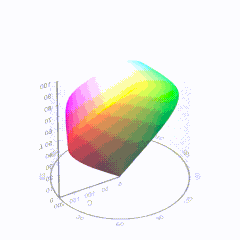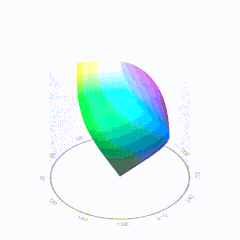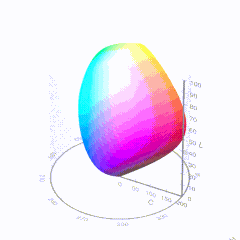
In HD we often refer to the range of available colors as a color gamut. Such a color gamut is typically plotted on a two-dimensional diagram, called a CIE chart, as shown in at the top of this blog. Each color is characterized by its x/y coordinates.
Good enough for government work, perhaps. But for HDR, with its higher luminance levels and wider color, the gamut becomes three-dimensional.
For HDR the color gamut therefore becomes a characteristic we now call the color volume. It isn’t easy to show color volume on a two-dimensional medium like the printed page or a computer screen, but one method is shown below. As the luminance becomes higher, the picture eventually turns to white. As it becomes darker, it fades to black. The traditional color gamut shown on the CIE chart is simply a slice through this color volume at a selected luminance level, such as 50%.
Three different color volumes—we still refer to them as color gamuts though their third dimension is important—are currently the most significant. The first is BT.709 (sometimes referred to as Rec.709), the color gamut used for pre-UHD/HDR formats, including standard HD.
The largest is known as BT.2020; it encompasses (roughly) the range of colors visible to the human eye (though ET might find it insufficient!).
Between these two is the color gamut used in digital cinema, known as DCI-P3.
sRGB
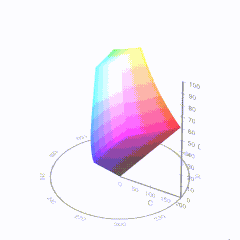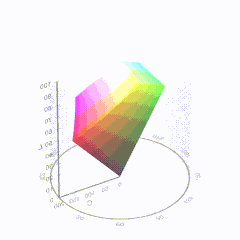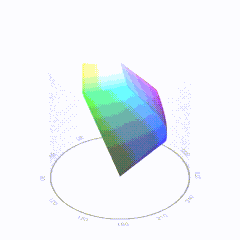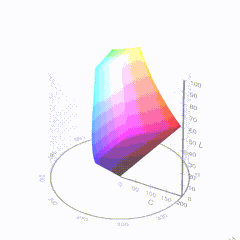
D65
LIGHTING
-
What is physically correct lighting all about?
Read more: What is physically correct lighting all about?http://gamedev.stackexchange.com/questions/60638/what-is-physically-correct-lighting-all-about
2012-08 Nathan Reed wrote:
Physically-based shading means leaving behind phenomenological models, like the Phong shading model, which are simply built to “look good” subjectively without being based on physics in any real way, and moving to lighting and shading models that are derived from the laws of physics and/or from actual measurements of the real world, and rigorously obey physical constraints such as energy conservation.
For example, in many older rendering systems, shading models included separate controls for specular highlights from point lights and reflection of the environment via a cubemap. You could create a shader with the specular and the reflection set to wildly different values, even though those are both instances of the same physical process. In addition, you could set the specular to any arbitrary brightness, even if it would cause the surface to reflect more energy than it actually received.
In a physically-based system, both the point light specular and the environment reflection would be controlled by the same parameter, and the system would be set up to automatically adjust the brightness of both the specular and diffuse components to maintain overall energy conservation. Moreover you would want to set the specular brightness to a realistic value for the material you’re trying to simulate, based on measurements.
Physically-based lighting or shading includes physically-based BRDFs, which are usually based on microfacet theory, and physically correct light transport, which is based on the rendering equation (although heavily approximated in the case of real-time games).
It also includes the necessary changes in the art process to make use of these features. Switching to a physically-based system can cause some upsets for artists. First of all it requires full HDR lighting with a realistic level of brightness for light sources, the sky, etc. and this can take some getting used to for the lighting artists. It also requires texture/material artists to do some things differently (particularly for specular), and they can be frustrated by the apparent loss of control (e.g. locking together the specular highlight and environment reflection as mentioned above; artists will complain about this). They will need some time and guidance to adapt to the physically-based system.
On the plus side, once artists have adapted and gained trust in the physically-based system, they usually end up liking it better, because there are fewer parameters overall (less work for them to tweak). Also, materials created in one lighting environment generally look fine in other lighting environments too. This is unlike more ad-hoc models, where a set of material parameters might look good during daytime, but it comes out ridiculously glowy at night, or something like that.
Here are some resources to look at for physically-based lighting in games:
SIGGRAPH 2013 Physically Based Shading Course, particularly the background talk by Naty Hoffman at the beginning. You can also check out the previous incarnations of this course for more resources.
Sébastien Lagarde, Adopting a physically-based shading model and Feeding a physically-based shading model
And of course, I would be remiss if I didn’t mention Physically-Based Rendering by Pharr and Humphreys, an amazing reference on this whole subject and well worth your time, although it focuses on offline rather than real-time rendering.
-
What is the Light Field?
Read more: What is the Light Field?http://lightfield-forum.com/what-is-the-lightfield/
The light field consists of the total of all light rays in 3D space, flowing through every point and in every direction.
How to Record a Light Field
- a single, robotically controlled camera
- a rotating arc of cameras
- an array of cameras or camera modules
- a single camera or camera lens fitted with a microlens array
-
Composition – 5 tips for creating perfect cinematic lighting and making your work look stunning
Read more: Composition – 5 tips for creating perfect cinematic lighting and making your work look stunninghttp://www.diyphotography.net/5-tips-creating-perfect-cinematic-lighting-making-work-look-stunning/
1. Learn the rules of lighting
2. Learn when to break the rules
3. Make your key light larger
4. Reverse keying
5. Always be backlighting
-
studiobinder.com – What is Tenebrism and Hard Lighting — The Art of Light and Shadow and chiaroscuro Explained
Read more: studiobinder.com – What is Tenebrism and Hard Lighting — The Art of Light and Shadow and chiaroscuro Explainedhttps://www.studiobinder.com/blog/what-is-tenebrism-art-definition/
https://www.studiobinder.com/blog/what-is-hard-light-photography/
COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.








