COMPOSITION
-
Types of Film Lights and their efficiency – CRI, Color Temperature and Luminous Efficacy
Read more: Types of Film Lights and their efficiency – CRI, Color Temperature and Luminous Efficacynofilmschool.com/types-of-film-lights
“Not every light performs the same way. Lights and lighting are tricky to handle. You have to plan for every circumstance. But the good news is, lighting can be adjusted. Let’s look at different factors that affect lighting in every scene you shoot. ”
Use CRI, Luminous Efficacy and color temperature controls to match your needs.
Color Temperature
Color temperature describes the “color” of white light by a light source radiated by a perfect black body at a given temperature measured in degrees Kelvinhttps://www.pixelsham.com/2019/10/18/color-temperature/
CRI
“The Color Rendering Index is a measurement of how faithfully a light source reveals the colors of whatever it illuminates, it describes the ability of a light source to reveal the color of an object, as compared to the color a natural light source would provide. The highest possible CRI is 100. A CRI of 100 generally refers to a perfect black body, like a tungsten light source or the sun. ”https://www.studiobinder.com/blog/what-is-color-rendering-index/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Color_rendering_index
Light source CCT (K) CRI Low-pressure sodium (LPS/SOX) 1800 −44 Clear mercury-vapor 6410 17 High-pressure sodium (HPS/SON) 2100 24 Coated mercury-vapor 3600 49 Halophosphate warm-white fluorescent 2940 51 Halophosphate cool-white fluorescent 4230 64 Tri-phosphor warm-white fluorescent 2940 73 Halophosphate cool-daylight fluorescent 6430 76 “White” SON 2700 82 Standard LED Lamp 2700–5000 83 Quartz metal halide 4200 85 Tri-phosphor cool-white fluorescent 4080 89 High-CRI LED lamp (blue LED) 2700–5000 95 Ceramic discharge metal-halide lamp 5400 96 Ultra-high-CRI LED lamp (violet LED) 2700–5000 99 Incandescent/halogen bulb 3200 100 Luminous Efficacy
Luminous efficacy is a measure of how well a light source produces visible light, watts out versus watts in, measured in lumens per watt. In other words it is a measurement that indicates the ability of a light source to emit visible light using a given amount of power. It is a ratio of the visible energy to the power that goes into the bulb.FILM LIGHT TYPES
Consumer light types
Tungsten Lights
Light interiors and match domestic places or office locations. Daylight.Advantages of Tungsten Lights
Almost perfect color rendition
Low cost
Does not use mercury like CFLs (fluorescent) or mercury vapor lights
Better color temperature than standard tungsten
Longer life than a conventional incandescent
Instant on to full brightness, no warm-up time, and it is dimmableDisadvantages of Tungsten Lights
Extremely hot
High power requirement
The lamp is sensitive to oils and cannot be touched
The bulb is capable of blowing and sending hot glass shards outward. A screen or layer of glass on the outside of the lamp can protect users.Hydrargyrum medium-arc iodide lights
HMI’s are used when high output is required. They are also used to recreate sun shining through windows or to fake additional sun while shooting exteriors. HMIs can light huge areas at once.Advantages of HMI lights
High light output
Higher efficiency
High color temperatureDisadvantages of HMI lights:
High cost
High power requirement
Dims only to about 50%
the color temperature increases with dimming
HMI bulbs will explode is dropped and release toxic chemicalsFluorescent
Fluorescent film lighting is achieved by laying multiple tubes next to each other, combining as many as you want for the desired brightness. The good news is you can choose your bulbs to either be warm or cool depending on the scenario you’re shooting. You want to get these bulbs close to the subject because they’re not great at opening up spaces. Fluorescent lighting is used to light interiors and is more compact and cooler than tungsten or HMI lighting.Advantages of Fluorescent lights
High efficiency
Low power requirement
Low cost
Long lamp life
Cool
Capable of soft even lighting over a large area
LightweightDisadvantages of Fluorescent lights
Flicker
High CRI
Domestic tubes have low CRI & poor color rendition.LED
LED’s are more and more common on film sets. You can use batteries to power them. That makes them portable and sleek – no messy cabled needed. You can rig your own panels of LED lights to fit any space necessary as well. LED’s can also power Fresnel style lamp heads such as the Arri L-series.Advantages of LED light
Soft, even lighting
Pure light without UV-artifacts
High efficiency
Low power consumption, can be battery powered
Excellent dimming by means of pulse width modulation control
Long lifespan
Environmentally friendly
Insensitive to shock
No risk of explosionDisadvantages of LED light
High cost.
LED’s are currently still expensive for their total light output -
Composition – cinematography Cheat Sheet
Read more: Composition – cinematography Cheat SheetWhere is our eye attracted first? Why?
Size. Focus. Lighting. Color.
Size. Mr. White (Harvey Keitel) on the right.
Focus. He’s one of the two objects in focus.
Lighting. Mr. White is large and in focus and Mr. Pink (Steve Buscemi) is highlighted by
a shaft of light.
Color. Both are black and white but the read on Mr. White’s shirt now really stands out.
What type of lighting?-> High key lighting.
Features bright, even illumination and few conspicuous shadows. This lighting key is often used in musicals and comedies.Low key lighting
Features diffused shadows and atmospheric pools of light. This lighting key is often used in mysteries and thrillers.High contrast lighting
Features harsh shafts of lights and dramatic streaks of blackness. This type of lighting is often used in tragedies and melodramas.What type of shot?
Extreme long shot
Taken from a great distance, showing much of the locale. Ifpeople are included in these shots, they usually appear as mere specks-> Long shot
Corresponds to the space between the audience and the stage in a live theater. The long shots show the characters and some of the locale.Full shot
Range with just enough space to contain the human body in full. The full shot shows the character and a minimal amount of the locale.Medium shot
Shows the human figure from the knees or waist up.Close-Up
Concentrates on a relatively small object and show very little if any locale.Extreme close-up
Focuses on an unnaturally small portion of an object, giving that part great detail and symbolic significance.What angle?
Bird’s-eye view.
The shot is photographed directly from above. This type of shot can be disorienting, and the people photographed seem insignificant.High angle.
This angle reduces the size of the objects photographed. A person photographed from this angle seems harmless and insignificant, but to a lesser extent than with the bird’s-eye view.-> Eye-level shot.
The clearest view of an object, but seldom intrinsically dramatic, because it tends to be the norm.Low angle.
This angle increases high and a sense of verticality, heightening the importance of the object photographed. A person shot from this angle is given a sense of power and respect.Oblique angle.
For this angle, the camera is tilted laterally, giving the image a slanted appearance. Oblique angles suggest tension, transition, a impending movement. They are also called canted or dutch angles.What is the dominant color?
The use of color in this shot is symbolic. The scene is set in warehouse. Both the set and characters are blues, blacks and whites.
This was intentional allowing for the scenes and shots with blood to have a great level of contrast.
What is the Lens/Filter/Stock?
Telephoto lens.
A lens that draws objects closer but also diminishes the illusion of depth.Wide-angle lens.
A lens that takes in a broad area and increases the illusion of depth but sometimes distorts the edges of the image.Fast film stock.
Highly sensitive to light, it can register an image with little illumination. However, the final product tends to be grainy.Slow film stock.
Relatively insensitive to light, it requires a great deal of illumination. The final product tends to look polished.The lens is not wide-angle because there isn’t a great sense of depth, nor are several planes in focus. The lens is probably long but not necessarily a telephoto lens because the depth isn’t inordinately compressed.
The stock is fast because of the grainy quality of the image.
Subsidiary Contrast; where does the eye go next?
The two guns.
How much visual information is packed into the image? Is the texture stark, moderate, or highly detailed?
Minimalist clutter in the warehouse allows a focus on a character driven thriller.
What is the Composition?
Horizontal.
Compositions based on horizontal lines seem visually at rest and suggest placidity or peacefulness.Vertical.
Compositions based on vertical lines seem visually at rest and suggest strength.-> Diagonal.
Compositions based on diagonal, or oblique, lines seem dynamic and suggest tension or anxiety.-> Binary. Binary structures emphasize parallelism.
Triangle.
Triadic compositions stress the dynamic interplay among three mainCircle.
Circular compositions suggest security and enclosure.Is the form open or closed? Does the image suggest a window that arbitrarily isolates a fragment of the scene? Or a proscenium arch, in which the visual elements are carefully arranged and held in balance?
The most nebulous of all the categories of mise en scene, the type of form is determined by how consciously structured the mise en scene is. Open forms stress apparently simple techniques, because with these unself-conscious methods the filmmaker is able to emphasize the immediate, the familiar, the intimate aspects of reality. In open-form images, the frame tends to be deemphasized. In closed form images, all the necessary information is carefully structured within the confines of the frame. Space seems enclosed and self-contained rather than continuous.
Could argue this is a proscenium arch because this is such a classic shot with parallels and juxtapositions.
Is the framing tight or loose? Do the character have no room to move around, or can they move freely without impediments?
Shots where the characters are placed at the edges of the frame and have little room to move around within the frame are considered tight.
Longer shots, in which characters have room to move around within the frame, are considered loose and tend to suggest freedom.
Center-framed giving us the entire scene showing isolation, place and struggle.
Depth of Field. On how many planes is the image composed (how many are in focus)? Does the background or foreground comment in any way on the mid-ground?
Standard DOF, one background and clearly defined foreground.
Which way do the characters look vis-a-vis the camera?
An actor can be photographed in any of five basic positions, each conveying different psychological overtones.
Full-front (facing the camera):
the position with the most intimacy. The character is looking in our direction, inviting our complicity.Quarter Turn:
the favored position of most filmmakers. This position offers a high degree of intimacy but with less emotional involvement than the full-front.-> Profile (looking of the frame left or right):
More remote than the quarter turn, the character in profile seems unaware of being observed, lost in his or her own thoughts.Three-quarter Turn:
More anonymous than the profile, this position is useful for conveying a character’s unfriendly or antisocial feelings, for in effect, the character is partially turning his or her back on us, rejecting our interest.Back to Camera:
The most anonymous of all positions, this position is often used to suggest a character’s alienation from the world. When a character has his or her back to the camera, we can only guess what’s taking place internally, conveying a sense of concealment, or mystery.How much space is there between the characters?
Extremely close, for a gunfight.
The way people use space can be divided into four proxemic patterns.
Intimate distances.
The intimate distance ranges from skin contact to about eighteen inches away. This is the distance of physical involvement–of love, comfort, and tenderness between individuals.-> Personal distances.
The personal distance ranges roughly from eighteen inches away to about four feet away. These distances tend to be reserved for friends and acquaintances. Personal distances preserve the privacy between individuals, yet these rages don’t necessarily suggest exclusion, as intimate distances often do.Social distances.
The social distance rages from four feet to about twelve feet. These distances are usually reserved for impersonal business and casual social gatherings. It’s a friendly range in most cases, yet somewhat more formal than the personal distance.Public distances.
The public distance extends from twelve feet to twenty-five feet or more. This range tends to be formal and rather detached.
DESIGN
COLOR
-
The Color of Infinite Temperature
Read more: The Color of Infinite TemperatureThis is the color of something infinitely hot.

Of course you’d instantly be fried by gamma rays of arbitrarily high frequency, but this would be its spectrum in the visible range.
johncarlosbaez.wordpress.com/2022/01/16/the-color-of-infinite-temperature/
This is also the color of a typical neutron star. They’re so hot they look the same.
It’s also the color of the early Universe!This was worked out by David Madore.
The color he got is sRGB(148,177,255).
www.htmlcsscolor.com/hex/94B1FFAnd according to the experts who sip latte all day and make up names for colors, this color is called ‘Perano’.
-
Björn Ottosson – OKHSV and OKHSL – Two new color spaces for color picking
Read more: Björn Ottosson – OKHSV and OKHSL – Two new color spaces for color pickinghttps://bottosson.github.io/misc/colorpicker
https://bottosson.github.io/posts/colorpicker/
https://www.smashingmagazine.com/2024/10/interview-bjorn-ottosson-creator-oklab-color-space/
One problem with sRGB is that in a gradient between blue and white, it becomes a bit purple in the middle of the transition. That’s because sRGB really isn’t created to mimic how the eye sees colors; rather, it is based on how CRT monitors work. That means it works with certain frequencies of red, green, and blue, and also the non-linear coding called gamma. It’s a miracle it works as well as it does, but it’s not connected to color perception. When using those tools, you sometimes get surprising results, like purple in the gradient.
There were also attempts to create simple models matching human perception based on XYZ, but as it turned out, it’s not possible to model all color vision that way. Perception of color is incredibly complex and depends, among other things, on whether it is dark or light in the room and the background color it is against. When you look at a photograph, it also depends on what you think the color of the light source is. The dress is a typical example of color vision being very context-dependent. It is almost impossible to model this perfectly.
I based Oklab on two other color spaces, CIECAM16 and IPT. I used the lightness and saturation prediction from CIECAM16, which is a color appearance model, as a target. I actually wanted to use the datasets used to create CIECAM16, but I couldn’t find them.
IPT was designed to have better hue uniformity. In experiments, they asked people to match light and dark colors, saturated and unsaturated colors, which resulted in a dataset for which colors, subjectively, have the same hue. IPT has a few other issues but is the basis for hue in Oklab.
In the Munsell color system, colors are described with three parameters, designed to match the perceived appearance of colors: Hue, Chroma and Value. The parameters are designed to be independent and each have a uniform scale. This results in a color solid with an irregular shape. The parameters are designed to be independent and each have a uniform scale. This results in a color solid with an irregular shape. Modern color spaces and models, such as CIELAB, Cam16 and Björn Ottosson own Oklab, are very similar in their construction.
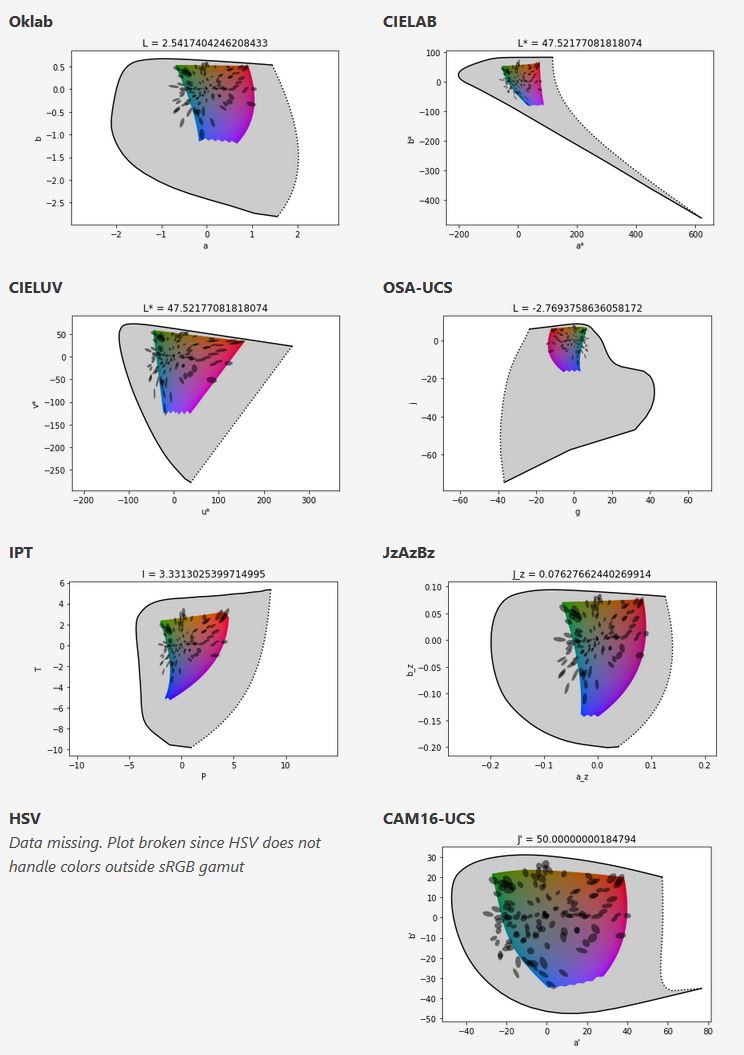
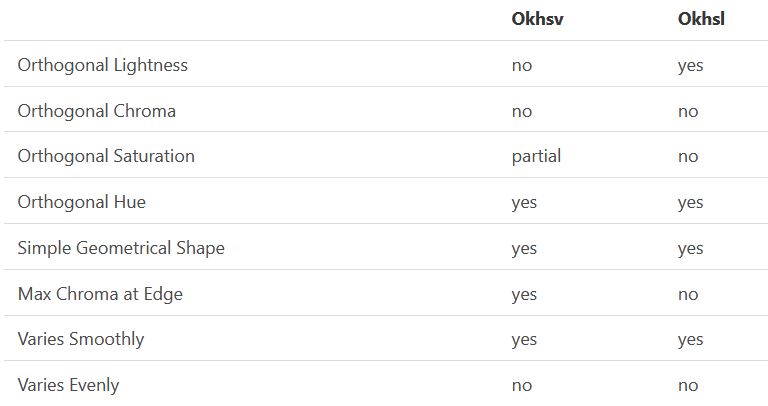
By far the most used color spaces today for color picking are HSL and HSV, two representations introduced in the classic 1978 paper “Color Spaces for Computer Graphics”. HSL and HSV designed to roughly correlate with perceptual color properties while being very simple and cheap to compute.
Today HSL and HSV are most commonly used together with the sRGB color space.

One of the main advantages of HSL and HSV over the different Lab color spaces is that they map the sRGB gamut to a cylinder. This makes them easy to use since all parameters can be changed independently, without the risk of creating colors outside of the target gamut.
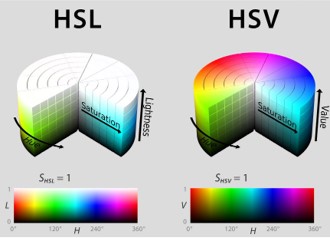
The main drawback on the other hand is that their properties don’t match human perception particularly well.
Reconciling these conflicting goals perfectly isn’t possible, but given that HSV and HSL don’t use anything derived from experiments relating to human perception, creating something that makes a better tradeoff does not seem unreasonable.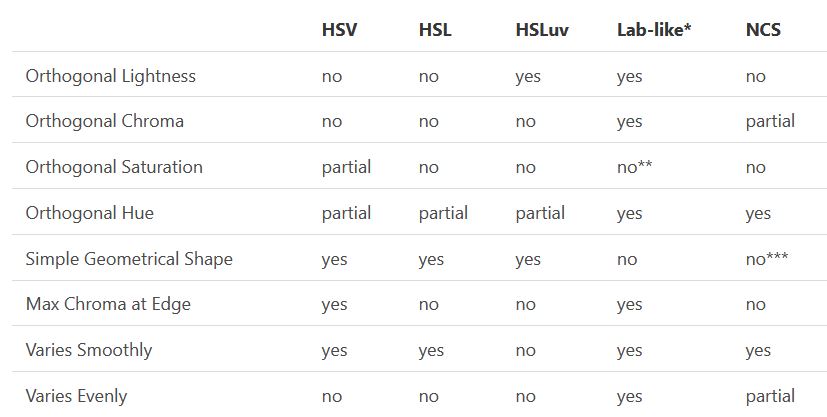
With this new lightness estimate, we are ready to look into the construction of Okhsv and Okhsl.
-
Björn Ottosson – How software gets color wrong
Read more: Björn Ottosson – How software gets color wronghttps://bottosson.github.io/posts/colorwrong/
Most software around us today are decent at accurately displaying colors. Processing of colors is another story unfortunately, and is often done badly.
To understand what the problem is, let’s start with an example of three ways of blending green and magenta:
- Perceptual blend – A smooth transition using a model designed to mimic human perception of color. The blending is done so that the perceived brightness and color varies smoothly and evenly.
- Linear blend – A model for blending color based on how light behaves physically. This type of blending can occur in many ways naturally, for example when colors are blended together by focus blur in a camera or when viewing a pattern of two colors at a distance.
- sRGB blend – This is how colors would normally be blended in computer software, using sRGB to represent the colors.
Let’s look at some more examples of blending of colors, to see how these problems surface more practically. The examples use strong colors since then the differences are more pronounced. This is using the same three ways of blending colors as the first example.
Instead of making it as easy as possible to work with color, most software make it unnecessarily hard, by doing image processing with representations not designed for it. Approximating the physical behavior of light with linear RGB models is one easy thing to do, but more work is needed to create image representations tailored for image processing and human perception.
Also see:
-
Sensitivity of human eye
Read more: Sensitivity of human eyehttp://www.wikilectures.eu/index.php/Spectral_sensitivity_of_the_human_eye
http://www.normankoren.com/Human_spectral_sensitivity_small.jpg
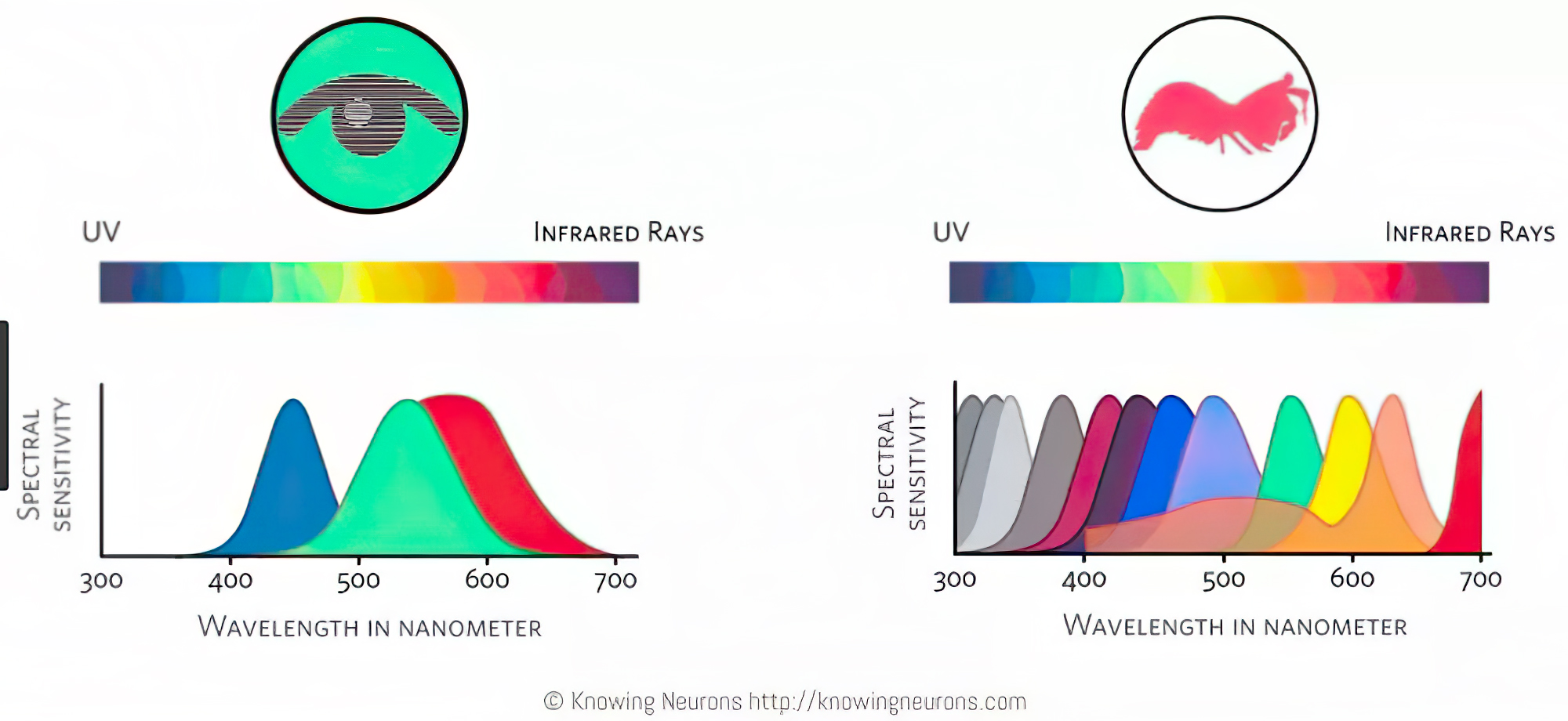
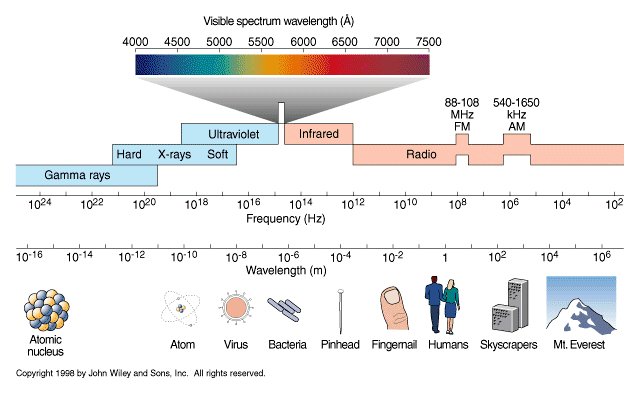
Spectral sensitivity of eye is influenced by light intensity. And the light intensity determines the level of activity of cones cell and rod cell. This is the main characteristic of human vision. Sensitivity to individual colors, in other words, wavelengths of the light spectrum, is explained by the RGB (red-green-blue) theory. This theory assumed that there are three kinds of cones. It’s selectively sensitive to red (700-630 nm), green (560-500 nm), and blue (490-450 nm) light. And their mutual interaction allow to perceive all colors of the spectrum.
http://weeklysciencequiz.blogspot.com/2013/01/violet-skies-are-for-birds.html

Sensitivity of human eye Sensitivity of human eyes to light increase with the decrease in light intensity. In day-light condition, the cones cell is responding to this condition. And the eye is most sensitive at 555 nm. In darkness condition, the rod cell is responding to this condition. And the eye is most sensitive at 507 nm.
As light intensity decreases, cone function changes more effective way. And when decrease the light intensity, it prompt to accumulation of rhodopsin. Furthermore, in activates rods, it allow to respond to stimuli of light in much lower intensity.
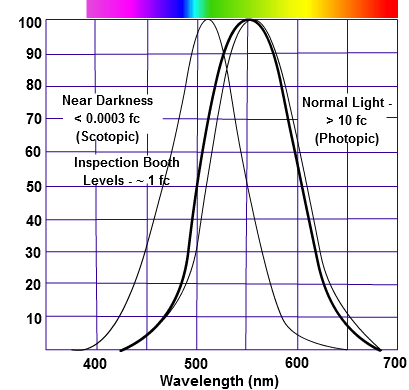
The three curves in the figure above shows the normalized response of an average human eye to various amounts of ambient light. The shift in sensitivity occurs because two types of photoreceptors called cones and rods are responsible for the eye’s response to light. The curve on the right shows the eye’s response under normal lighting conditions and this is called the photopic response. The cones respond to light under these conditions.
As mentioned previously, cones are composed of three different photo pigments that enable color perception. This curve peaks at 555 nanometers, which means that under normal lighting conditions, the eye is most sensitive to a yellowish-green color. When the light levels drop to near total darkness, the response of the eye changes significantly as shown by the scotopic response curve on the left. At this level of light, the rods are most active and the human eye is more sensitive to the light present, and less sensitive to the range of color. Rods are highly sensitive to light but are comprised of a single photo pigment, which accounts for the loss in ability to discriminate color. At this very low light level, sensitivity to blue, violet, and ultraviolet is increased, but sensitivity to yellow and red is reduced. The heavier curve in the middle represents the eye’s response at the ambient light level found in a typical inspection booth. This curve peaks at 550 nanometers, which means the eye is most sensitive to yellowish-green color at this light level. Fluorescent penetrant inspection materials are designed to fluoresce at around 550 nanometers to produce optimal sensitivity under dim lighting conditions.

-
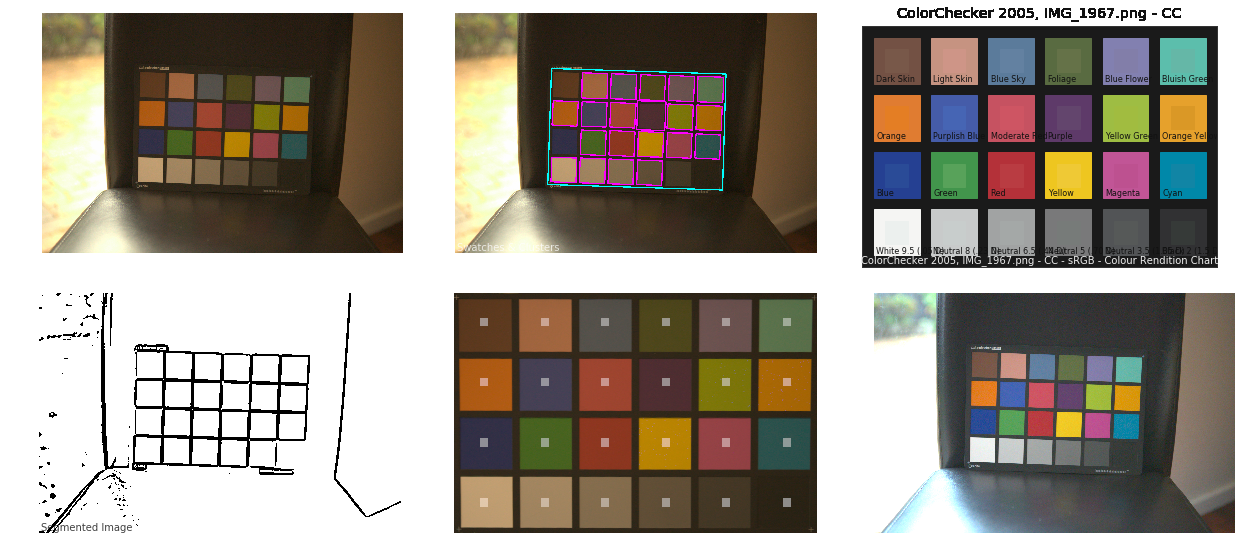
Colour – MacBeth Chart Checker Detection
Read more: Colour – MacBeth Chart Checker Detectiongithub.com/colour-science/colour-checker-detection
A Python package implementing various colour checker detection algorithms and related utilities.
-
“Reality” is constructed by your brain. Here’s what that means, and why it matters.
Read more: “Reality” is constructed by your brain. Here’s what that means, and why it matters.“Fix your gaze on the black dot on the left side of this image. But wait! Finish reading this paragraph first. As you gaze at the left dot, try to answer this question: In what direction is the object on the right moving? Is it drifting diagonally, or is it moving up and down?”

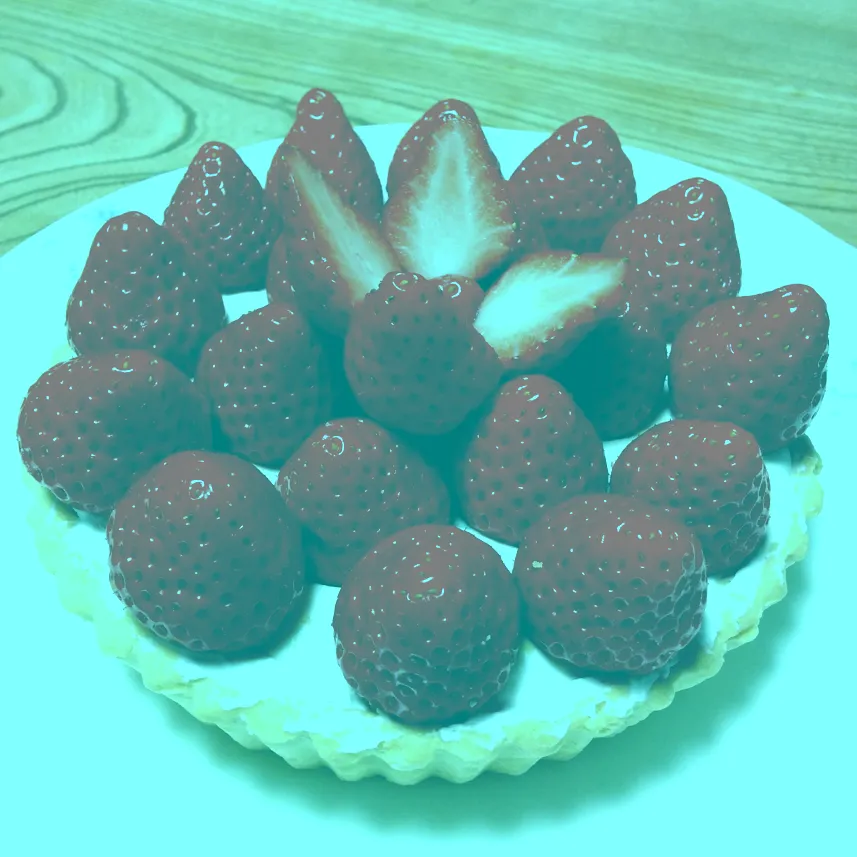
What color are these strawberries?

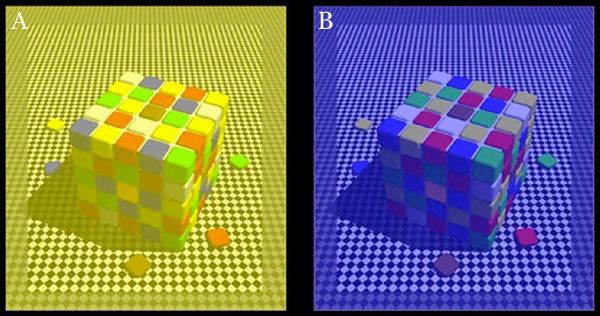
Are A and B the same gray?

-
No one could see the colour blue until modern times
Read more: No one could see the colour blue until modern timeshttps://www.businessinsider.com/what-is-blue-and-how-do-we-see-color-2015-2

The way that humans see the world… until we have a way to describe something, even something so fundamental as a colour, we may not even notice that something it’s there.
Ancient languages didn’t have a word for blue — not Greek, not Chinese, not Japanese, not Hebrew, not Icelandic cultures. And without a word for the colour, there’s evidence that they may not have seen it at all.
https://www.wnycstudios.org/story/211119-colors
Every language first had a word for black and for white, or dark and light. The next word for a colour to come into existence — in every language studied around the world — was red, the colour of blood and wine.
After red, historically, yellow appears, and later, green (though in a couple of languages, yellow and green switch places). The last of these colours to appear in every language is blue.
The only ancient culture to develop a word for blue was the Egyptians — and as it happens, they were also the only culture that had a way to produce a blue dye.
https://mymodernmet.com/shades-of-blue-color-history/
https://www.msn.com/en-us/news/technology/scientists-recreate-lost-recipes-for-a-5-000-year-old-egyptian-blue-dye/ar-AA1FXcj1
Assessment of process variability and color in synthesized and ancient Egyptian blue pigments | npj Heritage ScienceThe approximately 5,000-year-old dye wasn’t a single color, but instead encompassed a range of hues, from deep blues to duller grays and greens. Artisans first crafted Egyptian blue during the Fourth Dynasty (roughly 2613 to 2494 BCE) from recipes reliant on calcium-copper silicate. These techniques were later adopted by Romans in lieu of more expensive materials like lapis lazuli and turquoise. But the additional ingredient lists were lost to history by the time of the Renaissance.
McCloy’s team confirmed that cuprorivaite—the naturally occurring mineral equivalent to Egyptian blue—remains the primary color influence in each hue. Despite the presence of other components, Egyptian blue appears as a uniform color after the cuprorivaite becomes encased in colorless particles such as silicate during the heating process.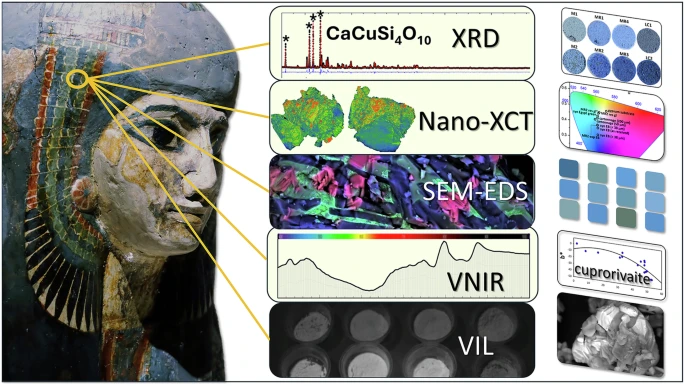
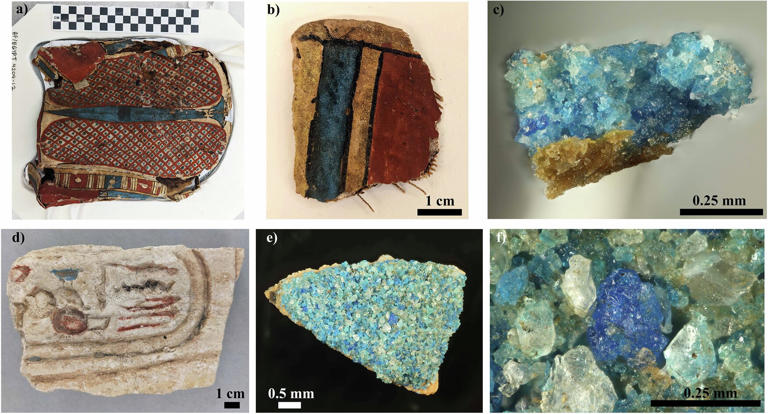
Considered to be the first ever synthetically produced color pigment, Egyptian blue (also known as cuprorivaite) was created around 2,200 B.C. It was made from ground limestone mixed with sand and a copper-containing mineral, such as azurite or malachite, which was then heated between 1470 and 1650°F. The result was an opaque blue glass which then had to be crushed and combined with thickening agents such as egg whites to create a long-lasting paint or glaze.

If you think about it, blue doesn’t appear much in nature — there aren’t animals with blue pigments (except for one butterfly, Obrina Olivewing, all animals generate blue through light scattering), blue eyes are rare (also blue through light scattering), and blue flowers are mostly human creations. There is, of course, the sky, but is that really blue?
So before we had a word for it, did people not naturally see blue? Do you really see something if you don’t have a word for it?
A researcher named Jules Davidoff traveled to Namibia to investigate this, where he conducted an experiment with the Himba tribe, who speak a language that has no word for blue or distinction between blue and green. When shown a circle with 11 green squares and one blue, they couldn’t pick out which one was different from the others.
When looking at a circle of green squares with only one slightly different shade, they could immediately spot the different one. Can you?
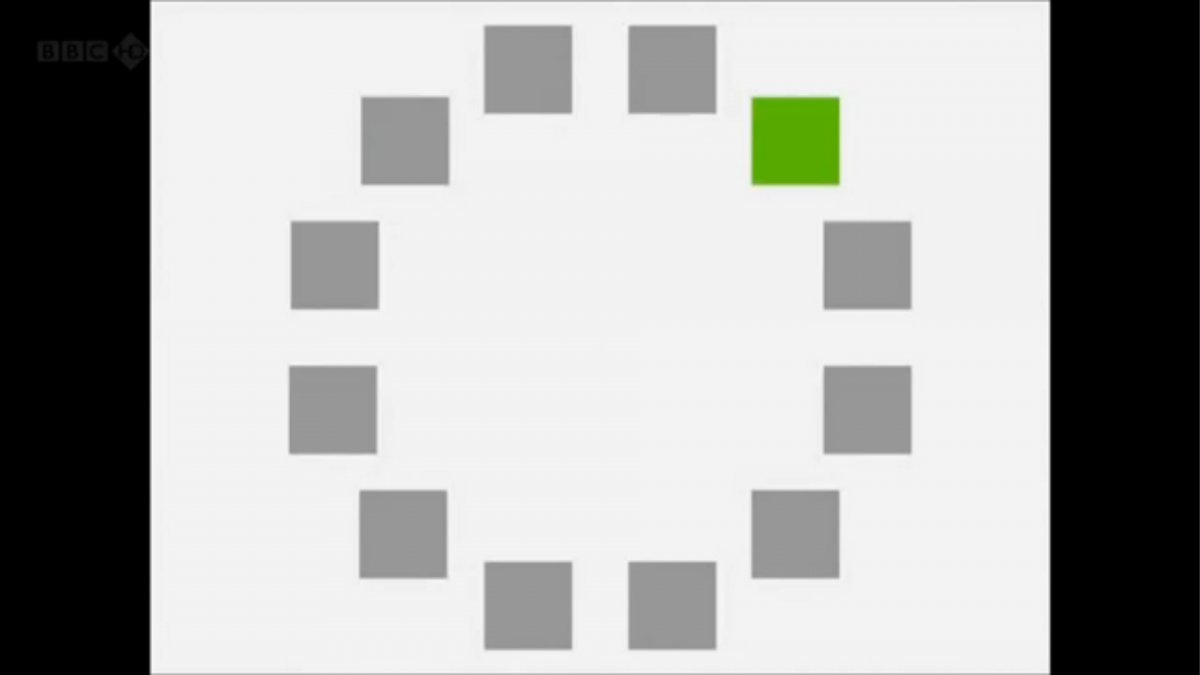
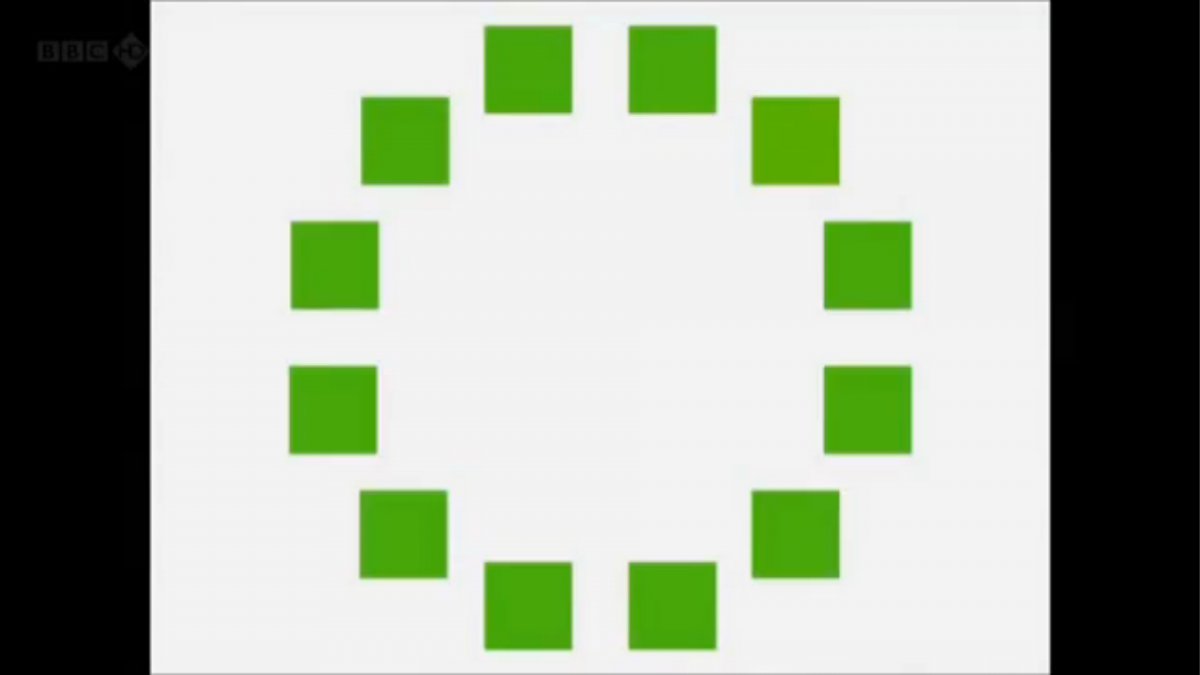

Davidoff says that without a word for a colour, without a way of identifying it as different, it’s much harder for us to notice what’s unique about it — even though our eyes are physically seeing the blocks it in the same way.
Further research brought to wider discussions about color perception in humans. Everything that we make is based on the fact that humans are trichromatic. The television only has 3 colors. Our color printers have 3 different colors. But some people, and in specific some women seemed to be more sensible to color differences… mainly because they’re just more aware or – because of the job that they do.
Eventually this brought to the discovery of a small percentage of the population, referred to as tetrachromats, which developed an extra cone sensitivity to yellow, likely due to gene modifications.
The interesting detail about these is that even between tetrachromats, only the ones that had a reason to develop, label and work with extra color sensitivity actually developed the ability to use their native skills.
So before blue became a common concept, maybe humans saw it. But it seems they didn’t know they were seeing it.
If you see something yet can’t see it, does it exist? Did colours come into existence over time? Not technically, but our ability to notice them… may have…
-
The Forbidden colors – Red-Green & Blue-Yellow: The Stunning Colors You Can’t See
Read more: The Forbidden colors – Red-Green & Blue-Yellow: The Stunning Colors You Can’t Seewww.livescience.com/17948-red-green-blue-yellow-stunning-colors.html
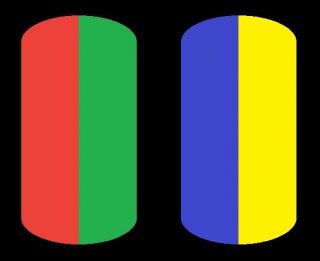
While the human eye has red, green, and blue-sensing cones, those cones are cross-wired in the retina to produce a luminance channel plus a red-green and a blue-yellow channel, and it’s data in that color space (known technically as “LAB”) that goes to the brain. That’s why we can’t perceive a reddish-green or a yellowish-blue, whereas such colors can be represented in the RGB color space used by digital cameras.
https://en.rockcontent.com/blog/the-use-of-yellow-in-data-design
The back of the retina is covered in light-sensitive neurons known as cone cells and rod cells. There are three types of cone cells, each sensitive to different ranges of light. These ranges overlap, but for convenience the cones are referred to as blue (short-wavelength), green (medium-wavelength), and red (long-wavelength). The rod cells are primarily used in low-light situations, so we’ll ignore those for now.
When light enters the eye and hits the cone cells, the cones get excited and send signals to the brain through the visual cortex. Different wavelengths of light excite different combinations of cones to varying levels, which generates our perception of color. You can see that the red cones are most sensitive to light, and the blue cones are least sensitive. The sensitivity of green and red cones overlaps for most of the visible spectrum.
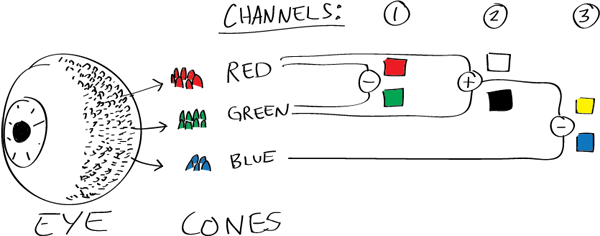
Here’s how your brain takes the signals of light intensity from the cones and turns it into color information. To see red or green, your brain finds the difference between the levels of excitement in your red and green cones. This is the red-green channel.
To get “brightness,” your brain combines the excitement of your red and green cones. This creates the luminance, or black-white, channel. To see yellow or blue, your brain then finds the difference between this luminance signal and the excitement of your blue cones. This is the yellow-blue channel.
From the calculations made in the brain along those three channels, we get four basic colors: blue, green, yellow, and red. Seeing blue is what you experience when low-wavelength light excites the blue cones more than the green and red.
Seeing green happens when light excites the green cones more than the red cones. Seeing red happens when only the red cones are excited by high-wavelength light.
Here’s where it gets interesting. Seeing yellow is what happens when BOTH the green AND red cones are highly excited near their peak sensitivity. This is the biggest collective excitement that your cones ever have, aside from seeing pure white.
Notice that yellow occurs at peak intensity in the graph to the right. Further, the lens and cornea of the eye happen to block shorter wavelengths, reducing sensitivity to blue and violet light.
LIGHTING
-
LUX vs LUMEN vs NITS vs CANDELA – What is the difference
Read more: LUX vs LUMEN vs NITS vs CANDELA – What is the differenceMore details here: Lumens vs Candelas (candle) vs Lux vs FootCandle vs Watts vs Irradiance vs Illuminance
https://www.inhouseav.com.au/blog/beginners-guide-nits-lumens-brightness/

Candela
Candela is the basic unit of measure of the entire volume of light intensity from any point in a single direction from a light source. Note the detail: it measures the total volume of light within a certain beam angle and direction.
While the luminance of starlight is around 0.001 cd/m2, that of a sunlit scene is around 100,000 cd/m2, which is a hundred millions times higher. The luminance of the sun itself is approximately 1,000,000,000 cd/m2.NIT
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Candela_per_square_metre
The candela per square metre (symbol: cd/m2) is the unit of luminance in the International System of Units (SI). The unit is based on the candela, the SI unit of luminous intensity, and the square metre, the SI unit of area. The nit (symbol: nt) is a non-SI name also used for this unit (1 nt = 1 cd/m2).[1] The term nit is believed to come from the Latin word nitēre, “to shine”. As a measure of light emitted per unit area, this unit is frequently used to specify the brightness of a display device.
NIT and cd/m2 (candela power) represent the same thing and can be used interchangeably. One nit is equivalent to one candela per square meter, where the candela is the amount of light which has been emitted by a common tallow candle, but NIT is not part of the International System of Units (abbreviated SI, from Systeme International, in French).
It’s easiest to think of a TV as emitting light directly, in much the same way as the Sun does. Nits are simply the measurement of the level of light (luminance) in a given area which the emitting source sends to your eyes or a camera sensor.
The Nit can be considered a unit of visible-light intensity which is often used to specify the brightness level of an LCD.
1 Nit is approximately equal to 3.426 Lumens. To work out a comparable number of Nits to Lumens, you need to multiply the number of Nits by 3.426. If you know the number of Lumens, and wish to know the Nits, simply divide the number of Lumens by 3.426.
Most consumer desktop LCDs have Nits of 200 to 300, the average TV most likely has an output capability of between 100 and 200 Nits, and an HDR TV ranges from 400 to 1,500 Nits.
Virtual Production sets currently sport around 6000 NIT ceiling and 1000 NIT wall panels.The ambient brightness of a sunny day with clear blue skies is between 7000-10,000 nits (between 3000-7000 nits for overcast skies and indirect sunlight).
A bright sunny day can have specular highlights that reach over 100,000 nits. Direct sunlight is around 1,600,000,000 nits.
10,000 nits is also the typical brightness of a fluorescent tube – bright, but not painful to look at.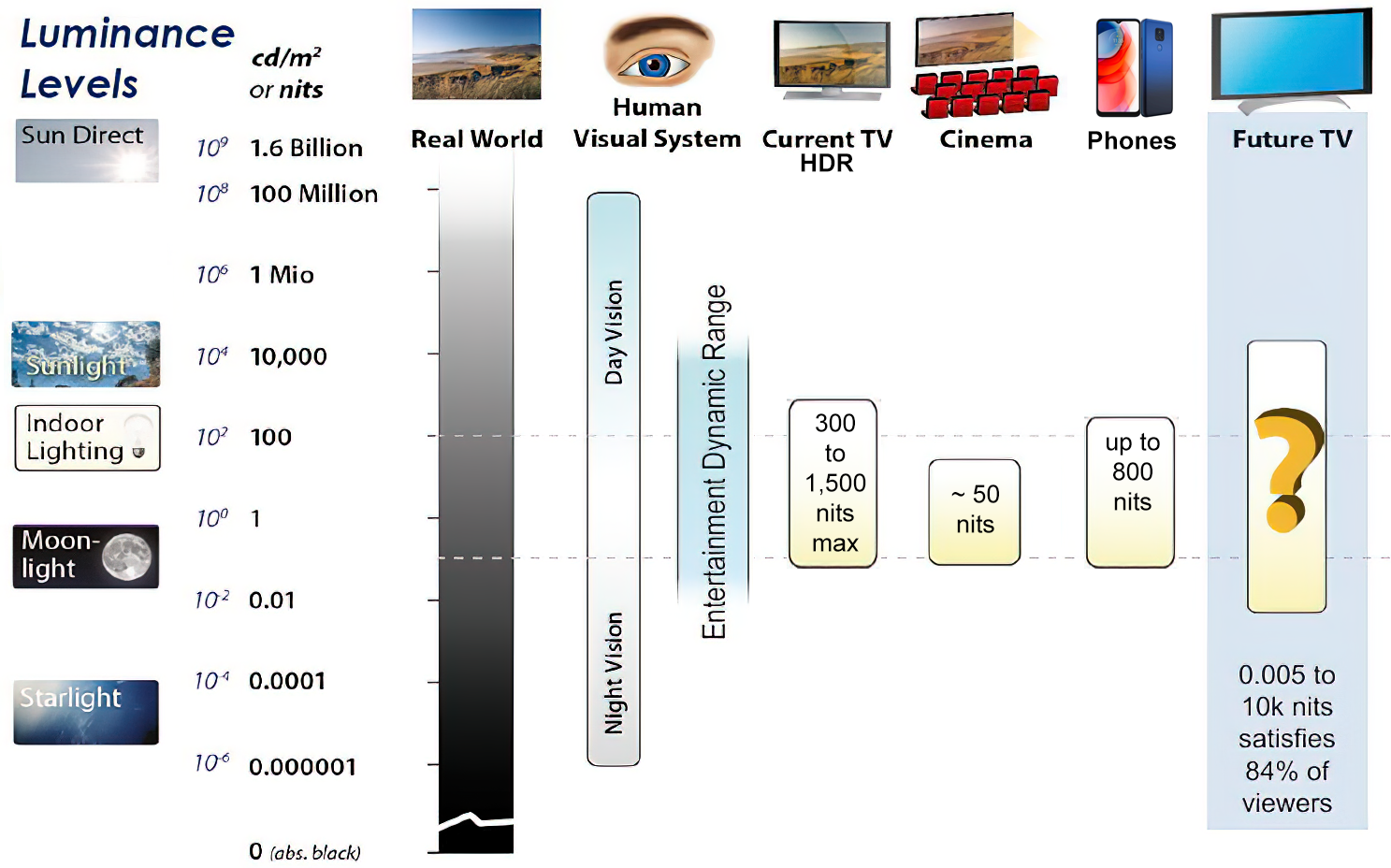
https://www.displaydaily.com/article/display-daily/dolby-vision-vs-hdr10-clarified
Tests showed that a “black level” of 0.005 nits (cd/m²) satisfied the vast majority of viewers. While 0.005 nits is very close to true black, Griffis says Dolby can go down to a black of 0.0001 nits, even though there is no need or ability for displays to get that dark today.
How bright is white? Dolby says the range of 0.005 nits – 10,000 nits satisfied 84% of the viewers in their viewing tests.
The brightest consumer HDR displays today are about 1,500 nits. Professional displays where HDR content is color-graded can achieve up to 4,000 nits peak brightness.High brightness that would be in danger of damaging the eye would be in the neighborhood of 250,000 nits.
Lumens
Lumen is a measure of how much light is emitted (luminance, luminous flux) by an object. It indicates the total potential amount of light from a light source that is visible to the human eye.
Lumen is commonly used in the context of light bulbs or video-projectors as a metric for their brightness power.Lumen is used to describe light output, and about video projectors, it is commonly referred to as ANSI Lumens. Simply put, lumens is how to find out how bright a LED display is. The higher the lumens, the brighter to display!
Technically speaking, a Lumen is the SI unit of luminous flux, which is equal to the amount of light which is emitted per second in a unit solid angle of one steradian from a uniform source of one-candela intensity radiating in all directions.
LUX
Lux (lx) or often Illuminance, is a photometric unit along a given area, which takes in account the sensitivity of human eye to different wavelenghts. It is the measure of light at a specific distance within a specific area at that distance. Often used to measure the incidental sun’s intensity.
-
Photography basics: Lumens vs Candelas (candle) vs Lux vs FootCandle vs Watts vs Irradiance vs Illuminance
Read more: Photography basics: Lumens vs Candelas (candle) vs Lux vs FootCandle vs Watts vs Irradiance vs Illuminancehttps://www.translatorscafe.com/unit-converter/en-US/illumination/1-11/
The power output of a light source is measured using the unit of watts W. This is a direct measure to calculate how much power the light is going to drain from your socket and it is not relatable to the light brightness itself.
The amount of energy emitted from it per second. That energy comes out in a form of photons which we can crudely represent with rays of light coming out of the source. The higher the power the more rays emitted from the source in a unit of time.
Not all energy emitted is visible to the human eye, so we often rely on photometric measurements, which takes in account the sensitivity of human eye to different wavelenghts
Details in the post
(more…) -
7 Easy Portrait Lighting Setups
Read more: 7 Easy Portrait Lighting SetupsButterfly
Loop
Rembrandt
Split
Rim
Broad
Short
-
Magnific.ai Relight – change the entire lighting of a scene
Read more: Magnific.ai Relight – change the entire lighting of a sceneIt’s a new Magnific spell that allows you to change the entire lighting of a scene and, optionally, the background with just:
1/ A prompt OR
2/ A reference image OR
3/ A light map (drawing your own lights)https://x.com/javilopen/status/1805274155065176489
-
Composition – These are the basic lighting techniques you need to know for photography and film
Read more: Composition – These are the basic lighting techniques you need to know for photography and filmhttp://www.diyphotography.net/basic-lighting-techniques-need-know-photography-film/
Amongst the basic techniques, there’s…
1- Side lighting – Literally how it sounds, lighting a subject from the side when they’re faced toward you
2- Rembrandt lighting – Here the light is at around 45 degrees over from the front of the subject, raised and pointing down at 45 degrees
3- Back lighting – Again, how it sounds, lighting a subject from behind. This can help to add drama with silouettes
4- Rim lighting – This produces a light glowing outline around your subject
5- Key light – The main light source, and it’s not necessarily always the brightest light source
6- Fill light – This is used to fill in the shadows and provide detail that would otherwise be blackness
7- Cross lighting – Using two lights placed opposite from each other to light two subjects
-
9 Best Hacks to Make a Cinematic Video with Any Camera
Read more: 9 Best Hacks to Make a Cinematic Video with Any Camerahttps://www.flexclip.com/learn/cinematic-video.html
- Frame Your Shots to Create Depth
- Create Shallow Depth of Field
- Avoid Shaky Footage and Use Flexible Camera Movements
- Properly Use Slow Motion
- Use Cinematic Lighting Techniques
- Apply Color Grading
- Use Cinematic Music and SFX
- Add Cinematic Fonts and Text Effects
- Create the Cinematic Bar at the Top and the Bottom

COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
-
Glossary of Lighting Terms – cheat sheet
-
GretagMacbeth Color Checker Numeric Values and Middle Gray
-
Photography basics: Shutter angle and shutter speed and motion blur
-
What the Boeing 737 MAX’s crashes can teach us about production business – the effects of commoditisation
-
Jesse Zumstein – Jobs in games
-
HDRI Median Cut plugin
-
Tencent Hunyuan3D 2.1 goes Open Source and adds MV (Multi-view) and MV Mini
-
Want to build a start up company that lasts? Think three-layer cake
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.