COMPOSITION
-
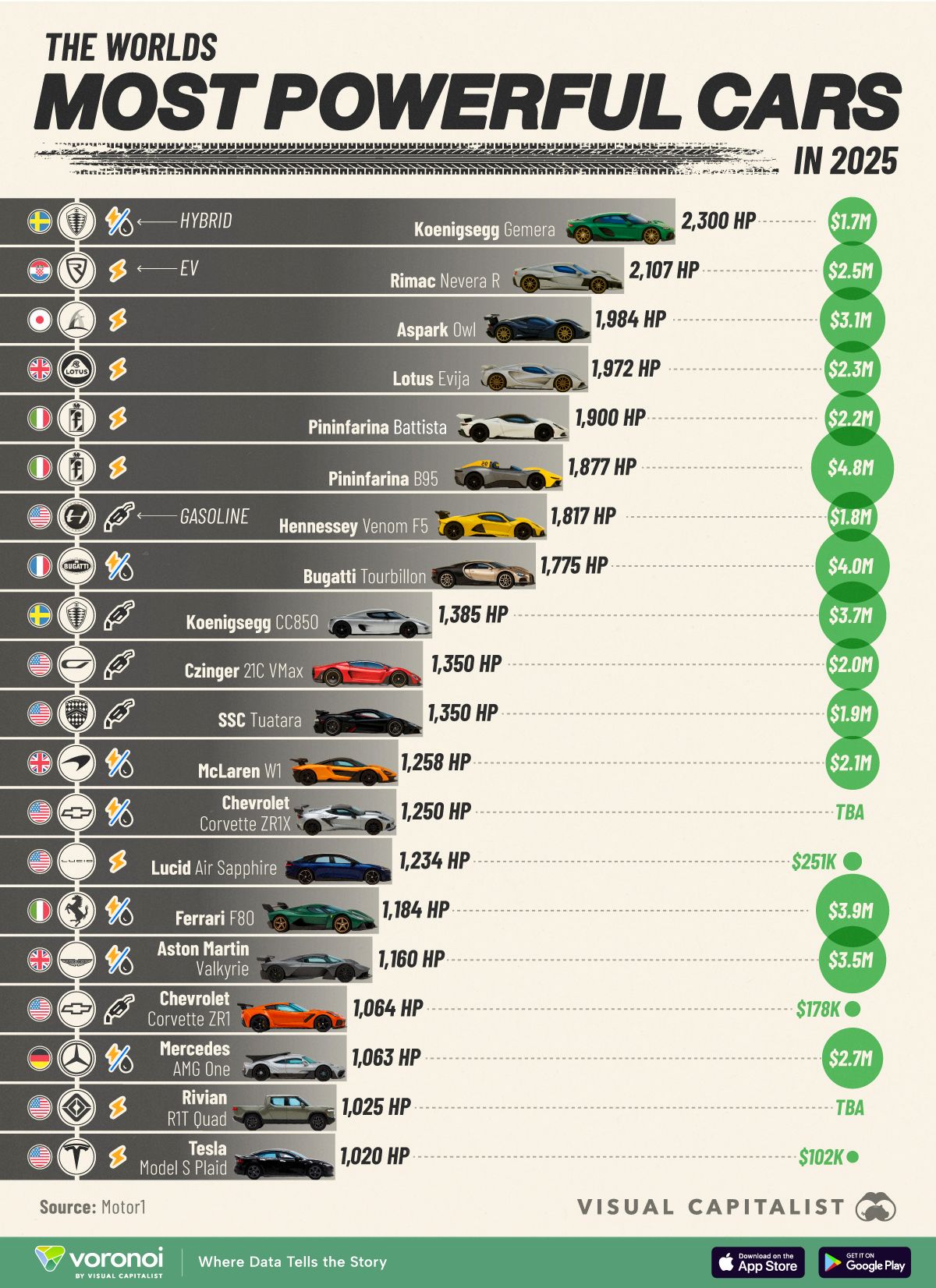
Types of Film Lights and their efficiency – CRI, Color Temperature and Luminous Efficacy
Read more: Types of Film Lights and their efficiency – CRI, Color Temperature and Luminous Efficacynofilmschool.com/types-of-film-lights
“Not every light performs the same way. Lights and lighting are tricky to handle. You have to plan for every circumstance. But the good news is, lighting can be adjusted. Let’s look at different factors that affect lighting in every scene you shoot. “
Use CRI, Luminous Efficacy and color temperature controls to match your needs.Color Temperature
Color temperature describes the “color” of white light by a light source radiated by a perfect black body at a given temperature measured in degrees Kelvinhttps://www.pixelsham.com/2019/10/18/color-temperature/
CRI
“The Color Rendering Index is a measurement of how faithfully a light source reveals the colors of whatever it illuminates, it describes the ability of a light source to reveal the color of an object, as compared to the color a natural light source would provide. The highest possible CRI is 100. A CRI of 100 generally refers to a perfect black body, like a tungsten light source or the sun. “https://www.studiobinder.com/blog/what-is-color-rendering-index
(more…)
DESIGN
-
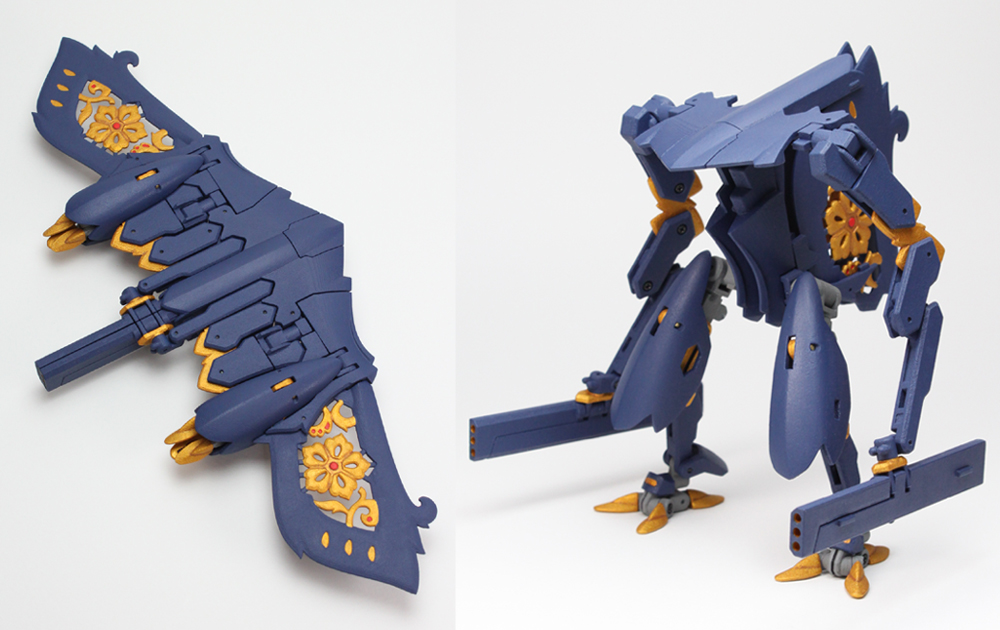
Japanese Designer Tomoo Yamaji Offers 3D Printed Transformer Kit, Stingray, Through Shapeways
Read more: Japanese Designer Tomoo Yamaji Offers 3D Printed Transformer Kit, Stingray, Through Shapewayshttps://3dprint.com/55799/transformer-kit-shapeways/
http://www.shapeways.com/product/5YHJL6XSZ/t060101-stingray?li=shareProduct
COLOR
-
Akiyoshi Kitaoka – Surround biased illumination perception
Read more: Akiyoshi Kitaoka – Surround biased illumination perceptionhttps://x.com/AkiyoshiKitaoka/status/1798705648001327209
The left face appears whitish and the right one blackish, but they are made up of the same luminance.
https://community.wolfram.com/groups/-/m/t/3191015
Illusory staircase Gelb effect
https://www.psy.ritsumei.ac.jp/akitaoka/illgelbe.html -
Capturing the world in HDR for real time projects – Call of Duty: Advanced Warfare
Read more: Capturing the world in HDR for real time projects – Call of Duty: Advanced WarfareReal-World Measurements for Call of Duty: Advanced Warfare
www.activision.com/cdn/research/Real_World_Measurements_for_Call_of_Duty_Advanced_Warfare.pdf
Local version
Real_World_Measurements_for_Call_of_Duty_Advanced_Warfare.pdf
-
Mysterious animation wins best illusion of 2011 – Motion silencing illusion
Read more: Mysterious animation wins best illusion of 2011 – Motion silencing illusionThe 2011 Best Illusion of the Year uses motion to render color changes invisible, and so reveals a quirk in our visual systems that is new to scientists.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Motion_silencing_illusion
“It is a really beautiful effect, revealing something about how our visual system works that we didn’t know before,” said Daniel Simons, a professor at the University of Illinois, Champaign-Urbana. Simons studies visual cognition, and did not work on this illusion. Before its creation, scientists didn’t know that motion had this effect on perception, Simons said.
A viewer stares at a speck at the center of a ring of colored dots, which continuously change color. When the ring begins to rotate around the speck, the color changes appear to stop. But this is an illusion. For some reason, the motion causes our visual system to ignore the color changes. (You can, however, see the color changes if you follow the rotating circles with your eyes.)
LIGHTING
-
NVidia DiffusionRenderer – Neural Inverse and Forward Rendering with Video Diffusion Models. How NVIDIA reimagined relighting
Read more: NVidia DiffusionRenderer – Neural Inverse and Forward Rendering with Video Diffusion Models. How NVIDIA reimagined relightinghttps://www.fxguide.com/quicktakes/diffusing-reality-how-nvidia-reimagined-relighting/
https://research.nvidia.com/labs/toronto-ai/DiffusionRenderer/
-
Terminators and Iron Men: HDRI, Image-based lighting and physical shading at ILM – Siggraph 2010
Read more: Terminators and Iron Men: HDRI, Image-based lighting and physical shading at ILM – Siggraph 2010 -
domeble – Hi-Resolution CGI Backplates and 360° HDRI
Read more: domeble – Hi-Resolution CGI Backplates and 360° HDRIWhen collecting hdri make sure the data supports basic metadata, such as:
- Iso
- Aperture
- Exposure time or shutter time
- Color temperature
- Color space Exposure value (what the sensor receives of the sun intensity in lux)
- 7+ brackets (with 5 or 6 being the perceived balanced exposure)
In image processing, computer graphics, and photography, high dynamic range imaging (HDRI or just HDR) is a set of techniques that allow a greater dynamic range of luminances (a Photometry measure of the luminous intensity per unit area of light travelling in a given direction. It describes the amount of light that passes through or is emitted from a particular area, and falls within a given solid angle) between the lightest and darkest areas of an image than standard digital imaging techniques or photographic methods. This wider dynamic range allows HDR images to represent more accurately the wide range of intensity levels found in real scenes ranging from direct sunlight to faint starlight and to the deepest shadows.
The two main sources of HDR imagery are computer renderings and merging of multiple photographs, which in turn are known as low dynamic range (LDR) or standard dynamic range (SDR) images. Tone Mapping (Look-up) techniques, which reduce overall contrast to facilitate display of HDR images on devices with lower dynamic range, can be applied to produce images with preserved or exaggerated local contrast for artistic effect. Photography
In photography, dynamic range is measured in Exposure Values (in photography, exposure value denotes all combinations of camera shutter speed and relative aperture that give the same exposure. The concept was developed in Germany in the 1950s) differences or stops, between the brightest and darkest parts of the image that show detail. An increase of one EV or one stop is a doubling of the amount of light.
The human response to brightness is well approximated by a Steven’s power law, which over a reasonable range is close to logarithmic, as described by the Weber�Fechner law, which is one reason that logarithmic measures of light intensity are often used as well.
HDR is short for High Dynamic Range. It’s a term used to describe an image which contains a greater exposure range than the “black” to “white” that 8 or 16-bit integer formats (JPEG, TIFF, PNG) can describe. Whereas these Low Dynamic Range images (LDR) can hold perhaps 8 to 10 f-stops of image information, HDR images can describe beyond 30 stops and stored in 32 bit images.

-
Photography basics: Color Temperature and White Balance
Read more: Photography basics: Color Temperature and White BalanceColor Temperature of a light source describes the spectrum of light which is radiated from a theoretical “blackbody” (an ideal physical body that absorbs all radiation and incident light – neither reflecting it nor allowing it to pass through) with a given surface temperature.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Color_temperature
Or. Most simply it is a method of describing the color characteristics of light through a numerical value that corresponds to the color emitted by a light source, measured in degrees of Kelvin (K) on a scale from 1,000 to 10,000.
More accurately. The color temperature of a light source is the temperature of an ideal backbody that radiates light of comparable hue to that of the light source.
(more…) -
Insta360-Research-Team DiT360 – High-Fidelity Panoramic Image Generation via Hybrid Training
Read more: Insta360-Research-Team DiT360 – High-Fidelity Panoramic Image Generation via Hybrid Traininghttps://github.com/Insta360-Research-Team/DiT360
DiT360 is a framework for high-quality panoramic image generation, leveraging both perspective and panoramic data in a hybrid training scheme. It adopts a two-level strategy—image-level cross-domain guidance and token-level hybrid supervision—to enhance perceptual realism and geometric fidelity.

COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
-
JavaScript how-to free resources
-
N8N.io – From Zero to Your First AI Agent in 25 Minutes
-
AI Data Laundering: How Academic and Nonprofit Researchers Shield Tech Companies from Accountability
-
Yann Lecun: Meta AI, Open Source, Limits of LLMs, AGI & the Future of AI | Lex Fridman Podcast #416
-
Cinematographers Blueprint 300dpi poster
-
Ross Pettit on The Agile Manager – How tech firms went for prioritizing cash flow instead of talent (and artists)
-
AnimationXpress.com interviews Daniele Tosti for TheCgCareer.com channel
-
Rec-2020 – TVs new color gamut standard used by Dolby Vision?
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.