COMPOSITION
DESIGN
COLOR
-
Photography basics: Why Use a (MacBeth) Color Chart?
Read more: Photography basics: Why Use a (MacBeth) Color Chart?Start here: https://www.pixelsham.com/2013/05/09/gretagmacbeth-color-checker-numeric-values/
https://www.studiobinder.com/blog/what-is-a-color-checker-tool/
In LightRoom
in Final Cut
in Nuke
Note: In Foundry’s Nuke, the software will map 18% gray to whatever your center f/stop is set to in the viewer settings (f/8 by default… change that to EV by following the instructions below).
You can experiment with this by attaching an Exposure node to a Constant set to 0.18, setting your viewer read-out to Spotmeter, and adjusting the stops in the node up and down. You will see that a full stop up or down will give you the respective next value on the aperture scale (f8, f11, f16 etc.).One stop doubles or halves the amount or light that hits the filmback/ccd, so everything works in powers of 2.
So starting with 0.18 in your constant, you will see that raising it by a stop will give you .36 as a floating point number (in linear space), while your f/stop will be f/11 and so on.If you set your center stop to 0 (see below) you will get a relative readout in EVs, where EV 0 again equals 18% constant gray.
In other words. Setting the center f-stop to 0 means that in a neutral plate, the middle gray in the macbeth chart will equal to exposure value 0. EV 0 corresponds to an exposure time of 1 sec and an aperture of f/1.0.
This will set the sun usually around EV12-17 and the sky EV1-4 , depending on cloud coverage.
To switch Foundry’s Nuke’s SpotMeter to return the EV of an image, click on the main viewport, and then press s, this opens the viewer’s properties. Now set the center f-stop to 0 in there. And the SpotMeter in the viewport will change from aperture and fstops to EV.
-
About green screens
Read more: About green screenshackaday.com/2015/02/07/how-green-screen-worked-before-computers/
www.newtek.com/blog/tips/best-green-screen-materials/
www.chromawall.com/blog//chroma-key-green
Chroma Key Green, the color of green screens is also known as Chroma Green and is valued at approximately 354C in the Pantone color matching system (PMS).
Chroma Green can be broken down in many different ways. Here is green screen green as other values useful for both physical and digital production:
Green Screen as RGB Color Value: 0, 177, 64
Green Screen as CMYK Color Value: 81, 0, 92, 0
Green Screen as Hex Color Value: #00b140
Green Screen as Websafe Color Value: #009933Chroma Key Green is reasonably close to an 18% gray reflectance.
Illuminate your green screen with an uniform source with less than 2/3 EV variation.
The level of brightness at any given f-stop should be equivalent to a 90% white card under the same lighting. -
Colour – MacBeth Chart Checker Detection
Read more: Colour – MacBeth Chart Checker Detectiongithub.com/colour-science/colour-checker-detection
A Python package implementing various colour checker detection algorithms and related utilities.
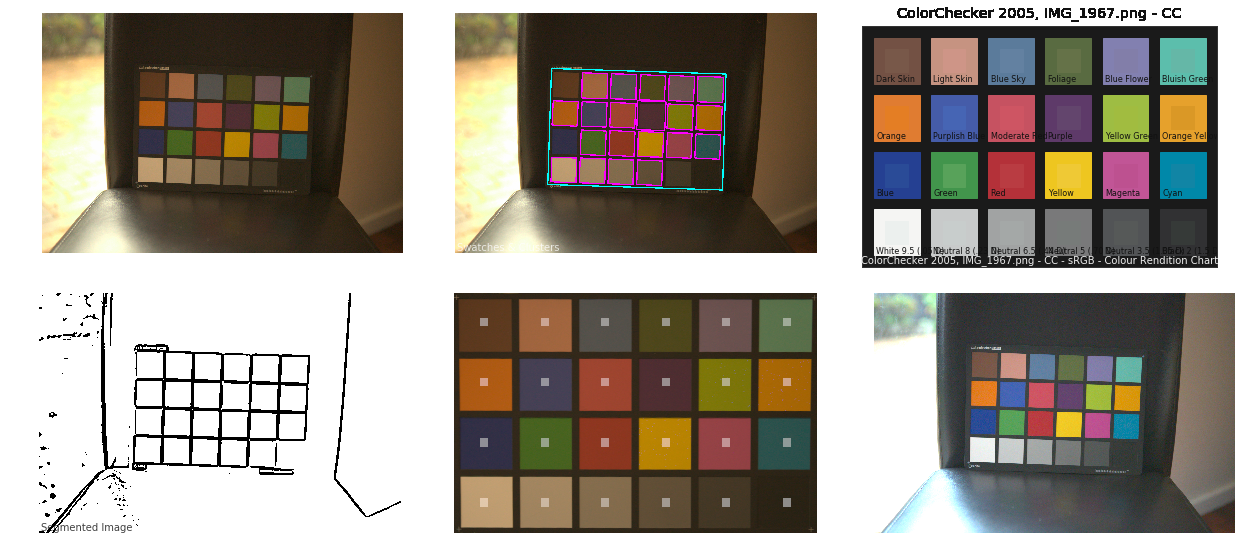
-
RawTherapee – a free, open source, cross-platform raw image and HDRi processing program
Read more: RawTherapee – a free, open source, cross-platform raw image and HDRi processing program5.10 of this tool includes excellent tools to clean up cr2 and cr3 used on set to support HDRI processing.
Converting raw to AcesCG 32 bit tiffs with metadata. -
Photography basics: Lumens vs Candelas (candle) vs Lux vs FootCandle vs Watts vs Irradiance vs Illuminance
Read more: Photography basics: Lumens vs Candelas (candle) vs Lux vs FootCandle vs Watts vs Irradiance vs Illuminancehttps://www.translatorscafe.com/unit-converter/en-US/illumination/1-11/
The power output of a light source is measured using the unit of watts W. This is a direct measure to calculate how much power the light is going to drain from your socket and it is not relatable to the light brightness itself.
The amount of energy emitted from it per second. That energy comes out in a form of photons which we can crudely represent with rays of light coming out of the source. The higher the power the more rays emitted from the source in a unit of time.
Not all energy emitted is visible to the human eye, so we often rely on photometric measurements, which takes in account the sensitivity of human eye to different wavelenghts
Details in the post
(more…) -
SecretWeapons MixBox – a practical library for paint-like digital color mixing
Read more: SecretWeapons MixBox – a practical library for paint-like digital color mixingInternally, Mixbox treats colors as real-life pigments using the Kubelka & Munk theory to predict realistic color behavior.
https://scrtwpns.com/mixbox/painter/
https://scrtwpns.com/mixbox.pdf
https://github.com/scrtwpns/mixbox
https://scrtwpns.com/mixbox/docs/
-
3D Lighting Tutorial by Amaan Kram
Read more: 3D Lighting Tutorial by Amaan Kramhttp://www.amaanakram.com/lightingT/part1.htm
The goals of lighting in 3D computer graphics are more or less the same as those of real world lighting.
Lighting serves a basic function of bringing out, or pushing back the shapes of objects visible from the camera’s view.
It gives a two-dimensional image on the monitor an illusion of the third dimension-depth.But it does not just stop there. It gives an image its personality, its character. A scene lit in different ways can give a feeling of happiness, of sorrow, of fear etc., and it can do so in dramatic or subtle ways. Along with personality and character, lighting fills a scene with emotion that is directly transmitted to the viewer.
Trying to simulate a real environment in an artificial one can be a daunting task. But even if you make your 3D rendering look absolutely photo-realistic, it doesn’t guarantee that the image carries enough emotion to elicit a “wow” from the people viewing it.
Making 3D renderings photo-realistic can be hard. Putting deep emotions in them can be even harder. However, if you plan out your lighting strategy for the mood and emotion that you want your rendering to express, you make the process easier for yourself.
Each light source can be broken down in to 4 distinct components and analyzed accordingly.
· Intensity
· Direction
· Color
· SizeThe overall thrust of this writing is to produce photo-realistic images by applying good lighting techniques.
-
What is OLED and what can it do for your TV
Read more: What is OLED and what can it do for your TVhttps://www.cnet.com/news/what-is-oled-and-what-can-it-do-for-your-tv/
OLED stands for Organic Light Emitting Diode. Each pixel in an OLED display is made of a material that glows when you jab it with electricity. Kind of like the heating elements in a toaster, but with less heat and better resolution. This effect is called electroluminescence, which is one of those delightful words that is big, but actually makes sense: “electro” for electricity, “lumin” for light and “escence” for, well, basically “essence.”
OLED TV marketing often claims “infinite” contrast ratios, and while that might sound like typical hyperbole, it’s one of the extremely rare instances where such claims are actually true. Since OLED can produce a perfect black, emitting no light whatsoever, its contrast ratio (expressed as the brightest white divided by the darkest black) is technically infinite.
OLED is the only technology capable of absolute blacks and extremely bright whites on a per-pixel basis. LCD definitely can’t do that, and even the vaunted, beloved, dearly departed plasma couldn’t do absolute blacks.
LIGHTING
-
NVidia DiffusionRenderer – Neural Inverse and Forward Rendering with Video Diffusion Models. How NVIDIA reimagined relighting
Read more: NVidia DiffusionRenderer – Neural Inverse and Forward Rendering with Video Diffusion Models. How NVIDIA reimagined relightinghttps://www.fxguide.com/quicktakes/diffusing-reality-how-nvidia-reimagined-relighting/
https://research.nvidia.com/labs/toronto-ai/DiffusionRenderer/
-
Photography basics: How Exposure Stops (Aperture, Shutter Speed, and ISO) Affect Your Photos – cheat sheet cards
Read more: Photography basics: How Exposure Stops (Aperture, Shutter Speed, and ISO) Affect Your Photos – cheat sheet cardsAlso see:
https://www.pixelsham.com/2018/11/22/exposure-value-measurements/
https://www.pixelsham.com/2016/03/03/f-stop-vs-t-stop/
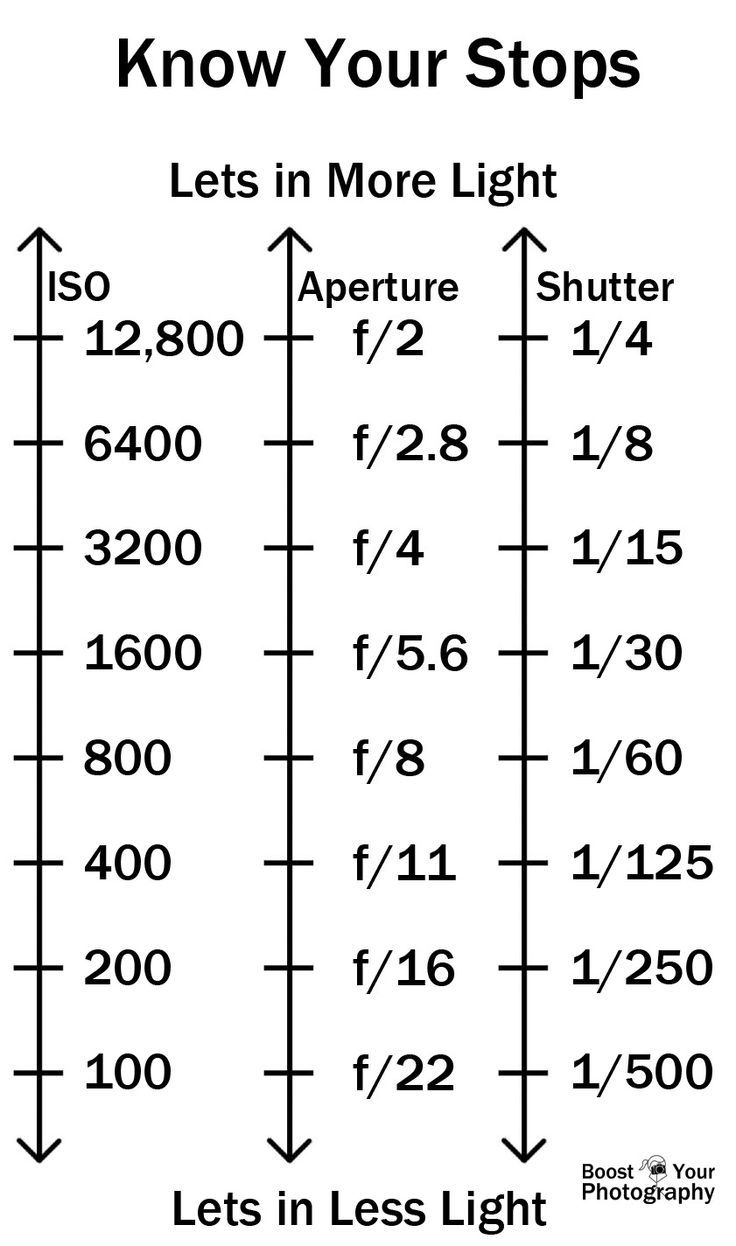
An exposure stop is a unit measurement of Exposure as such it provides a universal linear scale to measure the increase and decrease in light, exposed to the image sensor, due to changes in shutter speed, iso and f-stop.
+-1 stop is a doubling or halving of the amount of light let in when taking a photo
1 EV (exposure value) is just another way to say one stop of exposure change.
https://www.photographymad.com/pages/view/what-is-a-stop-of-exposure-in-photography
Same applies to shutter speed, iso and aperture.
Doubling or halving your shutter speed produces an increase or decrease of 1 stop of exposure.
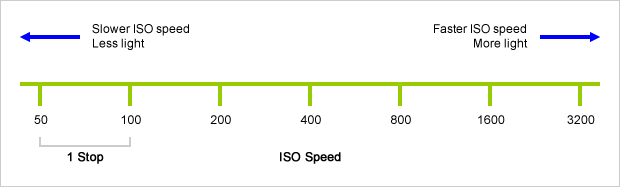
Doubling or halving your iso speed produces an increase or decrease of 1 stop of exposure.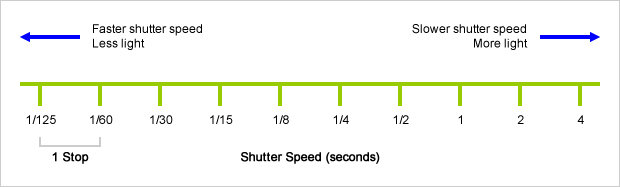

Because of the way f-stop numbers are calculated (ratio of focal length/lens diameter, where focal length is the distance between the lens and the sensor), an f-stop doesn’t relate to a doubling or halving of the value, but to the doubling/halving of the area coverage of a lens in relation to its focal length. And as such, to a multiplying or dividing by 1.41 (the square root of 2). For example, going from f/2.8 to f/4 is a decrease of 1 stop because 4 = 2.8 * 1.41. Changing from f/16 to f/11 is an increase of 1 stop because 11 = 16 / 1.41.
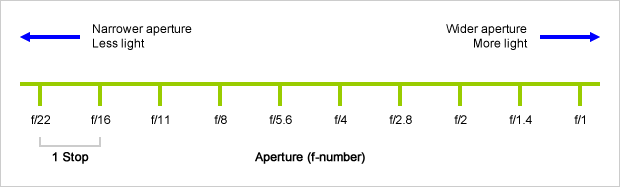
A wider aperture means that light proceeding from the foreground, subject, and background is entering at more oblique angles than the light entering less obliquely.
Consider that absolutely everything is bathed in light, therefore light bouncing off of anything is effectively omnidirectional. Your camera happens to be picking up a tiny portion of the light that’s bouncing off into infinity.
Now consider that the wider your iris/aperture, the more of that omnidirectional light you’re picking up:
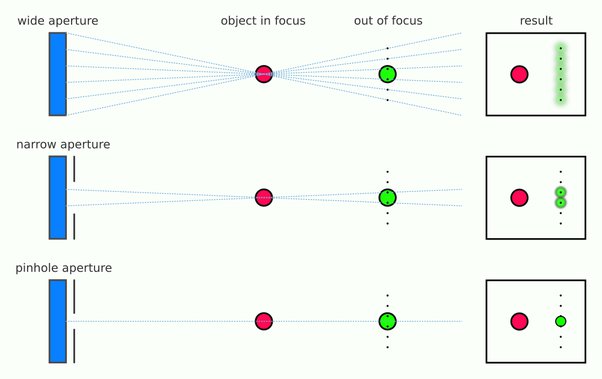
When you have a very narrow iris you are eliminating a lot of oblique light. Whatever light enters, from whatever distance, enters moderately parallel as a whole. When you have a wide aperture, much more light is entering at a multitude of angles. Your lens can only focus the light from one depth – the foreground/background appear blurred because it cannot be focused on.
https://frankwhitephotography.com/index.php?id=28:what-is-a-stop-in-photography
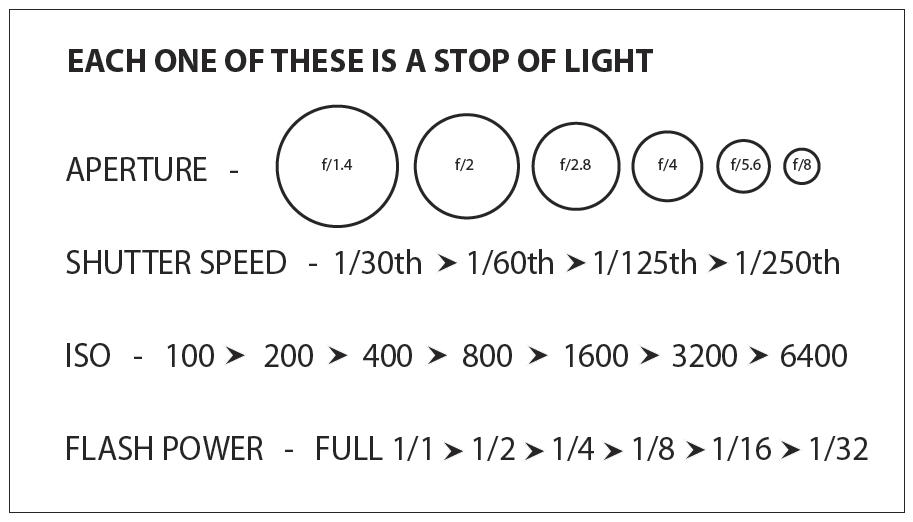
The great thing about stops is that they give us a way to directly compare shutter speed, aperture diameter, and ISO speed. This means that we can easily swap these three components about while keeping the overall exposure the same.
http://lifehacker.com/how-aperture-shutter-speed-and-iso-affect-pictures-sh-1699204484
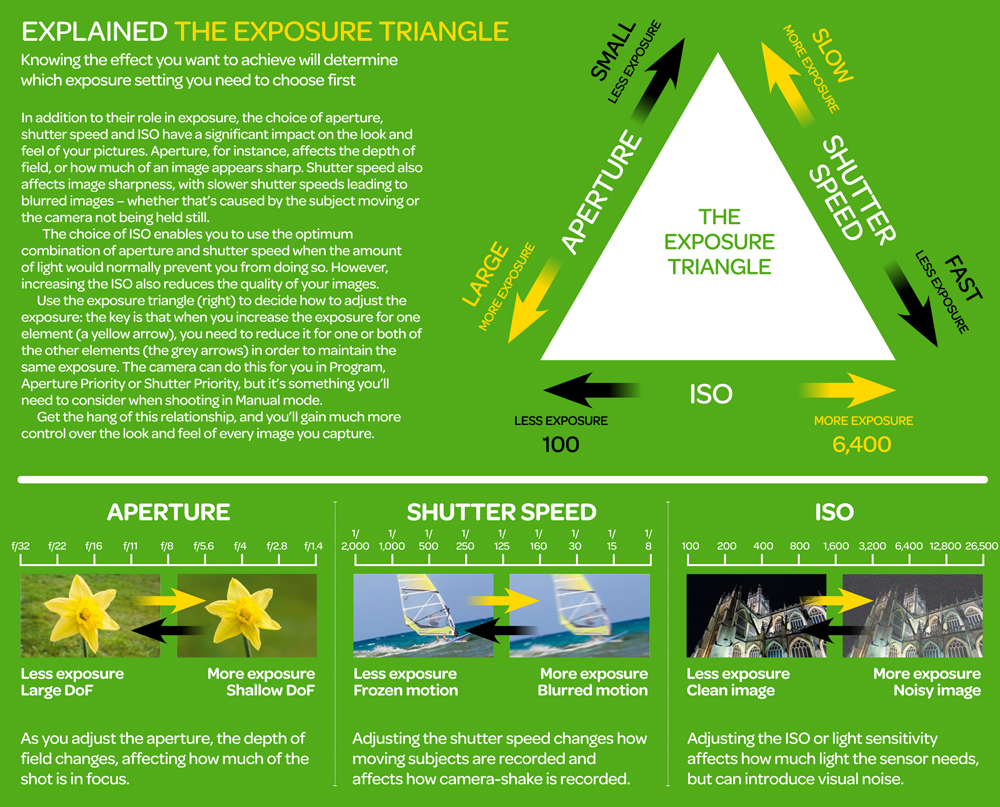
https://www.techradar.com/how-to/the-exposure-triangle
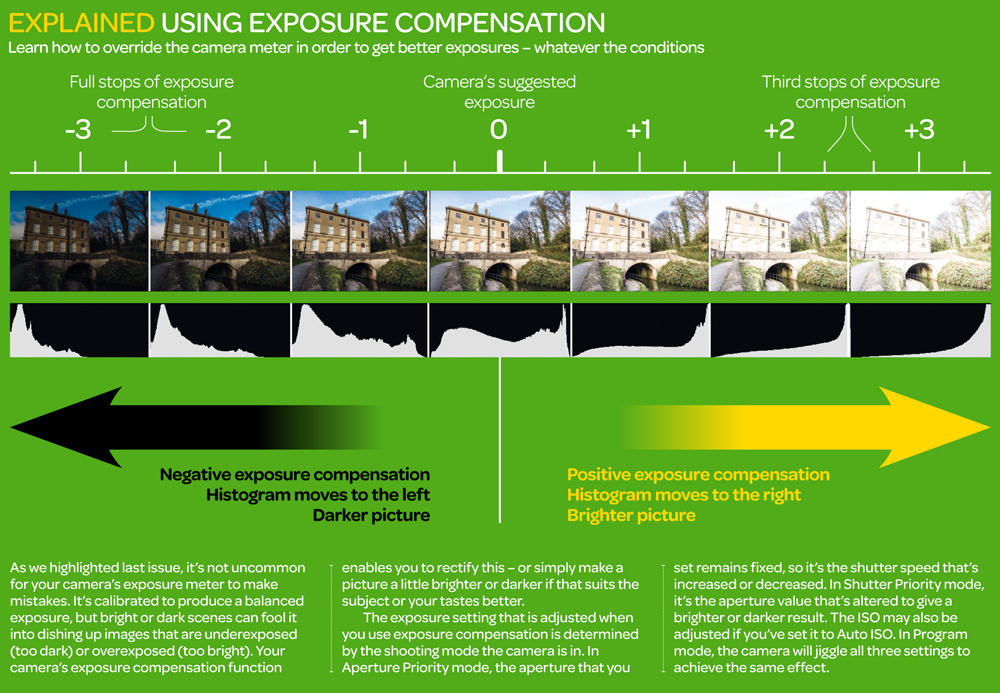
https://www.videoschoolonline.com/what-is-an-exposure-stop
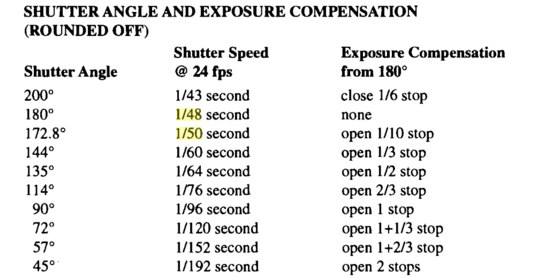
Note. All three of these measurements (aperture, shutter, iso) have full stops, half stops and third stops, but if you look at the numbers they aren’t always consistent. For example, a one third stop between ISO100 and ISO 200 would be ISO133, yet most cameras are marked at ISO125.
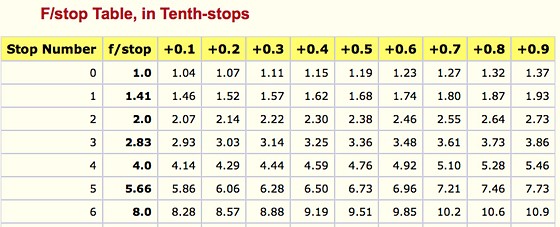
Third-stops are especially important as they’re the increment that most cameras use for their settings. These are just imaginary divisions in each stop.
From a practical standpoint manufacturers only standardize the full stops, meaning that while they try and stay somewhat consistent there is some rounding up going on between the smaller numbers.
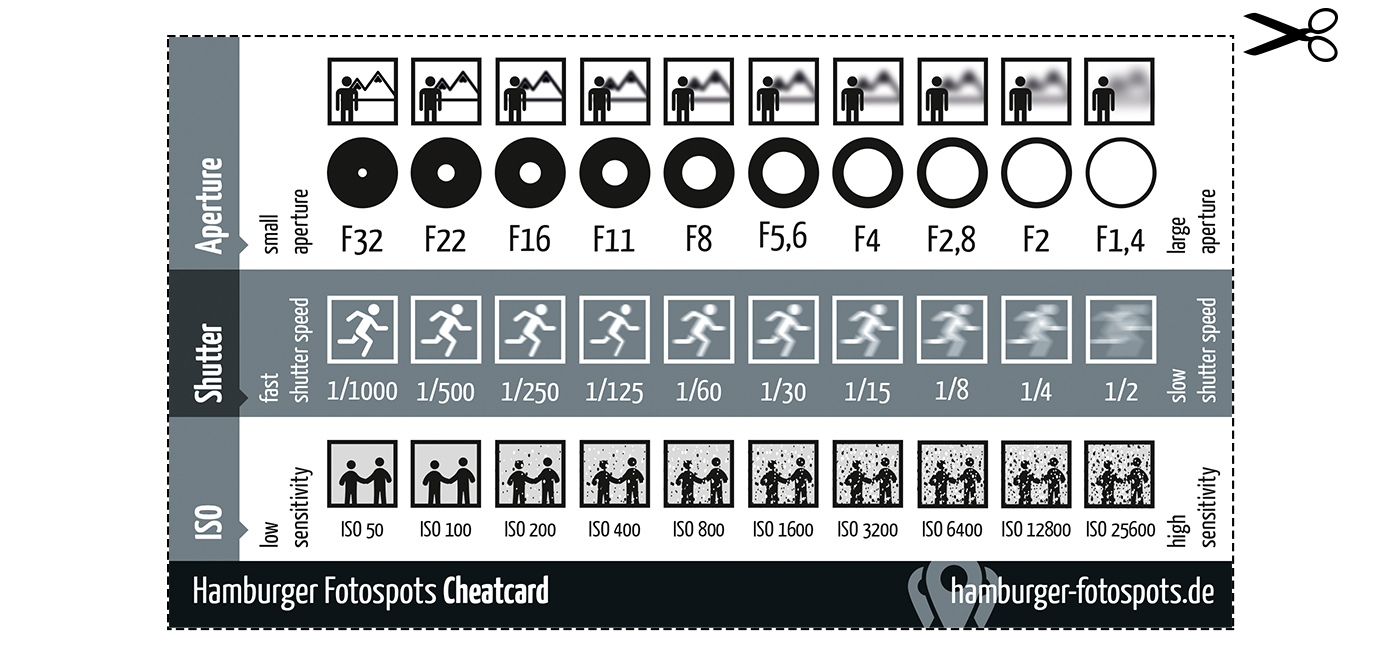
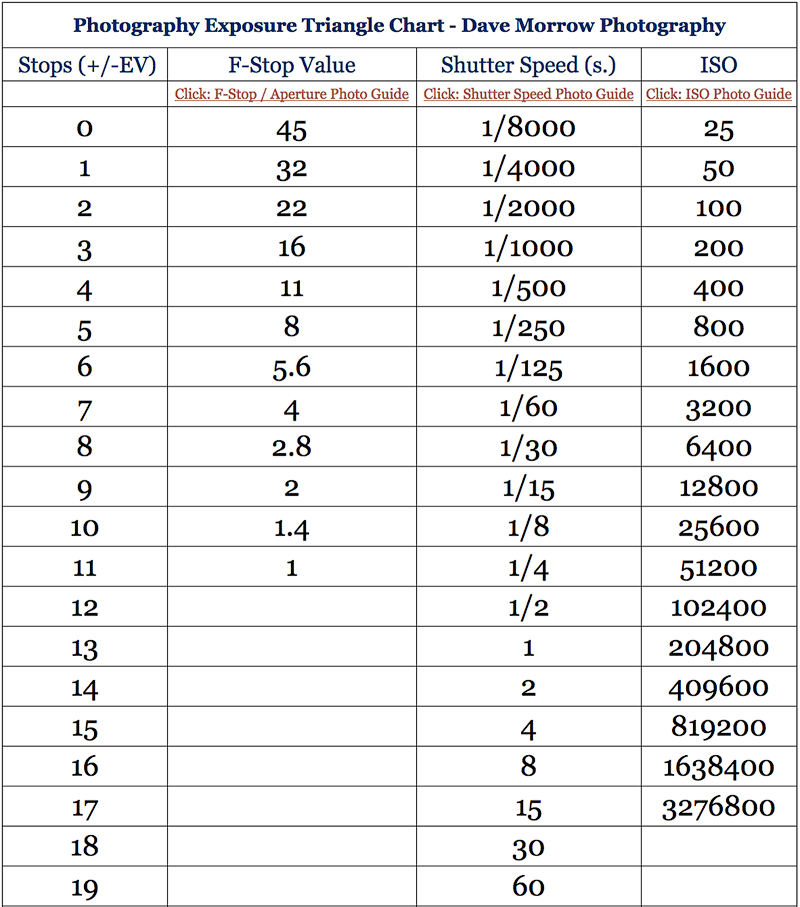
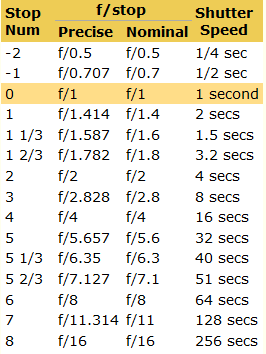
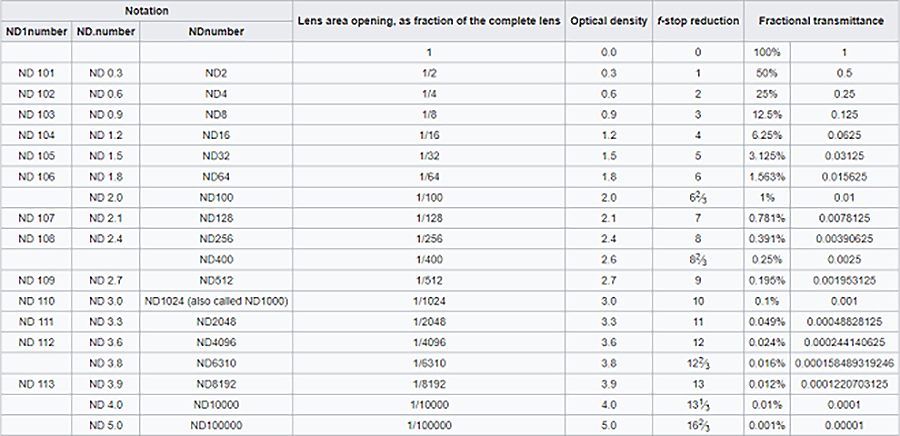
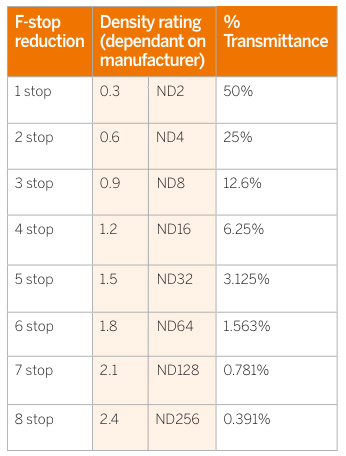
Note that ND Filters directly modify the exposure triangle.

COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.









