www.sharegrid.com/learn/lens-test-data
www.sharegrid.com/learn/the-3-tests
www.sharegrid.com/learn/lens-test-approach





3Dprinting (178) A.I. (835) animation (349) blender (207) colour (233) commercials (52) composition (152) cool (363) design (648) Featured (79) hardware (313) IOS (109) jokes (138) lighting (288) modeling (144) music (186) photogrammetry (190) photography (754) production (1289) python (92) quotes (496) reference (314) software (1350) trailers (306) ves (550) VR (221)
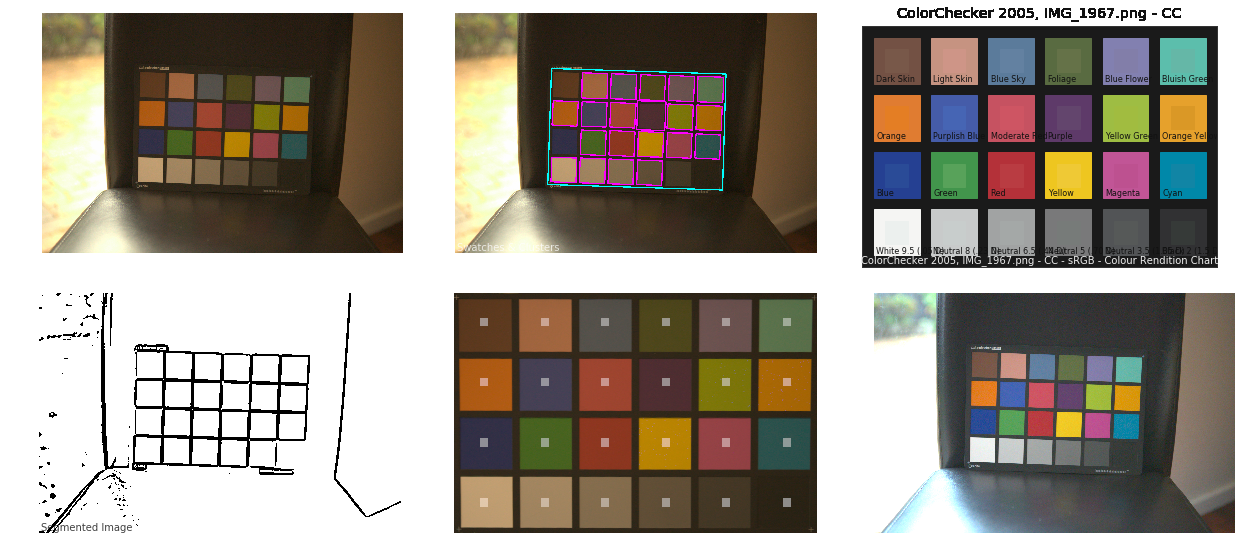
github.com/colour-science/colour-checker-detection
A Python package implementing various colour checker detection algorithms and related utilities.
The 300dpi digital poster is now available to all PixelSham.com subscribers.
If you have already subscribed and wish a copy, please send me a note through the contact page.
COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.
