BREAKING NEWS
LATEST POSTS
-
Odyssey.systems Explorer – pioneering generative world models and gaussian splatting
Odyssey and a Pixar co-founder, Ed Catmull (also an investor), just dropped Explorer, a revolutionary 3D world generator that turns any image into an editable 3D world.
https://odyssey.systems/introducing-explorer
-
Genesis AI – a physics platform designed for general purpose Robotics/Embodied AI/Physical AI applications
https://github.com/Genesis-Embodied-AI/Genesis
https://genesis-world.readthedocs.io/en/latest
Genesis is a physics platform designed for general purpose Robotics/Embodied AI/Physical AI applications. It is simultaneously multiple things:
- A universal physics engine re-built from the ground up, capable of simulating a wide range of materials and physical phenomena.
- A lightweight, ultra-fast, pythonic, and user-friendly robotics simulation platform.
- A powerful and fast photo-realistic rendering system.
- A generative data engine that transforms user-prompted natural language description into various modalities of data.
FEATURED POSTS
-
The Perils of Technical Debt – Understanding Its Impact on Security, Usability, and Stability
In software development, “technical debt” is a term used to describe the accumulation of shortcuts, suboptimal solutions, and outdated code that occur as developers rush to meet deadlines or prioritize immediate goals over long-term maintainability. While this concept initially seems abstract, its consequences are concrete and can significantly affect the security, usability, and stability of software systems.
The Nature of Technical Debt
Technical debt arises when software engineers choose a less-than-ideal implementation in the interest of saving time or reducing upfront effort. Much like financial debt, these decisions come with an interest rate: over time, the cost of maintaining and updating the system increases, and more effort is required to fix problems that stem from earlier choices. In extreme cases, technical debt can slow development to a crawl, causing future updates or improvements to become far more difficult than they would have been with cleaner, more scalable code.
Impact on Security
One of the most significant threats posed by technical debt is the vulnerability it creates in terms of software security. Outdated code often lacks the latest security patches or is built on legacy systems that are no longer supported. Attackers can exploit these weaknesses, leading to data breaches, ransomware, or other forms of cybercrime. Furthermore, as systems grow more complex and the debt compounds, identifying and fixing vulnerabilities becomes increasingly challenging. Failing to address technical debt leaves an organization exposed to security risks that may only become apparent after a costly incident.
Impact on Usability
Technical debt also affects the user experience. Systems burdened by outdated code often become clunky and slow, leading to poor usability. Engineers may find themselves continuously patching minor issues rather than implementing larger, user-centric improvements. Over time, this results in a product that feels antiquated, is difficult to use, or lacks modern functionality. In a competitive market, poor usability can alienate users, causing a loss of confidence and driving them to alternative products or services.
Impact on Stability
Stability is another critical area impacted by technical debt. As developers add features or make updates to systems weighed down by previous quick fixes, they run the risk of introducing bugs or causing system crashes. The tangled, fragile nature of code laden with technical debt makes troubleshooting difficult and increases the likelihood of cascading failures. Over time, instability in the software can erode both the trust of users and the efficiency of the development team, as more resources are dedicated to resolving recurring issues rather than innovating or expanding the system’s capabilities.
The Long-Term Costs of Ignoring Technical Debt
While technical debt can provide short-term gains by speeding up initial development, the long-term costs are much higher. Unaddressed technical debt can lead to project delays, escalating maintenance costs, and an ever-widening gap between current code and modern best practices. The more technical debt accumulates, the harder and more expensive it becomes to address. For many companies, failing to pay down this debt eventually results in a critical juncture: either invest heavily in refactoring the codebase or face an expensive overhaul to rebuild from the ground up.
Conclusion
Technical debt is an unavoidable aspect of software development, but understanding its perils is essential for minimizing its impact on security, usability, and stability. By actively managing technical debt—whether through regular refactoring, code audits, or simply prioritizing long-term quality over short-term expedience—organizations can avoid the most dangerous consequences and ensure their software remains robust and reliable in an ever-changing technological landscape.
-
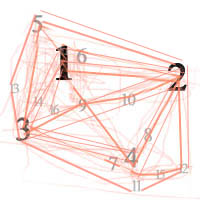
Survivorship Bias: The error resulting from systematically focusing on successes and ignoring failures. How a young statistician saved his planes during WW2.
A young statistician saved their lives.
His insight (and how it can change yours):
(more…)
During World War II, the U.S. wanted to add reinforcement armor to specific areas of its planes.
Analysts examined returning bombers, plotted the bullet holes and damage on them (as in the image below), and came to the conclusion that adding armor to the tail, body, and wings would improve their odds of survival.
But a young statistician named Abraham Wald noted that this would be a tragic mistake. By only plotting data on the planes that returned, they were systematically omitting the data on a critical, informative subset: The planes that were damaged and unable to return.
-
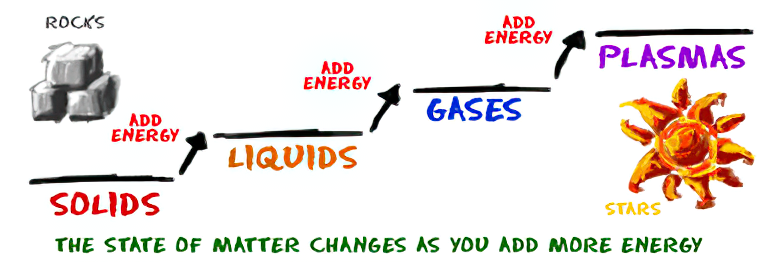
How are Energy and Matter the Same?
www.turnerpublishing.com/blog/detail/everything-is-energy-everything-is-one-everything-is-possible/
www.universetoday.com/116615/how-are-energy-and-matter-the-same/
As Einstein showed us, light and matter and just aspects of the same thing. Matter is just frozen light. And light is matter on the move. Albert Einstein’s most famous equation says that energy and matter are two sides of the same coin. How does one become the other?
Relativity requires that the faster an object moves, the more mass it appears to have. This means that somehow part of the energy of the car’s motion appears to transform into mass. Hence the origin of Einstein’s equation. How does that happen? We don’t really know. We only know that it does.
Matter is 99.999999999999 percent empty space. Not only do the atom and solid matter consist mainly of empty space, it is the same in outer space
The quantum theory researchers discovered the answer: Not only do particles consist of energy, but so does the space between. This is the so-called zero-point energy. Therefore it is true: Everything consists of energy.
Energy is the basis of material reality. Every type of particle is conceived of as a quantum vibration in a field: Electrons are vibrations in electron fields, protons vibrate in a proton field, and so on. Everything is energy, and everything is connected to everything else through fields.