BREAKING NEWS
LATEST POSTS
-
Back Button Focus advantages
http://thephotographerwithin.com/2015/05/back-button-focus/
What are the advantages of BBF?
Faster shooting with static subjects: you can lock focus with the AF-ON button once then let go of the button for subjects that don’t move. Great for landscapes, macro, even sleepy newborns. No need to refocus every time you press the shutter.
Easier to focus and recompose: you can lock focus using your center focal point with the AF-ON button then let go of the button and recompose your image very easily without having to re-do your focus each and every time you press the shutter. Useful for Canon cameras with limited focal points or if your initial composition isn’t optimal.
Better focus for moving subjects: you can shoot continuously with the AF-ON button depressed and your focus will track your moving subject.
Override and fine-tune autofocus: you can ensure tack sharp images when using Live View and zooming your focal point in to 100%, then locking in that focus by using the AF-ON button. You can even adjust your focus manually by turning your focus ring on the lens without turning the switch to MF on the front of the camera (if required).
And finally, and this is the HUGEST advantage I’ve found, you never, ever need to change your auto focus mode again. Setting it to AF-C/AI Servo AF and using BBF allows you to access all of the focus modes with this one button. BBF eliminates the need for switching focus modes between AF-S/One Shot, AF-C/AI Servo, and AF-Auto. BBF makes AF-C/AI Servo AF usable for both moving and stationary subjects. Wow, right?!
-
Shooting and editing macro stereo
The average interocular of humans is considered to be about 65mm (2.5 inches.) When this same distance is used as the interaxial distance between two shooting cameras then the resulting stereoscopic effect is typically known as “Ortho-stereo.” Many stereographers choose 2.5” as a stereo-base for this reason.
If the interaxial distance used to shoot is smaller than 2.5 inches then you are shooting “Hypo-stereo.” This technique is common for theatrically released films to accommodate the effects of the big screen. It is also used for macro stereoscopic photography.
Hyper-stereo refers to interaxial distances greater than 2.5 inches. As I mentioned earlier the greater the interaxial separation, the greater the depth effect. An elephant can perceive much more depth than a human, and a human can perceive more depth than a mouse.
However, using this same analogy, the mouse can get close and peer inside the petals of a flower with very good depth perception, and the human will just go “cross-eyed.” Therefore decreasing the interaxial separation between two cameras to 1” or less will allow you to shoot amazing macro stereo-photos and separating the cameras to several feet apart will allow great depth on mountain ranges, city skylines and other vistas.
The trouble with using hyper-stereo is that scenes with gigantic objects in real-life may appear as small models. This phenomenon is known as dwarfism and we perceive it this way because the exaggerated separation between the taking lenses allows us to see around big objects much more that we do in the real world. Our brain interprets this as meaning the object must be small.
The opposite happens with hypo-stereo, where normal sized objects appear gigantic. (Gigantism.)
http://dashwood3d.com/blog/beginners-guide-to-shooting-stereoscopic-3d/index.html
http://3d-con.com/2014/files/NSA2014-MACRO1.pdf
http://nzphoto.tripod.com/stereo/macrostereo/macro3dwindows.htm
FEATURED POSTS
-
Martin Gent – Comparing current video AI models
https://www.linkedin.com/posts/martingent_imagineapp-veo2-kling-activity-7298979787962806272-n0Sn
🔹 𝗩𝗲𝗼 2 – After the legendary prompt adherence of Veo 2 T2V, I have to say I2V is a little disappointing, especially when it comes to camera moves. You often get those Sora-like jump-cuts too which can be annoying.
🔹 𝗞𝗹𝗶𝗻𝗴 1.6 Pro – Still the one to beat for I2V, both for image quality and prompt adherence. It’s also a lot cheaper than Veo 2. Generations can be slow, but are usually worth the wait.
🔹 𝗥𝘂𝗻𝘄𝗮𝘆 Gen 3 – Useful for certain shots, but overdue an update. The worst performer here by some margin. Bring on Gen 4!
🔹 𝗟𝘂𝗺𝗮 Ray 2 – I love the energy and inventiveness Ray 2 brings, but those came with some image quality issues. I want to test more with this model though for sure.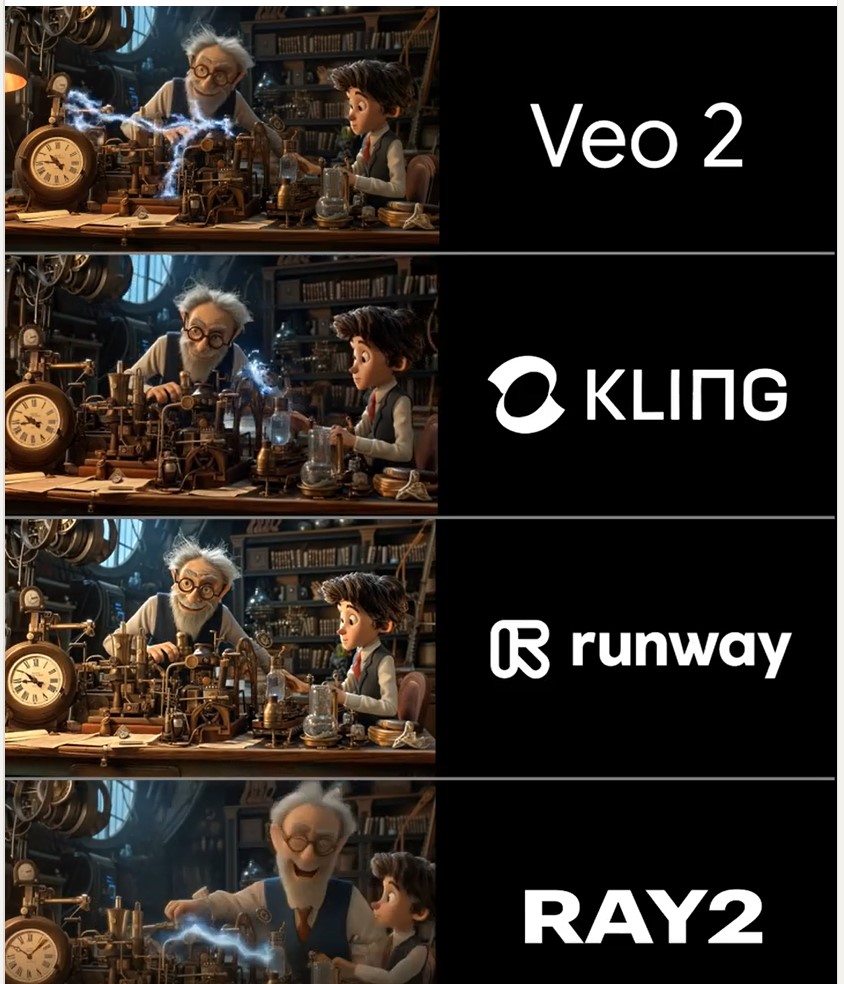
-
CASSINI MISSION
Somewhere, something incredible is waiting to be known.
The footage in this little film was captured by the hardworking men and women at NASA with the Cassini Imaging Science System. If you’re interested in learning more about Cassini and the on-going Cassini Solstice Mission, check it out at NASA’s website:
saturn.jpl.nasa.gov/science/index.cfm
-
Photography basics: Solid Angle measures
http://www.calculator.org/property.aspx?name=solid+angle
A measure of how large the object appears to an observer looking from that point. Thus. A measure for objects in the sky. Useful to retuen the size of the sun and moon… and in perspective, how much of their contribution to lighting. Solid angle can be represented in ‘angular diameter’ as well.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Solid_angle
http://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/steradian.html
A solid angle is expressed in a dimensionless unit called a steradian (symbol: sr). By default in terms of the total celestial sphere and before atmospheric’s scattering, the Sun and the Moon subtend fractional areas of 0.000546% (Sun) and 0.000531% (Moon).
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Solid_angle#Sun_and_Moon
On earth the sun is likely closer to 0.00011 solid angle after athmospheric scattering. The sun as perceived from earth has a diameter of 0.53 degrees. This is about 0.000064 solid angle.
http://www.numericana.com/answer/angles.htm
The mean angular diameter of the full moon is 2q = 0.52° (it varies with time around that average, by about 0.009°). This translates into a solid angle of 0.0000647 sr, which means that the whole night sky covers a solid angle roughly one hundred thousand times greater than the full moon.
More info
http://lcogt.net/spacebook/using-angles-describe-positions-and-apparent-sizes-objects
http://amazing-space.stsci.edu/glossary/def.php.s=topic_astronomy
Angular Size
The apparent size of an object as seen by an observer; expressed in units of degrees (of arc), arc minutes, or arc seconds. The moon, as viewed from the Earth, has an angular diameter of one-half a degree.
The angle covered by the diameter of the full moon is about 31 arcmin or 1/2°, so astronomers would say the Moon’s angular diameter is 31 arcmin, or the Moon subtends an angle of 31 arcmin.