BREAKING NEWS
LATEST POSTS
-
OpenAI – Sora 2 is here, more physically accurate, realistic, and more controllable than prior systems
https://openai.com/index/sora-2/
It also features synchronized dialogue and sound effects. Create with it in the new Sora app.
-
DokuWiki and TiddlyWiki- Free Self Hosted Wikis
https://www.dokuwiki.org/dokuwiki
DokuWiki (PHP, flat-file)
- Maturity & stability: Actively developed since 2004, very stable.
- Storage: All content stored in plain text files (no DB at all).
- Portability: Just copy the folder; backups are trivial.
- Features: User management, access control lists, plugins, templates.
- Syntax: Own lightweight markup, but easy to learn.
- Use case: Great for documentation, personal wikis, code snippets, knowledge bases.
This is probably the closest modern equivalent to self hosted Wikie in philosophy.
TiddlyWiki (Single-file wiki in HTML/JS)
- Maturity: First released in 2004, still maintained.
- Storage: Everything in a single self-contained HTML file (JavaScript inside).
- Portability: Just copy one file, runs in any browser.
- Hosting: Can be self-hosted on any web server, or even run locally.
- Features: Plugin ecosystem, themes, good for personal notes and code snippets.
- Use case: Perfect for highly portable personal wikis, though less suited for multi-user environments.
This is the most portable option — literally one file to back up.
-
Geometry Nodes – New essential assets for Blender 5.0
https://projects.blender.org/blender/blender/pulls/145645
High level tools to make the power of Geometry Nodes accessible to any user familiar with modifiers.
The focus here is (opposite to builtin Geometry Nodes) to combine lots of options and functionality into one convenient package, that can be extended by editing the nodes, or integrating it into a node-setup, but is focused on being used without node editing.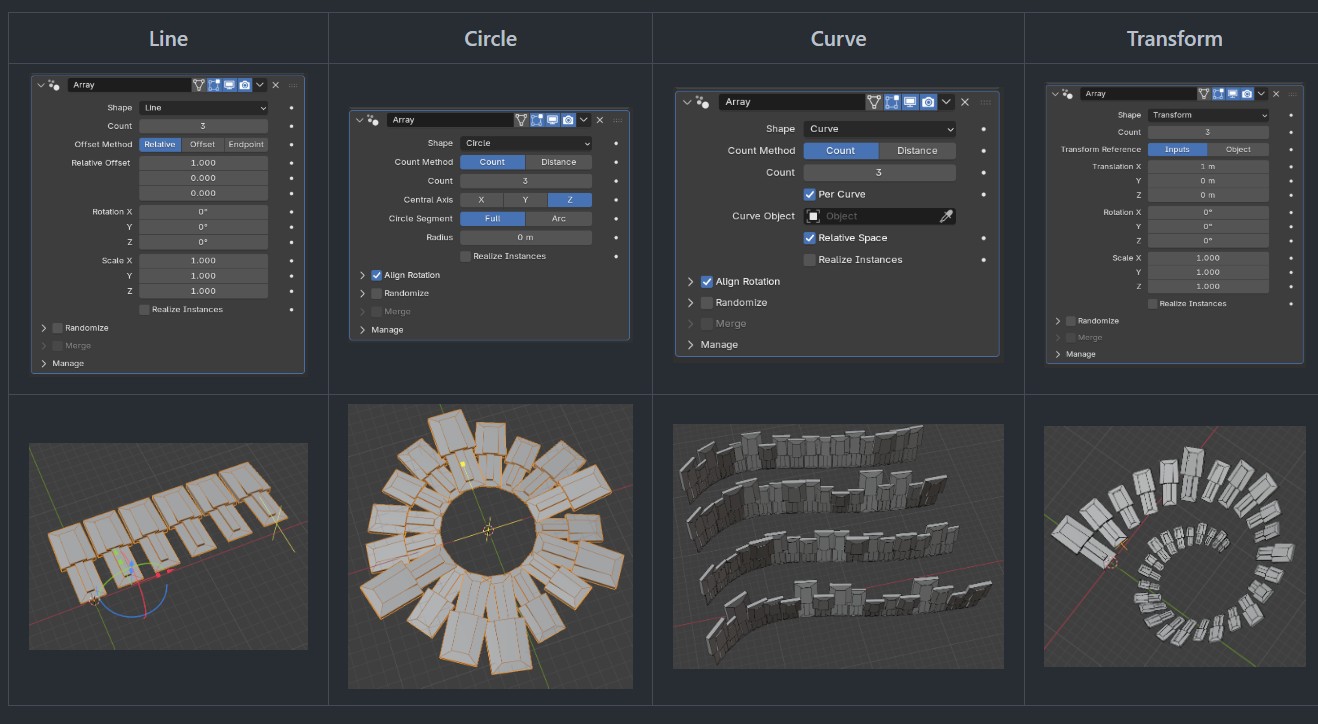
-
Ian Curtis – AI world models generated these 3D environments from a single image in minutes, and I turned them into a custom spaceship game level in an afternoon
Here’s how I created it:
Design: I started by generating cohesive concept images in Midjourney, with sleek white interiors with yellow accents to define the overall vibe.
Generate: Using World Labs, I transformed those images into fully explorable and persistent 3D environments in minutes.
Assemble: I cropped out doorways inside the Gaussian splats, then aligned and stitched multiple rooms together using PlayCanvas Supersplat, creating a connected spaceship layout.
Experience: Just a few hours later, I was walking through a custom interactive game level that started as a simple idea earlier that day.
FEATURED POSTS
-
VFX pipeline – Render Wall Farm management topics
1: Introduction Title: Managing a VFX Facility’s Render Wall
- Briefly introduce the importance of managing a VFX facility’s render wall.
- Highlight how efficient management contributes to project timelines and overall productivity.
2: Daily Overview Title: Daily Management Routine
- Monitor Queues: Begin each day by reviewing render queues to assess workload and priorities.
- Resource Allocation: Allocate resources based on project demands and available hardware.
- Job Prioritization: Set rendering priorities according to project deadlines and importance.
- Queue Optimization: Adjust queue settings to maximize rendering efficiency.
3: Resource Allocation Title: Efficient Resource Management
- Hardware Utilization: Distribute rendering tasks across available machines for optimal resource usage.
- Balance Workloads: Avoid overloading specific machines while others remain underutilized.
- Consider Off-Peak Times: Schedule resource-intensive tasks during off-peak hours to enhance overall performance.
4: Job Prioritization Title: Prioritizing Rendering Tasks
- Deadline Sensitivity: Give higher priority to tasks with imminent deadlines to ensure timely delivery.
- Critical Shots: Identify shots crucial to the project’s narrative or visual impact for prioritization.
- Dependent Shots: Sequence shots that depend on others should be prioritized together.
5: Queue Optimization and Reporting Title: Streamlining Render Queues
- Dependency Management: Set up dependencies to ensure shots are rendered in the correct order.
- Error Handling: Implement automated error detection and requeueing mechanisms.
- Progress Tracking: Regularly monitor rendering progress and update stakeholders.
- Data Management: Archive completed renders and remove redundant data to free up storage.
- Reporting: Provide daily reports on rendering status, resource usage, and potential bottlenecks.
6: Conclusion Title: Enhancing VFX Workflow
- Effective management of a VFX facility’s render wall is essential for project success.
- Daily monitoring, resource allocation, job prioritization, queue optimization, and reporting are key components.
- A well-managed render wall ensures efficient production, timely delivery, and overall project success.
-
Want to build a start up company that lasts? Think three-layer cake
https://www.fastcompany.com/91131427/want-to-build-a-company-that-lasts-think-three-layer-cake
Building a successful business requires a focus on three key elements: product excellence, go-to-market strategy, and operational excellence. Neglecting any of these areas can lead to failure, as evidenced by the high percentage of startups that don’t make it past the five-year mark. Founders and CEOs must ensure a solid product foundation while also integrating effective sales, marketing, and management strategies to achieve sustainable growth and scale.
- Foundation: Product Excellence, Core Values and Mission
- Core Values: These are the guiding principles that dictate behavior and action within the company. They form the ethical foundation and are crucial for maintaining consistency in decision-making.
- Mission: This defines the company’s purpose and goals. A clear and compelling mission helps align the team and provides a sense of direction.
- Efficiency and Scalability: This layer focuses on creating efficient processes that can scale as the company grows. Streamlined operations reduce costs and increase productivity.
- Structure: Operational Excellence and Innovation
- Operational Excellence: Efficient processes, quality control, and continuous improvement fall into this layer. Ensuring that the company operates smoothly and effectively is crucial for sustainability.
- Innovation: Staying competitive requires innovation. This involves developing new products, services, or processes that add value and keep the company relevant in the market.
- Quality Control and Continuous Improvement: Ensuring that operational processes are of high quality and constantly improving helps maintain product excellence and customer satisfaction.
- Technology and Infrastructure: Investing in the right technology and infrastructure to support business operations is vital. This includes everything from manufacturing equipment to software systems that enhance operational efficiency.
- Strategy: Go-to-Market Strategy, Vision and Long-Term Planning
- Vision: A forward-looking vision inspires and motivates the team. It outlines where the company aims to be in the future and helps in setting long-term goals.
- Strategic Planning: This involves setting long-term goals and determining the actions and resources needed to achieve them. It includes market analysis, competitive strategy, and growth planning.
- Market Understanding: A deep understanding of the target market, including customer segments, competitors, and market trends, is essential. This knowledge helps in positioning the product effectively.
- Marketing and Sales Execution: This involves creating a robust marketing plan that includes branding, messaging, and advertising strategies to attract and retain customers. Additionally, building a strong sales strategy ensures that the product reaches the right customers through the right channels.
- Customer Acquisition and Retention: Effective strategies for acquiring new customers and retaining existing ones are critical. This includes loyalty programs, customer service excellence, and engagement initiatives.
- Foundation: Product Excellence, Core Values and Mission
-
Rec-2020 – TVs new color gamut standard used by Dolby Vision?
https://www.hdrsoft.com/resources/dri.html#bit-depth
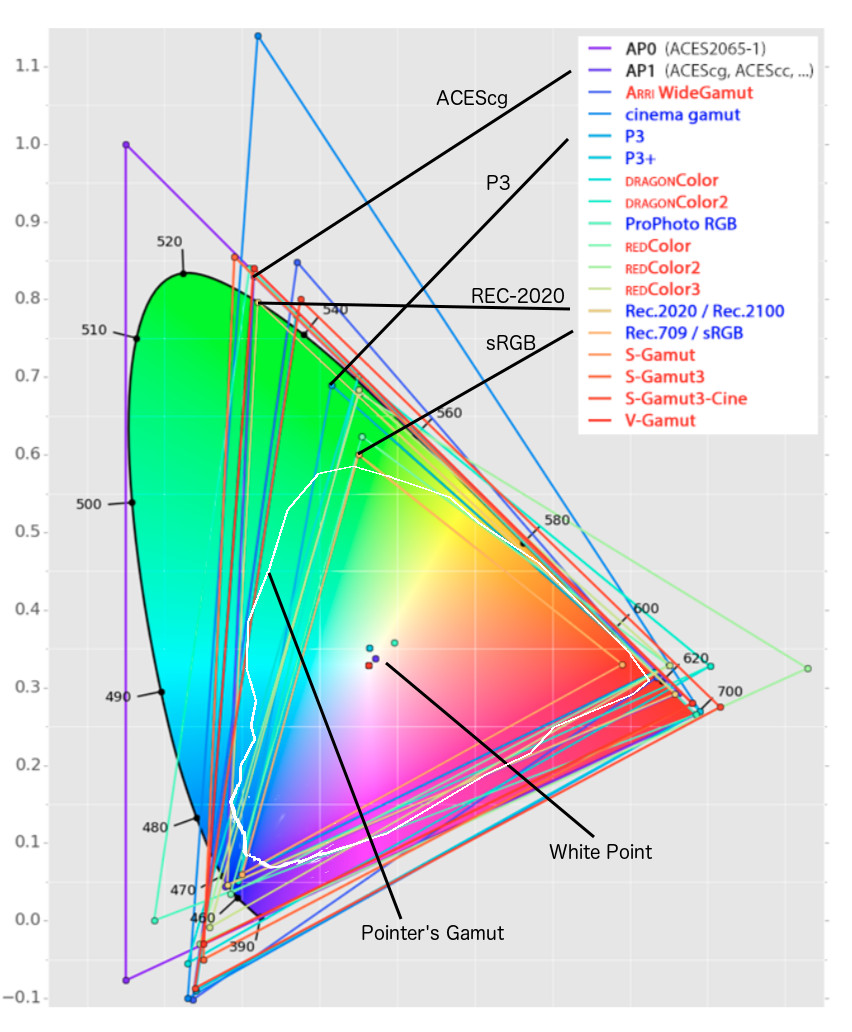
The dynamic range is a ratio between the maximum and minimum values of a physical measurement. Its definition depends on what the dynamic range refers to.
For a scene: Dynamic range is the ratio between the brightest and darkest parts of the scene.
For a camera: Dynamic range is the ratio of saturation to noise. More specifically, the ratio of the intensity that just saturates the camera to the intensity that just lifts the camera response one standard deviation above camera noise.
For a display: Dynamic range is the ratio between the maximum and minimum intensities emitted from the screen.
The Dynamic Range of real-world scenes can be quite high — ratios of 100,000:1 are common in the natural world. An HDR (High Dynamic Range) image stores pixel values that span the whole tonal range of real-world scenes. Therefore, an HDR image is encoded in a format that allows the largest range of values, e.g. floating-point values stored with 32 bits per color channel. Another characteristics of an HDR image is that it stores linear values. This means that the value of a pixel from an HDR image is proportional to the amount of light measured by the camera.
For TVs HDR is great, but it’s not the only new TV feature worth discussing.
(more…)