BREAKING NEWS
LATEST POSTS
-
Black Forest Labs released FLUX.1 Kontext
https://replicate.com/blog/flux-kontext
https://replicate.com/black-forest-labs/flux-kontext-pro
There are three models, two are available now, and a third open-weight version is coming soon:
- FLUX.1 Kontext [pro]: State-of-the-art performance for image editing. High-quality outputs, great prompt following, and consistent results.
- FLUX.1 Kontext [max]: A premium model that brings maximum performance, improved prompt adherence, and high-quality typography generation without compromise on speed.
- Coming soon: FLUX.1 Kontext [dev]: An open-weight, guidance-distilled version of Kontext.
We’re so excited with what Kontext can do, we’ve created a collection of models on Replicate to give you ideas:
- Multi-image kontext: Combine two images into one.
- Portrait series: Generate a series of portraits from a single image
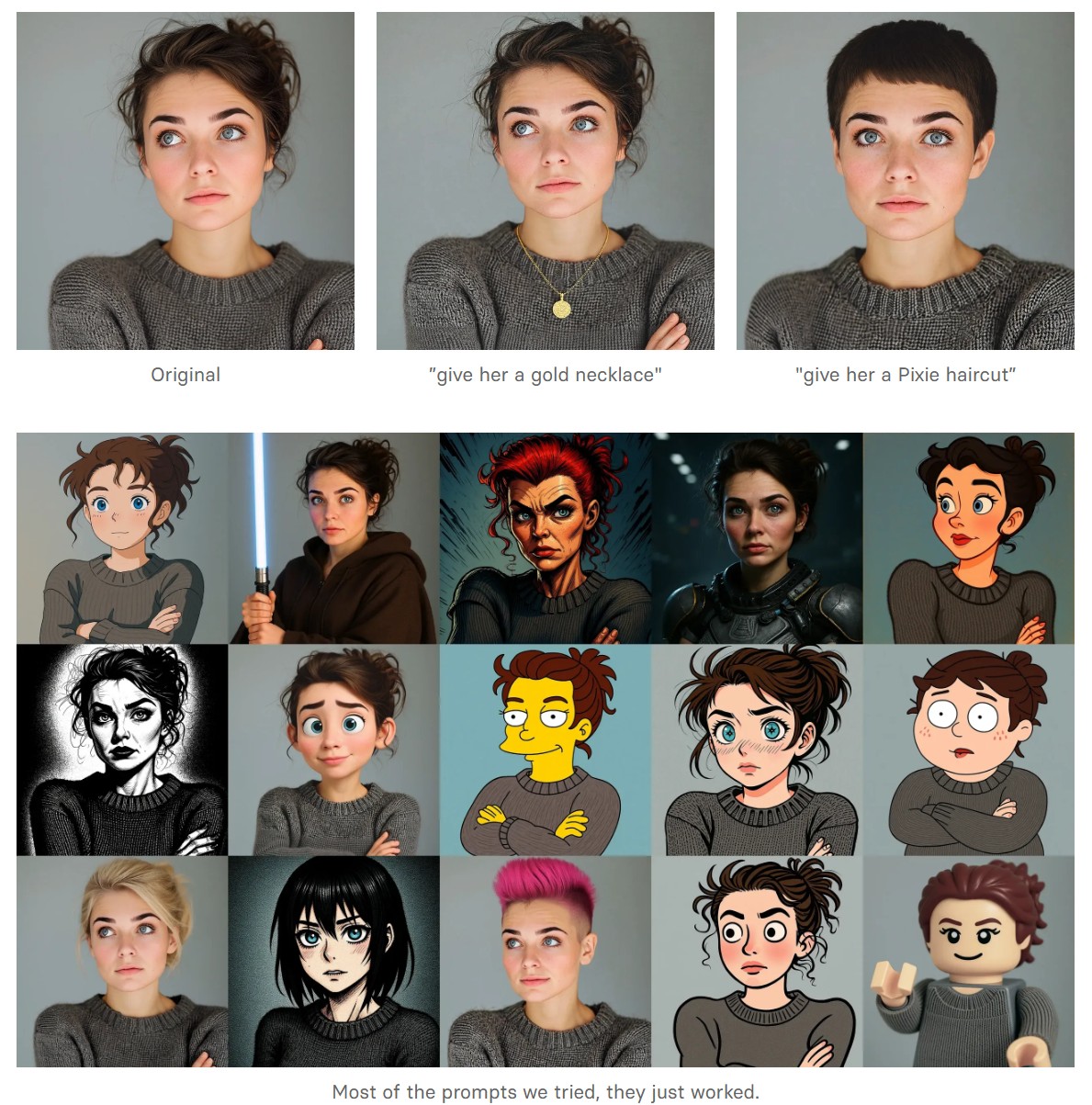
- Change haircut: Change a person’s hair style and color
- Iconic locations: Put yourself in front of famous landmarks
- Professional headshot: Generate a professional headshot from any image

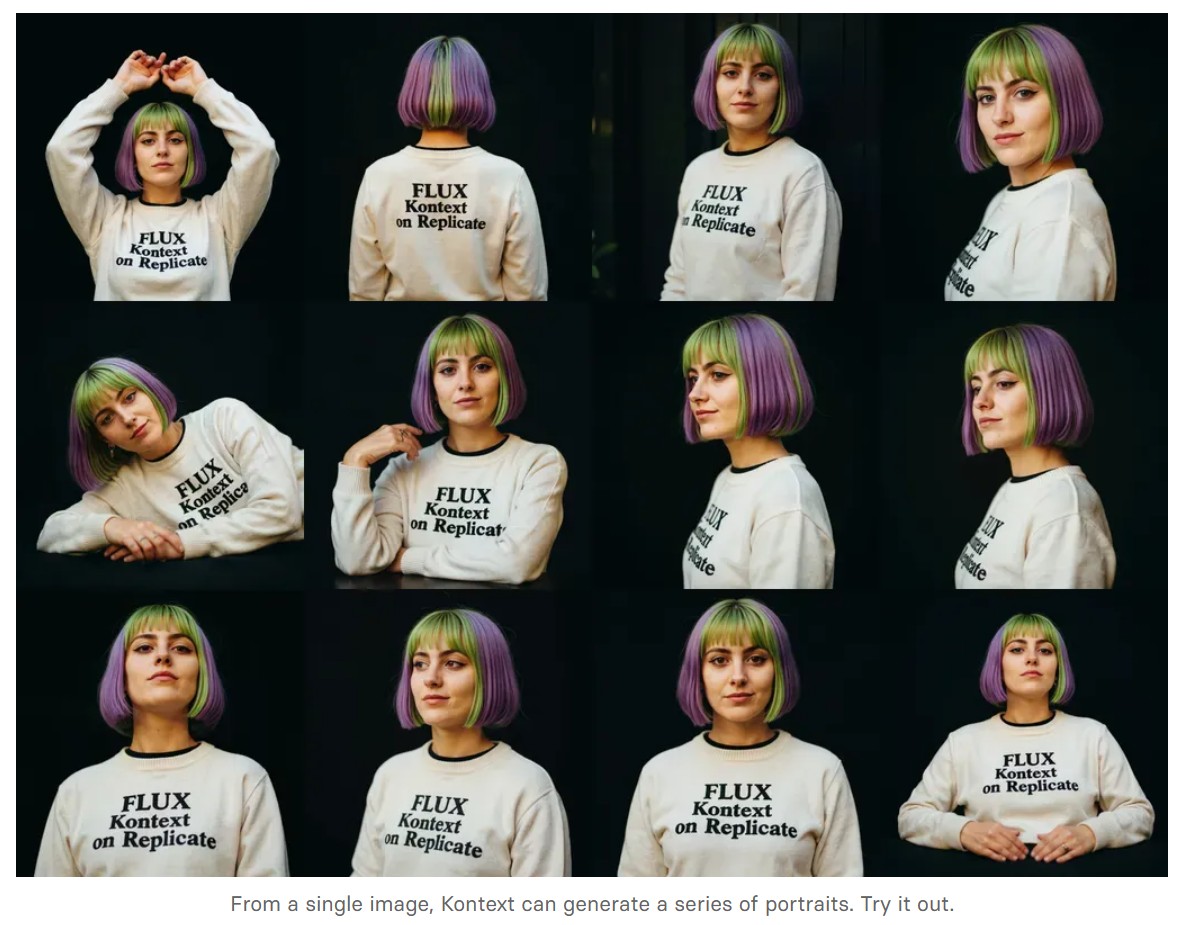
-
AI Models – A walkthrough by Andreas Horn
the 8 most important model types and what they’re actually built to do: ⬇️
1. 𝗟𝗟𝗠 – 𝗟𝗮𝗿𝗴𝗲 𝗟𝗮𝗻𝗴𝘂𝗮𝗴𝗲 𝗠𝗼𝗱𝗲𝗹
→ Your ChatGPT-style model.
Handles text, predicts the next token, and powers 90% of GenAI hype.
🛠 Use case: content, code, convos.
2. 𝗟𝗖𝗠 – 𝗟𝗮𝘁𝗲𝗻𝘁 𝗖𝗼𝗻𝘀𝗶𝘀𝘁𝗲𝗻𝗰𝘆 𝗠𝗼𝗱𝗲𝗹
→ Lightweight, diffusion-style models.
Fast, quantized, and efficient — perfect for real-time or edge deployment.
🛠 Use case: image generation, optimized inference.
3. 𝗟𝗔𝗠 – 𝗟𝗮𝗻𝗴𝘂𝗮𝗴𝗲 𝗔𝗰𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻 𝗠𝗼𝗱𝗲𝗹
→ Where LLM meets planning.
Adds memory, task breakdown, and intent recognition.
🛠 Use case: AI agents, tool use, step-by-step execution.
4. 𝗠𝗼𝗘 – 𝗠𝗶𝘅𝘁𝘂𝗿𝗲 𝗼𝗳 𝗘𝘅𝗽𝗲𝗿𝘁𝘀
→ One model, many minds.
Routes input to the right “expert” model slice — dynamic, scalable, efficient.
🛠 Use case: high-performance model serving at low compute cost.
5. 𝗩𝗟𝗠 – 𝗩𝗶𝘀𝗶𝗼𝗻 𝗟𝗮𝗻𝗴𝘂𝗮𝗴𝗲 𝗠𝗼𝗱𝗲𝗹
→ Multimodal beast.
Combines image + text understanding via shared embeddings.
🛠 Use case: Gemini, GPT-4o, search, robotics, assistive tech.
6. 𝗦𝗟𝗠 – 𝗦𝗺𝗮𝗹𝗹 𝗟𝗮𝗻𝗴𝘂𝗮𝗴𝗲 𝗠𝗼𝗱𝗲𝗹
→ Tiny but mighty.
Designed for edge use, fast inference, low latency, efficient memory.
🛠 Use case: on-device AI, chatbots, privacy-first GenAI.
7. 𝗠𝗟𝗠 – 𝗠𝗮𝘀𝗸𝗲𝗱 𝗟𝗮𝗻𝗴𝘂𝗮𝗴𝗲 𝗠𝗼𝗱𝗲𝗹
→ The OG foundation model.
Predicts masked tokens using bidirectional context.
🛠 Use case: search, classification, embeddings, pretraining.
8. 𝗦𝗔𝗠 – 𝗦𝗲𝗴𝗺𝗲𝗻𝘁 𝗔𝗻𝘆𝘁𝗵𝗶𝗻𝗴 𝗠𝗼𝗱𝗲𝗹
→ Vision model for pixel-level understanding.
Highlights, segments, and understands *everything* in an image.
🛠 Use case: medical imaging, AR, robotics, visual agents.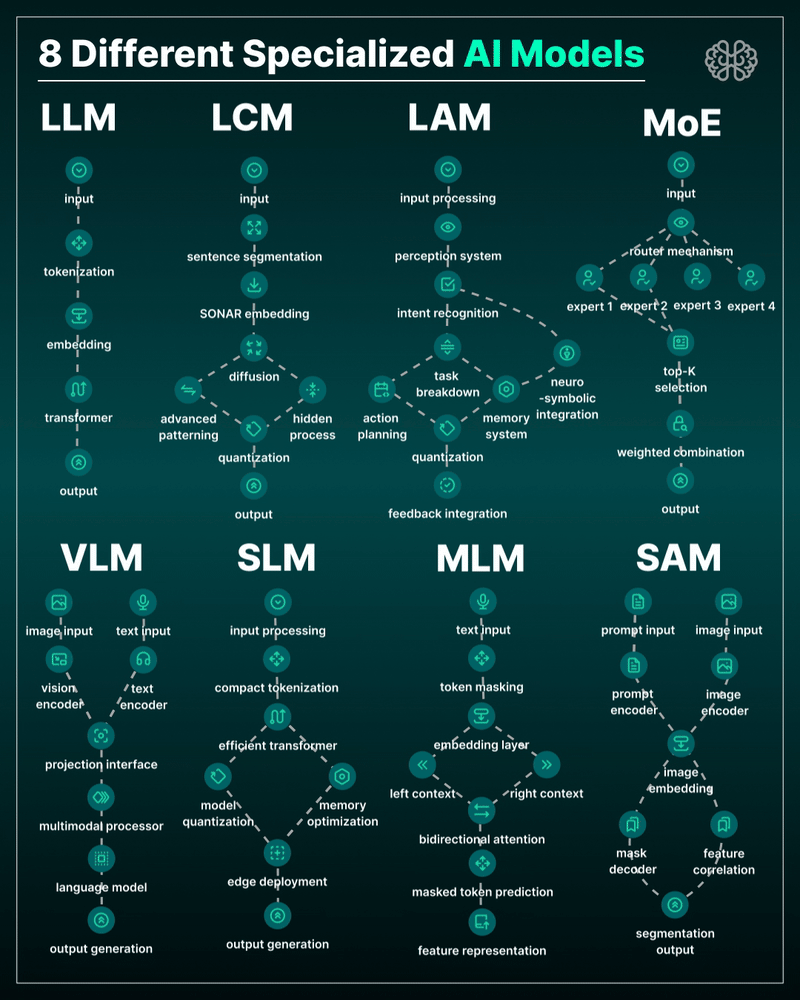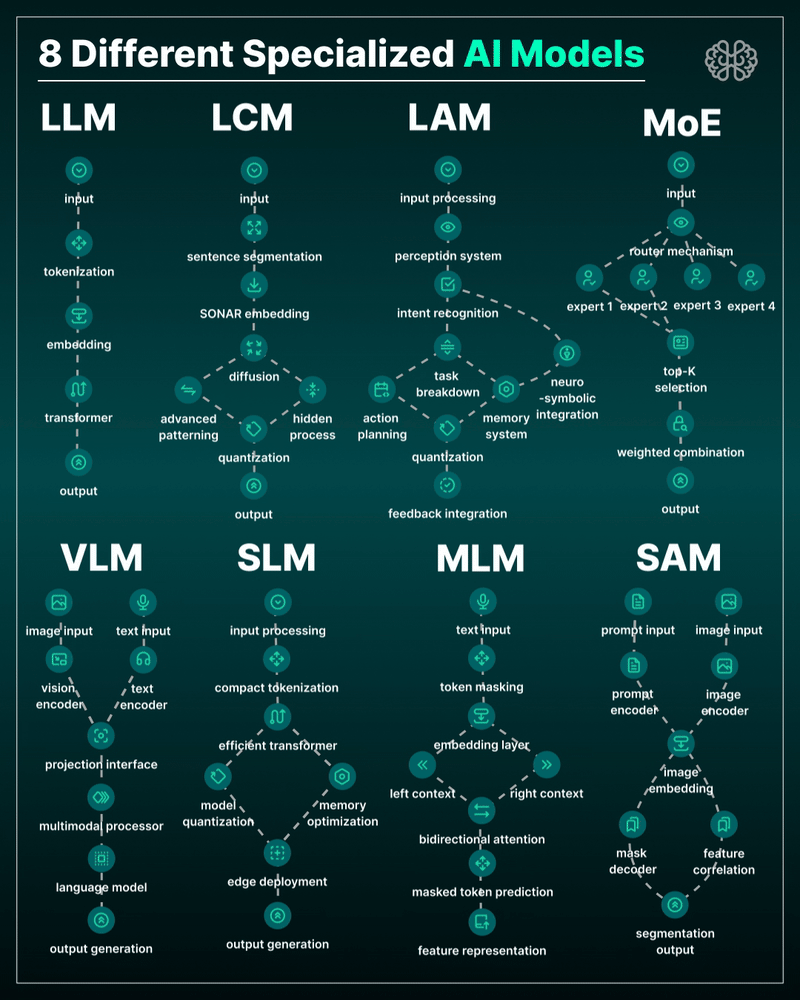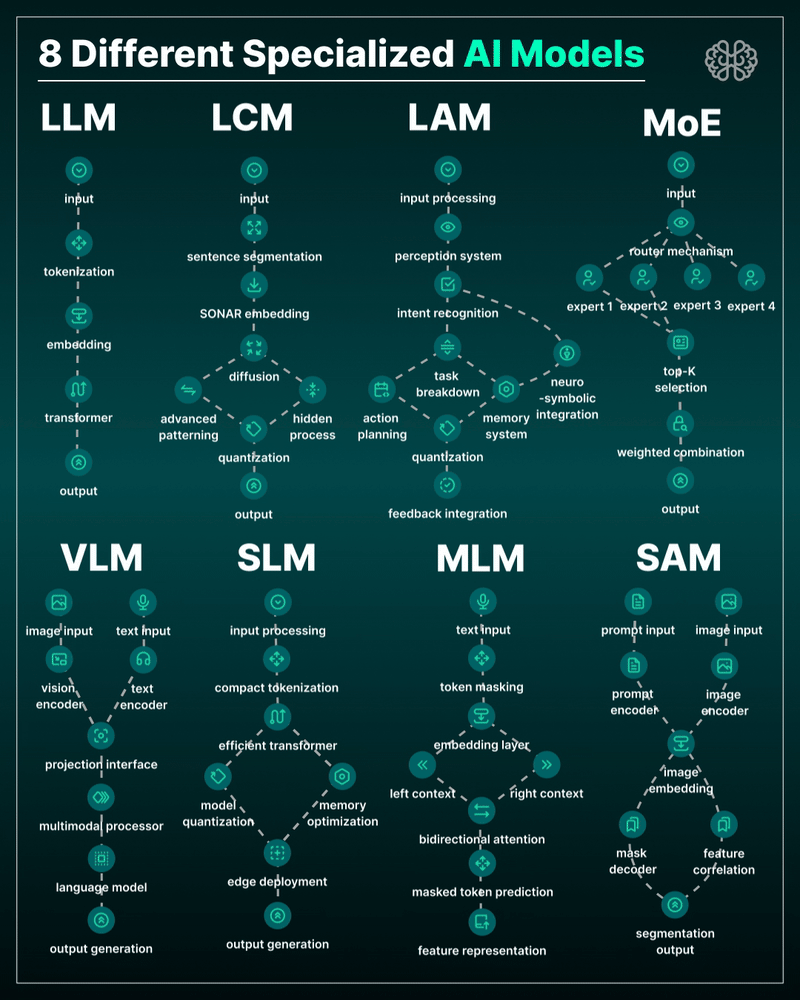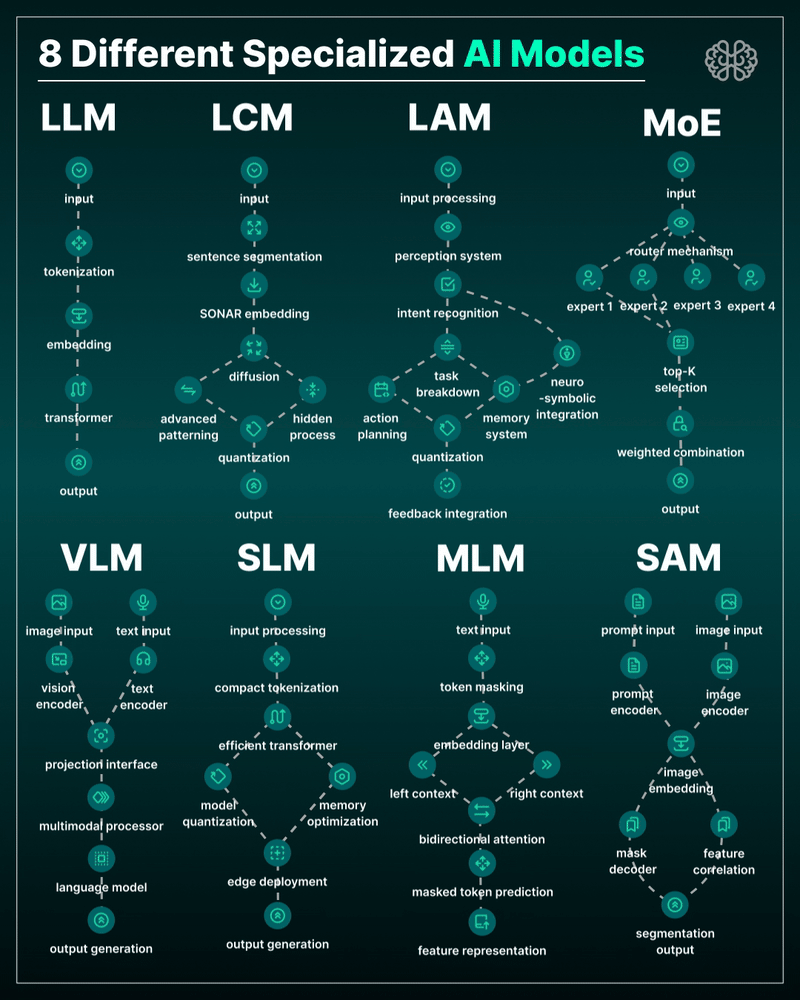
-
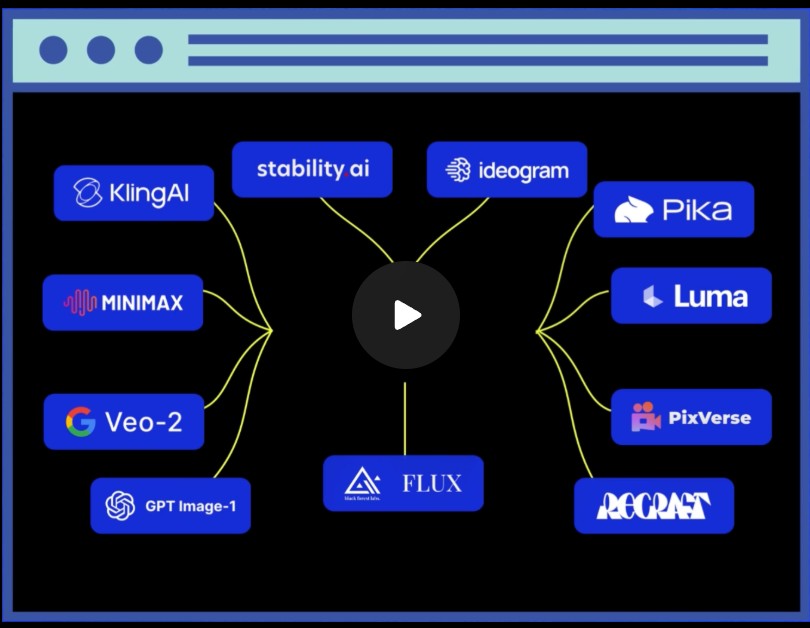
Introducting ComfyUI Native API Nodes
https://blog.comfy.org/p/comfyui-native-api-nodes
Models Supported
- Black Forest Labs Flux 1.1[pro] Ultra, Flux .1[pro]
- Kling 2.0, 1.6, 1.5 & Various Effects
- Luma Photon, Ray2, Ray1.6
- MiniMax Text-to-Video, Image-to-Video
- PixVerse V4 & Effects
- Recraft V3, V2 & Various Tools
- Stability AI Stable Image Ultra, Stable Diffusion 3.5 Large
- Google Veo2
- Ideogram V3, V2, V1
- OpenAI GPT4o image
- Pika 2.2
-
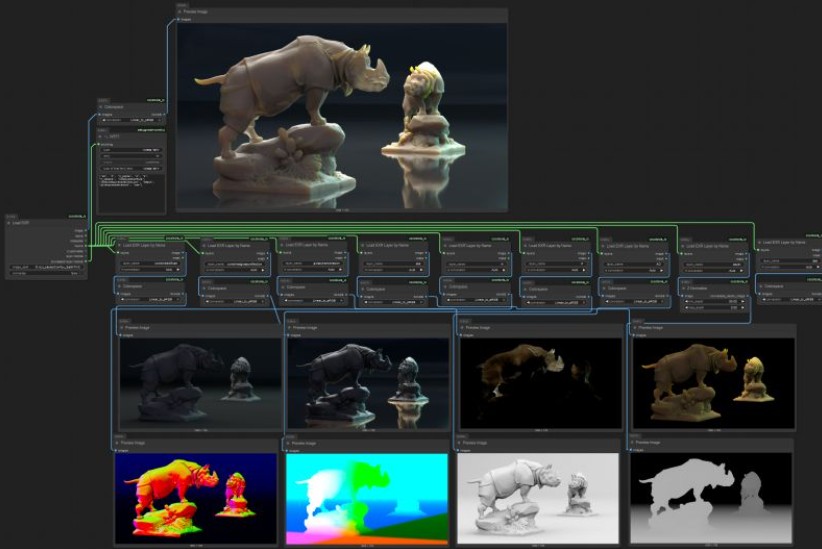
ComfyUI-CoCoTools_IO – A set of nodes focused on advanced image I/O operations, particularly for EXR file handling
https://github.com/Conor-Collins/ComfyUI-CoCoTools_IO
Features
- Advanced EXR image input with multilayer support
- EXR layer extraction and manipulation
- High-quality image saving with format-specific options
- Standard image format loading with bit depth awareness
Current Nodes
Image I/O
- Image Loader: Load standard image formats (PNG, JPG, WebP, etc.) with proper bit depth handling
- Load EXR: Comprehensive EXR file loading with support for multiple layers, channels, and cryptomatte data
- Load EXR Layer by Name: Extract specific layers from EXR files (similar to Nuke’s Shuffle node)
- Cryptomatte Layer: Specialized handling for cryptomatte layers in EXR files
- Image Saver: Save images in various formats with format-specific options (bit depth, compression, etc.)
Image Processing
- Colorspace: Convert between sRGB and Linear colorspaces
- Z Normalize: Normalize depth maps and other single-channel data
-
Claudio Tosti – La vita pittoresca dell’abate Uggeri
https://vivariumnovum.it/saggistica/varia/la-vita-pittoresca-dellabate-uggeri
Book author: Claudio Tosti
Title: La vita pittoresca dell’abate Uggeri – Vol. I – La Giornata Tuscolana- ISBN: 978-8895611990
Video made with Pixverse.ai and DaVinci Resolve
FEATURED POSTS
-
Use macro stacking to create 3D models and stereo photography
www.heliconsoft.com/heliconsoft-products/helicon-3d-viewer/
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LiwxPsOGQOY (more…)
-
59 AI Filmmaking Tools For Your Workflow
https://curiousrefuge.com/blog/ai-filmmaking-tools-for-filmmakers
- Runway
- PikaLabs
- Pixverse (free)
- Haiper (free)
- Moonvalley (free)
- Morph Studio (free)
- SORA
- Google Veo
- Stable Video Diffusion (free)
- Leonardo
- Krea
- Kaiber
- Letz.AI
- Midjourney
- Ideogram
- DALL-E
- Firefly
- Stable Diffusion
- Google Imagen 3
- Polycam
- LTX Studio
- Simulon
- Elevenlabs
- Auphonic
- Adobe Enhance
- Adobe’s AI Rotoscoping
- Adobe Photoshop Generative Fill
- Canva Magic Brush
- Akool
- Topaz Labs
- Magnific.AI
- FreePik
- BigJPG
- LeiaPix
- Move AI
- Mootion
- Heygen
- Synthesia
- Chat GPT-4
- Claude 3
- Nolan AI
- Google Gemini
- Meta Llama 3
- Suno
- Udio
- Stable Audio
- Soundful
- Google MusicML
- Viggle
- SyncLabs
- Lalamu
- LensGo
- D-ID
- WonderStudio
- Cuebric
- Blockade Labs
- Chat GPT-4o
- Luma Dream Machine
- Pallaidium (free)
-
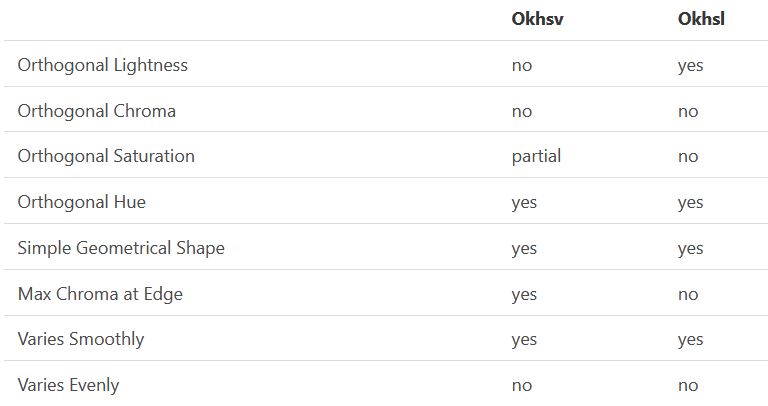
Björn Ottosson – OKHSV and OKHSL – Two new color spaces for color picking
https://bottosson.github.io/misc/colorpicker
https://bottosson.github.io/posts/colorpicker/
https://www.smashingmagazine.com/2024/10/interview-bjorn-ottosson-creator-oklab-color-space/
One problem with sRGB is that in a gradient between blue and white, it becomes a bit purple in the middle of the transition. That’s because sRGB really isn’t created to mimic how the eye sees colors; rather, it is based on how CRT monitors work. That means it works with certain frequencies of red, green, and blue, and also the non-linear coding called gamma. It’s a miracle it works as well as it does, but it’s not connected to color perception. When using those tools, you sometimes get surprising results, like purple in the gradient.
There were also attempts to create simple models matching human perception based on XYZ, but as it turned out, it’s not possible to model all color vision that way. Perception of color is incredibly complex and depends, among other things, on whether it is dark or light in the room and the background color it is against. When you look at a photograph, it also depends on what you think the color of the light source is. The dress is a typical example of color vision being very context-dependent. It is almost impossible to model this perfectly.
I based Oklab on two other color spaces, CIECAM16 and IPT. I used the lightness and saturation prediction from CIECAM16, which is a color appearance model, as a target. I actually wanted to use the datasets used to create CIECAM16, but I couldn’t find them.
IPT was designed to have better hue uniformity. In experiments, they asked people to match light and dark colors, saturated and unsaturated colors, which resulted in a dataset for which colors, subjectively, have the same hue. IPT has a few other issues but is the basis for hue in Oklab.
In the Munsell color system, colors are described with three parameters, designed to match the perceived appearance of colors: Hue, Chroma and Value. The parameters are designed to be independent and each have a uniform scale. This results in a color solid with an irregular shape. The parameters are designed to be independent and each have a uniform scale. This results in a color solid with an irregular shape. Modern color spaces and models, such as CIELAB, Cam16 and Björn Ottosson own Oklab, are very similar in their construction.
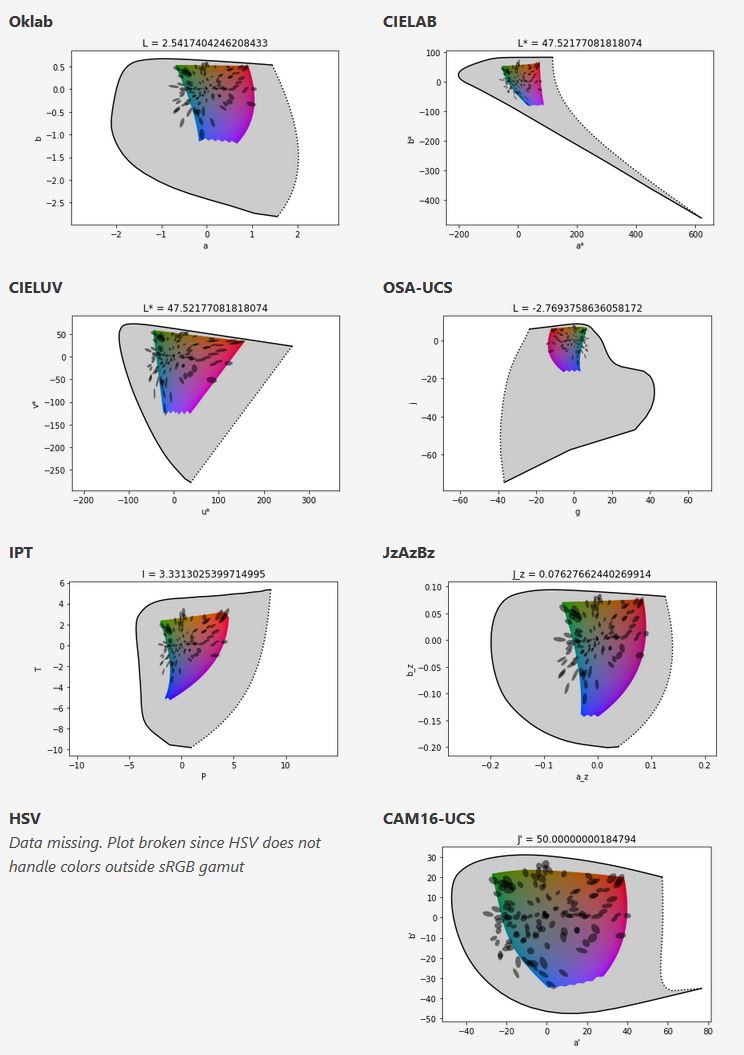
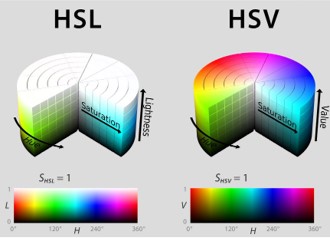
By far the most used color spaces today for color picking are HSL and HSV, two representations introduced in the classic 1978 paper “Color Spaces for Computer Graphics”. HSL and HSV designed to roughly correlate with perceptual color properties while being very simple and cheap to compute.
Today HSL and HSV are most commonly used together with the sRGB color space.

One of the main advantages of HSL and HSV over the different Lab color spaces is that they map the sRGB gamut to a cylinder. This makes them easy to use since all parameters can be changed independently, without the risk of creating colors outside of the target gamut.
The main drawback on the other hand is that their properties don’t match human perception particularly well.
Reconciling these conflicting goals perfectly isn’t possible, but given that HSV and HSL don’t use anything derived from experiments relating to human perception, creating something that makes a better tradeoff does not seem unreasonable.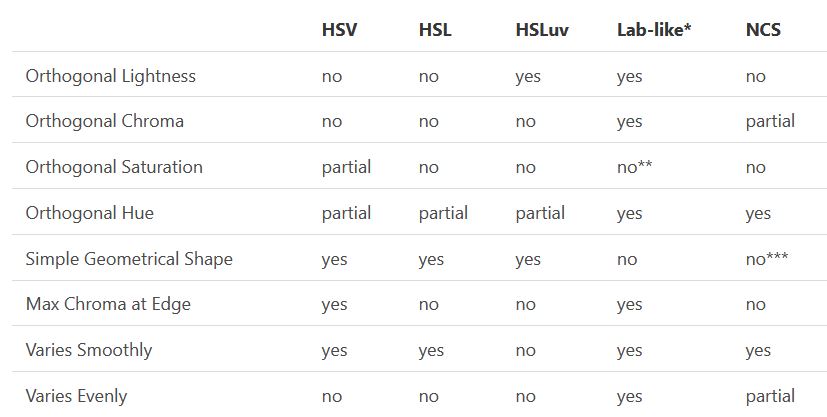
With this new lightness estimate, we are ready to look into the construction of Okhsv and Okhsl.