BREAKING NEWS
LATEST POSTS
-
AI and the Law – InvokeAI Got a Copyright for an Image Made Entirely With AI. Here’s How
-
Micro LED displays
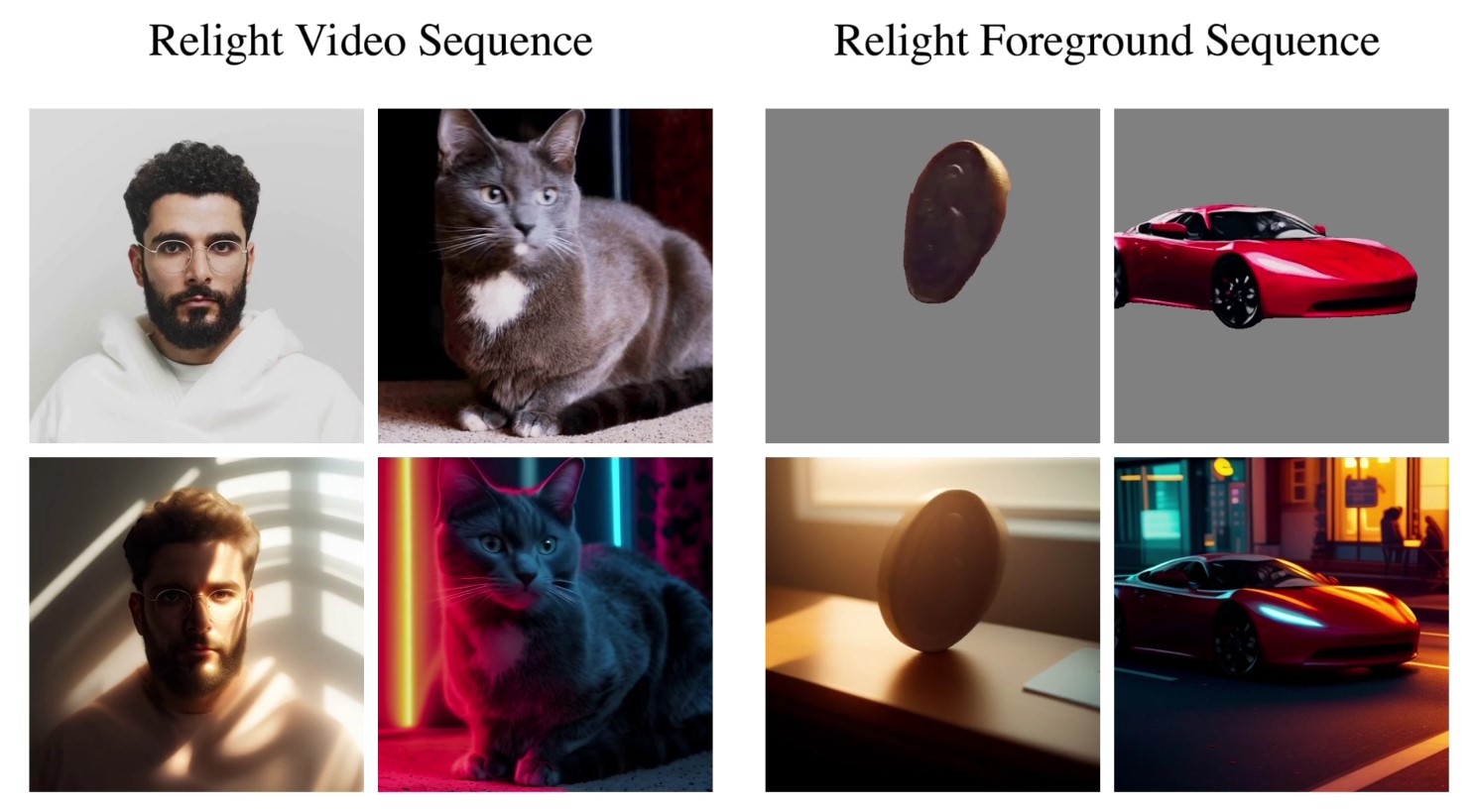
Micro LED displays are a cutting-edge technology that promise significant improvements over existing display methods like OLED and LCD. By using tiny, individual LEDs for each pixel, these displays can deliver exceptional brightness, contrast, and energy efficiency. Their inherent durability and superior performance make them an attractive option for high-end consumer electronics, wearable devices, and even large-scale display panels.
The technology is seen as the future of display innovation, aiming to merge high-quality visuals with low power consumption and long-lasting performance.Despite their advantages, micro LED displays face substantial manufacturing hurdles that have slowed their mass-market adoption. The production process requires the precise transfer and alignment of millions of microscopic LEDs onto a substrate—a task that is both technically challenging and cost-intensive. Issues with yield, scalability, and quality control continue to persist, making it difficult to achieve the economies of scale necessary for widespread commercial use. As industry leaders invest heavily in research and development to overcome these obstacles, the technology remains on the cusp of becoming a viable alternative to current display technologies.
-
Nvidia CUDA Toolkit – a development environment for creating high-performance, GPU-accelerated applications
https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-toolkit
With it, you can develop, optimize, and deploy your applications on GPU-accelerated embedded systems, desktop workstations, enterprise data centers, cloud-based platforms, and supercomputers. The toolkit includes GPU-accelerated libraries, debugging and optimization tools, a C/C++ compiler, and a runtime library.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-P28LKWTzrI
Check your Cuda version, it will be the release version here:
>>> nvcc --version nvcc: NVIDIA (R) Cuda compiler driver Copyright (c) 2005-2024 NVIDIA Corporation Built on Wed_Apr_17_19:36:51_Pacific_Daylight_Time_2024 Cuda compilation tools, release 12.5, V12.5.40 Build cuda_12.5.r12.5/compiler.34177558_0or from here:
>>> nvidia-smi Mon Jun 16 12:35:20 2025 +-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | NVIDIA-SMI 555.85 Driver Version: 555.85 CUDA Version: 12.5 | |-----------------------------------------+------------------------+----------------------+
FEATURED POSTS
-
Photography basics: Shutter angle and shutter speed and motion blur
http://www.shutterangle.com/2012/cinematic-look-frame-rate-shutter-speed/
https://www.cinema5d.com/global-vs-rolling-shutter
https://www.wikihow.com/Choose-a-Camera-Shutter-Speed
Shutter is the device that controls the amount of light through a lens. Basically in general it controls the amount of time a film is exposed.
Shutter speed is how long this device is open for, which also defines motion blur… the longer it stays open the blurrier the image captured.
The number refers to the amount of light actually allowed through.As a reference, shooting at 24fps, at 180 shutter angle or 1/48th of shutter speed (0.0208 exposure time) will produce motion blur which is similar to what we perceive at naked eye
Talked of as in (shutter) angles, for historical reasons, as the original exposure mechanism was controlled through a pie shaped mirror in front of the lens.
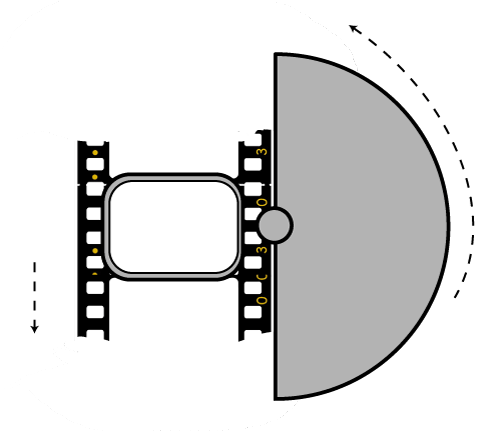
A shutter of 180 degrees is blocking/allowing light for half circle. (half blocked, half open). 270 degrees is one quarter pie shaped, which would allow for a higher exposure time (3 quarter pie open, vs one quarter closed) 90 degrees is three quarter pie shaped, which would allow for a lower exposure (one quarter open, three quarters closed)
(more…)
-
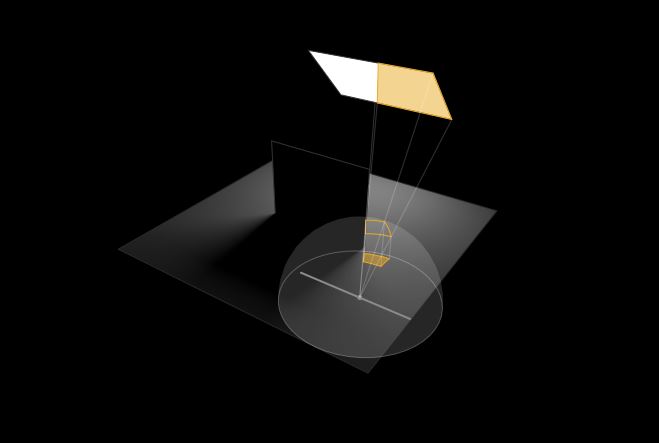
Sun cone angle (angular diameter) as perceived by earth viewers
Also see:
https://www.pixelsham.com/2020/08/01/solid-angle-measures/
The cone angle of the sun refers to the angular diameter of the sun as observed from Earth, which is related to the apparent size of the sun in the sky.
The angular diameter of the sun, or the cone angle of the sunlight as perceived from Earth, is approximately 0.53 degrees on average. This value can vary slightly due to the elliptical nature of Earth’s orbit around the sun, but it generally stays within a narrow range.
Here’s a more precise breakdown:
-
- Average Angular Diameter: About 0.53 degrees (31 arcminutes)
- Minimum Angular Diameter: Approximately 0.52 degrees (when Earth is at aphelion, the farthest point from the sun)
- Maximum Angular Diameter: Approximately 0.54 degrees (when Earth is at perihelion, the closest point to the sun)
This angular diameter remains relatively constant throughout the day because the sun’s distance from Earth does not change significantly over a single day.
To summarize, the cone angle of the sun’s light, or its angular diameter, is typically around 0.53 degrees, regardless of the time of day.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Angular_diameter
-