BREAKING NEWS
LATEST POSTS
-
Sangeet Paul Choudary – AI won’t eat your job, but it will eat your salary
https://medium.com/@sanguit/ai-wont-eat-your-job-but-it-will-eat-your-salary-a810121d89e4
intelligence (AI) is likely to impact job salaries rather than eliminating jobs entirely. The primary argument is that AI will erode the skill premium traditionally commanded by high-skilled workers. This erosion happens through three key mechanisms:
- Skill Premium on Specialized Tasks: AI enables low-skilled workers to perform tasks at a level comparable to high-skilled workers, making skilled workers more substitutable and reducing their wage premium.
- Skill Premium on Learning Advantages: AI’s ability to continuously learn and improve from vast amounts of data threatens professions that rely on continuous learning and skill development. For example, in healthcare, AI can absorb and replicate the learning and expertise of doctors, diminishing their unique value.
- Skill Premium on Managerial Advantages: AI agents can take over managerial tasks like planning and resource allocation, which have traditionally required human intervention. As AI becomes more sophisticated, even complex managerial roles might lose their premium as AI performs these functions more efficiently.
These factors collectively lead to a commoditization of skills, reducing the relative advantage and salary premium of traditionally high-skilled and managerial roles. The article emphasizes that while AI may not replace jobs outright, it will significantly affect how jobs are valued and compensated.
-
-
John Cutler – The production Failure Threshold (for Start Ups)
https://cutlefish.substack.com/p/tbm-290-the-dependency-threshold
There’s a point beyond which no individual, no team, and no company can solve the dependency and constraint puzzle using brute-force methods.
Imagine a company where 10% of the work involves multiple teams, touches different codebases, requires careful coordination, and requires frequent meetings that span organizational boundaries and challenge local incentives. This situation might still be feasible.
Now imagine that this percentage is more like 25%. Very quickly, the constraint satisfaction problem becomes an order of magnitude more complex.
What might a heuristic approach look like in product development?
- Reducing work-in-progress limits
- Force ranking priorities
- Weighted-shortest-job-first
There (is) a chance that teams will miss an opportunity to find an optimal solution? Yes. But the probability of that happening is far outweighed by the likelihood that 1) bad things will NOT happen, and 2) good things may emerge.
The trouble, I believe, is that it can be incredibly hard for managers to make the case for, on the surface, doing less. Discussions about WIP limits and prioritization often devolve into debates over the actual WIP limit and precise estimates! Instead of seeing the forest through the trees, we obsess about finding the optimal answer.
-
The Three Laws of Software Code Complexity
https://maheshba.bitbucket.io/blog/2024/05/08/2024-ThreeLaws.html
- A well-designed system will degrade into a badly designed system over time.
- Complexity is a Moat (filled by Leaky Abstractions).
- There is no fundamental upper limit on Software Complexity.
FEATURED POSTS
-
Animation/VFX/Game Industry JOB POSTINGS by Chris Mayne
Chris is now using Google’s Looker Studio (this may better help those that aren’t able to use the filters on the spreadsheet):
https://lookerstudio.google.com/u/0/reporting/2f39b56e-7393-4aa2-9fd5-bf8bf615c95f/page/5koHB
Older format: docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1eR2oAXOuflr8CZeGoz3JTrsgNj3KuefbdXJOmNtjEVM/edit#gid=0
For any studios that would like to add positions to this, please feel free to use the following form:
https://docs.google.com/forms/d/e/1FAIpQLSeXziY3GQ8N7bxM-GxwDoZ7AimguHru0105PLVQtNYygswIlw/viewform
-
Scientists claim to have discovered ‘new colour’ no one has seen before: Olo
https://www.bbc.com/news/articles/clyq0n3em41o
By stimulating specific cells in the retina, the participants claim to have witnessed a blue-green colour that scientists have called “olo”, but some experts have said the existence of a new colour is “open to argument”.
The findings, published in the journal Science Advances on Friday, have been described by the study’s co-author, Prof Ren Ng from the University of California, as “remarkable”.
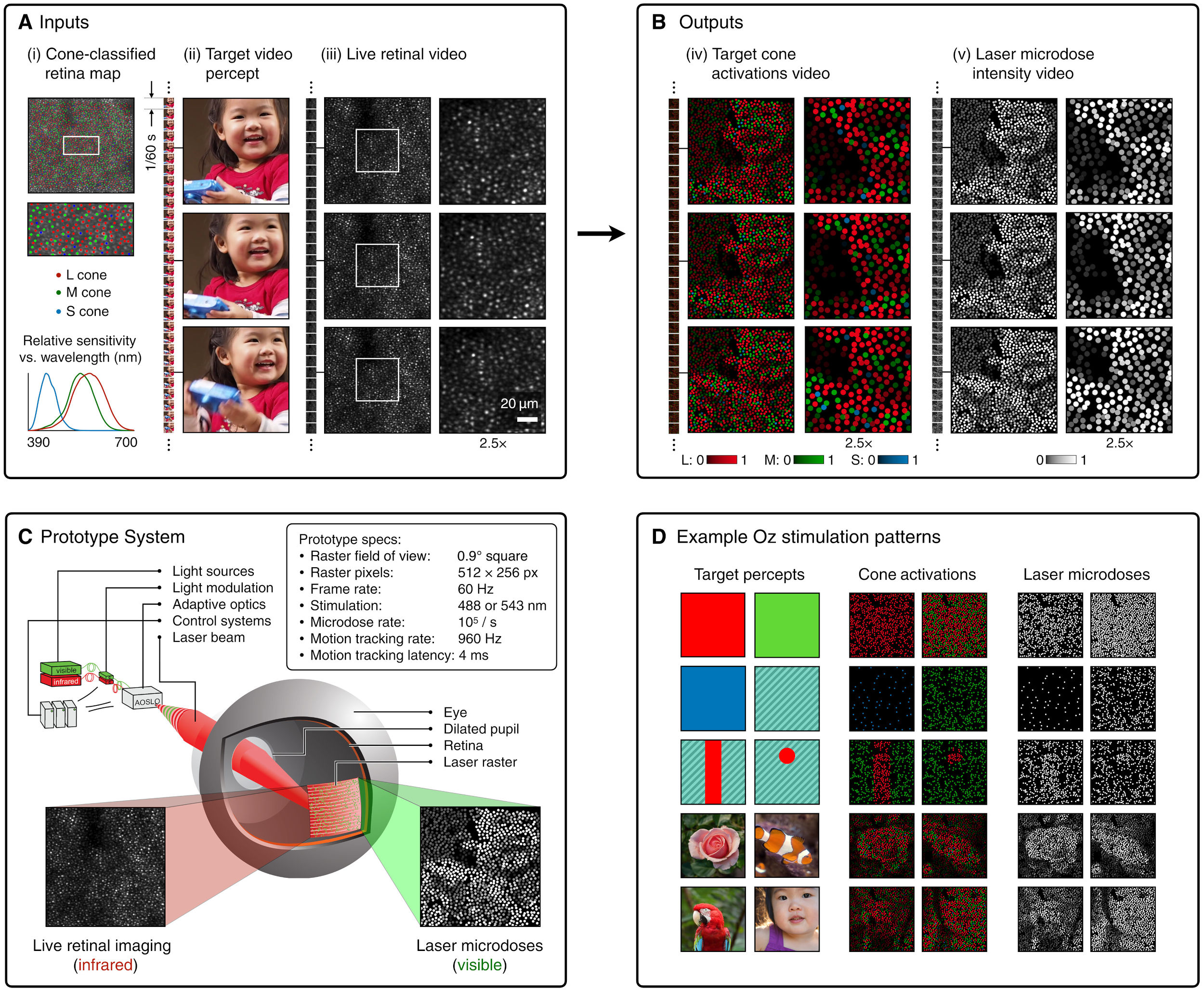
(A) System inputs. (i) Retina map of 103 cone cells preclassified by spectral type (7). (ii) Target visual percept (here, a video of a child, see movie S1 at 1:04). (iii) Infrared cellular-scale imaging of the retina with 60-frames-per-second rolling shutter. Fixational eye movement is visible over the three frames shown.
(B) System outputs. (iv) Real-time per-cone target activation levels to reproduce the target percept, computed by: extracting eye motion from the input video relative to the retina map; identifying the spectral type of every cone in the field of view; computing the per-cone activation the target percept would have produced. (v) Intensities of visible-wavelength 488-nm laser microdoses at each cone required to achieve its target activation level.
(C) Infrared imaging and visible-wavelength stimulation are physically accomplished in a raster scan across the retinal region using AOSLO. By modulating the visible-wavelength beam’s intensity, the laser microdoses shown in (v) are delivered. Drawing adapted with permission [Harmening and Sincich (54)].
(D) Examples of target percepts with corresponding cone activations and laser microdoses, ranging from colored squares to complex imagery. Teal-striped regions represent the color “olo” of stimulating only M cones.





