BREAKING NEWS
LATEST POSTS
-
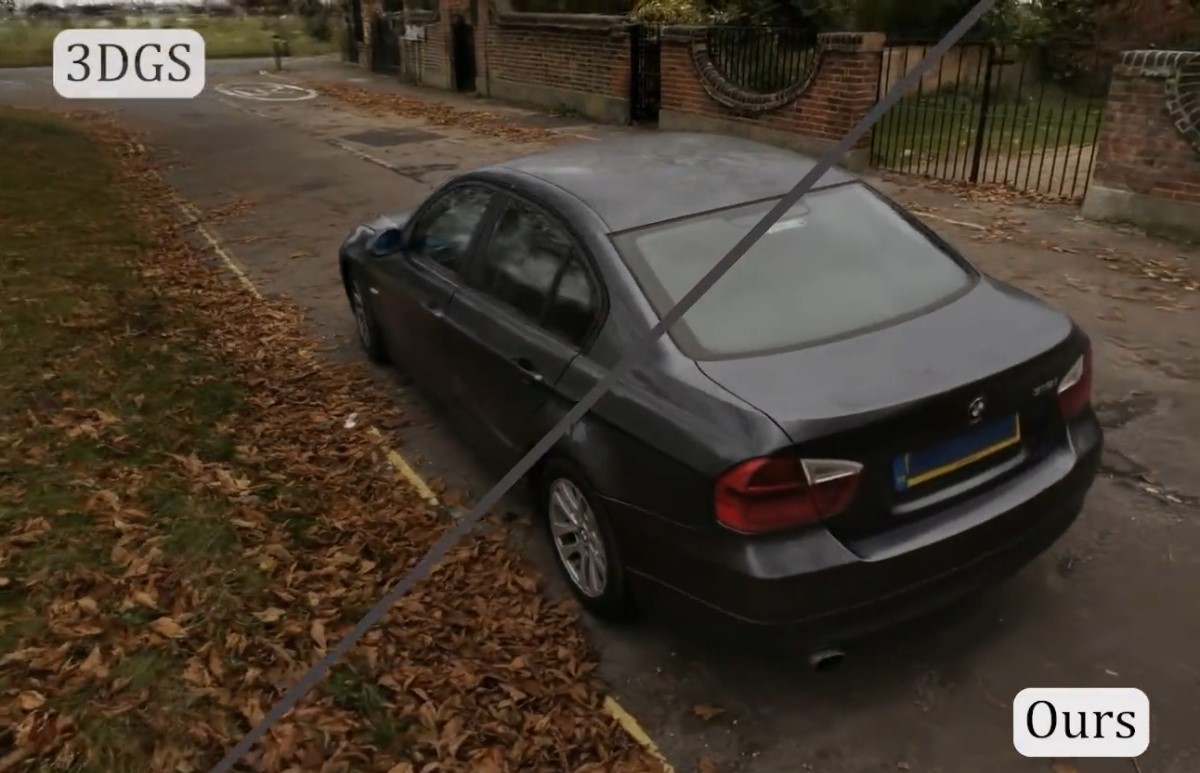
A Looming Threat to Bitcoin (and the financial world)- The Risk of a Quantum Hack
Advancements in quantum computing pose a potential threat to Bitcoin’s security. Google’s recent progress with its Willow quantum-computing chip has highlighted the possibility that future quantum computers could break the encryption protecting Bitcoin, enabling hackers to access secure digital wallets and potentially causing significant devaluation.
Researchers estimate that a quantum computer capable of such decryption is likely more than a decade away. Nonetheless, the Bitcoin developer community faces the complex task of upgrading the system to incorporate quantum-resistant encryption methods. Achieving consensus within the decentralized community may be a slow process, and users would eventually need to transfer their holdings to quantum-resistant addresses to safeguard their assets.
A quantum-powered attack on Bitcoin could also negatively impact traditional financial markets, possibly leading to substantial losses and a deep recession. To mitigate such threats, President-elect Donald Trump has proposed creating a strategic reserve for the government’s Bitcoin holdings.

-
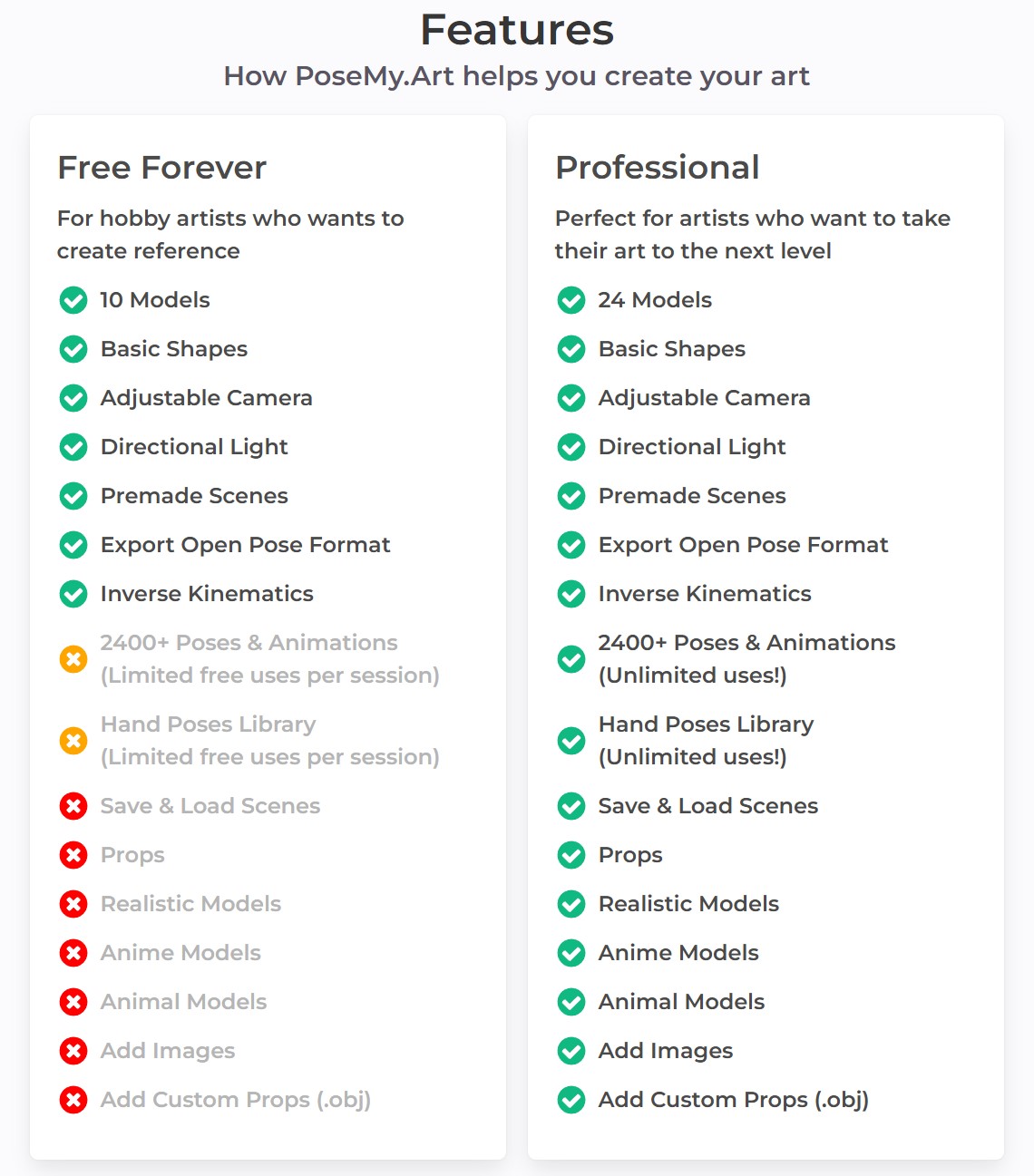
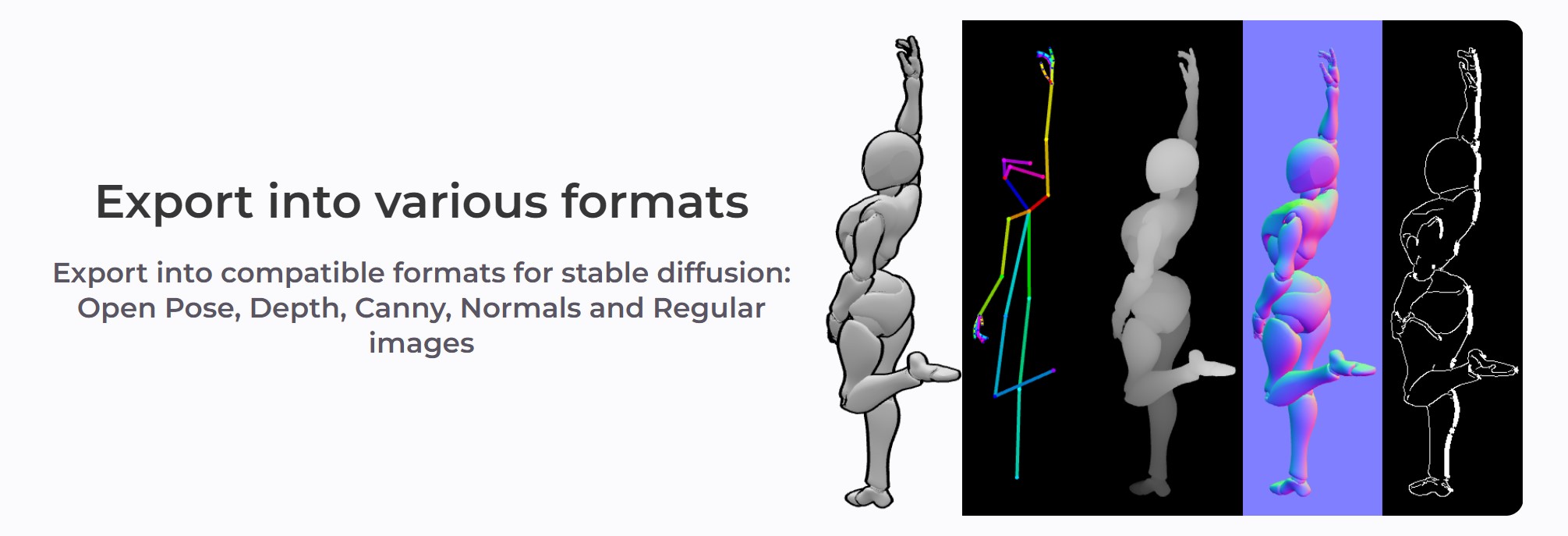
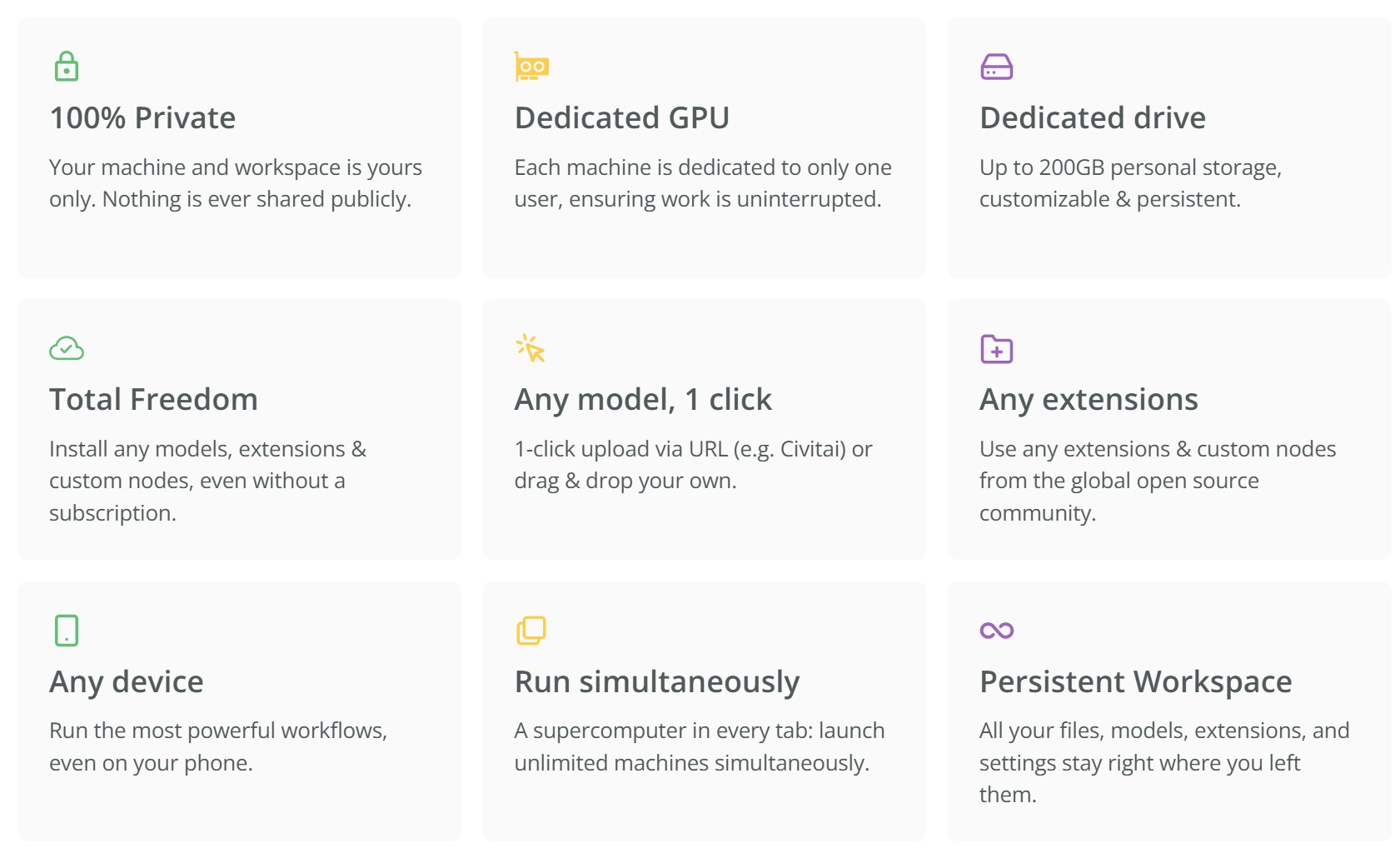
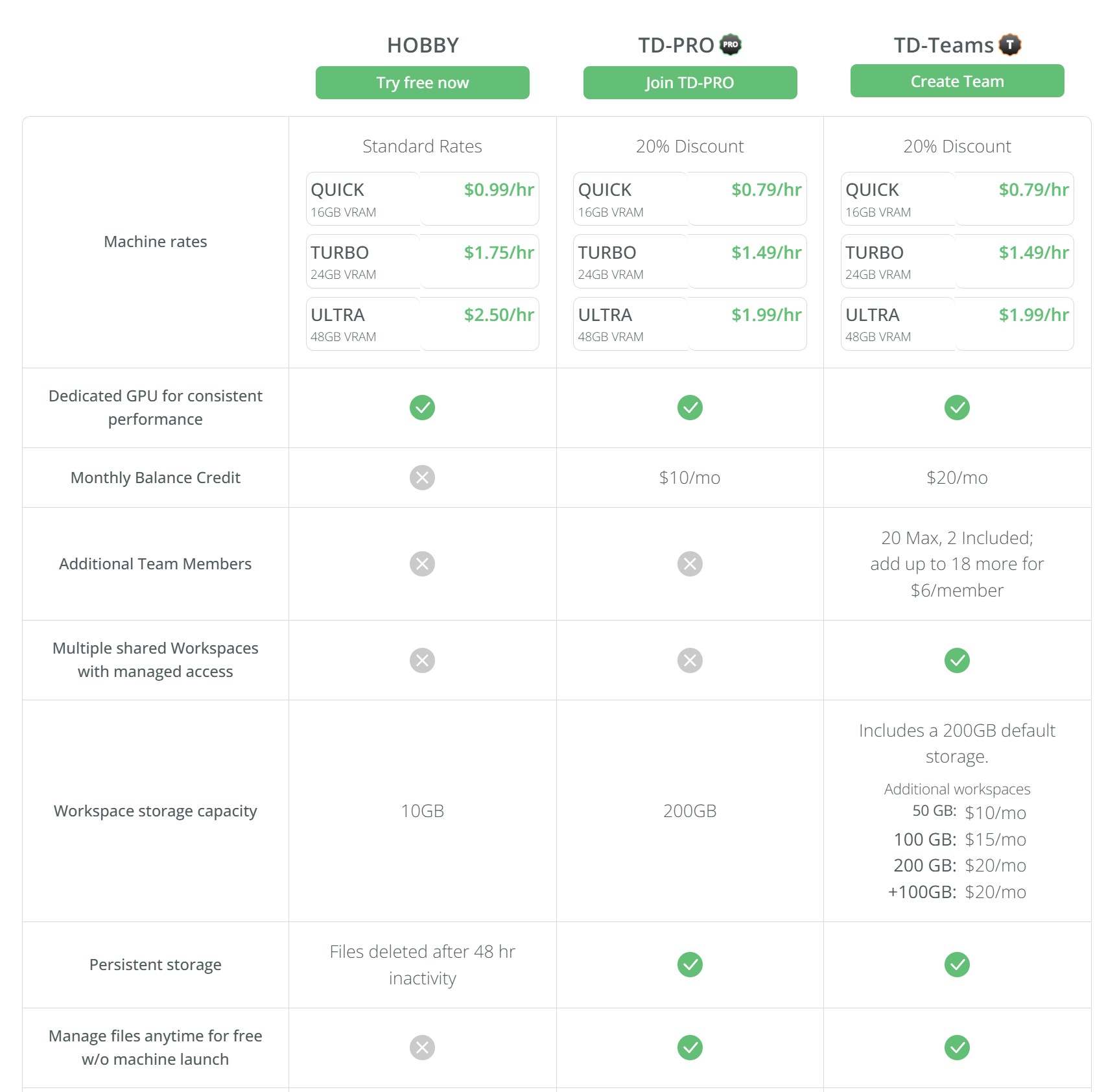
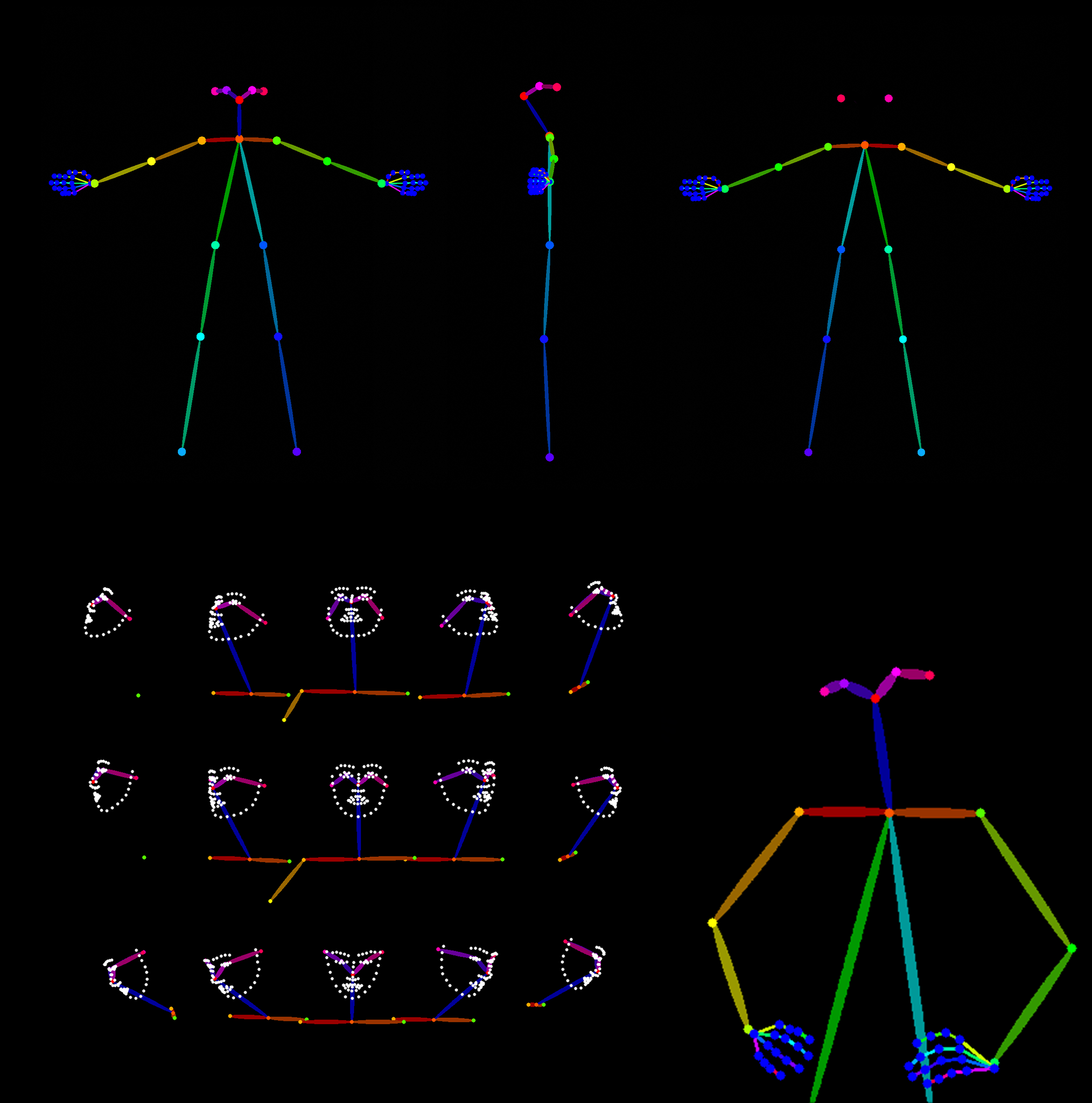
posemy.art – Create Poses for Drawing Reference and AI apps in Seconds for Free
-
Mickmumpitz – Create CONSISTENT CHARACTERS from an INPUT IMAGE with FLUX and a character sheet! (ComfyUI Tutorial + Installation Guide + Lora training)
https://www.patreon.com/posts/create-from-with-115147229
Note: the image below is not from the workflow
Nodes:
Install missing nodes in the workflow through the manager.
Models:
Make sure not to mix SD1.5 and SDLX models.
Follow the details under the pdf below.
General suggesions:
– Comfy Org / Flux.1 [dev] Checkpoint model (fp8)
The manager will put it under checkpoints, which will not work.
Make sure to put it under the models/unet folder for the Load Diffusion Model node to work.
– same for realvisxlV50_v50LightningBakedvae.safetensors
it should go under models/vae
-
Emmanuel Tsekleves – Writing Research Papers
Here’s the journey of crafting a compelling paper:
1️. ABSTRACT
This is your elevator pitch.
Give a methodology overview.
Paint the problem you’re solving.
Highlight key findings and their impact.
2️. INTRODUCTION
Start with what we know.
Set the stage for our current understanding.
Hook your reader with the relevance of your work.
3️. LITERATURE REVIEW
Identify what’s unknown.
Spot the gaps in current knowledge.
Your job in the next sections is to fill this gap.
4️. METHODOLOGY
What did you do?
Outline how you’ll fill that gap.
Be transparent about your approach.
Make it reproducible so others can follow.
5️. RESULTS
Let the data speak for itself.
Present your findings clearly.
Keep it concise and focused.
6️. DISCUSSION
Now, connect the dots.
Discuss implications and significance.
How do your findings bridge the knowledge gap?
7️. CONCLUSION
Wrap it up with future directions.
What does this mean for us moving forward?
Leave the reader with a call to action or reflection.
8️. REFERENCES
Acknowledge the giants whose shoulders you stand on.
A robust reference list shows the depth of your research.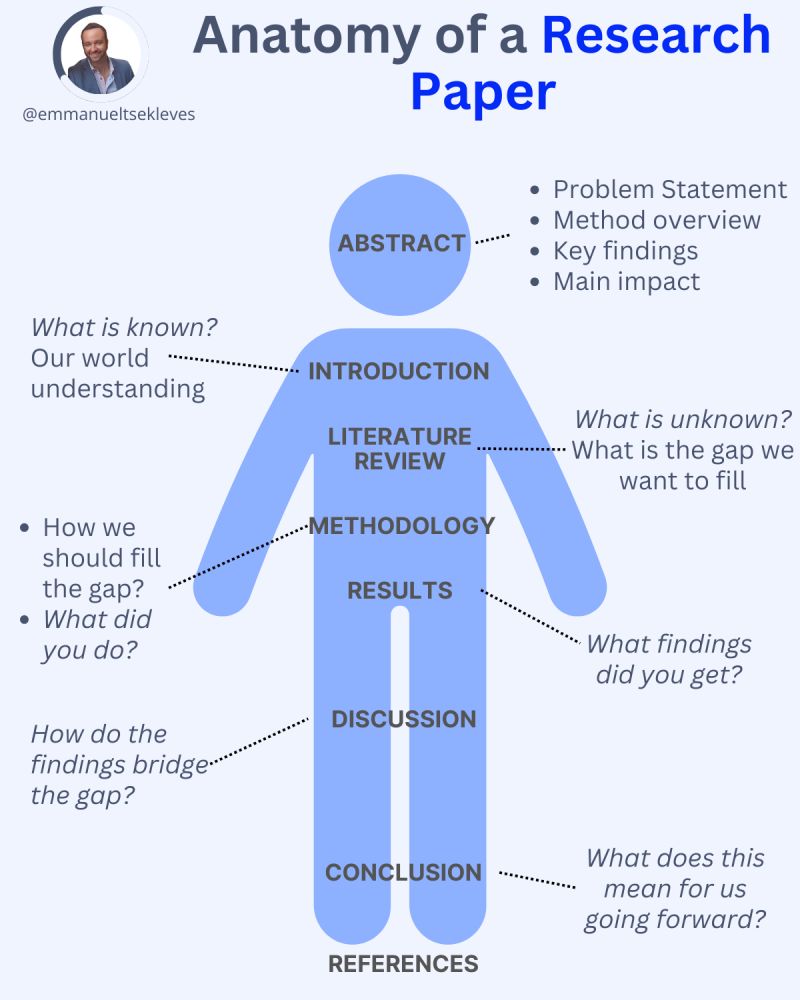


FEATURED POSTS
-
What is deepfake GAN (Generative Adversarial Network) technology?
https://www.techtarget.com/whatis/definition/deepfake
Deepfake technology is a type of artificial intelligence used to create convincing fake images, videos and audio recordings. The term describes both the technology and the resulting bogus content and is a portmanteau of deep learning and fake.
Deepfakes often transform existing source content where one person is swapped for another. They also create entirely original content where someone is represented doing or saying something they didn’t do or say.
Deepfakes aren’t edited or photoshopped videos or images. In fact, they’re created using specialized algorithms that blend existing and new footage. For example, subtle facial features of people in images are analyzed through machine learning (ML) to manipulate them within the context of other videos.
Deepfakes uses two algorithms — a generator and a discriminator — to create and refine fake content. The generator builds a training data set based on the desired output, creating the initial fake digital content, while the discriminator analyzes how realistic or fake the initial version of the content is. This process is repeated, enabling the generator to improve at creating realistic content and the discriminator to become more skilled at spotting flaws for the generator to correct.
The combination of the generator and discriminator algorithms creates a generative adversarial network.
A GAN uses deep learning to recognize patterns in real images and then uses those patterns to create the fakes.
When creating a deepfake photograph, a GAN system views photographs of the target from an array of angles to capture all the details and perspectives.
When creating a deepfake video, the GAN views the video from various angles and analyzes behavior, movement and speech patterns.
This information is then run through the discriminator multiple times to fine-tune the realism of the final image or video.
-
Photography basics: Color Temperature and White Balance
Color Temperature of a light source describes the spectrum of light which is radiated from a theoretical “blackbody” (an ideal physical body that absorbs all radiation and incident light – neither reflecting it nor allowing it to pass through) with a given surface temperature.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Color_temperature
Or. Most simply it is a method of describing the color characteristics of light through a numerical value that corresponds to the color emitted by a light source, measured in degrees of Kelvin (K) on a scale from 1,000 to 10,000.
More accurately. The color temperature of a light source is the temperature of an ideal backbody that radiates light of comparable hue to that of the light source.
(more…)
-
Photography basics: Exposure Value vs Photographic Exposure vs Il/Luminance vs Pixel luminance measurements
Also see: https://www.pixelsham.com/2015/05/16/how-aperture-shutter-speed-and-iso-affect-your-photos/
In photography, exposure value (EV) is a number that represents a combination of a camera’s shutter speed and f-number, such that all combinations that yield the same exposure have the same EV (for any fixed scene luminance).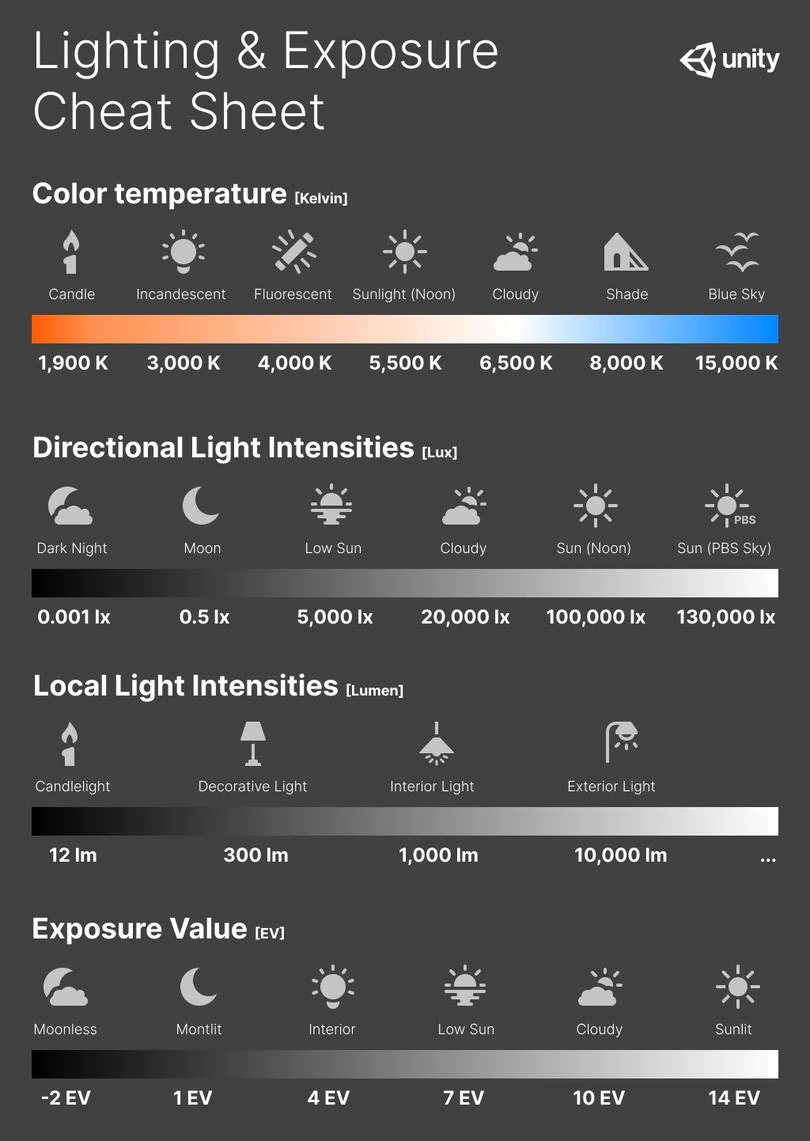
The EV concept was developed in an attempt to simplify choosing among combinations of equivalent camera settings. Although all camera settings with the same EV nominally give the same exposure, they do not necessarily give the same picture. EV is also used to indicate an interval on the photographic exposure scale. 1 EV corresponding to a standard power-of-2 exposure step, commonly referred to as a stop
EV 0 corresponds to an exposure time of 1 sec and a relative aperture of f/1.0. If the EV is known, it can be used to select combinations of exposure time and f-number.Note EV does not equal to photographic exposure. Photographic Exposure is defined as how much light hits the camera’s sensor. It depends on the camera settings mainly aperture and shutter speed. Exposure value (known as EV) is a number that represents the exposure setting of the camera.
Thus, strictly, EV is not a measure of luminance (indirect or reflected exposure) or illuminance (incidentl exposure); rather, an EV corresponds to a luminance (or illuminance) for which a camera with a given ISO speed would use the indicated EV to obtain the nominally correct exposure. Nonetheless, it is common practice among photographic equipment manufacturers to express luminance in EV for ISO 100 speed, as when specifying metering range or autofocus sensitivity.
The exposure depends on two things: how much light gets through the lenses to the camera’s sensor and for how long the sensor is exposed. The former is a function of the aperture value while the latter is a function of the shutter speed. Exposure value is a number that represents this potential amount of light that could hit the sensor. It is important to understand that exposure value is a measure of how exposed the sensor is to light and not a measure of how much light actually hits the sensor. The exposure value is independent of how lit the scene is. For example a pair of aperture value and shutter speed represents the same exposure value both if the camera is used during a very bright day or during a dark night.
Each exposure value number represents all the possible shutter and aperture settings that result in the same exposure. Although the exposure value is the same for different combinations of aperture values and shutter speeds the resulting photo can be very different (the aperture controls the depth of field while shutter speed controls how much motion is captured).
EV 0.0 is defined as the exposure when setting the aperture to f-number 1.0 and the shutter speed to 1 second. All other exposure values are relative to that number. Exposure values are on a base two logarithmic scale. This means that every single step of EV – plus or minus 1 – represents the exposure (actual light that hits the sensor) being halved or doubled.Formulas
(more…)