BREAKING NEWS
LATEST POSTS
-
HoloPart -Generative 3D Models Part Amodal Segmentation
https://vast-ai-research.github.io/HoloPart
https://huggingface.co/VAST-AI/HoloPart
https://github.com/VAST-AI-Research/HoloPart
Applications:
– 3d printing segmentation
– texturing segmentation
– animation segmentation
– modeling segmentation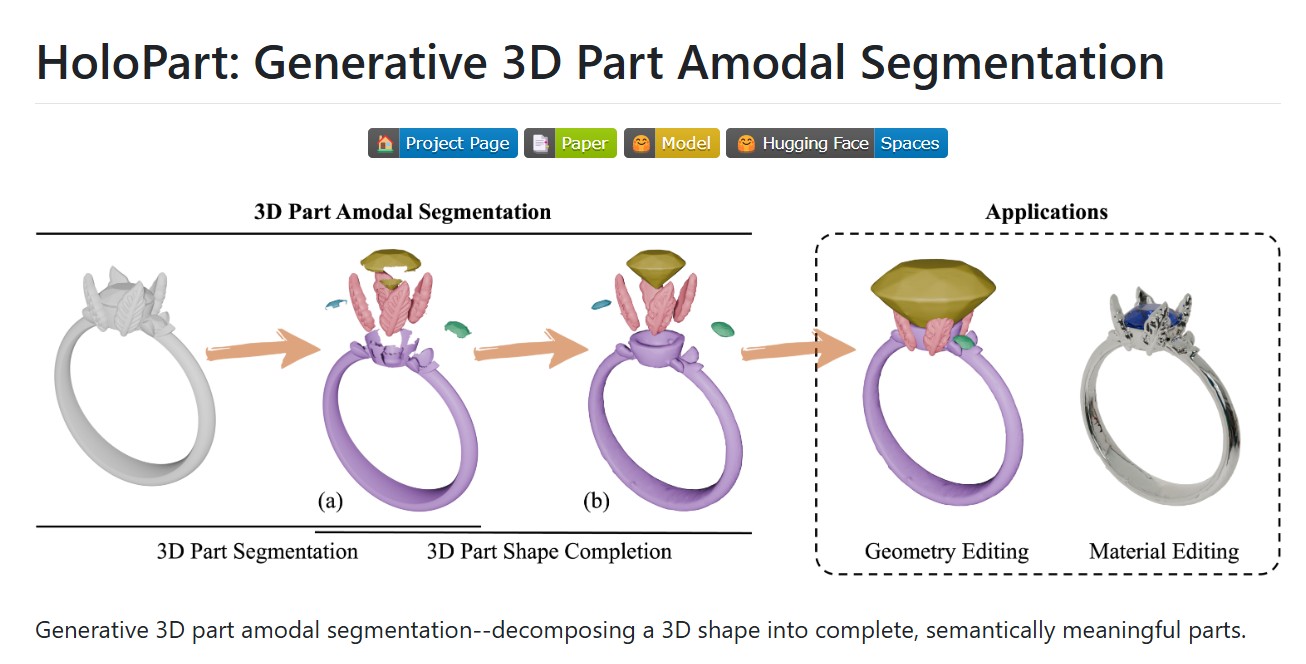
-
The Diary Of A CEO – A talk with Dr. Bessel Van Der Kolk described as “perhaps the most influential psychiatrist of the 21st century”
– Why traumatic memories are not like normal memories?
– What it was like working in a mental asylum.
– Does childhood trauma impact us permanently?
– Can yoga reverse deep past trauma? -
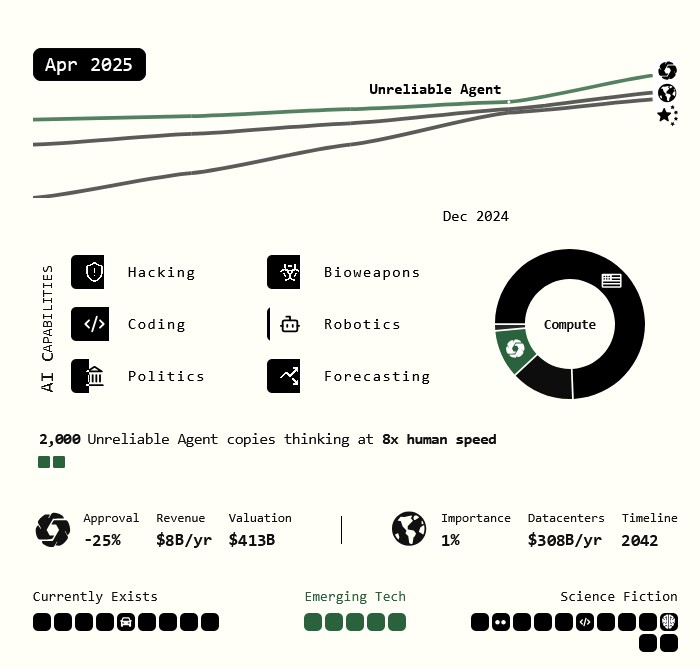
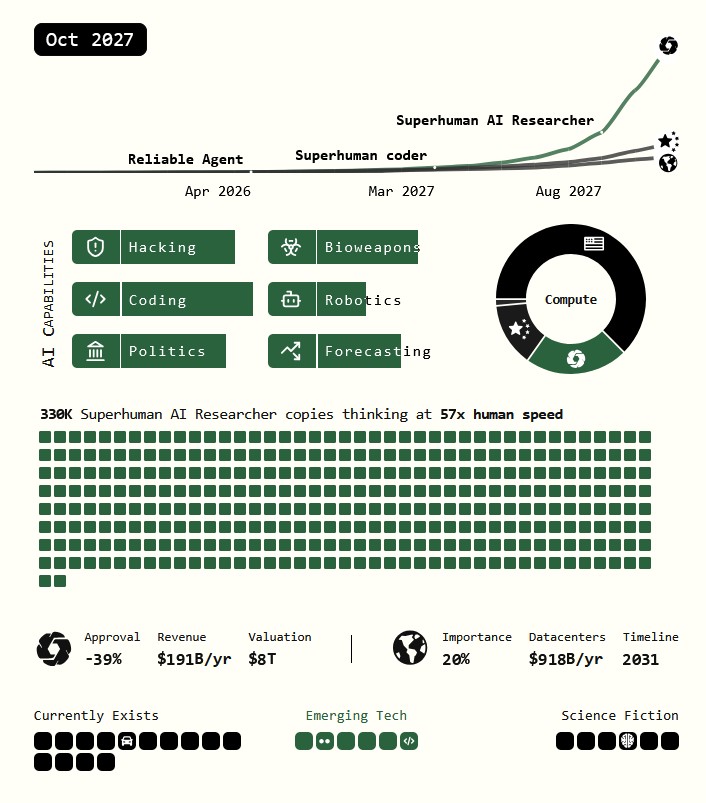
AI 2027 – Predicting the impact of superhuman AI over the next decade
We predict that the impact of superhuman AI over the next decade will be enormous, exceeding that of the Industrial Revolution.
We wrote a scenario that represents our best guess about what that might look like.1 It’s informed by trend extrapolations, wargames, expert feedback, experience at OpenAI, and previous forecasting successes.
-
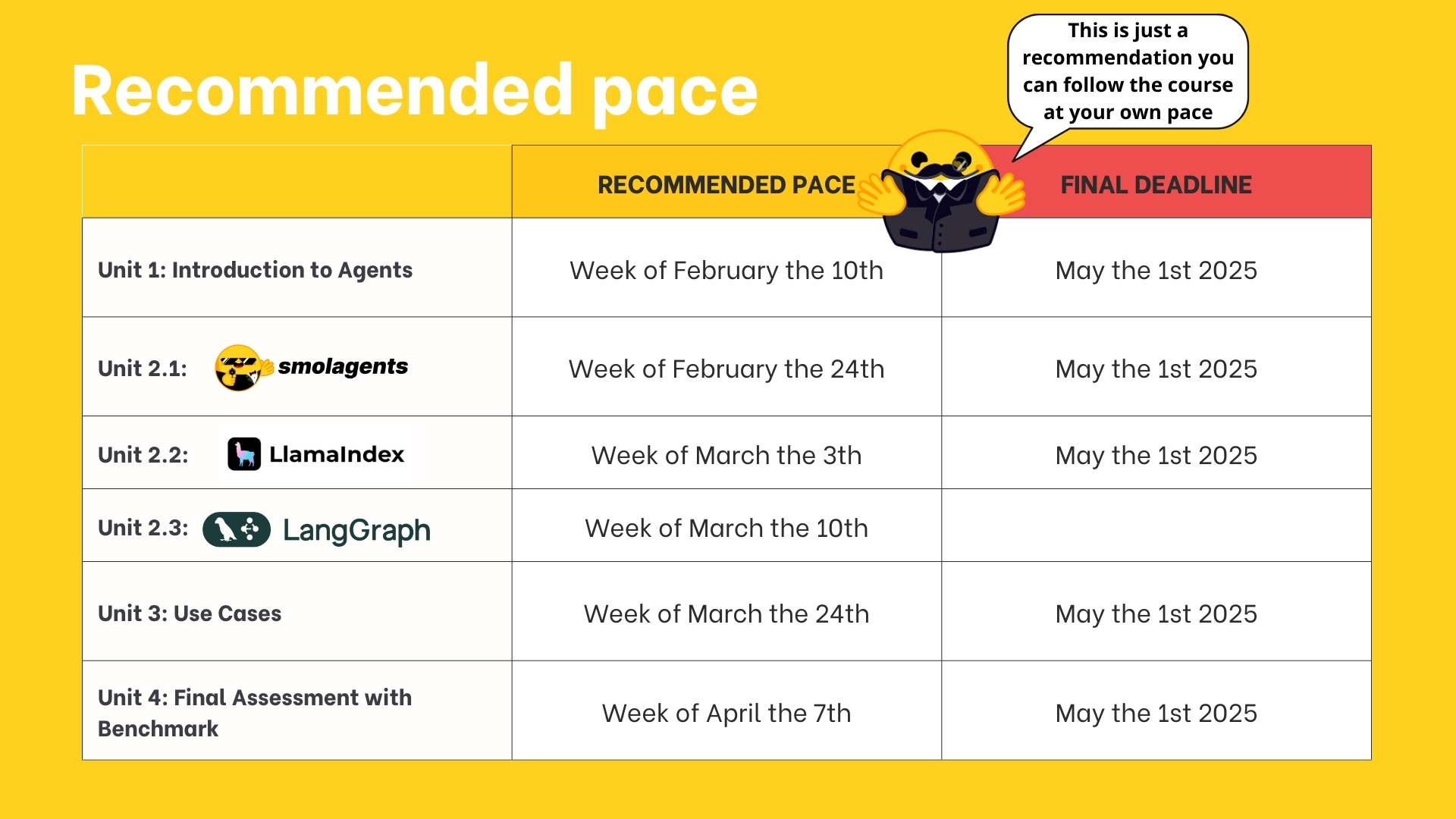
HuggingFace – AI Agents Course
https://huggingface.co/learn/agents-course/en/unit0/introduction
In this course, you will:
- 📖 Study AI Agents in theory, design, and practice.
- 🧑💻 Learn to use established AI Agent libraries such as smolagents, LlamaIndex, and LangGraph.
- 💾 Share your agents on the Hugging Face Hub and explore agents created by the community.
- 🏆 Participate in challenges where you will evaluate your agents against other students’.
- 🎓 Earn a certificate of completion by completing assignments.
-
The best music management software for PC, Android and iOS
https://audials.com/en/apps/manage-music?utm_source=chatgpt.com
https://umatechnology.org/the-best-free-music-management-tools-for-organizing-your-mp3s
- Audials Play
- Media Monkey
- Musicbee
- AIMP
- Mp3tag
- Helium
- MusicBrainz Picard
- iTunes
- Magix MP3 Deluxe 19
- Foobar 2000
- Clementine
- Tuneup Media
- Organize Your Music
- Musicnizer
- Bliss
- Music Connect
- VLC Media Player
- TagScanner
- Greenify
- KeepVid Music

-
NVIDIA Adds Native Python Support to CUDA
https://thenewstack.io/nvidia-finally-adds-native-python-support-to-cuda
https://nvidia.github.io/cuda-python/latest

Check your Cuda version, it will be the release version here:
>>> nvcc --version nvcc: NVIDIA (R) Cuda compiler driver Copyright (c) 2005-2024 NVIDIA Corporation Built on Wed_Apr_17_19:36:51_Pacific_Daylight_Time_2024 Cuda compilation tools, release 12.5, V12.5.40 Build cuda_12.5.r12.5/compiler.34177558_0or from here:
>>> nvidia-smi Mon Jun 16 12:35:20 2025 +-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | NVIDIA-SMI 555.85 Driver Version: 555.85 CUDA Version: 12.5 | |-----------------------------------------+------------------------+----------------------+ -
Matt Gray – How to generate a profitable business

In the last 10 years, over 1,000 people have asked me how to start a business. The truth? They’re all paralyzed by limiting beliefs. What they are and how to break them today:
(more…)
Before we get into the How, let’s first unpack why people think they can’t start a business.
Here are the biggest reasons I’ve found: -
Turn Yourself Into an Action Figure Using ChatGPT
ChatGPT Action Figure Prompts:
Create an action figure from the photo. It must be visualised in a realistic way. There should be accessories next to the figure like a UX designer have, Macbook Pro, a camera, drawing tablet, headset etc. Add a hole to the top of the box in the action figure. Also write the text “UX Mate” and below it “Keep Learning! Keep Designing
Use this image to create a picture of a action figure toy of a construction worker in a blister package from head to toe with accessories including a hammer, a staple gun and a ladder. The package should read “Kirk The Handy Man”
Create a realistic image of a toy action figure box. The box should be designed in a toy-equipment/action-figure style, with a cut-out window at the top like classic action figure packaging. The main color of the box and moleskine notebook should match the color of my jacket (referenced visually). Add colorful Mexican skull decorations across the box for a vibrant and artistic flair. Inside the box, include a “Your name” action figure, posed heroically. Next to the figure, arrange the following “equipment” in a stylized layout: • item 1 • item 2 … On the box, write: “Your name” (bold title font) Underneath: “Your role or anything else” The entire scene should look like a real product mockup, highly realistic, lit like a studio product photo. On the box, write: “Your name” (bold title font) Underneath: “Your role or description” The entire scene should look like a real product mockup, highly realistic, lit like a studio product photo. Prompt on Kling AI The figure steps out of its toy packaging and begins walking forward. As he continues to walk, the camera gradually zooms out in sync with his movement.
“Create image. Create a toy of the person in the photo. Let it be an action figure. Next to the figure, there should be the toy’s equipment, each in its individual blisters. 1) a book called “Tecnoforma”. 2) A 3-headed dog with a tag that says “Troika” and a bone at its feet with word “austerity” written on it. 3) a three-headed Hydra with with a tag called “Geringonça”. 4) a book titled “D. Sebastião”. Don’t repeat the equipment under any circumstance. The card holding the blister should be strong orange. Also, on top of the box, write ‘Pedro Passos Coelho’ and underneath it, ‘PSD action figure’. The figure and equipment must all be inside blisters. Visualize this in a realistic way.”
FEATURED POSTS
-
Rec-2020 – TVs new color gamut standard used by Dolby Vision?
https://www.hdrsoft.com/resources/dri.html#bit-depth
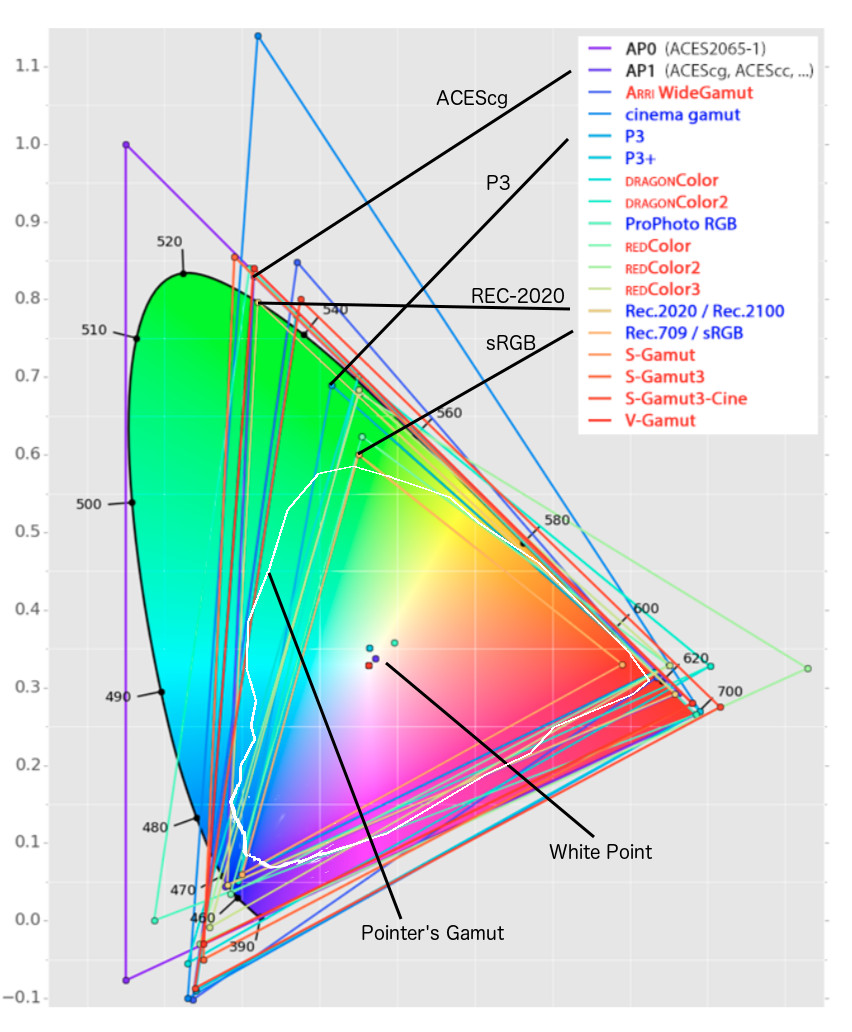
The dynamic range is a ratio between the maximum and minimum values of a physical measurement. Its definition depends on what the dynamic range refers to.
For a scene: Dynamic range is the ratio between the brightest and darkest parts of the scene.
For a camera: Dynamic range is the ratio of saturation to noise. More specifically, the ratio of the intensity that just saturates the camera to the intensity that just lifts the camera response one standard deviation above camera noise.
For a display: Dynamic range is the ratio between the maximum and minimum intensities emitted from the screen.
The Dynamic Range of real-world scenes can be quite high — ratios of 100,000:1 are common in the natural world. An HDR (High Dynamic Range) image stores pixel values that span the whole tonal range of real-world scenes. Therefore, an HDR image is encoded in a format that allows the largest range of values, e.g. floating-point values stored with 32 bits per color channel. Another characteristics of an HDR image is that it stores linear values. This means that the value of a pixel from an HDR image is proportional to the amount of light measured by the camera.
For TVs HDR is great, but it’s not the only new TV feature worth discussing.
(more…)
-
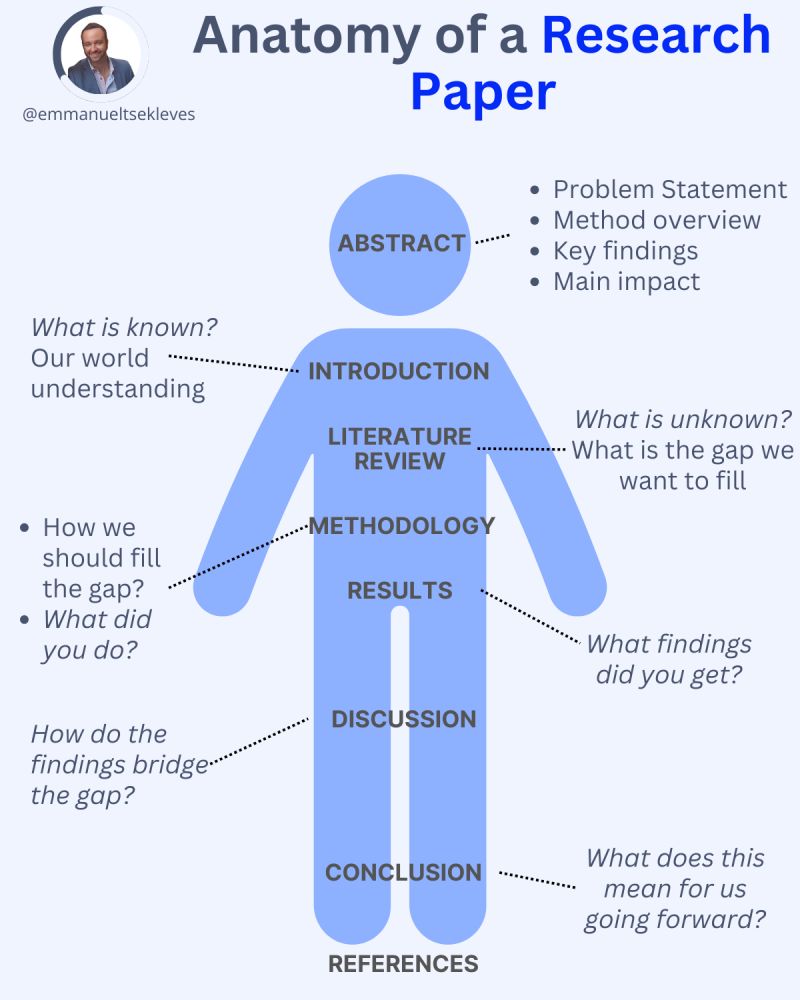
Emmanuel Tsekleves – Writing Research Papers
Here’s the journey of crafting a compelling paper:
1️. ABSTRACT
This is your elevator pitch.
Give a methodology overview.
Paint the problem you’re solving.
Highlight key findings and their impact.
2️. INTRODUCTION
Start with what we know.
Set the stage for our current understanding.
Hook your reader with the relevance of your work.
3️. LITERATURE REVIEW
Identify what’s unknown.
Spot the gaps in current knowledge.
Your job in the next sections is to fill this gap.
4️. METHODOLOGY
What did you do?
Outline how you’ll fill that gap.
Be transparent about your approach.
Make it reproducible so others can follow.
5️. RESULTS
Let the data speak for itself.
Present your findings clearly.
Keep it concise and focused.
6️. DISCUSSION
Now, connect the dots.
Discuss implications and significance.
How do your findings bridge the knowledge gap?
7️. CONCLUSION
Wrap it up with future directions.
What does this mean for us moving forward?
Leave the reader with a call to action or reflection.
8️. REFERENCES
Acknowledge the giants whose shoulders you stand on.
A robust reference list shows the depth of your research.