BREAKING NEWS
LATEST POSTS
-
VFX Giant MPC and Parent Company Technicolor Shut Down Amid ‘Severe Financial Challenges
https://variety.com/2025/film/global/technicolor-vfx-mpc-shutter-severe-challenges-1236316354
Shaun Severi, Head of Creative Production at the Mill, claimed in a LinkedIn post that 4,500 had lost their jobs in 24 hours: “The problem wasn’t talent or execution — it was mismanagement at the highest levels…the incompetence at the top was nothing short of disastrous.”
According to Severi, successive company presidents “buried the company under massive debt by acquiring VFX Studios…the second president, after a disastrous merger of the post houses, took us public, artificially inflating the company’s value — only for it to come crashing down when the real numbers were revealed….and the third and final president, who came from a car rental company, had no vision of what she was building, selling or managing.”

-
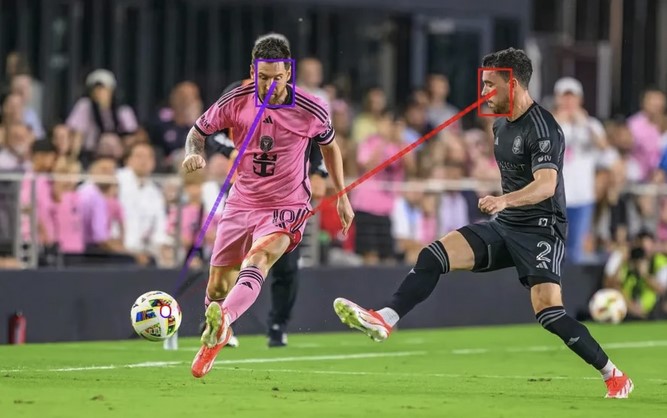
Moondream Gaze Detection – Open source code
This is convenient for captioning videos, understanding social dynamics, and for specific cases such as sports analytics, or detecting when drivers or operators are distracted.
https://huggingface.co/spaces/moondream/gaze-demo
https://moondream.ai/blog/announcing-gaze-detection

-
X-Dyna – Expressive Dynamic Human Image Animation
https://x-dyna.github.io/xdyna.github.io
A novel zero-shot, diffusion-based pipeline for animating a single human image using facial expressions and body movements derived from a driving video, that generates realistic, context-aware dynamics for both the subject and the surrounding environment.

-
Flex 1 Alpha – a pre-trained base 8 billion parameter rectified flow transformer
https://huggingface.co/ostris/Flex.1-alpha
Flex.1 started as the FLUX.1-schnell-training-adapter to make training LoRAs on FLUX.1-schnell possible.

-
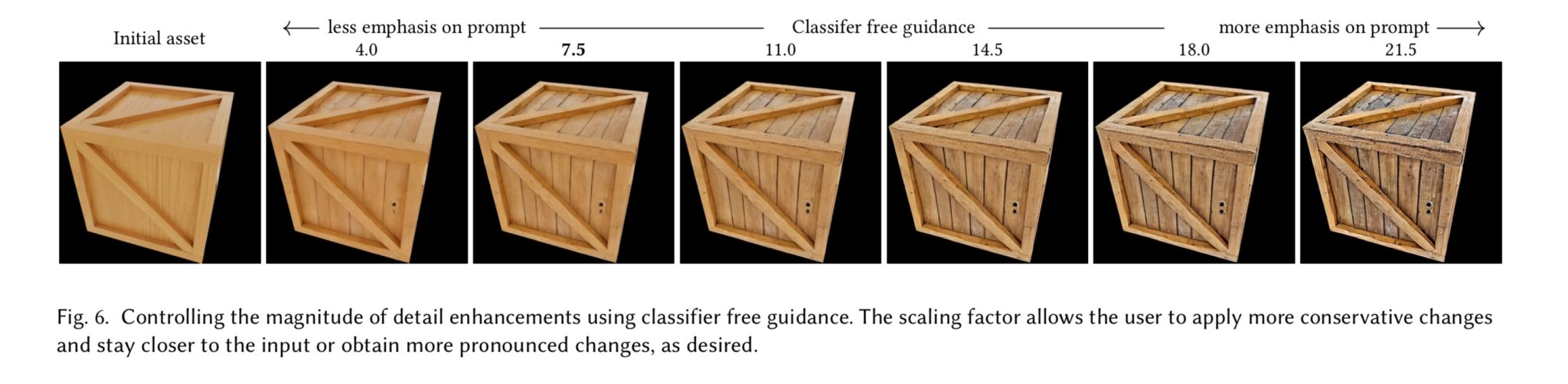
Generative Detail Enhancement for Physically Based Materials
https://arxiv.org/html/2502.13994v1
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2502.13994
A tool for enhancing the detail of physically based materials using an off-the-shelf diffusion model and inverse rendering.
-
Camera Metadata Toolkit (camdkit) for Virtual Production
https://github.com/SMPTE/ris-osvp-metadata-camdkit
Today
camdkitsupports mapping (or importing, if you will) of metadata from five popular digital cinema cameras into a canonical form; it also supports a mapping of the metadata defined in the F4 protocol used by tracking system components from Mo-Sys.
-
OpenTrackIO – free and open-source protocol designed to improve interoperability in Virtual Production
OpenTrackIO defines the schema of JSON samples that contain a wide range of metadata about the device, its transform(s), associated camera and lens. The full schema is given below and can be downloaded here.
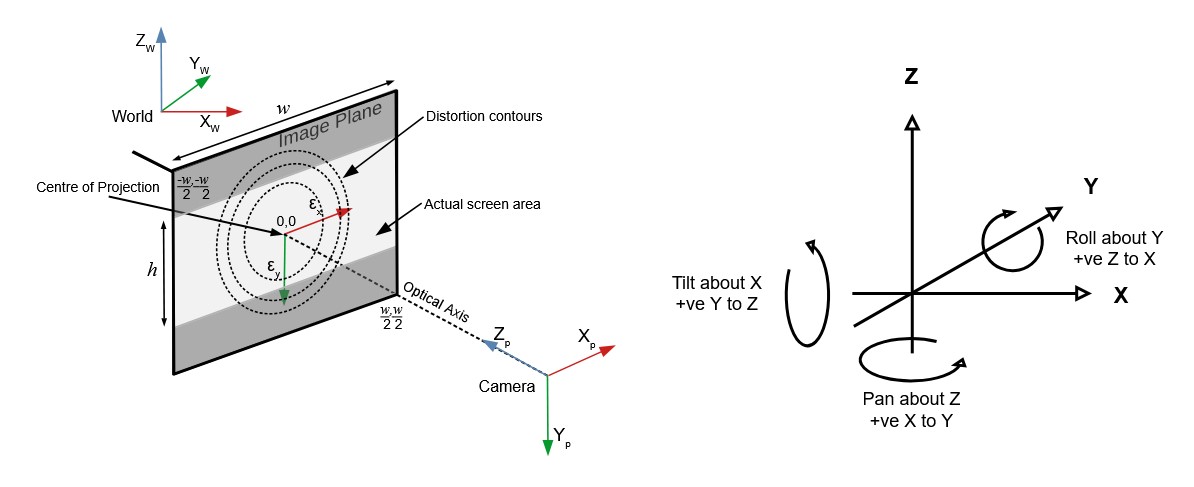
-
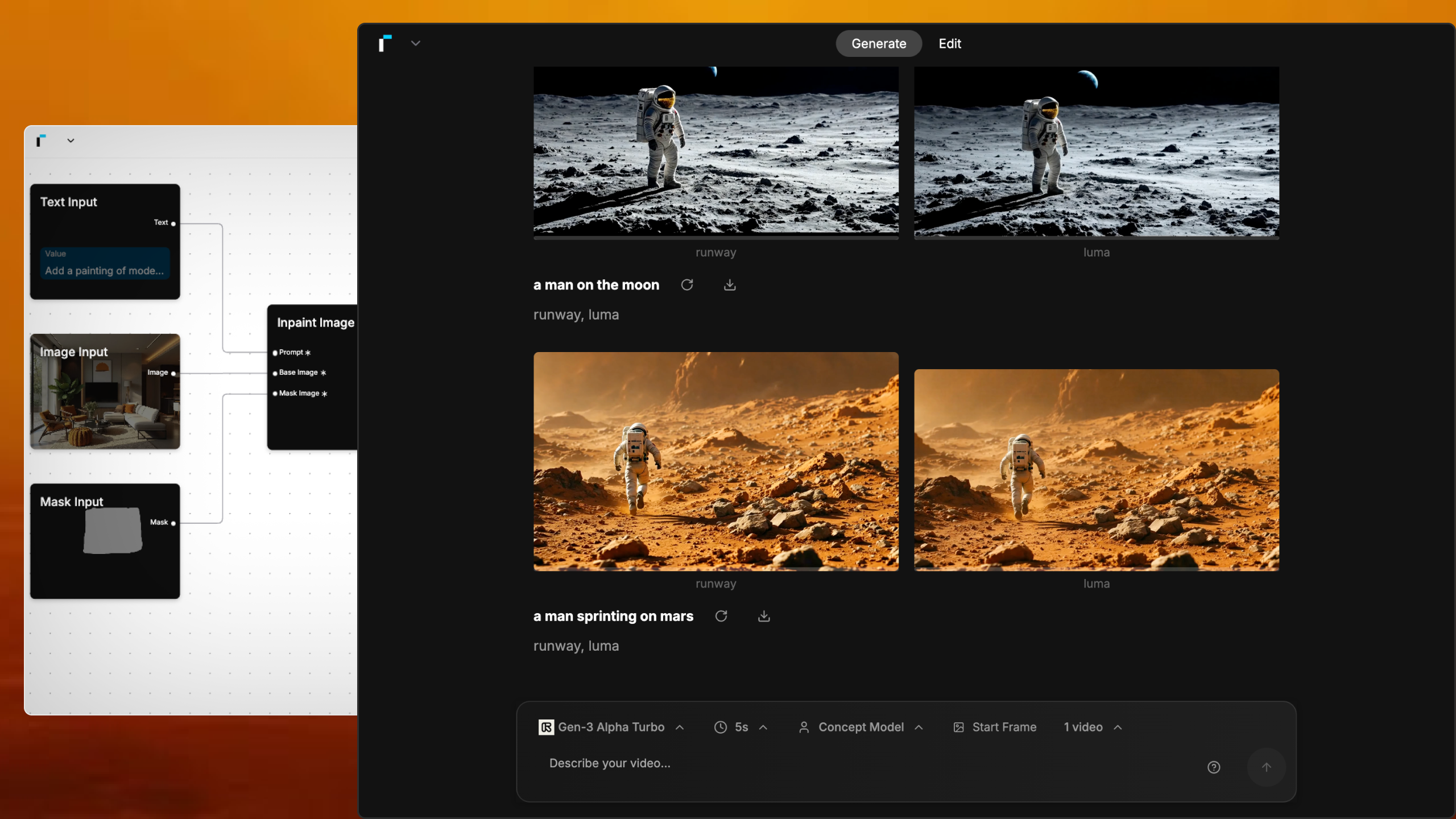
Martin Gent – Comparing current video AI models
https://www.linkedin.com/posts/martingent_imagineapp-veo2-kling-activity-7298979787962806272-n0Sn
🔹 𝗩𝗲𝗼 2 – After the legendary prompt adherence of Veo 2 T2V, I have to say I2V is a little disappointing, especially when it comes to camera moves. You often get those Sora-like jump-cuts too which can be annoying.
🔹 𝗞𝗹𝗶𝗻𝗴 1.6 Pro – Still the one to beat for I2V, both for image quality and prompt adherence. It’s also a lot cheaper than Veo 2. Generations can be slow, but are usually worth the wait.
🔹 𝗥𝘂𝗻𝘄𝗮𝘆 Gen 3 – Useful for certain shots, but overdue an update. The worst performer here by some margin. Bring on Gen 4!
🔹 𝗟𝘂𝗺𝗮 Ray 2 – I love the energy and inventiveness Ray 2 brings, but those came with some image quality issues. I want to test more with this model though for sure.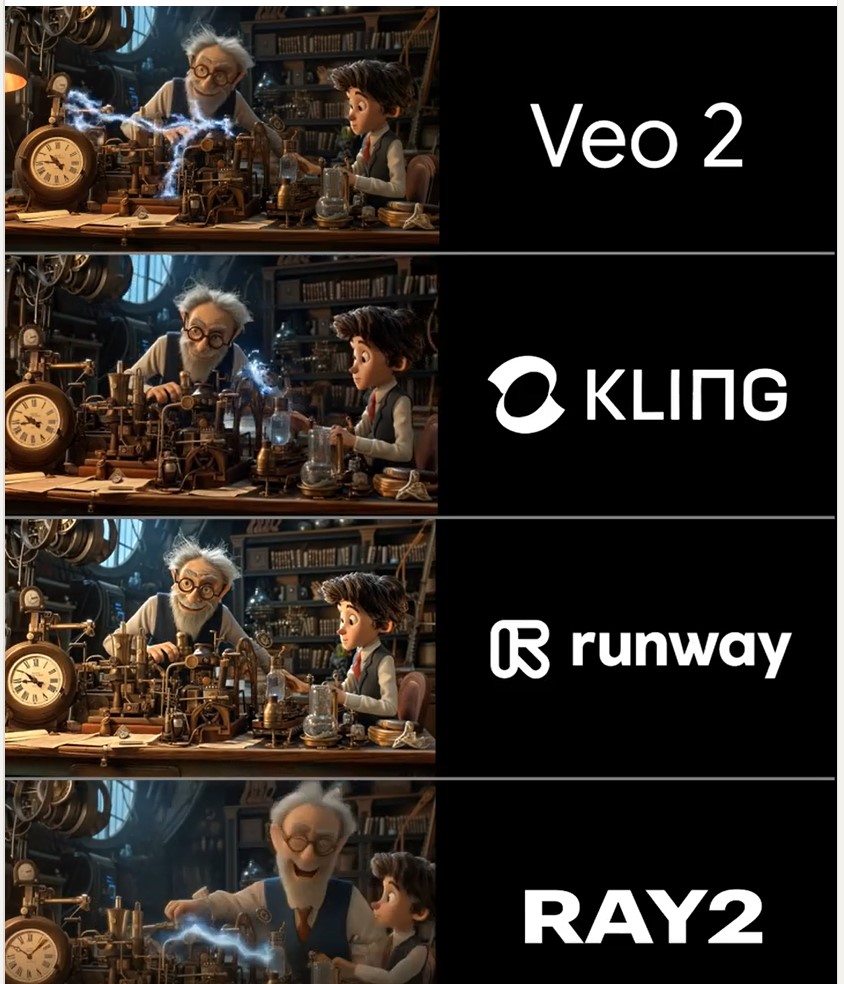
FEATURED POSTS
-
Embedding frame ranges into Quicktime movies with FFmpeg
QuickTime (.mov) files are fundamentally time-based, not frame-based, and so don’t have a built-in, uniform “first frame/last frame” field you can set as numeric frame IDs. Instead, tools like Shotgun Create rely on the timecode track and the movie’s duration to infer frame numbers. If you want Shotgun to pick up a non-default frame range (e.g. start at 1001, end at 1064), you must bake in an SMPTE timecode that corresponds to your desired start frame, and ensure the movie’s duration matches your clip length.
How Shotgun Reads Frame Ranges
- Default start frame is 1. If no timecode metadata is present, Shotgun assumes the movie begins at frame 1.
- Timecode ⇒ frame number. Shotgun Create “honors the timecodes of media sources,” mapping the embedded TC to frame IDs. For example, a 24 fps QuickTime tagged with a start timecode of 00:00:41:17 will be interpreted as beginning on frame 1001 (1001 ÷ 24 fps ≈ 41.71 s).
Embedding a Start Timecode
QuickTime uses a
tmcd(timecode) track. You can bake in an SMPTE track via FFmpeg’s-timecodeflag or via Compressor/encoder settings:- Compute your start TC.
- Desired start frame = 1001
- Frame 1001 at 24 fps ⇒ 1001 ÷ 24 ≈ 41.708 s ⇒ TC 00:00:41:17
- FFmpeg example:
ffmpeg -i input.mov \ -c copy \ -timecode 00:00:41:17 \ output.movThis adds a timecode track beginning at 00:00:41:17, which Shotgun maps to frame 1001.
Ensuring the Correct End Frame
Shotgun infers the last frame from the movie’s duration. To end on frame 1064:
- Frame count = 1064 – 1001 + 1 = 64 frames
- Duration = 64 ÷ 24 fps ≈ 2.667 s
FFmpeg trim example:
ffmpeg -i input.mov \ -c copy \ -timecode 00:00:41:17 \ -t 00:00:02.667 \ output_trimmed.movThis results in a 64-frame clip (1001→1064) at 24 fps.