BREAKING NEWS
LATEST POSTS
-
GIMP 3.0 review – 20 years on from 2.0, has GIMP kept up with the times?
https://www.gimp.org/release-notes/gimp-3.0.html
Highlights
- Need to tweak a filter you applied hours ago? New in GIMP 3.0 is non-destructive editing for most commonly-used filters. See the changes in real time with on-canvas preview.
- Exchange files with more applications, including BC7 DDS files as well as better PSD export and many new formats.
- Don’t know how big to make your drawing? Simply set your paint tool to expand layers automatically as needed.
- Making pro-quality text got easier, too. Style your text, apply outlines, shadows, bevels, and more, and you can still edit your text, change font and size, and even tweak the style settings.
- Organizing your layers has become much easier with the ability to select multiple items at once, move them or transform them all together!
- Color Management was again improved, as our long-term project to make GIMP an advanced image editor for all usages.
- Updated graphical toolkit (GTK3) for modern desktop usage.
- New Wilber logo!
-
Reve Image 1.0 Halfmoon – A new model trained from the ground up to excel at prompt adherence, aesthetics, and typography
A little-known AI image generator called Reve Image 1.0 is trying to make a name in the text-to-image space, potentially outperforming established tools like Midjourney, Flux, and Ideogram. Users receive 100 free credits to test the service after signing up, with additional credits available at $5 for 500 generations—pretty cheap when compared to options like MidJourney or Ideogram, which start at $8 per month and can reach $120 per month, depending on the usage. It also offers 20 free generations per day.

FEATURED POSTS
-
AI and the Law – AI Creativity – Genius or Gimmick?
7:59-9:50 Justine Bateman:
“I mean first I want to give people, help people have a little bit of a definition of what generative AI is—
think of it as like a blender and if you have a blender at home and you turn it on, what does it do? It depends on what I put into it, so it cannot function unless it’s fed things.
Then you turn on the blender and you give it a prompt, which is your little spoon, and you get a little spoonful—little Frankenstein spoonful—out of what you asked for.
So what is going into the blender? Every but a hundred years of film and television or many, many years of, you know, doctor’s reports or students’ essays or whatever it is.
In the film business, in particular, that’s what we call theft; it’s the biggest violation. And the term that continues to be used is “all we did.” I think the CTO of OpenAI—believe that’s her position; I forget her name—when she was asked in an interview recently what she had to say about the fact that they didn’t ask permission to take it in, she said, “Well, it was all publicly available.”
And I will say this: if you own a car—I know we’re in New York City, so it’s not going to be as applicable—but if I see a car in the street, it’s publicly available, but somehow it’s illegal for me to take it. That’s what we have the copyright office for, and I don’t know how well staffed they are to handle something like this, but this is the biggest copyright violation in the history of that office and the US government”
-
Emmanuel Tsekleves – Writing Research Papers
Here’s the journey of crafting a compelling paper:
1️. ABSTRACT
This is your elevator pitch.
Give a methodology overview.
Paint the problem you’re solving.
Highlight key findings and their impact.
2️. INTRODUCTION
Start with what we know.
Set the stage for our current understanding.
Hook your reader with the relevance of your work.
3️. LITERATURE REVIEW
Identify what’s unknown.
Spot the gaps in current knowledge.
Your job in the next sections is to fill this gap.
4️. METHODOLOGY
What did you do?
Outline how you’ll fill that gap.
Be transparent about your approach.
Make it reproducible so others can follow.
5️. RESULTS
Let the data speak for itself.
Present your findings clearly.
Keep it concise and focused.
6️. DISCUSSION
Now, connect the dots.
Discuss implications and significance.
How do your findings bridge the knowledge gap?
7️. CONCLUSION
Wrap it up with future directions.
What does this mean for us moving forward?
Leave the reader with a call to action or reflection.
8️. REFERENCES
Acknowledge the giants whose shoulders you stand on.
A robust reference list shows the depth of your research.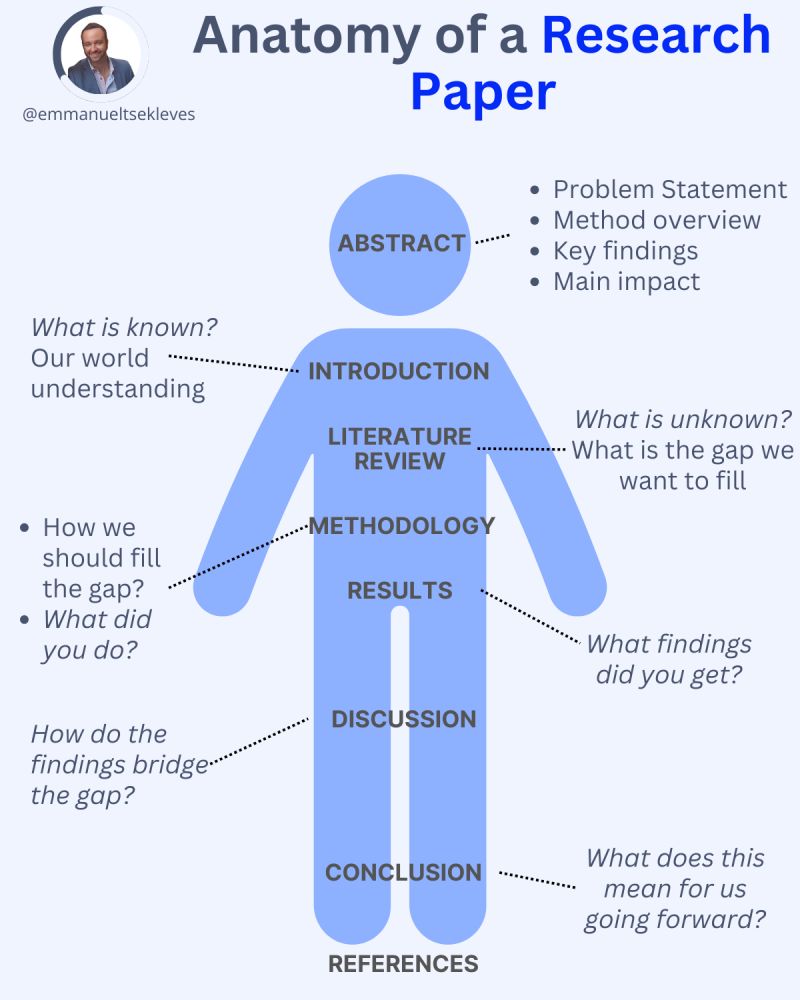


-
Björn Ottosson – How software gets color wrong
https://bottosson.github.io/posts/colorwrong/
Most software around us today are decent at accurately displaying colors. Processing of colors is another story unfortunately, and is often done badly.
To understand what the problem is, let’s start with an example of three ways of blending green and magenta:
- Perceptual blend – A smooth transition using a model designed to mimic human perception of color. The blending is done so that the perceived brightness and color varies smoothly and evenly.
- Linear blend – A model for blending color based on how light behaves physically. This type of blending can occur in many ways naturally, for example when colors are blended together by focus blur in a camera or when viewing a pattern of two colors at a distance.
- sRGB blend – This is how colors would normally be blended in computer software, using sRGB to represent the colors.
Let’s look at some more examples of blending of colors, to see how these problems surface more practically. The examples use strong colors since then the differences are more pronounced. This is using the same three ways of blending colors as the first example.
Instead of making it as easy as possible to work with color, most software make it unnecessarily hard, by doing image processing with representations not designed for it. Approximating the physical behavior of light with linear RGB models is one easy thing to do, but more work is needed to create image representations tailored for image processing and human perception.
Also see: