BREAKING NEWS
LATEST POSTS
-
David Heinemeier Hansson – Software development estimates have never worked and never will
https://world.hey.com/dhh/software-estimates-have-never-worked-and-never-will-a41a9c71
The fundamental problem is that as soon as a type of software development becomes so routine that it would be possible to estimate, it turns into a product or a service you can just buy rather than build.
-
Open3d.org – An open source library that supports rapid development of software that deals with 3D data
Core features
- 3D data structures
- 3D data processing algorithms
- Scene reconstruction
- Surface alignment
- 3D visualization with Physically based rendering (PBR)
- 3D machine learning support with PyTorch and TensorFlow
- GPU acceleration for core 3D operations
- Available in C++ and Python with a 3D viewer app.
-
H. Jensons TWISTED by Sebastian Ungrad – AI Muppets video
“From start to finish it took just 9 hours to produce. That was so much fun to do.
Lyrics: ChatGpt
Song: Suno
Images: Midjourney & ComfyUI
Video: u/runwayml Gen-3″
(more…)
FEATURED POSTS
-
AI 2025 – The house of cards
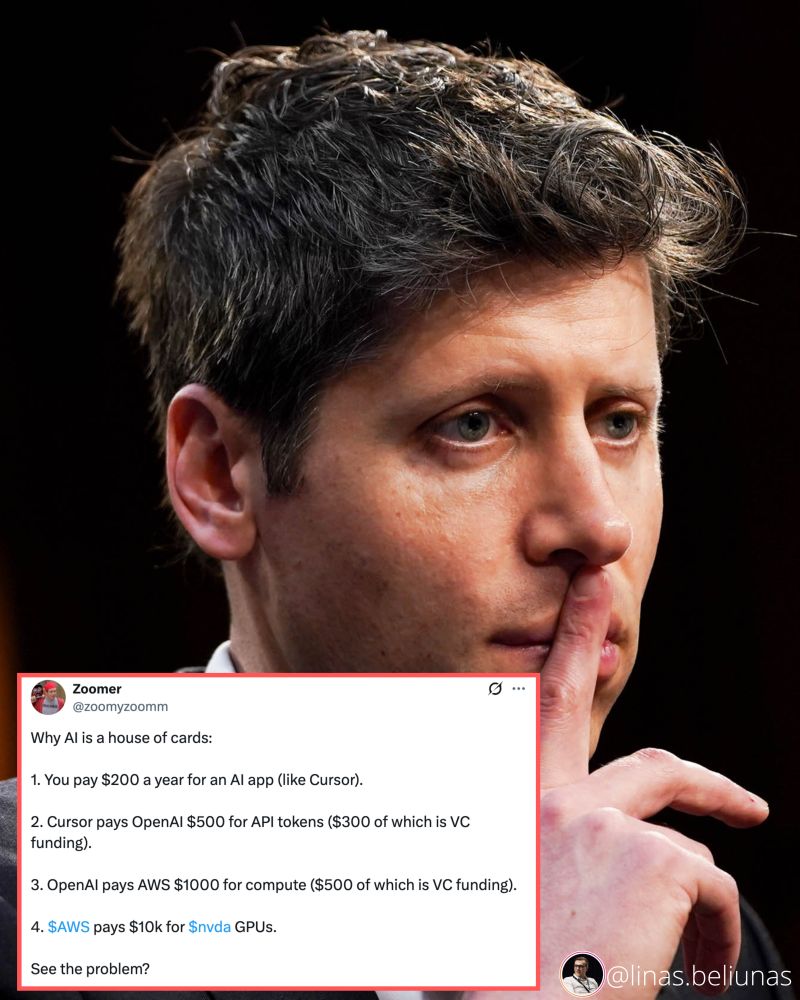
The gap is covered by venture capitals.
Three possible futures:
Price hikes – users pay $1,000+/year (will they?)
Cost collapse – cheaper GPUs, efficient models, decentralized compute.
Implosion – AI apps and LLMs vanish in a mass shakeout.
-
Google – Artificial Intelligence free courses
1. Introduction to Large Language Models: Learn about the use cases and how to enhance the performance of large language models.
https://www.cloudskillsboost.google/course_templates/5392. Introduction to Generative AI: Discover the differences between Generative AI and traditional machine learning methods.
https://www.cloudskillsboost.google/course_templates/5363. Generative AI Fundamentals: Earn a skill badge by demonstrating your understanding of foundational concepts in Generative AI.
https://www.cloudskillsboost.google/paths4. Introduction to Responsible AI: Learn about the importance of Responsible AI and how Google implements it in its products.
https://www.cloudskillsboost.google/course_templates/5545. Encoder-Decoder Architecture: Learn about the encoder-decoder architecture, a critical component of machine learning for sequence-to-sequence tasks.
https://www.cloudskillsboost.google/course_templates/5436. Introduction to Image Generation: Discover diffusion models, a promising family of machine learning models in the image generation space.
https://www.cloudskillsboost.google/course_templates/5417. Transformer Models and BERT Model: Get a comprehensive introduction to the Transformer architecture and the Bidirectional Encoder Representations from the Transformers (BERT) model.
https://www.cloudskillsboost.google/course_templates/5388. Attention Mechanism: Learn about the attention mechanism, which allows neural networks to focus on specific parts of an input sequence.
https://www.cloudskillsboost.google/course_templates/537
-
Photography basics: Exposure Value vs Photographic Exposure vs Il/Luminance vs Pixel luminance measurements
Also see: https://www.pixelsham.com/2015/05/16/how-aperture-shutter-speed-and-iso-affect-your-photos/
In photography, exposure value (EV) is a number that represents a combination of a camera’s shutter speed and f-number, such that all combinations that yield the same exposure have the same EV (for any fixed scene luminance).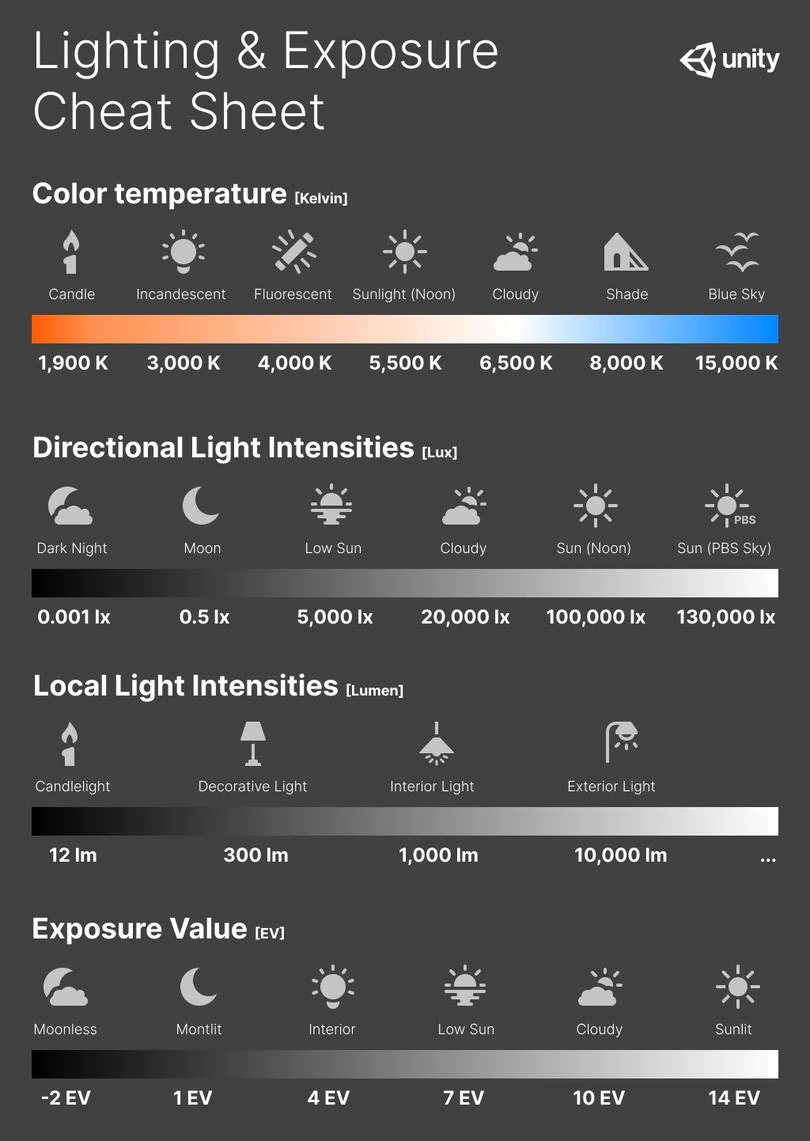
The EV concept was developed in an attempt to simplify choosing among combinations of equivalent camera settings. Although all camera settings with the same EV nominally give the same exposure, they do not necessarily give the same picture. EV is also used to indicate an interval on the photographic exposure scale. 1 EV corresponding to a standard power-of-2 exposure step, commonly referred to as a stop
EV 0 corresponds to an exposure time of 1 sec and a relative aperture of f/1.0. If the EV is known, it can be used to select combinations of exposure time and f-number.Note EV does not equal to photographic exposure. Photographic Exposure is defined as how much light hits the camera’s sensor. It depends on the camera settings mainly aperture and shutter speed. Exposure value (known as EV) is a number that represents the exposure setting of the camera.
Thus, strictly, EV is not a measure of luminance (indirect or reflected exposure) or illuminance (incidentl exposure); rather, an EV corresponds to a luminance (or illuminance) for which a camera with a given ISO speed would use the indicated EV to obtain the nominally correct exposure. Nonetheless, it is common practice among photographic equipment manufacturers to express luminance in EV for ISO 100 speed, as when specifying metering range or autofocus sensitivity.
The exposure depends on two things: how much light gets through the lenses to the camera’s sensor and for how long the sensor is exposed. The former is a function of the aperture value while the latter is a function of the shutter speed. Exposure value is a number that represents this potential amount of light that could hit the sensor. It is important to understand that exposure value is a measure of how exposed the sensor is to light and not a measure of how much light actually hits the sensor. The exposure value is independent of how lit the scene is. For example a pair of aperture value and shutter speed represents the same exposure value both if the camera is used during a very bright day or during a dark night.
Each exposure value number represents all the possible shutter and aperture settings that result in the same exposure. Although the exposure value is the same for different combinations of aperture values and shutter speeds the resulting photo can be very different (the aperture controls the depth of field while shutter speed controls how much motion is captured).
EV 0.0 is defined as the exposure when setting the aperture to f-number 1.0 and the shutter speed to 1 second. All other exposure values are relative to that number. Exposure values are on a base two logarithmic scale. This means that every single step of EV – plus or minus 1 – represents the exposure (actual light that hits the sensor) being halved or doubled.Formulas
(more…)
-
How are Energy and Matter the Same?
www.turnerpublishing.com/blog/detail/everything-is-energy-everything-is-one-everything-is-possible/
www.universetoday.com/116615/how-are-energy-and-matter-the-same/
As Einstein showed us, light and matter and just aspects of the same thing. Matter is just frozen light. And light is matter on the move. Albert Einstein’s most famous equation says that energy and matter are two sides of the same coin. How does one become the other?
Relativity requires that the faster an object moves, the more mass it appears to have. This means that somehow part of the energy of the car’s motion appears to transform into mass. Hence the origin of Einstein’s equation. How does that happen? We don’t really know. We only know that it does.
Matter is 99.999999999999 percent empty space. Not only do the atom and solid matter consist mainly of empty space, it is the same in outer space
The quantum theory researchers discovered the answer: Not only do particles consist of energy, but so does the space between. This is the so-called zero-point energy. Therefore it is true: Everything consists of energy.
Energy is the basis of material reality. Every type of particle is conceived of as a quantum vibration in a field: Electrons are vibrations in electron fields, protons vibrate in a proton field, and so on. Everything is energy, and everything is connected to everything else through fields.