BREAKING NEWS
LATEST POSTS
-
Seaweed APT – Diffusion Adversarial Post-Training for One-Step Video Generation
https://cdn.seaweed-apt.com/assets/showreel/seaweed-apt.mp4
This demonstrate large-scale text-to-video generation with a single neural function evaluation (1NFE) by using our proposed adversarial post-training technique. Our model generates 2 seconds of 1280×720 24fps videos in real-time

-
Pyper – a flexible framework for concurrent and parallel data-processing in Python
Pyper is a flexible framework for concurrent and parallel data-processing, based on functional programming patterns.
https://github.com/pyper-dev/pyper

-
Jacob Bartlett – Apple is Killing Swift
https://blog.jacobstechtavern.com/p/apple-is-killing-swift
Jacob Bartlett argues that Swift, once envisioned as a simple and composable programming language by its creator Chris Lattner, has become overly complex due to Apple’s governance. Bartlett highlights that Swift now contains 217 reserved keywords, deviating from its original goal of simplicity. He contrasts Swift’s governance model, where Apple serves as the project lead and arbiter, with other languages like Python and Rust, which have more community-driven or balanced governance structures. Bartlett suggests that Apple’s control has led to Swift’s current state, moving away from Lattner’s initial vision.

-
Don’t Splat your Gaussians – Volumetric Ray-Traced Primitives for Modeling and Rendering Scattering and Emissive Media
https://arcanous98.github.io/projectPages/gaussianVolumes.html
We propose a compact and efficient alternative to existing volumetric representations for rendering such as voxel grids.
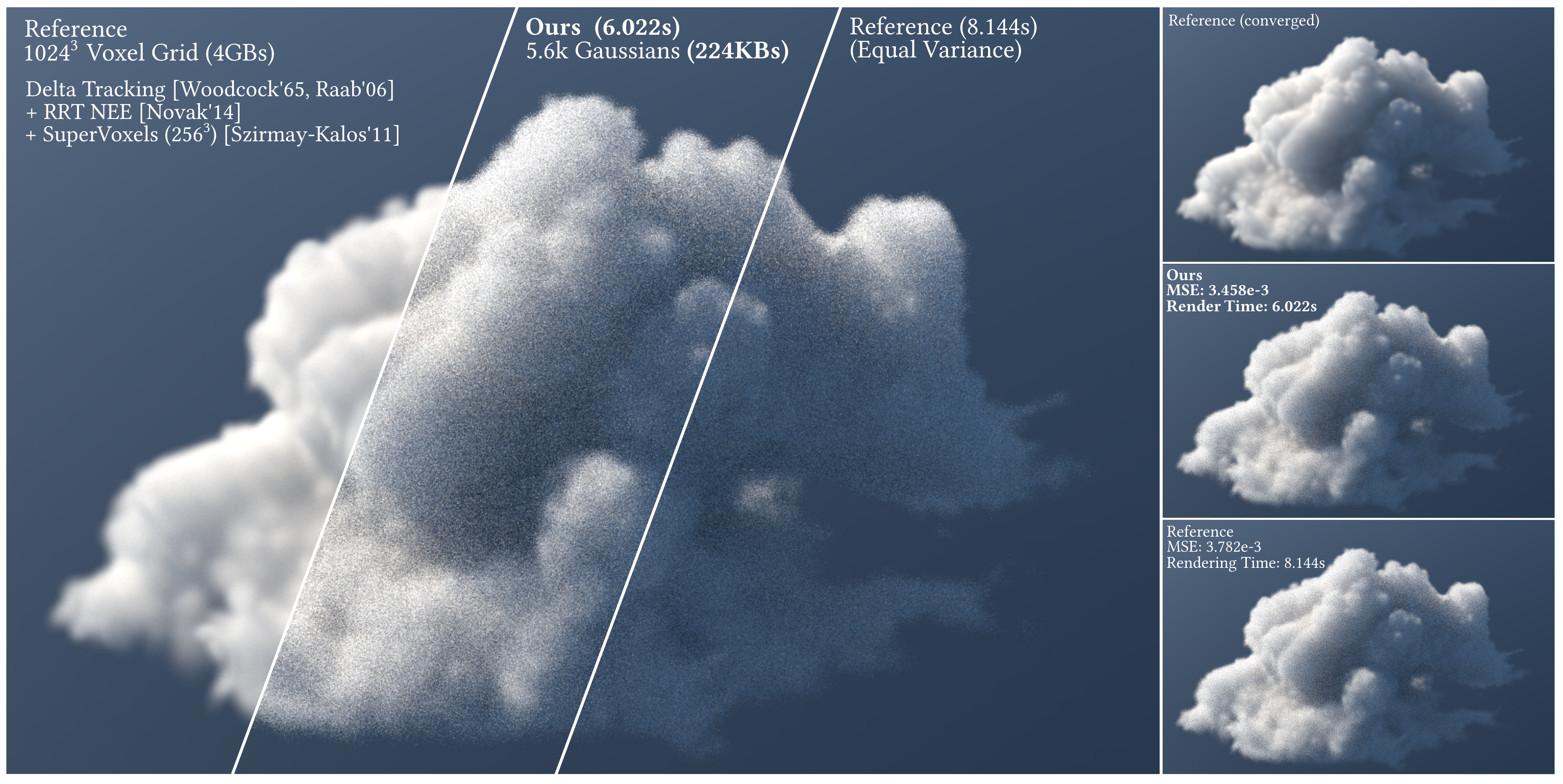
-
IPAdapter – Text Compatible Image Prompt Adapter for Text-to-Image Image-to-Image Diffusion Models and ComfyUI implementation
github.com/tencent-ailab/IP-Adapter
The IPAdapter are very powerful models for image-to-image conditioning. The subject or even just the style of the reference image(s) can be easily transferred to a generation. Think of it as a 1-image lora. They are an effective and lightweight adapter to achieve image prompt capability for the pre-trained text-to-image diffusion models. An IP-Adapter with only 22M parameters can achieve comparable or even better performance to a fine-tuned image prompt model.
Once the IP-Adapter is trained, it can be directly reusable on custom models fine-tuned from the same base model.The IP-Adapter is fully compatible with existing controllable tools, e.g., ControlNet and T2I-Adapter.
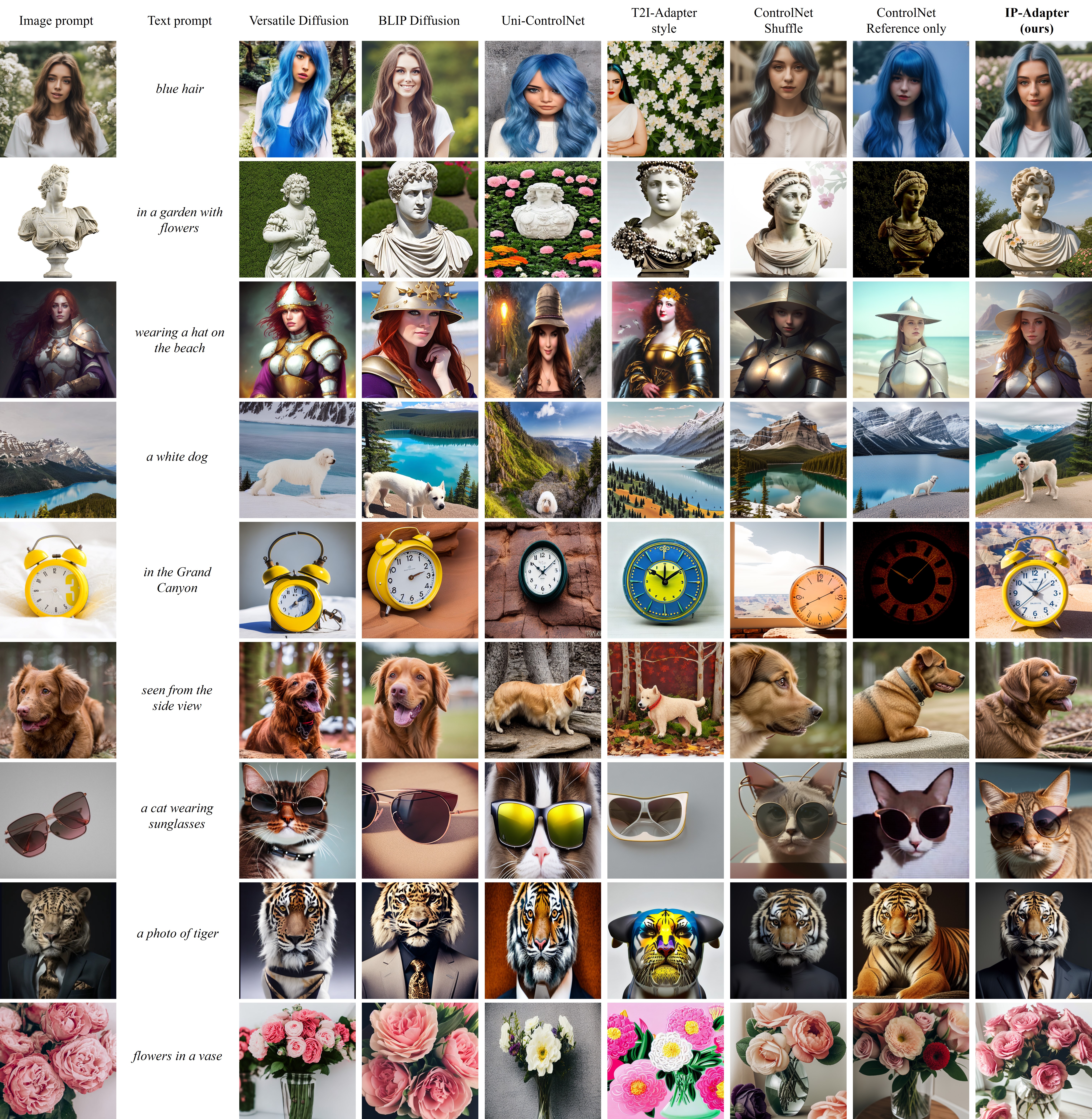
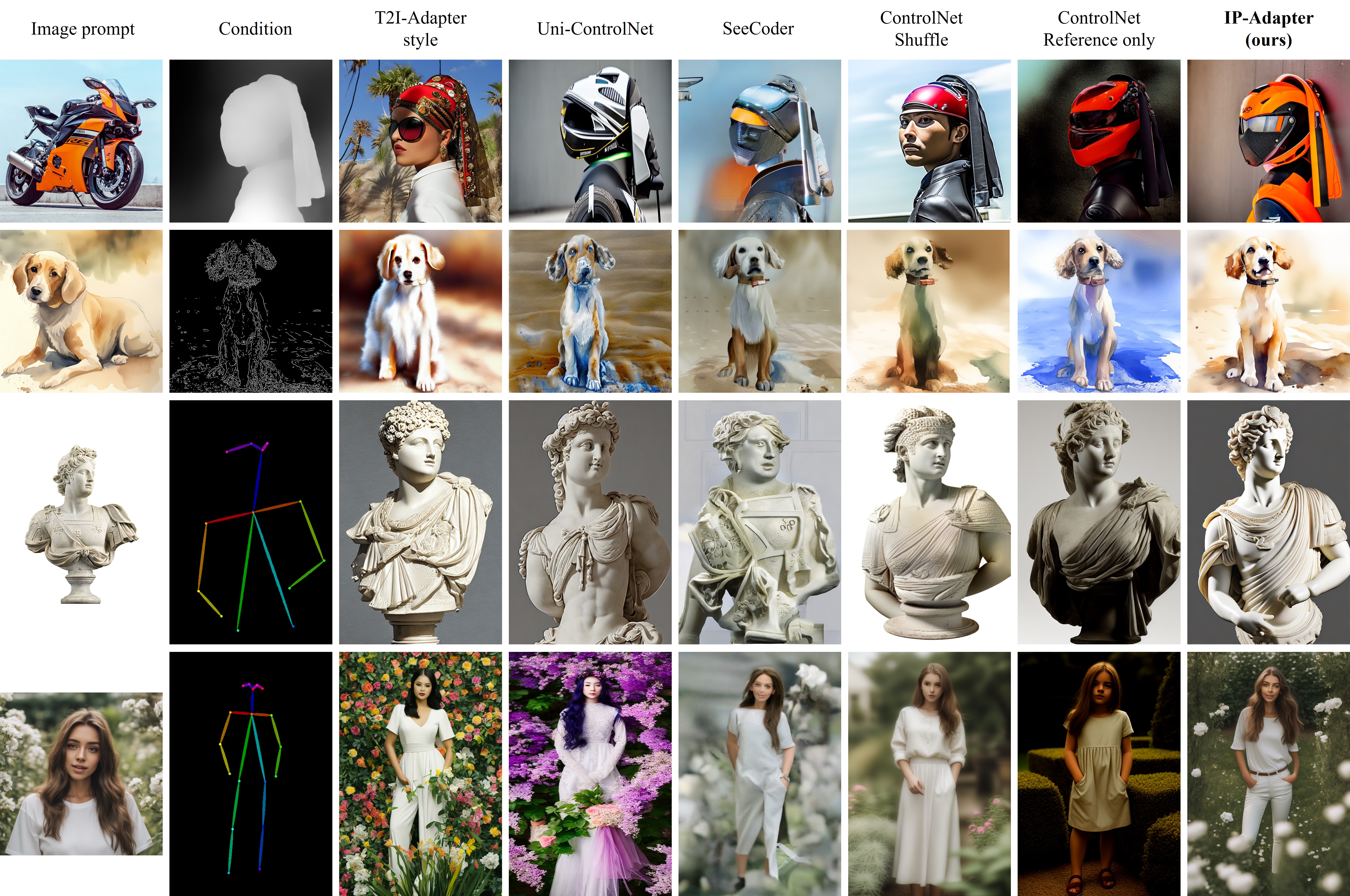
-
SPAR3D – Stable Point-Aware Reconstruction of 3D Objects from Single Images
SPAR3D is a fast single-image 3D reconstructor with intermediate point cloud generation, which allows for interactive user edits and achieves state-of-the-art performance.
https://github.com/Stability-AI/stable-point-aware-3d
https://stability.ai/news/stable-point-aware-3d?utm_source=x&utm_medium=social&utm_campaign=SPAR3D
-
MiniMax-01 goes open source
MiniMax is thrilled to announce the release of the MiniMax-01 series, featuring two groundbreaking models:
MiniMax-Text-01: A foundational language model.
MiniMax-VL-01: A visual multi-modal model.Both models are now open-source, paving the way for innovation and accessibility in AI development!
🔑 Key Innovations
1. Lightning Attention Architecture: Combines 7/8 Lightning Attention with 1/8 Softmax Attention, delivering unparalleled performance.
2. Massive Scale with MoE (Mixture of Experts): 456B parameters with 32 experts and 45.9B activated parameters.
3. 4M-Token Context Window: Processes up to 4 million tokens, 20–32x the capacity of leading models, redefining what’s possible in long-context AI applications.💡 Why MiniMax-01 Matters
1. Innovative Architecture for Top-Tier Performance
The MiniMax-01 series introduces the Lightning Attention mechanism, a bold alternative to traditional Transformer architectures, delivering unmatched efficiency and scalability.2. 4M Ultra-Long Context: Ushering in the AI Agent Era
With the ability to handle 4 million tokens, MiniMax-01 is designed to lead the next wave of agent-based applications, where extended context handling and sustained memory are critical.3. Unbeatable Cost-Effectiveness
Through proprietary architectural innovations and infrastructure optimization, we’re offering the most competitive pricing in the industry:
$0.2 per million input tokens
$1.1 per million output tokens🌟 Experience the Future of AI Today
We believe MiniMax-01 is poised to transform AI applications across industries. Whether you’re building next-gen AI agents, tackling ultra-long context tasks, or exploring new frontiers in AI, MiniMax-01 is here to empower your vision.✅ Try it now for free: hailuo.ai
📄 Read the technical paper: filecdn.minimax.chat/_Arxiv_MiniMax_01_Report.pdf
🌐 Learn more: minimaxi.com/en/news/minimax-01-series-2
💡API Platform: intl.minimaxi.com/

FEATURED POSTS
-
AI and the Law – Why The New York Times might win its copyright lawsuit against OpenAI
Daniel Jeffries wrote:
“Trying to get everyone to license training data is not going to work because that’s not what copyright is about,” Jeffries wrote. “Copyright law is about preventing people from producing exact copies or near exact copies of content and posting it for commercial gain. Period. Anyone who tells you otherwise is lying or simply does not understand how copyright works.”
The AI community is full of people who understand how models work and what they’re capable of, and who are working to improve their systems so that the outputs aren’t full of regurgitated inputs. Google won the Google Books case because it could explain both of these persuasively to judges. But the history of technology law is littered with the remains of companies that were less successful in getting judges to see things their way.
-
Google – Artificial Intelligence free courses
1. Introduction to Large Language Models: Learn about the use cases and how to enhance the performance of large language models.
https://www.cloudskillsboost.google/course_templates/5392. Introduction to Generative AI: Discover the differences between Generative AI and traditional machine learning methods.
https://www.cloudskillsboost.google/course_templates/5363. Generative AI Fundamentals: Earn a skill badge by demonstrating your understanding of foundational concepts in Generative AI.
https://www.cloudskillsboost.google/paths4. Introduction to Responsible AI: Learn about the importance of Responsible AI and how Google implements it in its products.
https://www.cloudskillsboost.google/course_templates/5545. Encoder-Decoder Architecture: Learn about the encoder-decoder architecture, a critical component of machine learning for sequence-to-sequence tasks.
https://www.cloudskillsboost.google/course_templates/5436. Introduction to Image Generation: Discover diffusion models, a promising family of machine learning models in the image generation space.
https://www.cloudskillsboost.google/course_templates/5417. Transformer Models and BERT Model: Get a comprehensive introduction to the Transformer architecture and the Bidirectional Encoder Representations from the Transformers (BERT) model.
https://www.cloudskillsboost.google/course_templates/5388. Attention Mechanism: Learn about the attention mechanism, which allows neural networks to focus on specific parts of an input sequence.
https://www.cloudskillsboost.google/course_templates/537
-
What’s the Difference Between Ray Casting, Ray Tracing, Path Tracing and Rasterization? Physical light tracing…
RASTERIZATION
Rasterisation (or rasterization) is the task of taking the information described in a vector graphics format OR the vertices of triangles making 3D shapes and converting them into a raster image (a series of pixels, dots or lines, which, when displayed together, create the image which was represented via shapes), or in other words “rasterizing” vectors or 3D models onto a 2D plane for display on a computer screen.For each triangle of a 3D shape, you project the corners of the triangle on the virtual screen with some math (projective geometry). Then you have the position of the 3 corners of the triangle on the pixel screen. Those 3 points have texture coordinates, so you know where in the texture are the 3 corners. The cost is proportional to the number of triangles, and is only a little bit affected by the screen resolution.
In computer graphics, a raster graphics or bitmap image is a dot matrix data structure that represents a generally rectangular grid of pixels (points of color), viewable via a monitor, paper, or other display medium.
With rasterization, objects on the screen are created from a mesh of virtual triangles, or polygons, that create 3D models of objects. A lot of information is associated with each vertex, including its position in space, as well as information about color, texture and its “normal,” which is used to determine the way the surface of an object is facing.
Computers then convert the triangles of the 3D models into pixels, or dots, on a 2D screen. Each pixel can be assigned an initial color value from the data stored in the triangle vertices.
Further pixel processing or “shading,” including changing pixel color based on how lights in the scene hit the pixel, and applying one or more textures to the pixel, combine to generate the final color applied to a pixel.
The main advantage of rasterization is its speed. However, rasterization is simply the process of computing the mapping from scene geometry to pixels and does not prescribe a particular way to compute the color of those pixels. So it cannot take shading, especially the physical light, into account and it cannot promise to get a photorealistic output. That’s a big limitation of rasterization.
There are also multiple problems:
If you have two triangles one is behind the other, you will draw twice all the pixels. you only keep the pixel from the triangle that is closer to you (Z-buffer), but you still do the work twice.
The borders of your triangles are jagged as it is hard to know if a pixel is in the triangle or out. You can do some smoothing on those, that is anti-aliasing.
You have to handle every triangles (including the ones behind you) and then see that they do not touch the screen at all. (we have techniques to mitigate this where we only look at triangles that are in the field of view)
Transparency is hard to handle (you can’t just do an average of the color of overlapping transparent triangles, you have to do it in the right order)
-
HDRI Median Cut plugin
www.hdrlabs.com/picturenaut/plugins.html
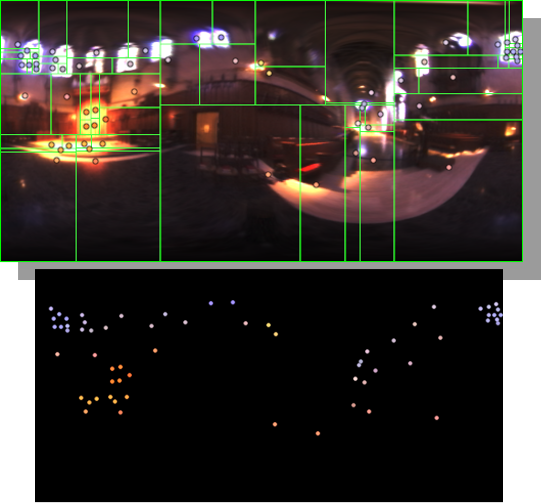
Note. The Median Cut algorithm is typically used for color quantization, which involves reducing the number of colors in an image while preserving its visual quality. It doesn’t directly provide a way to identify the brightest areas in an image. However, if you’re interested in identifying the brightest areas, you might want to look into other methods like thresholding, histogram analysis, or edge detection, through openCV for example.
Here is an openCV example:
(more…)







