BREAKING NEWS
LATEST POSTS
-
Rajiv Talreja on retaining talent through quality of life balance
Industrial revolution: people took a job for survival
Information revolution: people took a job for standard of living
Digital social revolution: people are taking a job for quality of life
-
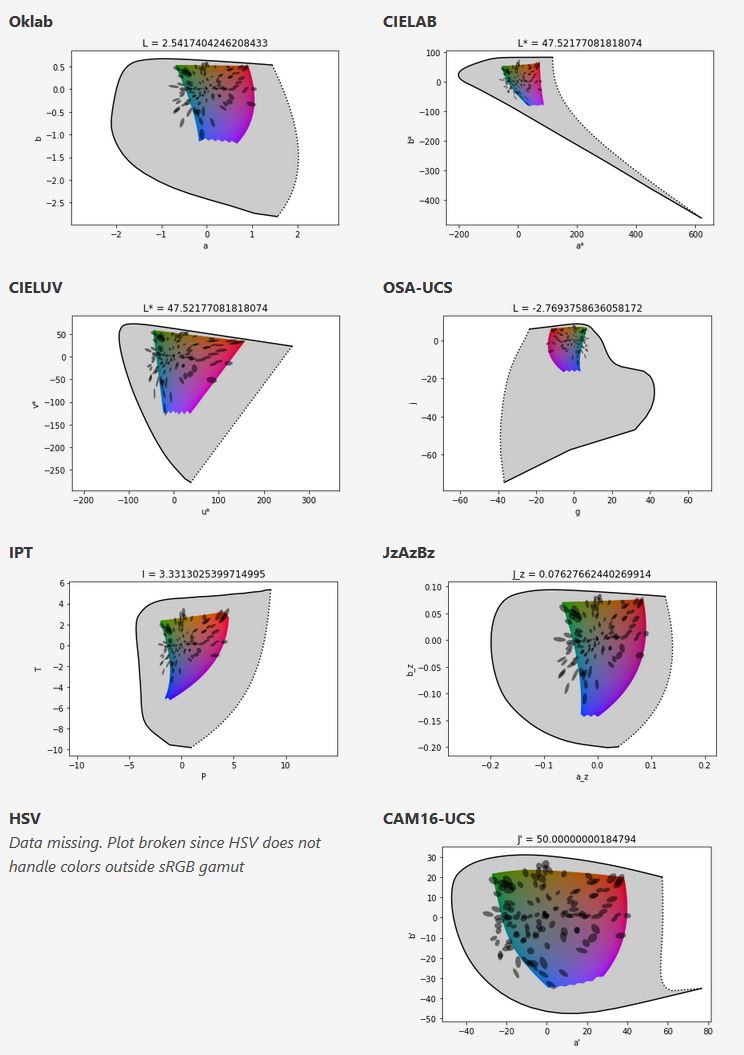
Björn Ottosson – OKHSV and OKHSL – Two new color spaces for color picking
https://bottosson.github.io/misc/colorpicker
https://bottosson.github.io/posts/colorpicker/
https://www.smashingmagazine.com/2024/10/interview-bjorn-ottosson-creator-oklab-color-space/
One problem with sRGB is that in a gradient between blue and white, it becomes a bit purple in the middle of the transition. That’s because sRGB really isn’t created to mimic how the eye sees colors; rather, it is based on how CRT monitors work. That means it works with certain frequencies of red, green, and blue, and also the non-linear coding called gamma. It’s a miracle it works as well as it does, but it’s not connected to color perception. When using those tools, you sometimes get surprising results, like purple in the gradient.
There were also attempts to create simple models matching human perception based on XYZ, but as it turned out, it’s not possible to model all color vision that way. Perception of color is incredibly complex and depends, among other things, on whether it is dark or light in the room and the background color it is against. When you look at a photograph, it also depends on what you think the color of the light source is. The dress is a typical example of color vision being very context-dependent. It is almost impossible to model this perfectly.
I based Oklab on two other color spaces, CIECAM16 and IPT. I used the lightness and saturation prediction from CIECAM16, which is a color appearance model, as a target. I actually wanted to use the datasets used to create CIECAM16, but I couldn’t find them.
IPT was designed to have better hue uniformity. In experiments, they asked people to match light and dark colors, saturated and unsaturated colors, which resulted in a dataset for which colors, subjectively, have the same hue. IPT has a few other issues but is the basis for hue in Oklab.
In the Munsell color system, colors are described with three parameters, designed to match the perceived appearance of colors: Hue, Chroma and Value. The parameters are designed to be independent and each have a uniform scale. This results in a color solid with an irregular shape. The parameters are designed to be independent and each have a uniform scale. This results in a color solid with an irregular shape. Modern color spaces and models, such as CIELAB, Cam16 and Björn Ottosson own Oklab, are very similar in their construction.
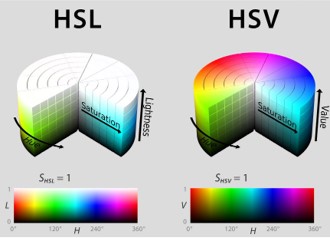
By far the most used color spaces today for color picking are HSL and HSV, two representations introduced in the classic 1978 paper “Color Spaces for Computer Graphics”. HSL and HSV designed to roughly correlate with perceptual color properties while being very simple and cheap to compute.
Today HSL and HSV are most commonly used together with the sRGB color space.

One of the main advantages of HSL and HSV over the different Lab color spaces is that they map the sRGB gamut to a cylinder. This makes them easy to use since all parameters can be changed independently, without the risk of creating colors outside of the target gamut.
The main drawback on the other hand is that their properties don’t match human perception particularly well.
Reconciling these conflicting goals perfectly isn’t possible, but given that HSV and HSL don’t use anything derived from experiments relating to human perception, creating something that makes a better tradeoff does not seem unreasonable.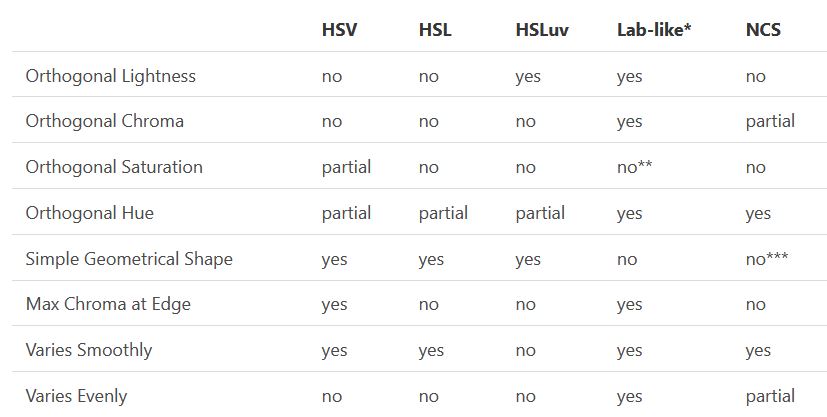
With this new lightness estimate, we are ready to look into the construction of Okhsv and Okhsl.
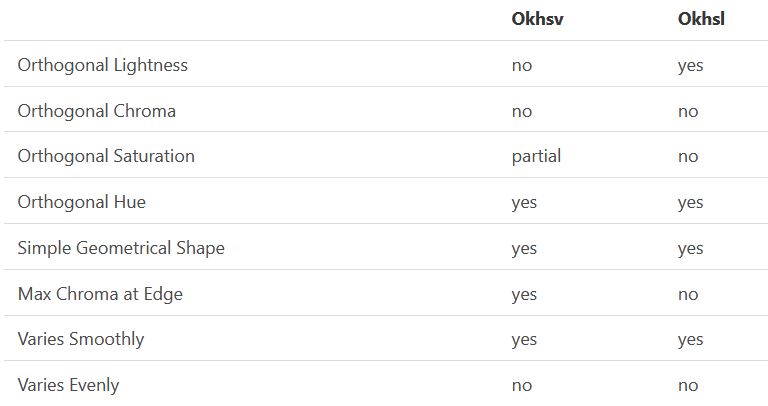
-
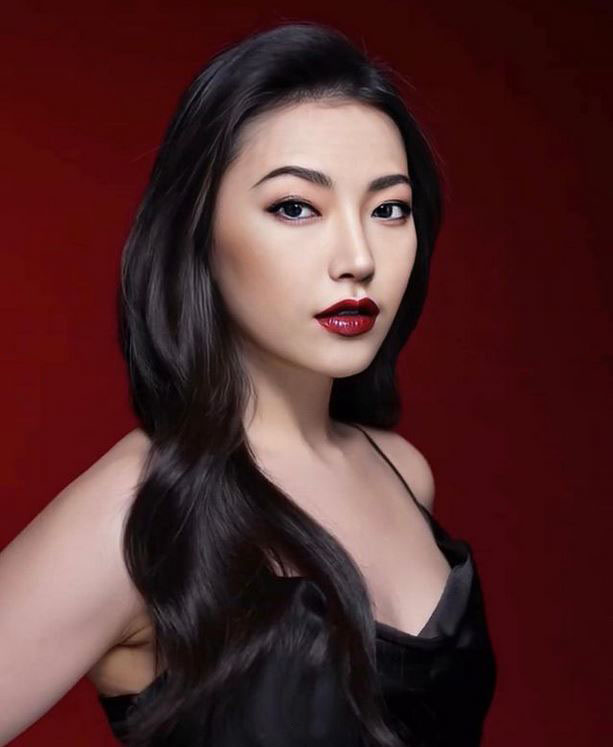
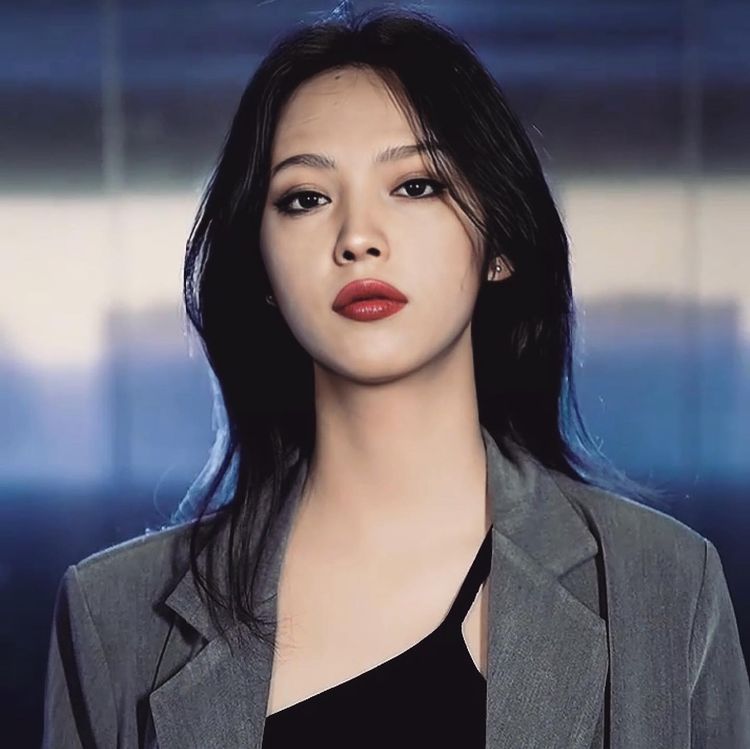
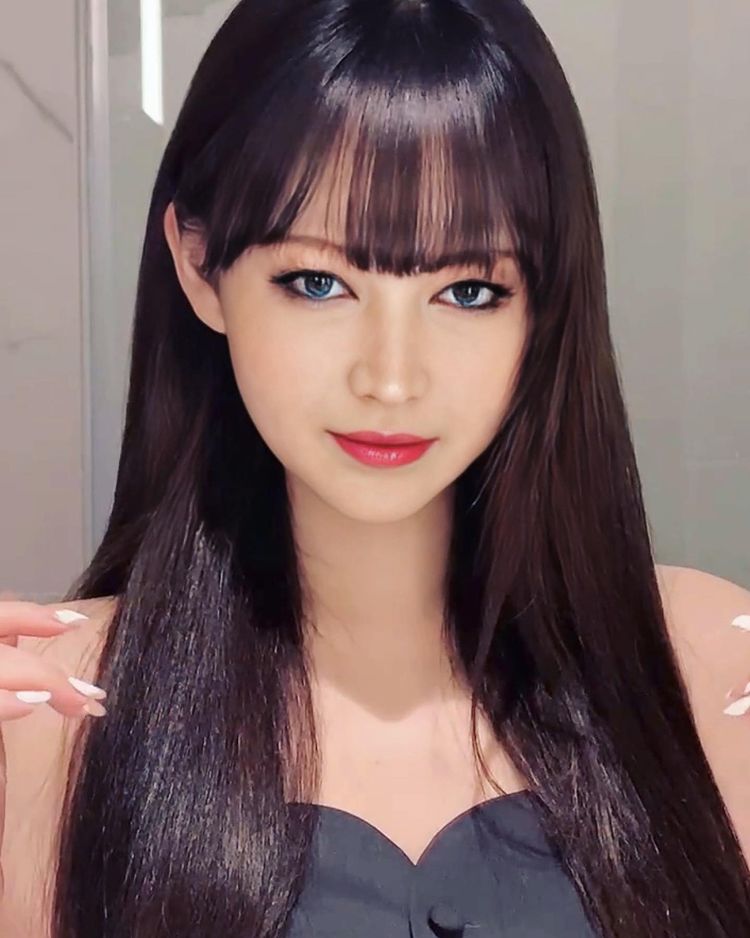
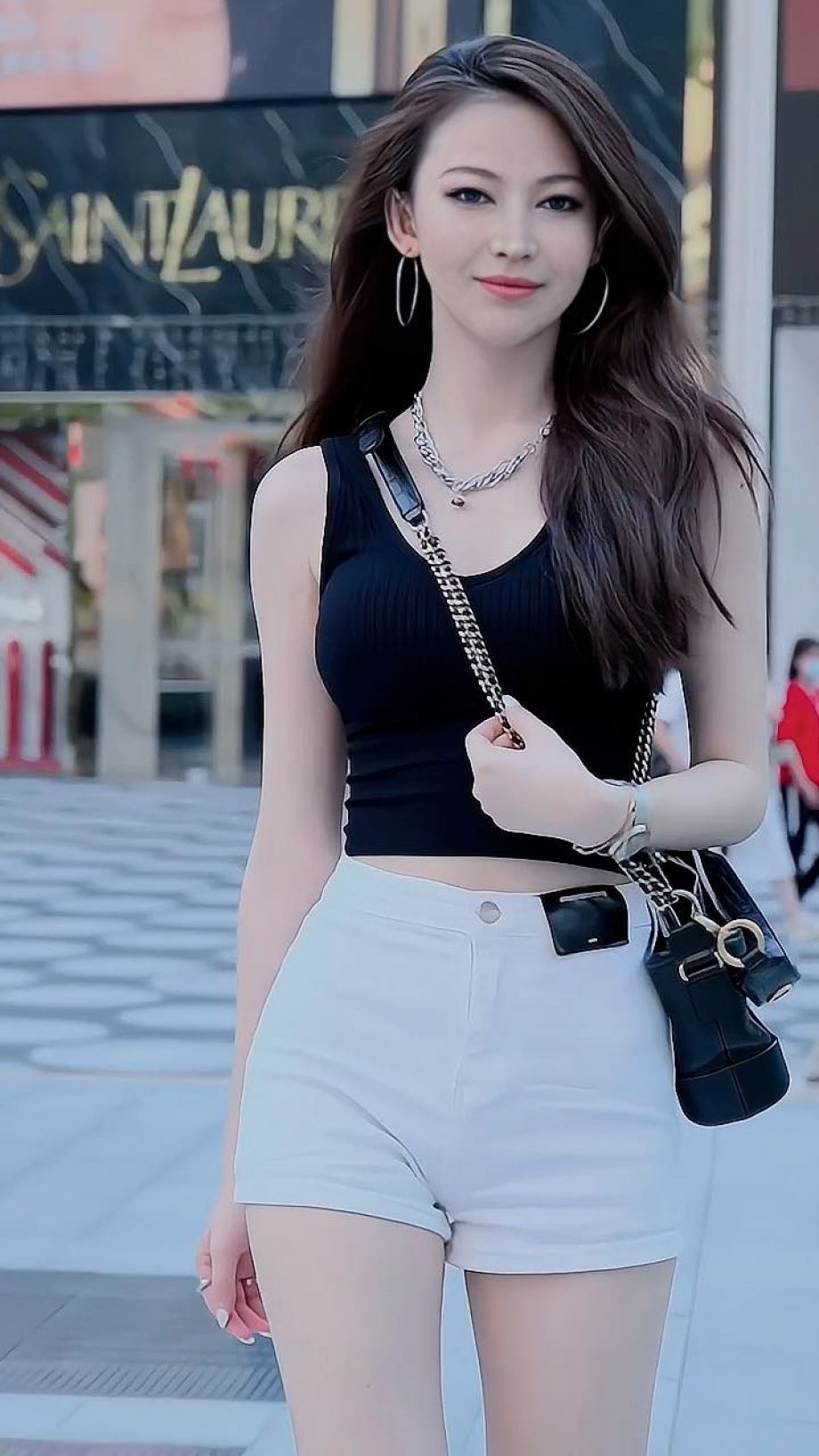
Mania Carta – Photorealistic Characters Made in Blender
Maniacarta is an Artist based in Tokyo, her Artworks are unique and she strive to create the best characters that have soul in the World.
https://80.lv/articles/marvelous-photorealistic-characters-made-in-blender-by-mania-carta/
https://www.instagram.com/mania_carta/




-
Gamification techniques for every day production
https://www.zippia.com/advice/gamification-statistics/
- 90% of employees say gamification makes them more productive at work.
- On average, employees experience a 60% engagement increase with a gamified work experience.
- Companies that use gamification are seven times more profitable than those that do not use gamified elements at work—whether with employees or consumers.
- The North American gamification industry, led primarily by the U.S., is valued at $2.72 billion.
- 72% of people say gamification motivates them to do tasks and work harder on the job.
- 67% of students agree that gamified learning is both more engaging and motivating than traditional classes.
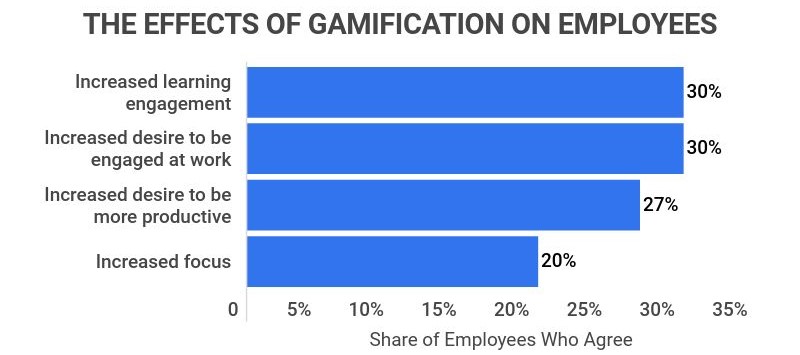
hatrabbits.com/en/gamification/
Gamification is the process of using game elements in a non-game context. It has many advantages over traditional learning approaches, including: Increasing learner motivation levels. Improving knowledge retention
10 gamification techniques you can use instantly
- – Create ‘flow’ If a task is too easy, you will get bored. …
- – Let users ‘complete’ a task. …
- – Set up appropriate challenges. …
- – Allow players to customise things. …
- – Allow users to ‘unlock’ stuff. …
- – Make people curious. …
- – Use the element of surprise. …
- – Recognize achievements.
FEATURED POSTS
-
Christopher Butler – Understanding the Eye-Mind Connection – Vision is a mental process
https://www.chrbutler.com/understanding-the-eye-mind-connection
The intricate relationship between the eyes and the brain, often termed the eye-mind connection, reveals that vision is predominantly a cognitive process. This understanding has profound implications for fields such as design, where capturing and maintaining attention is paramount. This essay delves into the nuances of visual perception, the brain’s role in interpreting visual data, and how this knowledge can be applied to effective design strategies.
This cognitive aspect of vision is evident in phenomena such as optical illusions, where the brain interprets visual information in a way that contradicts physical reality. These illusions underscore that what we “see” is not merely a direct recording of the external world but a constructed experience shaped by cognitive processes.
Understanding the cognitive nature of vision is crucial for effective design. Designers must consider how the brain processes visual information to create compelling and engaging visuals. This involves several key principles:
- Attention and Engagement
- Visual Hierarchy
- Cognitive Load Management
- Context and Meaning
-
AI and the Law: Anthropic to Pay $1.5 Billion to Settle Book Piracy Class Action Lawsuit
https://variety.com/2025/digital/news/anthropic-class-action-settlement-billion-1236509571
The settlement amounts to about $3,000 per book and is believed to be the largest ever recovery in a U.S. copyright case, according to the plaintiffs’ attorneys.





