BREAKING NEWS
LATEST POSTS
-
Vulkan Gaussian Splatting – Real-Time GPU-Accelerated Gaussian Splatting with NVIDIA DesignWorks Sample vk_gaussian_splatting
https://github.com/nvpro-samples/vk_gaussian_splatting
vk_gaussian_splatting is a new Vulkan-based sample that demonstrates real-time Gaussian splatting, a cutting-edge volume rendering technique that enables highly efficient representations of radiance fields. It is the latest addition to the NVIDIA DesignWorks Samples.

-
Foundry Nuke W_hotbox – A fully customisable ‘favourites menu’
https://www.nukepedia.com/python/ui/w_hotbox
W_hotbox is basically a fully customisable ‘favourites menu’ that pops up for as long as you press the shortcut and disappears as soon as you release. The buttons that make up the menu represent python scripts and change depending on you selection. The ‘Hotbox Manager’ offers you an user friendly interface which allows you to add new buttons on the fly. Those buttons are directly accessible via buttons that appear in the menu under your cursor.
-
Yasuharu YOSHIZAWA – Comparison of sRGB vs ACREScg in Nuke
Answering the question that is often asked, “Do I need to use ACEScg to display an sRGB monitor in the end?” (Demonstration shown at an in-house seminar)
Comparison of scanlineRender output with extreme color lights on color charts with sRGB/ACREScg in color – OCIO -working space in NukeDownload the Nuke script:
-
TED 2025 Rob Bredow – Artist-Driven Innovation in the Age of AI
https://robbredow.com/2025/05/ted-artist-driven-innovation/
https://www.ted.com/talks/rob_bredow_star_wars_changed_visual_effects_ai_is_doing_it_again
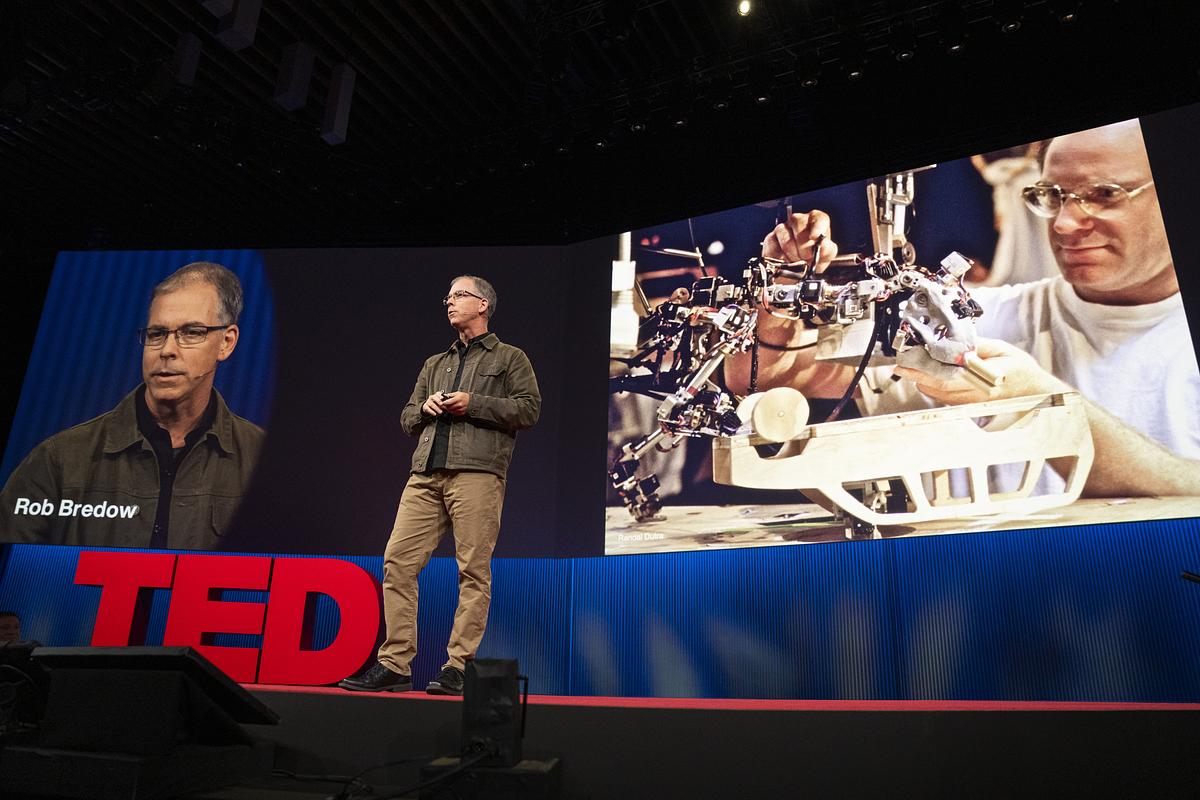

Rob Bredow speaks at SESSION 3 at TED 2025: Humanity Reimagined. April 7-11, 2025, Vancouver, BC. Photo: Gilberto Tadday / TED -
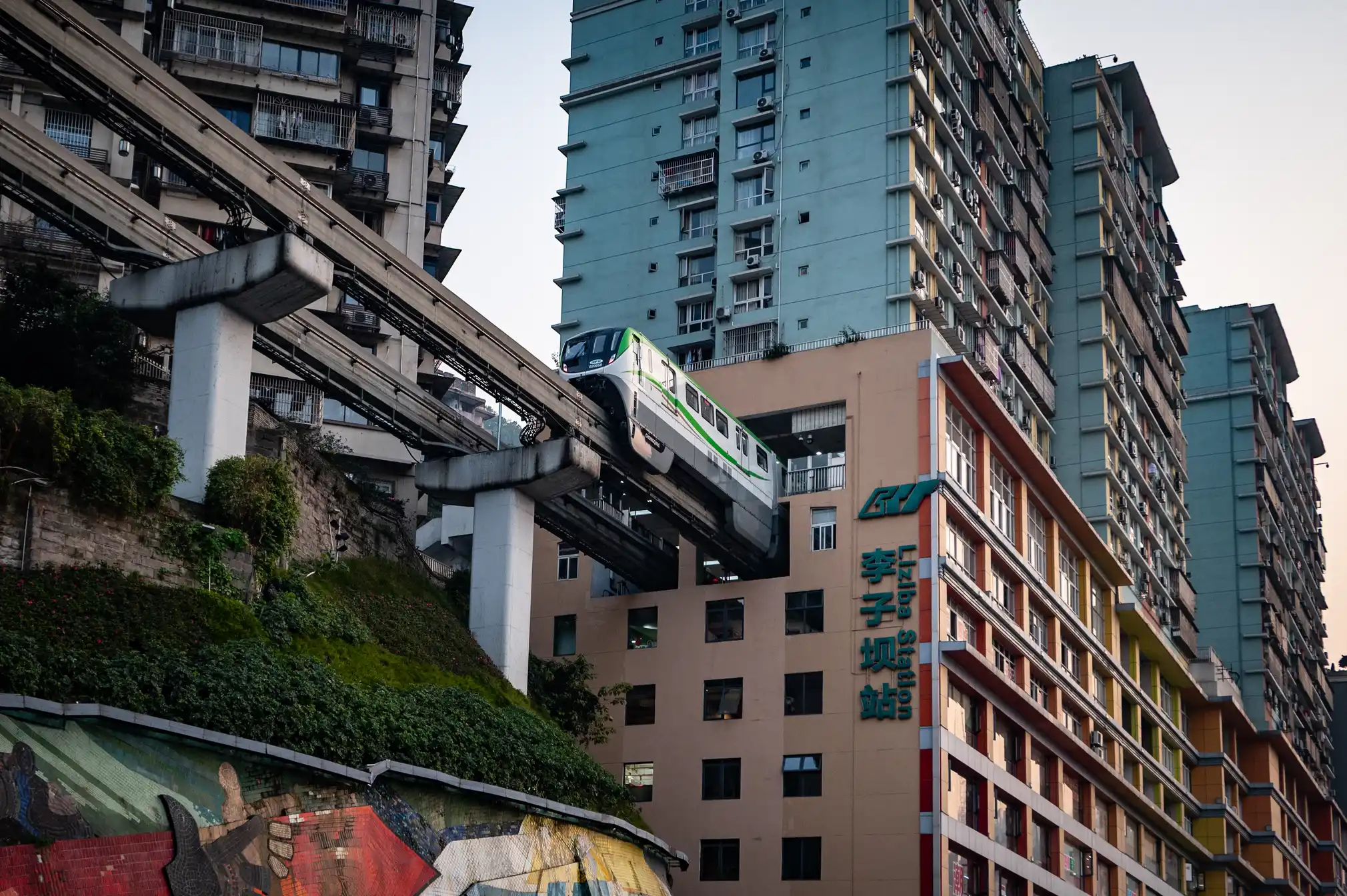
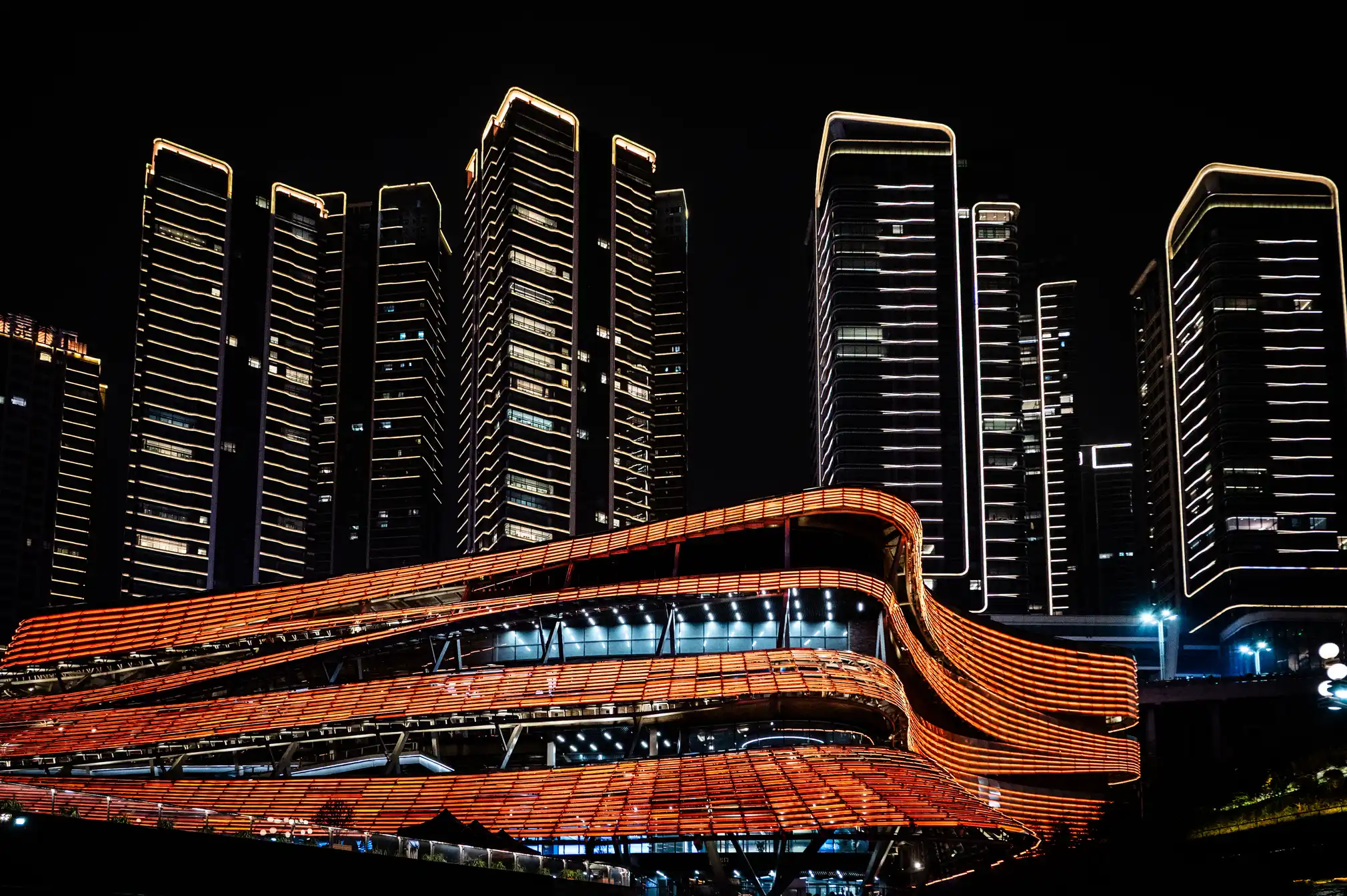
Chongqing the world’s largest city in pictures
https://www.theguardian.com/world/gallery/2025/apr/27/chongqing-the-worlds-largest-city-in-pictures
The largest city in the world is as big as Austria, but few people have ever heard of it. The megacity of 34 million people in central of China is the emblem of the fastest urban revolution on the planet.
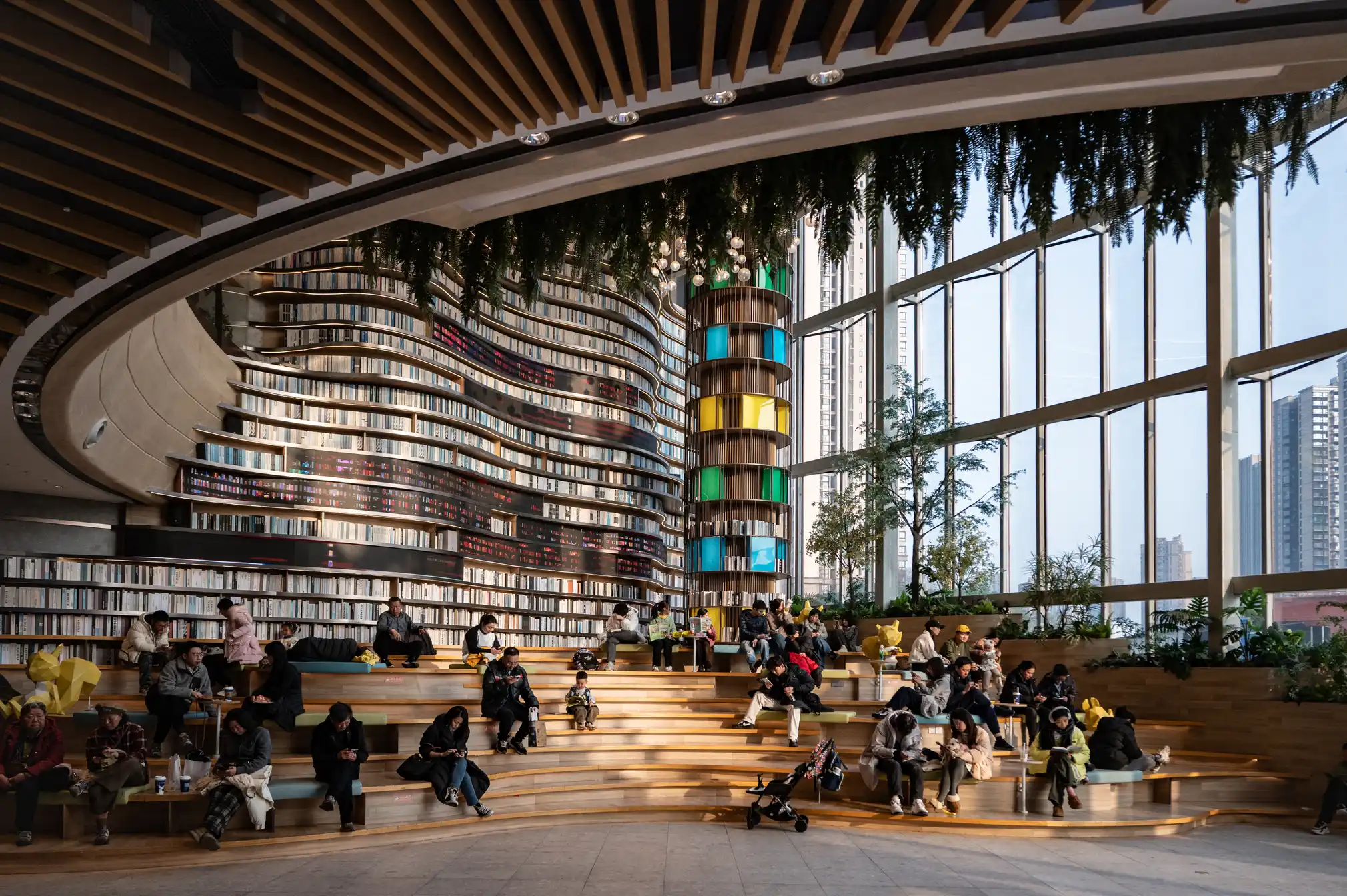
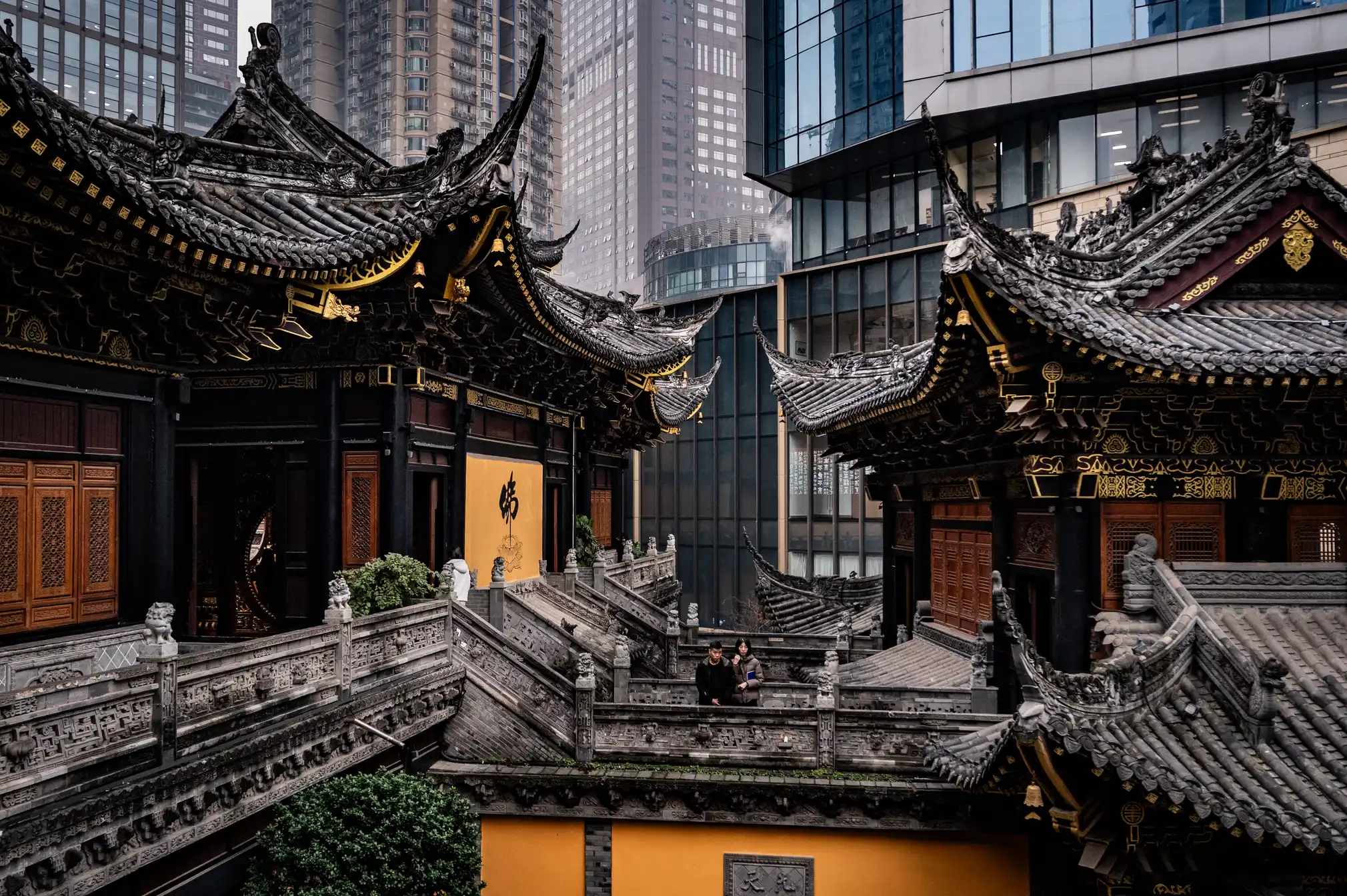




-
Fluent 4.0 released for Blender hard surface modeler
Beyond the boolean support, this add-on also provides cloth panel, grid, head screw, wire and pipe tool.
https://cgthoughts.gumroad.com/
https://superhivemarket.com/creators/cg-thoughts?ref=82
-
Arto T. – A workflow for creating photorealistic, equirectangular 360° panoramas in ComfyUI using Flux
https://civitai.com/models/735980/flux-equirectangular-360-panorama
https://civitai.com/models/745010?modelVersionId=833115
The trigger phrase is “equirectangular 360 degree panorama”. I would avoid saying “spherical projection” since that tends to result in non-equirectangular spherical images.
Image resolution should always be a 2:1 aspect ratio. 1024 x 512 or 1408 x 704 work quite well and were used in the training data. 2048 x 1024 also works.
I suggest using a weight of 0.5 – 1.5. If you are having issues with the image generating too flat instead of having the necessary spherical distortion, try increasing the weight above 1, though this could negatively impact small details of the image. For Flux guidance, I recommend a value of about 2.5 for realistic scenes.
8-bit output at the moment
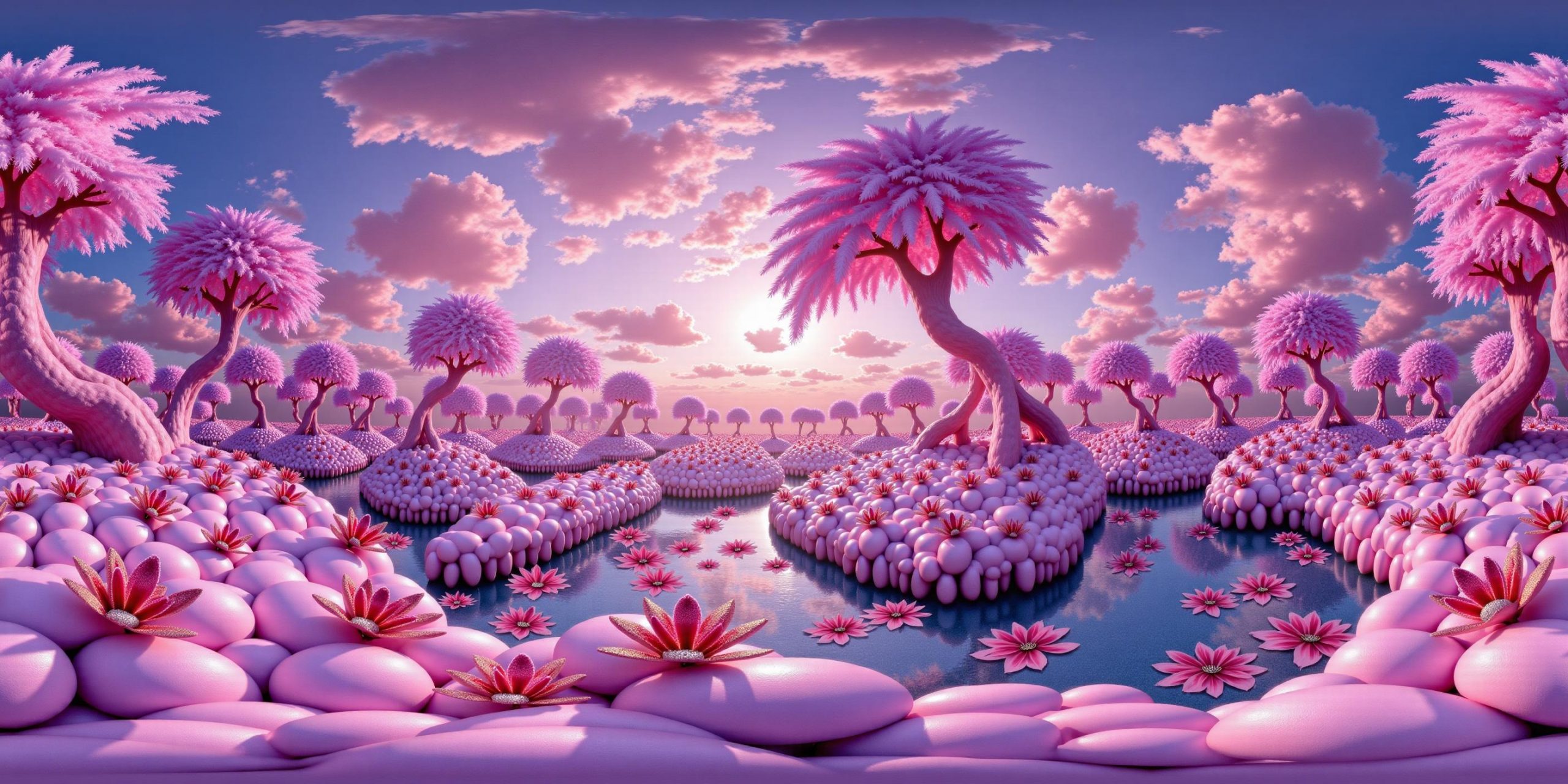

-
Scientists claim to have discovered ‘new colour’ no one has seen before: Olo
https://www.bbc.com/news/articles/clyq0n3em41o
By stimulating specific cells in the retina, the participants claim to have witnessed a blue-green colour that scientists have called “olo”, but some experts have said the existence of a new colour is “open to argument”.
The findings, published in the journal Science Advances on Friday, have been described by the study’s co-author, Prof Ren Ng from the University of California, as “remarkable”.
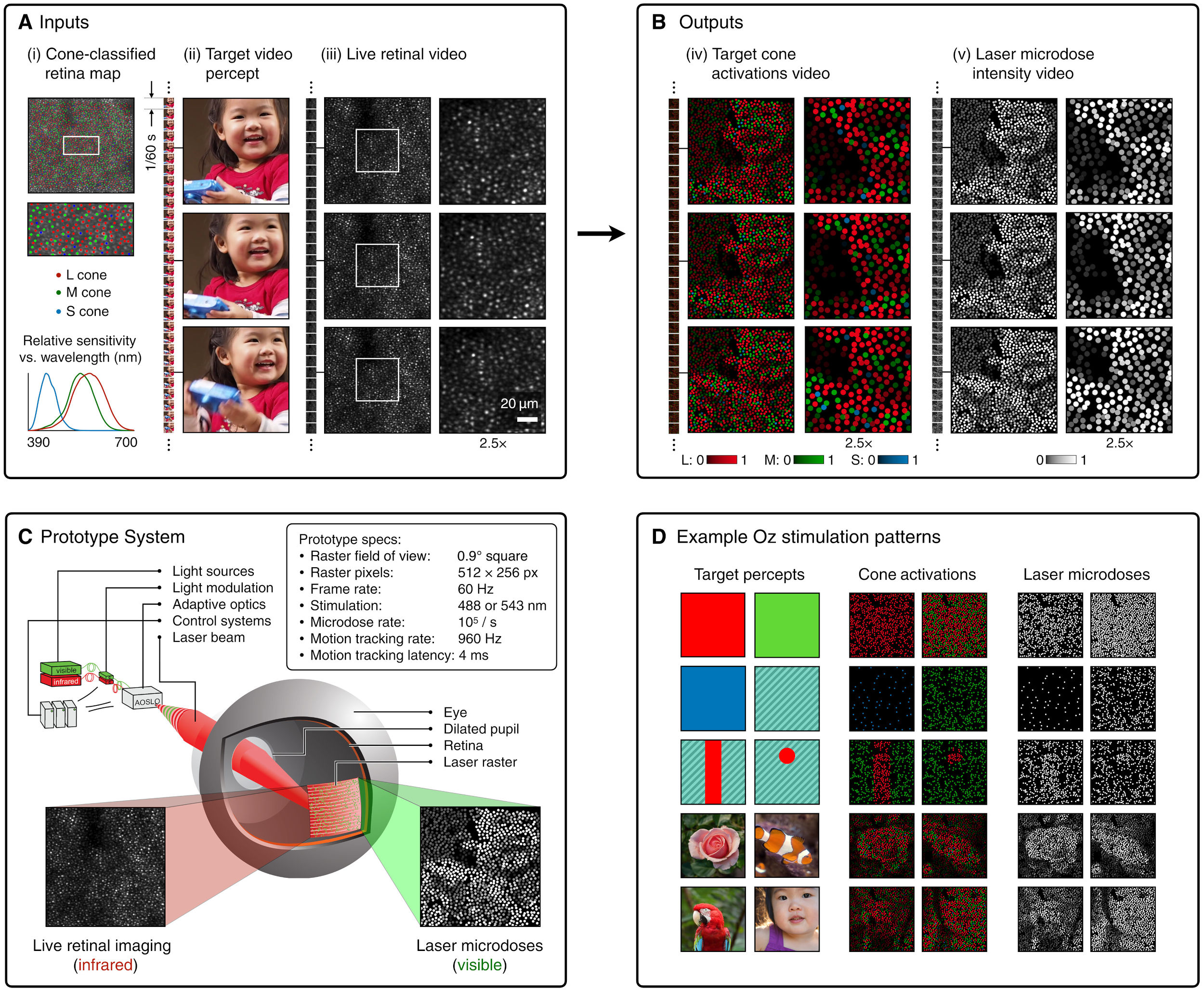
(A) System inputs. (i) Retina map of 103 cone cells preclassified by spectral type (7). (ii) Target visual percept (here, a video of a child, see movie S1 at 1:04). (iii) Infrared cellular-scale imaging of the retina with 60-frames-per-second rolling shutter. Fixational eye movement is visible over the three frames shown.
(B) System outputs. (iv) Real-time per-cone target activation levels to reproduce the target percept, computed by: extracting eye motion from the input video relative to the retina map; identifying the spectral type of every cone in the field of view; computing the per-cone activation the target percept would have produced. (v) Intensities of visible-wavelength 488-nm laser microdoses at each cone required to achieve its target activation level.
(C) Infrared imaging and visible-wavelength stimulation are physically accomplished in a raster scan across the retinal region using AOSLO. By modulating the visible-wavelength beam’s intensity, the laser microdoses shown in (v) are delivered. Drawing adapted with permission [Harmening and Sincich (54)].
(D) Examples of target percepts with corresponding cone activations and laser microdoses, ranging from colored squares to complex imagery. Teal-striped regions represent the color “olo” of stimulating only M cones.
-
FEATURED POSTS
-
Photography basics: Exposure Value vs Photographic Exposure vs Il/Luminance vs Pixel luminance measurements
Also see: https://www.pixelsham.com/2015/05/16/how-aperture-shutter-speed-and-iso-affect-your-photos/
In photography, exposure value (EV) is a number that represents a combination of a camera’s shutter speed and f-number, such that all combinations that yield the same exposure have the same EV (for any fixed scene luminance).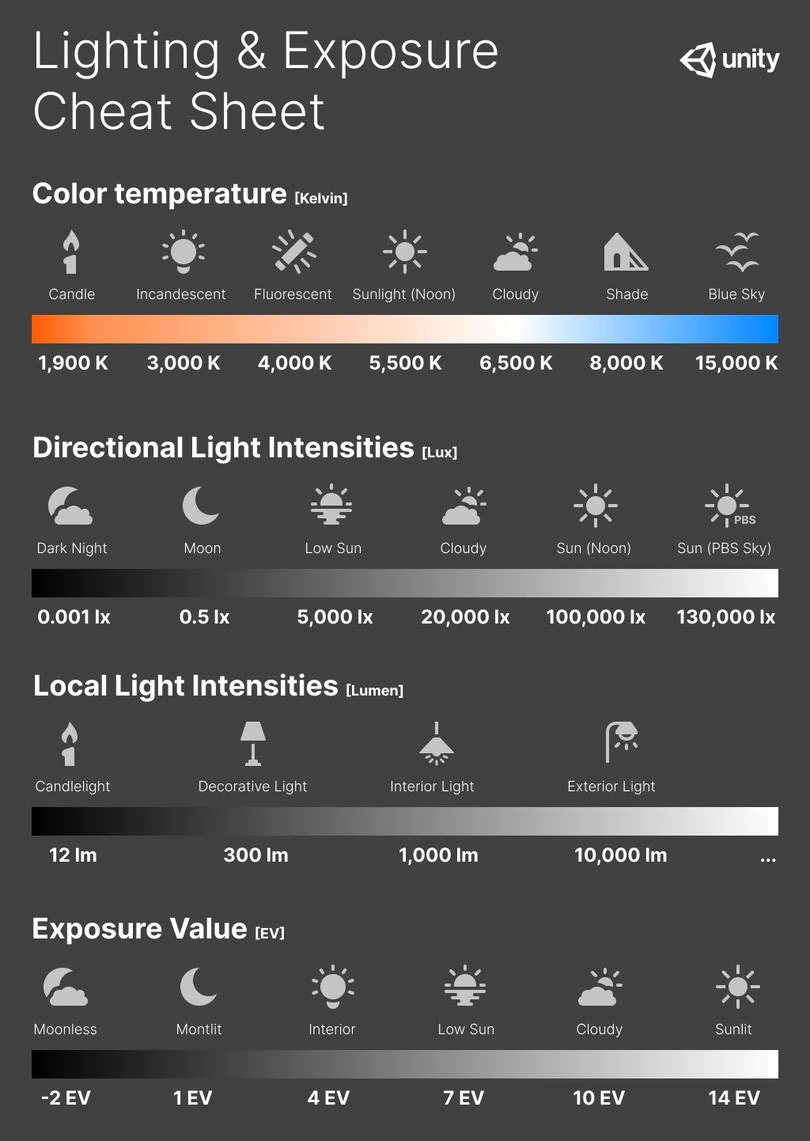
The EV concept was developed in an attempt to simplify choosing among combinations of equivalent camera settings. Although all camera settings with the same EV nominally give the same exposure, they do not necessarily give the same picture. EV is also used to indicate an interval on the photographic exposure scale. 1 EV corresponding to a standard power-of-2 exposure step, commonly referred to as a stop
EV 0 corresponds to an exposure time of 1 sec and a relative aperture of f/1.0. If the EV is known, it can be used to select combinations of exposure time and f-number.Note EV does not equal to photographic exposure. Photographic Exposure is defined as how much light hits the camera’s sensor. It depends on the camera settings mainly aperture and shutter speed. Exposure value (known as EV) is a number that represents the exposure setting of the camera.
Thus, strictly, EV is not a measure of luminance (indirect or reflected exposure) or illuminance (incidentl exposure); rather, an EV corresponds to a luminance (or illuminance) for which a camera with a given ISO speed would use the indicated EV to obtain the nominally correct exposure. Nonetheless, it is common practice among photographic equipment manufacturers to express luminance in EV for ISO 100 speed, as when specifying metering range or autofocus sensitivity.
The exposure depends on two things: how much light gets through the lenses to the camera’s sensor and for how long the sensor is exposed. The former is a function of the aperture value while the latter is a function of the shutter speed. Exposure value is a number that represents this potential amount of light that could hit the sensor. It is important to understand that exposure value is a measure of how exposed the sensor is to light and not a measure of how much light actually hits the sensor. The exposure value is independent of how lit the scene is. For example a pair of aperture value and shutter speed represents the same exposure value both if the camera is used during a very bright day or during a dark night.
Each exposure value number represents all the possible shutter and aperture settings that result in the same exposure. Although the exposure value is the same for different combinations of aperture values and shutter speeds the resulting photo can be very different (the aperture controls the depth of field while shutter speed controls how much motion is captured).
EV 0.0 is defined as the exposure when setting the aperture to f-number 1.0 and the shutter speed to 1 second. All other exposure values are relative to that number. Exposure values are on a base two logarithmic scale. This means that every single step of EV – plus or minus 1 – represents the exposure (actual light that hits the sensor) being halved or doubled.Formulas
(more…)
-
Want to build a start up company that lasts? Think three-layer cake
https://www.fastcompany.com/91131427/want-to-build-a-company-that-lasts-think-three-layer-cake
Building a successful business requires a focus on three key elements: product excellence, go-to-market strategy, and operational excellence. Neglecting any of these areas can lead to failure, as evidenced by the high percentage of startups that don’t make it past the five-year mark. Founders and CEOs must ensure a solid product foundation while also integrating effective sales, marketing, and management strategies to achieve sustainable growth and scale.
- Foundation: Product Excellence, Core Values and Mission
- Core Values: These are the guiding principles that dictate behavior and action within the company. They form the ethical foundation and are crucial for maintaining consistency in decision-making.
- Mission: This defines the company’s purpose and goals. A clear and compelling mission helps align the team and provides a sense of direction.
- Efficiency and Scalability: This layer focuses on creating efficient processes that can scale as the company grows. Streamlined operations reduce costs and increase productivity.
- Structure: Operational Excellence and Innovation
- Operational Excellence: Efficient processes, quality control, and continuous improvement fall into this layer. Ensuring that the company operates smoothly and effectively is crucial for sustainability.
- Innovation: Staying competitive requires innovation. This involves developing new products, services, or processes that add value and keep the company relevant in the market.
- Quality Control and Continuous Improvement: Ensuring that operational processes are of high quality and constantly improving helps maintain product excellence and customer satisfaction.
- Technology and Infrastructure: Investing in the right technology and infrastructure to support business operations is vital. This includes everything from manufacturing equipment to software systems that enhance operational efficiency.
- Strategy: Go-to-Market Strategy, Vision and Long-Term Planning
- Vision: A forward-looking vision inspires and motivates the team. It outlines where the company aims to be in the future and helps in setting long-term goals.
- Strategic Planning: This involves setting long-term goals and determining the actions and resources needed to achieve them. It includes market analysis, competitive strategy, and growth planning.
- Market Understanding: A deep understanding of the target market, including customer segments, competitors, and market trends, is essential. This knowledge helps in positioning the product effectively.
- Marketing and Sales Execution: This involves creating a robust marketing plan that includes branding, messaging, and advertising strategies to attract and retain customers. Additionally, building a strong sales strategy ensures that the product reaches the right customers through the right channels.
- Customer Acquisition and Retention: Effective strategies for acquiring new customers and retaining existing ones are critical. This includes loyalty programs, customer service excellence, and engagement initiatives.
- Foundation: Product Excellence, Core Values and Mission