BREAKING NEWS
LATEST POSTS
-
Micro LED displays
Micro LED displays are a cutting-edge technology that promise significant improvements over existing display methods like OLED and LCD. By using tiny, individual LEDs for each pixel, these displays can deliver exceptional brightness, contrast, and energy efficiency. Their inherent durability and superior performance make them an attractive option for high-end consumer electronics, wearable devices, and even large-scale display panels.
The technology is seen as the future of display innovation, aiming to merge high-quality visuals with low power consumption and long-lasting performance.Despite their advantages, micro LED displays face substantial manufacturing hurdles that have slowed their mass-market adoption. The production process requires the precise transfer and alignment of millions of microscopic LEDs onto a substrate—a task that is both technically challenging and cost-intensive. Issues with yield, scalability, and quality control continue to persist, making it difficult to achieve the economies of scale necessary for widespread commercial use. As industry leaders invest heavily in research and development to overcome these obstacles, the technology remains on the cusp of becoming a viable alternative to current display technologies.
-
Nvidia CUDA Toolkit – a development environment for creating high-performance, GPU-accelerated applications
https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-toolkit
With it, you can develop, optimize, and deploy your applications on GPU-accelerated embedded systems, desktop workstations, enterprise data centers, cloud-based platforms, and supercomputers. The toolkit includes GPU-accelerated libraries, debugging and optimization tools, a C/C++ compiler, and a runtime library.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-P28LKWTzrI
Check your Cuda version, it will be the release version here:
>>> nvcc --version nvcc: NVIDIA (R) Cuda compiler driver Copyright (c) 2005-2024 NVIDIA Corporation Built on Wed_Apr_17_19:36:51_Pacific_Daylight_Time_2024 Cuda compilation tools, release 12.5, V12.5.40 Build cuda_12.5.r12.5/compiler.34177558_0or from here:
>>> nvidia-smi Mon Jun 16 12:35:20 2025 +-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | NVIDIA-SMI 555.85 Driver Version: 555.85 CUDA Version: 12.5 | |-----------------------------------------+------------------------+----------------------+ -
HumanDiT – Pose-Guided Diffusion Transformer for Long-form Human Motion Video Generation
https://agnjason.github.io/HumanDiT-page
By inputting a single character image and template pose video, our method can generate vocal avatar videos featuring not only pose-accurate rendering but also realistic body shapes.
-
DynVFX – Augmenting Real Videoswith Dynamic Content
Given an input video and a simple user-provided text instruction describing the desired content, our method synthesizes dynamic objects or complex scene effects that naturally interact with the existing scene over time. The position, appearance, and motion of the new content are seamlessly integrated into the original footage while accounting for camera motion, occlusions, and interactions with other dynamic objects in the scene, resulting in a cohesive and realistic output video.
https://dynvfx.github.io/sm/index.html
FEATURED POSTS
-
copypastecharacter.com – alphabets, special characters, alt codes and symbols library
https://www.copypastecharacter.com
https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/alt-codes-special-characters-keyboard-symbols-windows-list/
Most used ones:
Alt + 0149 • bullet point
Alt + 0153 ™ trademark symbol
Alt + 0169 © copyright symbol
Alt + 0174 ® registered trademark symbol
Alt + 0176 ° degree symbol
Alt + 0177 ± plus-or-minus sign
Alt + 0215 × multiplication sign
Alt + 12 ♀ female sign
Alt + 11 ♂ male sign
Alt + 13 ♪ eighth note
Alt + 14 ♫ beamed eighth note
Alt + 251 √ square root check mark
Alt + 8236 ∞ infinity
Alt + 24 ↑ up arrow
Alt + 25 ↓ down arrow
Alt + 26 → right arrow
Alt + 27 ← left arrow
Alt + 29 ↔ left right arrow
Alt + 94 ^All of them:
૱ ꠸ ┯ ┰ ┱ ┲ ❗ ► ◄ Ă ă 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Ǖ ǖ Ꞁ ¤ Ð ¢ ℥ Ω ℧ K ℶ ℷ ℸ ⅇ ⅊ ⚌ ⚍ ⚎ ⚏ ⚭ ⚮ ⌀ ⏑ ⏒ ⏓ ⏔ ⏕ ⏖ ⏗ ⏘ ⏙ ⏠ ⏡ ⏦ ᶀ ᶁ ᶂ ᶃ ᶄ ᶆ ᶇ ᶈ ᶉ ᶊ ᶋ ᶌ ᶍ ᶎ ᶏ ᶐ ᶑ ᶒ ᶓ ᶔ ᶕ ᶖ ᶗ ᶘ ᶙ ᶚ ᶸ ᵯ ᵰ ᵴ ᵶ ᵹ ᵼ ᵽ ᵾ ᵿ ⁁ ⁊ ⸜ ⸝ ¶ ¥ £ ⅕ ⅙ ⅛ ⅔ ⅖ ⅗ ⅘ ⅜ ⅚ ⅐ ⅝ ↉ ⅓ ⅑ ⅒ ⅞ ← ↑ → ↓ ↔ ↕ ↖ ↗ ↘ ↙ ↚ ↛ ↜ ↝ ↞ ↟ ↠ ↡ ↢ ↣ ↤ ↥ ↦ ↧ ↨ ↩ ↪ ↫ ↬ ↭ ↮ ↯ ↰ ↱ ↲ ↳ ↴ ↵ ↶ ↷ ↸ ↹ ↺ ↻ ↼ ↽ ↾ ↿ ⇀ ⇁ ⇂ ⇃ ⇄ ⇅ ⇆ ⇇ ⇈ ⇉ ⇊ ⇋ ⇌ ⇍ ⇎ ⇏ ⇐ ⇑ ⇒ ⇓ ⇔ ⇕ ⇖ ⇗ ⇘ ⇙ ⇚ ⇛ ⇜ ⇝ ⇞ ⇟ ⇠ ⇡ ⇢ ⇣ ⇤ ⇥ ⇦ ⇨ ⇩ ⇪ ⇧ ⇫ ⇬ ⇭ ⇮ ⇯ ⇰ ⇱ ⇲ ⇳ ⇴ ⇵ ⇶ ⇷ ⇸ ⇹ ⇺ ⇻ ⇼ ⇽ ⇾ ⇿ ⟰ ⟱ ⟲ ⟳ ⟴ ⟵ ⟶ ⟷ ⟸ ⟹ ⟺ ⟻ ⟼ ⟽ ⟾ ⟿ ⤀ ⤁ ⤂ ⤃ ⤄ ⤅ ⤆ ⤇ ⤈ ⤉ ⤊ ⤋ ⤌ ⤍ ⤎ ⤏ ⤐ ⤑ ⤒ ⤓ ⤔ ⤕ ⤖ ⤗ ⤘ ⤙ ⤚ ⤛ ⤜ ⤝ ⤞ ⤟ ⤠ ⤡ ⤢ ⤣ ⤤ ⤥ ⤦ ⤧ ⤨ ⤩ ⤪ ⤫ ⤬ ⤭ ⤮ ⤯ ⤰ ⤱ ⤲ ⤳ ⤴ ⤵ ⤶ ⤷ ⤸ ⤹ ⤺ ⤻ ⤼ ⤽ ⤾ ⤿ ⥀ ⥁ ⥂ ⥃ ⥄ ⥅ ⥆ ⥇ ⥈ ⥉ ⥊ ⥋ ⥌ ⥍ ⥎ ⥏ ⥐ ⥑ ⥒ ⥓ ⥔ ⥕ ⥖ ⥗ ⥘ ⥙ ⥚ ⥛ ⥜ ⥝ ⥞ ⥟ ⥠ ⥡ ⥢ ⥣ ⥤ ⥥ ⥦ ⥧ ⥨ ⥩ ⥪ ⥫ ⥬ ⥭ ⥮ ⥯ ⥰ ⥱ ⥲ ⥳ ⥴ ⥵ ⥶ ⥷ ⥸ ⥹ ⥺ ⥻ ⥼ ⥽ ⥾ ⥿ ➔ ➘ ➙ ➚ ➛ ➜ ➝ ➞ ➝ ➞ ➟ ➠ ➡ ➢ ➣ ➤ ➥ ➦ ➧ ➨ ➩ ➩ ➪ ➫ ➬ ➭ ➮ ➯ ➱ ➲ ➳ ➴ ➵ ➶ ➷ ➸ ➹ ➺ ➻ ➼ ➽ ➾ ⬀ ⬁ ⬂ ⬃ ⬄ ⬅ ⬆ ⬇ ⬈ ⬉ ⬊ ⬋ ⬌ ⬍ ⬎ ⬏ ⬐ ⬑ ☇ ☈ ⏎ ⍃ ⍄ ⍅ ⍆ ⍇ ⍈ ⍐ ⍗ ⍌ ⍓ ⍍ ⍔ ⍏ ⍖ ♾ ⎌ ☊ ☋ ☌ ☍ ⌃ ⌄ ⌤ ⌅ ⌆ ⌇ ⚋ ⚊ ⌌ ⌍ ⌎ ⌏ ⌐ ⌑ ⌔ ⌕ ⌗ ⌙ ⌢ ⌣ ⌯ ⌬ ⌭ ⌮ ⌖ ⌰ ⌱ ⌲ ⌳ ⌴ ⌵ ⌶ ⌷ ⌸ ⌹ ⌺ ⌻ ⌼ ⍯ ⍰ ⌽ ⌾ ⌿ ⍀ ⍁ ⍂ ⍉ ⍊ ⍋ ⍎ ⍏ ⍑ ⍒ ⍕ ⍖ ⍘ ⍙ ⍚ ⍛ ⍜ ⍝ ⍞ ⍠ ⍟ ⍡ ⍢ ⍣ ⍤ ⍥ ⍨ ⍩ ⍦ ⍧ ⍬ ⍿ ⍪ ⍮ ⍫ ⍱ ⍲ ⍭ ⍳ ⍴ ⍵ ⍶ ⍷ ⍸ ⍹ ⍺ ⍼ ⍽ ⍾ ⎀ ⎁ ⎂ ⎃ ⎄ ⎅ ⎆ ⎉ ⎊ ⎋ ⎍ ⎎ ⎏ ⎐ ⎑ ⎒ ⎓ ⎔ ⎕ ⏣ ⌓ ⏥ ⏢ ⎖ ⎲ ⎳ ⎴ ⎵ ⎶ ⎸ ⎹ ⎺ ⎻ ⎼ ⎽ ⎾ ⎿ ⏀ ⏁ ⏂ ⏃ ⏄ ⏅ ⏆ ⏇ ⏈ ⏉ ⏉ ⏋ ⏌ ⏍ ⏐ ⏤ ⏚ ⏛ Ⓝ ℰ ⓦ ! ⌘ « » ‹ › ‘ ’ “ ” „ ‚ ❝ ❞ £ ¥ € $ ¢ ¬ ¶ @ § ® © ™ ° × π ± √ ‰ Ω ∞ ≈ ÷ ~ ≠ ¹ ² ³ ½ ¼ ¾ ‐ – — | ⁄ \ [ ] { } † ‡ … · • ● ⌥ ⌃ ⇧ ↩ ¡ ¿ ‽ ⁂ ∴ ∵ ◊ ※ ← → ↑ ↓ ☜ ☞ ☝ ☟ ✔ ★ ☆ ♺ ☼ ☂ ☺ ☹ ☃ ✉ ✿ ✄ ✈ ✌ ✎ ♠ ♦ ♣ ♥ ♪ ♫ ♯ ♀ ♂ α ß Á á À à Å å Ä ä Æ æ Ç ç É é È è Ê ê Í í Ì ì Î î Ñ ñ Ó ó Ò ò Ô ô Ö ö Ø ø Ú ú Ù ù Ü ü Ž ž ₳ ฿ ¢ € ₡ ¢ ₢ ₵ ₫ £ £ ₤ ₣ ƒ ₲ ₭ ₥ ₦ ₱ $ $ ₮ ₩ ₩ ¥ ¥ ₴ ₰ ¤ ៛ ₪ ₯ ₠ ₧ ₨ ௹ ﷼ ㍐ ৲ ৳ ~ ƻ Ƽ ƽ ¹ ¸ ¬ ¨ ɂ ǁ ¯ Ɂ ǂ ¡ ´ ° ꟾ ¦ } { | . , · ] ) [ / _ \ ¿ º § ” * – + ( ! & % $ ¼ ¾ ½ ¶ © ® @ ẟ Ɀ ` Ȿ ^ ꜠ ꜡ ỻ ‘ = : ; < ꞌ Ꞌ ꞊ ꞁ ꞈ ꞉ > ? ÷ ℾ ℿ ℔ ℩ ℉ ⅀ ℈ þ ð Þ µ ª ꝋ ꜿ Ꜿ ⱽ ⱺ ⱹ ⱷ ⱶ Ⱶ ⱴ ⱱ Ɒ ⱦ ȶ ȴ ȣ Ȣ ȡ ȝ Ȝ ț ȋ Ȋ ȉ Ȉ ǯ Ǯ ǃ ǀ ƿ ƾ ƺ ƹ Ƹ Ʒ Ʋ ư ƪ ƣ Ƣ Ɵ ƛ Ɩ ƕ ƍ ſ ỽ ⸀ ⸁ ⸂ ⸃ ⸄ ⸅ ⸆ ⸇ ⸈ ⸉ ⸊ ⸋ ⸌ ⸍ ⸎ ⸏ ⸐ ⸑ ⸒ ⸔ ⸕ ▲ ▼ ◀ ▶ ◢ ◣ ◥ ◤ △ ▽ ◿ ◺ ◹ ◸ ▴ ▾ ◂ ▸ ▵ ▿ ◃ ▹ ◁ ▷ ◅ ▻ ◬ ⟁ ⧋ ⧊ ⊿ ∆ ∇ ◭ ◮ ⧩ ⧨ ⌔ ⟐ ◇ ◆ ◈ ⬖ ⬗ ⬘ ⬙ ⬠ ⬡ ⎔ ⋄ ◊ ⧫ ⬢ ⬣ ▰ ▪ ◼ ▮ ◾ ▗ ▖ ■ ∎ ▃ ▄ ▅ ▆ ▇ █ ▌ ▐ ▍ ▎ ▉ ▊ ▋ ❘ ❙ ❚ ▀ ▘ ▝ ▙ ▚ ▛ ▜ ▟ ▞ ░ ▒ ▓ ▂ ▁ ▬ ▔ ▫ ▯ ▭ ▱ ◽ □ ◻ ▢ ⊞ ⊡ ⊟ ⊠ ▣ ▤ ▥ ▦ ⬚ ▧ ▨ ▩ ⬓ ◧ ⬒ ◨ ◩ ◪ ⬔ ⬕ ❏ ❐ ❑ ❒ ⧈ ◰ ◱ ◳ ◲ ◫ ⧇ ⧅ ⧄ ⍁ ⍂ ⟡ ⧉ ⚬ ○ ⚪ ◌ ◍ ◎ ◯ ❍ ◉ ⦾ ⊙ ⦿ ⊜ ⊖ ⊘ ⊚ ⊛ ⊝ ● ⚫ ⦁ ◐ ◑ ◒ ◓ ◔ ◕ ⦶ ⦸ ◵ ◴ ◶ ◷ ⊕ ⊗ ⦇ ⦈ ⦉ ⦊ ❨ ❩ ⸨ ⸩ ◖ ◗ ❪ ❫ ❮ ❯ ❬ ❭ ❰ ❱ ⊏ ⊐ ⊑ ⊒ ◘ ◙ ◚ ◛ ◜ ◝ ◞ ◟ ◠ ◡ ⋒ ⋓ ⋐ ⋑ ╰ ╮ ╭ ╯ ⌒ ╳ ✕ ╱ ╲ ⧸ ⧹ ⌓ ◦ ❖ ✖ ✚ ✜
(more…)
-
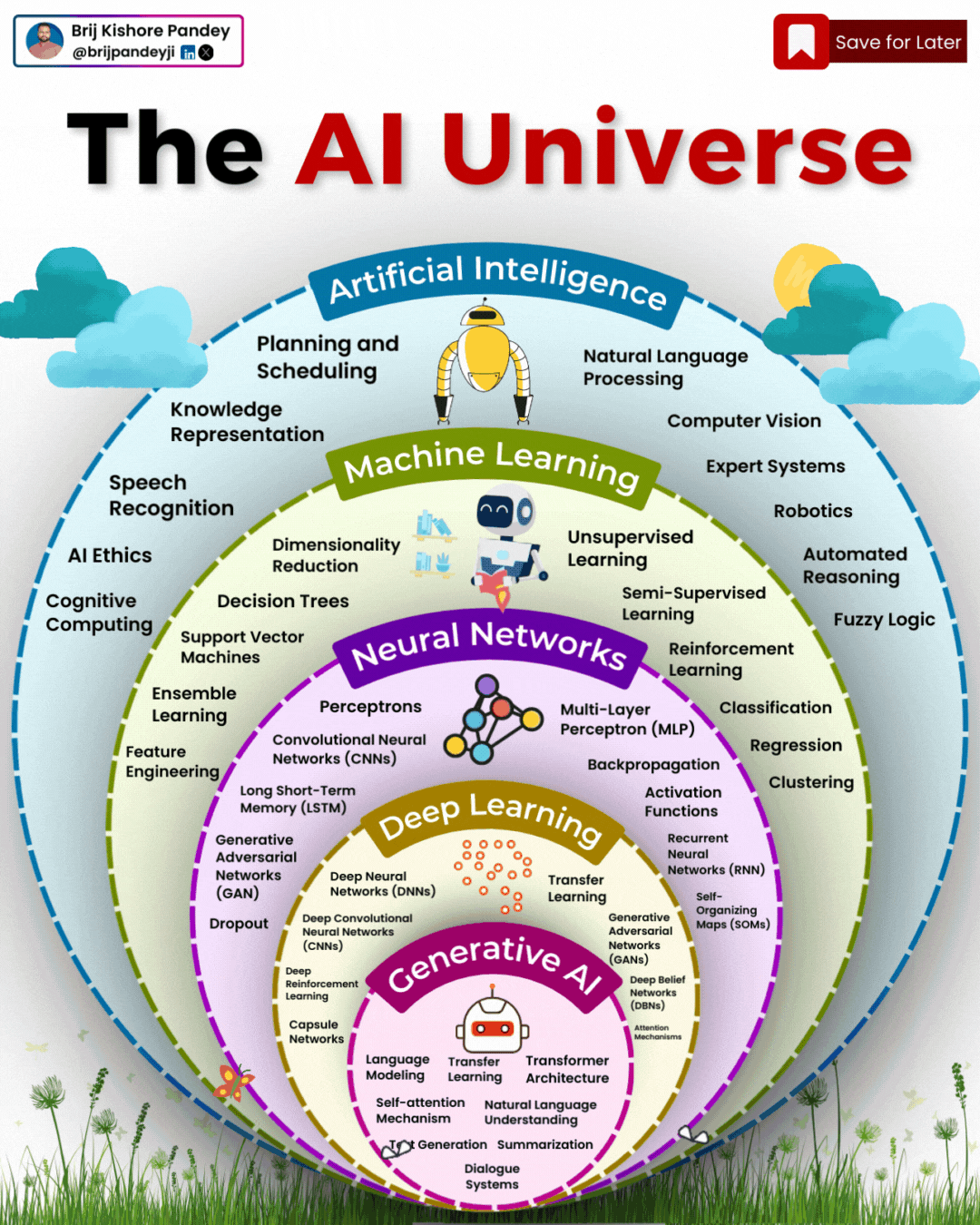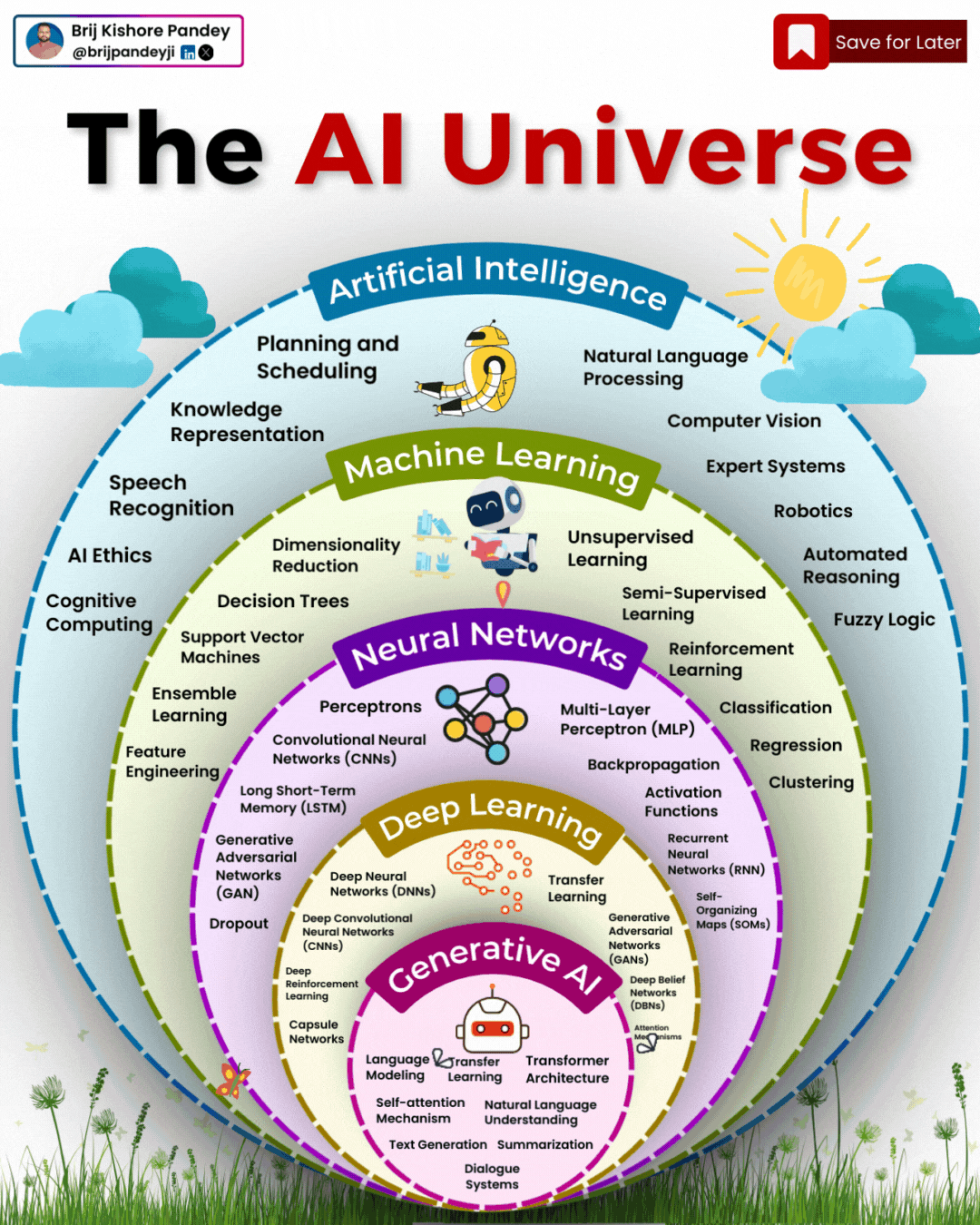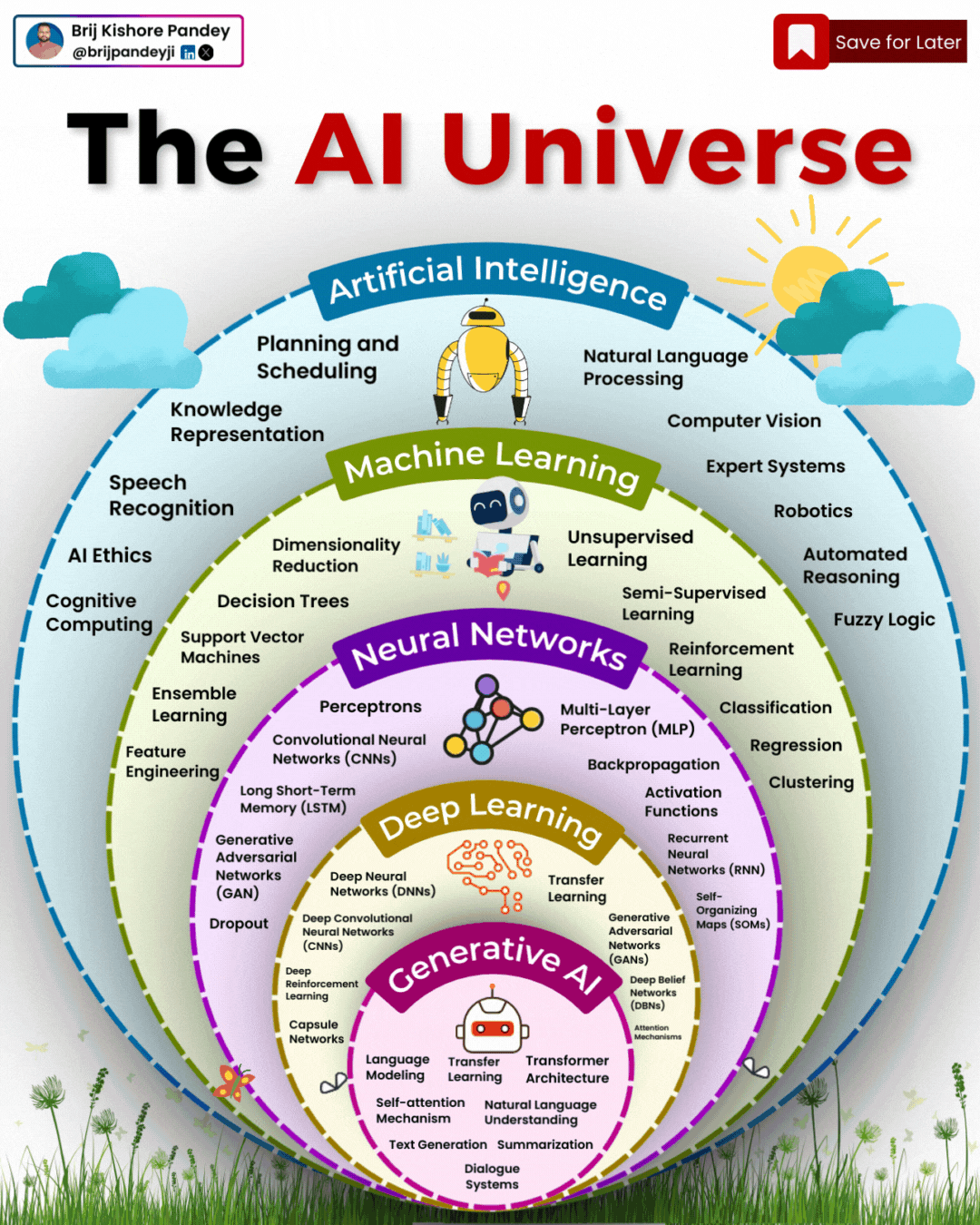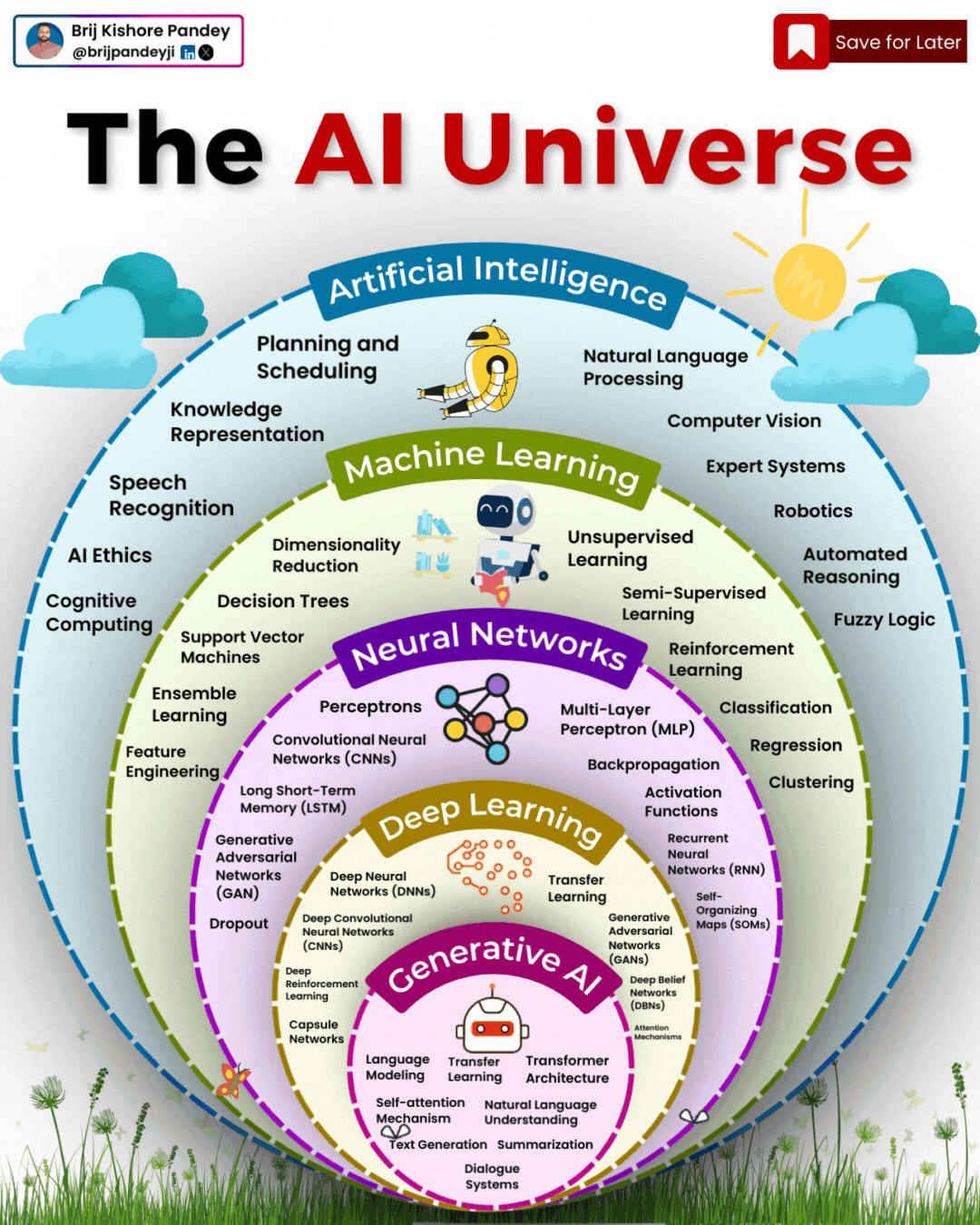
Types of AI Explained in a few Minutes – AI Glossary
1️⃣ 𝗔𝗿𝘁𝗶𝗳𝗶𝗰𝗶𝗮𝗹 𝗜𝗻𝘁𝗲𝗹𝗹𝗶𝗴𝗲𝗻𝗰𝗲 (𝗔𝗜) – The broadest category, covering automation, reasoning, and decision-making. Early AI was rule-based, but today, it’s mainly data-driven.
2️⃣ 𝗠𝗮𝗰𝗵𝗶𝗻𝗲 𝗟𝗲𝗮𝗿𝗻𝗶𝗻𝗴 (𝗠𝗟) – AI that learns patterns from data without explicit programming. Includes decision trees, clustering, and regression models.
3️⃣ 𝗡𝗲𝘂𝗿𝗮𝗹 𝗡𝗲𝘁𝘄𝗼𝗿𝗸𝘀 (𝗡𝗡) – A subset of ML, inspired by the human brain, designed for pattern recognition and feature extraction.
4️⃣ 𝗗𝗲𝗲𝗽 𝗟𝗲𝗮𝗿𝗻𝗶𝗻𝗴 (𝗗𝗟) – Multi-layered neural networks that drives a lot of modern AI advancements, for example enabling image recognition, speech processing, and more.
5️⃣ 𝗧𝗿𝗮𝗻𝘀𝗳𝗼𝗿𝗺𝗲𝗿𝘀 – A revolutionary deep learning architecture introduced by Google in 2017 that allows models to understand and generate language efficiently.
6️⃣ 𝗚𝗲𝗻𝗲𝗿𝗮𝘁𝗶𝘃𝗲 𝗔𝗜 (𝗚𝗲𝗻𝗔𝗜) – AI that doesn’t just analyze data—it creates. From text and images to music and code, this layer powers today’s most advanced AI models.
7️⃣ 𝗚𝗲𝗻𝗲𝗿𝗮𝘁𝗶𝘃𝗲 𝗣𝗿𝗲-𝗧𝗿𝗮𝗶𝗻𝗲𝗱 𝗧𝗿𝗮𝗻𝘀𝗳𝗼𝗿𝗺𝗲𝗿𝘀 (𝗚𝗣𝗧) – A specific subset of Generative AI that uses transformers for text generation.
8️⃣ 𝗟𝗮𝗿𝗴𝗲 𝗟𝗮𝗻𝗴𝘂𝗮𝗴𝗲 𝗠𝗼𝗱𝗲𝗹𝘀 (𝗟𝗟𝗠) – Massive AI models trained on extensive datasets to understand and generate human-like language.
9️⃣ 𝗚𝗣𝗧-4 – One of the most advanced LLMs, built on transformer architecture, trained on vast datasets to generate human-like responses.
🔟 𝗖𝗵𝗮𝘁𝗚𝗣𝗧 – A specific application of GPT-4, optimized for conversational AI and interactive use.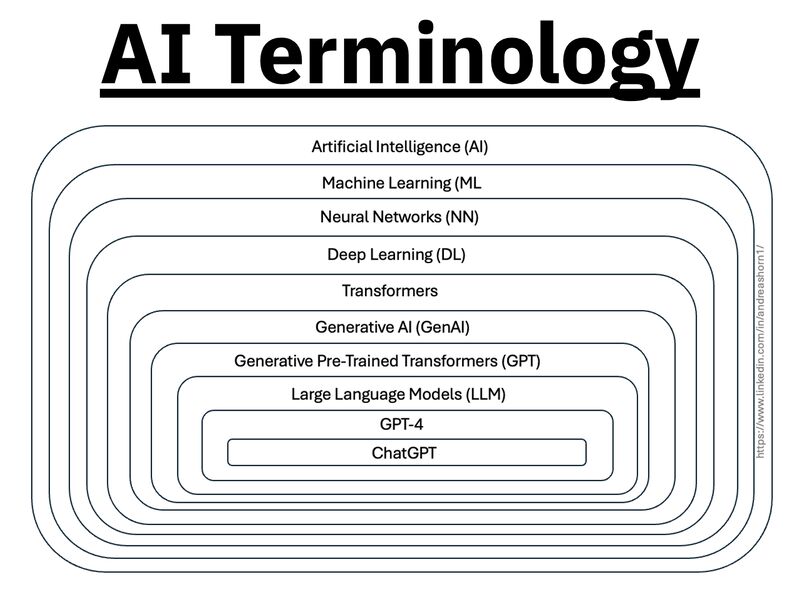
-
RawTherapee – a free, open source, cross-platform raw image and HDRi processing program
5.10 of this tool includes excellent tools to clean up cr2 and cr3 used on set to support HDRI processing.
Converting raw to AcesCG 32 bit tiffs with metadata.
-
Practical Aspects of Spectral Data and LEDs in Digital Content Production and Virtual Production – SIGGRAPH 2022
Comparison to the commercial side

https://www.ecolorled.com/blog/detail/what-is-rgb-rgbw-rgbic-strip-lights
RGBW (RGB + White) LED strip uses a 4-in-1 LED chip made up of red, green, blue, and white.
RGBWW (RGB + White + Warm White) LED strip uses either a 5-in-1 LED chip with red, green, blue, white, and warm white for color mixing. The only difference between RGBW and RGBWW is the intensity of the white color. The term RGBCCT consists of RGB and CCT. CCT (Correlated Color Temperature) means that the color temperature of the led strip light can be adjusted to change between warm white and white. Thus, RGBWW strip light is another name of RGBCCT strip.
RGBCW is the acronym for Red, Green, Blue, Cold, and Warm. These 5-in-1 chips are used in supper bright smart LED lighting products