BREAKING NEWS
LATEST POSTS
FEATURED POSTS
-
SkyworkAI Matrix-3D – Omnidirectional Explorable 3D World Generation
https://github.com/SkyworkAI/Matrix-3D
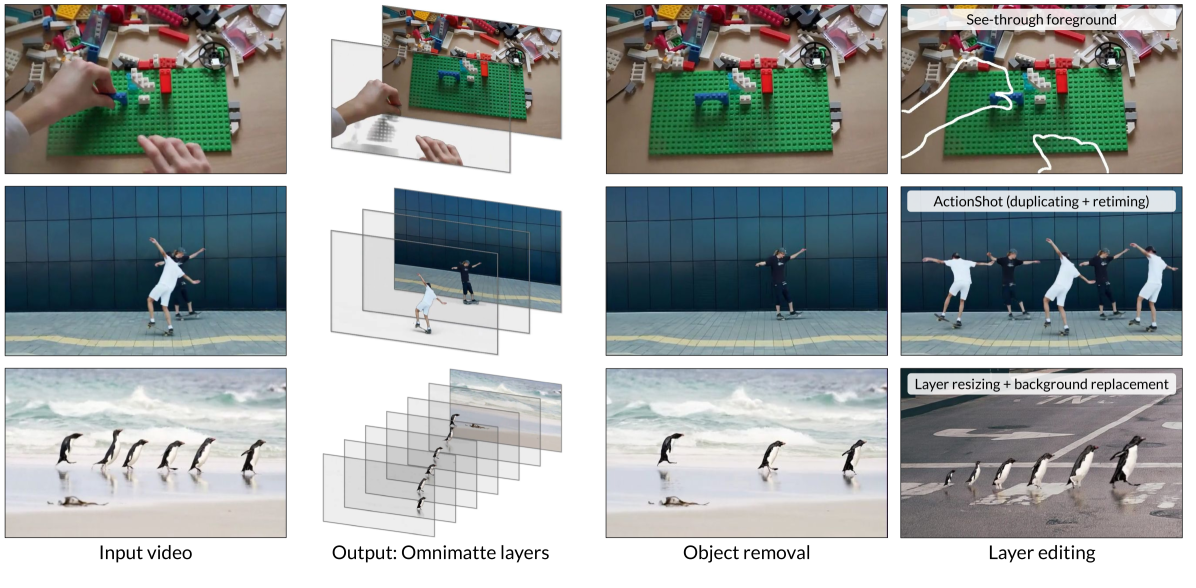
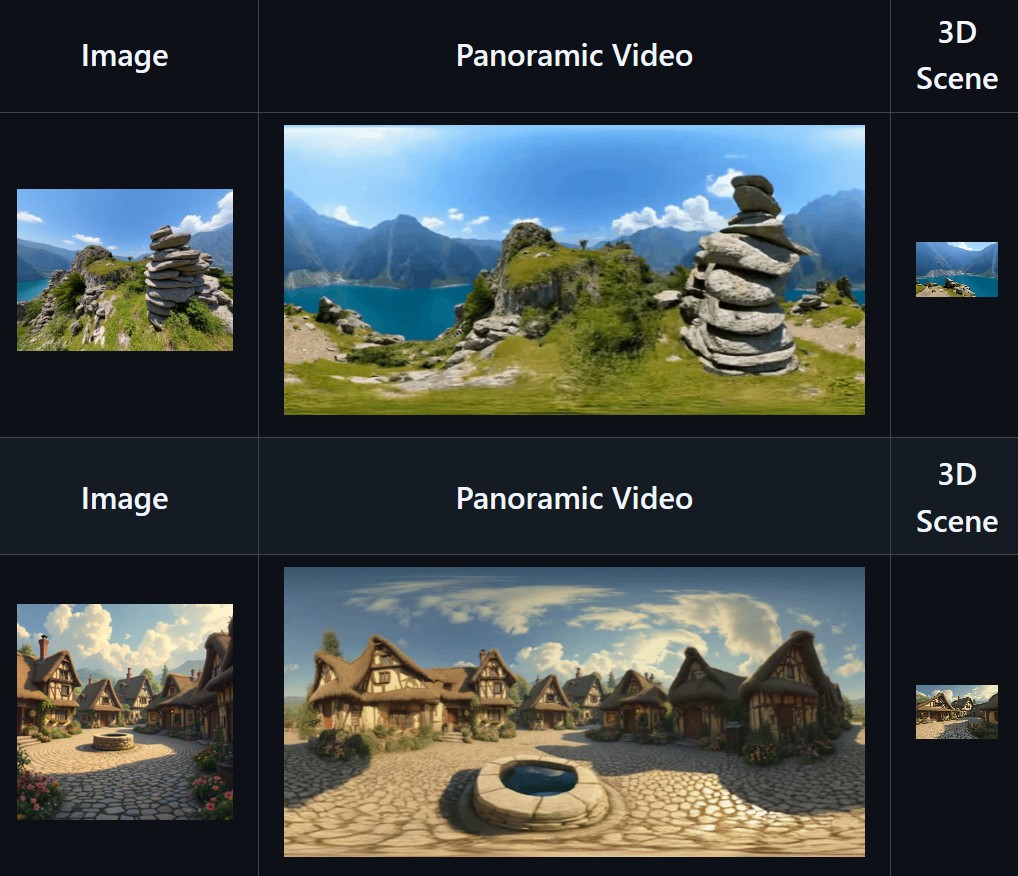
Matrix-3D utilizes panoramic representation for wide-coverage omnidirectional explorable 3D world generation that combines conditional video generation and panoramic 3D reconstruction.
- Large-Scale Scene Generation : Compared to existing scene generation approaches, Matrix-3D supports the generation of broader, more expansive scenes that allow for complete 360-degree free exploration.
- High Controllability : Matrix-3D supports both text and image inputs, with customizable trajectories and infinite extensibility.
- Strong Generalization Capability : Built upon self-developed 3D data and video model priors, Matrix-3D enables the generation of diverse and high-quality 3D scenes.
- Speed-Quality Balance: Two types of panoramic 3D reconstruction methods are proposed to achieve rapid and detailed 3D reconstruction respectively.
-
Photography basics: Lumens vs Candelas (candle) vs Lux vs FootCandle vs Watts vs Irradiance vs Illuminance
https://www.translatorscafe.com/unit-converter/en-US/illumination/1-11/
The power output of a light source is measured using the unit of watts W. This is a direct measure to calculate how much power the light is going to drain from your socket and it is not relatable to the light brightness itself.
The amount of energy emitted from it per second. That energy comes out in a form of photons which we can crudely represent with rays of light coming out of the source. The higher the power the more rays emitted from the source in a unit of time.
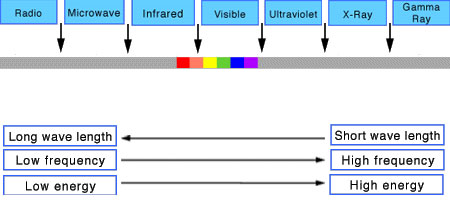
Not all energy emitted is visible to the human eye, so we often rely on photometric measurements, which takes in account the sensitivity of human eye to different wavelenghts
Details in the post
(more…)
-
Embedding frame ranges into Quicktime movies with FFmpeg
QuickTime (.mov) files are fundamentally time-based, not frame-based, and so don’t have a built-in, uniform “first frame/last frame” field you can set as numeric frame IDs. Instead, tools like Shotgun Create rely on the timecode track and the movie’s duration to infer frame numbers. If you want Shotgun to pick up a non-default frame range (e.g. start at 1001, end at 1064), you must bake in an SMPTE timecode that corresponds to your desired start frame, and ensure the movie’s duration matches your clip length.
How Shotgun Reads Frame Ranges
- Default start frame is 1. If no timecode metadata is present, Shotgun assumes the movie begins at frame 1.
- Timecode ⇒ frame number. Shotgun Create “honors the timecodes of media sources,” mapping the embedded TC to frame IDs. For example, a 24 fps QuickTime tagged with a start timecode of 00:00:41:17 will be interpreted as beginning on frame 1001 (1001 ÷ 24 fps ≈ 41.71 s).
Embedding a Start Timecode
QuickTime uses a
tmcd(timecode) track. You can bake in an SMPTE track via FFmpeg’s-timecodeflag or via Compressor/encoder settings:- Compute your start TC.
- Desired start frame = 1001
- Frame 1001 at 24 fps ⇒ 1001 ÷ 24 ≈ 41.708 s ⇒ TC 00:00:41:17
- FFmpeg example:
ffmpeg -i input.mov \ -c copy \ -timecode 00:00:41:17 \ output.movThis adds a timecode track beginning at 00:00:41:17, which Shotgun maps to frame 1001.
Ensuring the Correct End Frame
Shotgun infers the last frame from the movie’s duration. To end on frame 1064:
- Frame count = 1064 – 1001 + 1 = 64 frames
- Duration = 64 ÷ 24 fps ≈ 2.667 s
FFmpeg trim example:
ffmpeg -i input.mov \ -c copy \ -timecode 00:00:41:17 \ -t 00:00:02.667 \ output_trimmed.movThis results in a 64-frame clip (1001→1064) at 24 fps.