BREAKING NEWS
LATEST POSTS
-
FXGuide – ACES 2.0 with ILM’s Alex Fry
https://draftdocs.acescentral.com/background/whats-new/
ACES 2.0 is the second major release of the components that make up the ACES system. The most significant change is a new suite of rendering transforms whose design was informed by collected feedback and requests from users of ACES 1. The changes aim to improve the appearance of perceived artifacts and to complete previously unfinished components of the system, resulting in a more complete, robust, and consistent product.
Highlights of the key changes in ACES 2.0 are as follows:
- New output transforms, including:
- A less aggressive tone scale
- More intuitive controls to create custom outputs to non-standard displays
- Robust gamut mapping to improve perceptual uniformity
- Improved performance of the inverse transforms
- Enhanced AMF specification
- An updated specification for ACES Transform IDs
- OpenEXR compression recommendations
- Enhanced tools for generating Input Transforms and recommended procedures for characterizing prosumer cameras
- Look Transform Library
- Expanded documentation
Rendering Transform
The most substantial change in ACES 2.0 is a complete redesign of the rendering transform.
ACES 2.0 was built as a unified system, rather than through piecemeal additions. Different deliverable outputs “match” better and making outputs to display setups other than the provided presets is intended to be user-driven. The rendering transforms are less likely to produce undesirable artifacts “out of the box”, which means less time can be spent fixing problematic images and more time making pictures look the way you want.
Key design goals
- Improve consistency of tone scale and provide an easy to use parameter to allow for outputs between preset dynamic ranges
- Minimize hue skews across exposure range in a region of same hue
- Unify for structural consistency across transform type
- Easy to use parameters to create outputs other than the presets
- Robust gamut mapping to improve harsh clipping artifacts
- Fill extents of output code value cube (where appropriate and expected)
- Invertible – not necessarily reversible, but Output > ACES > Output round-trip should be possible
- Accomplish all of the above while maintaining an acceptable “out-of-the box” rendering
- New output transforms, including:
-
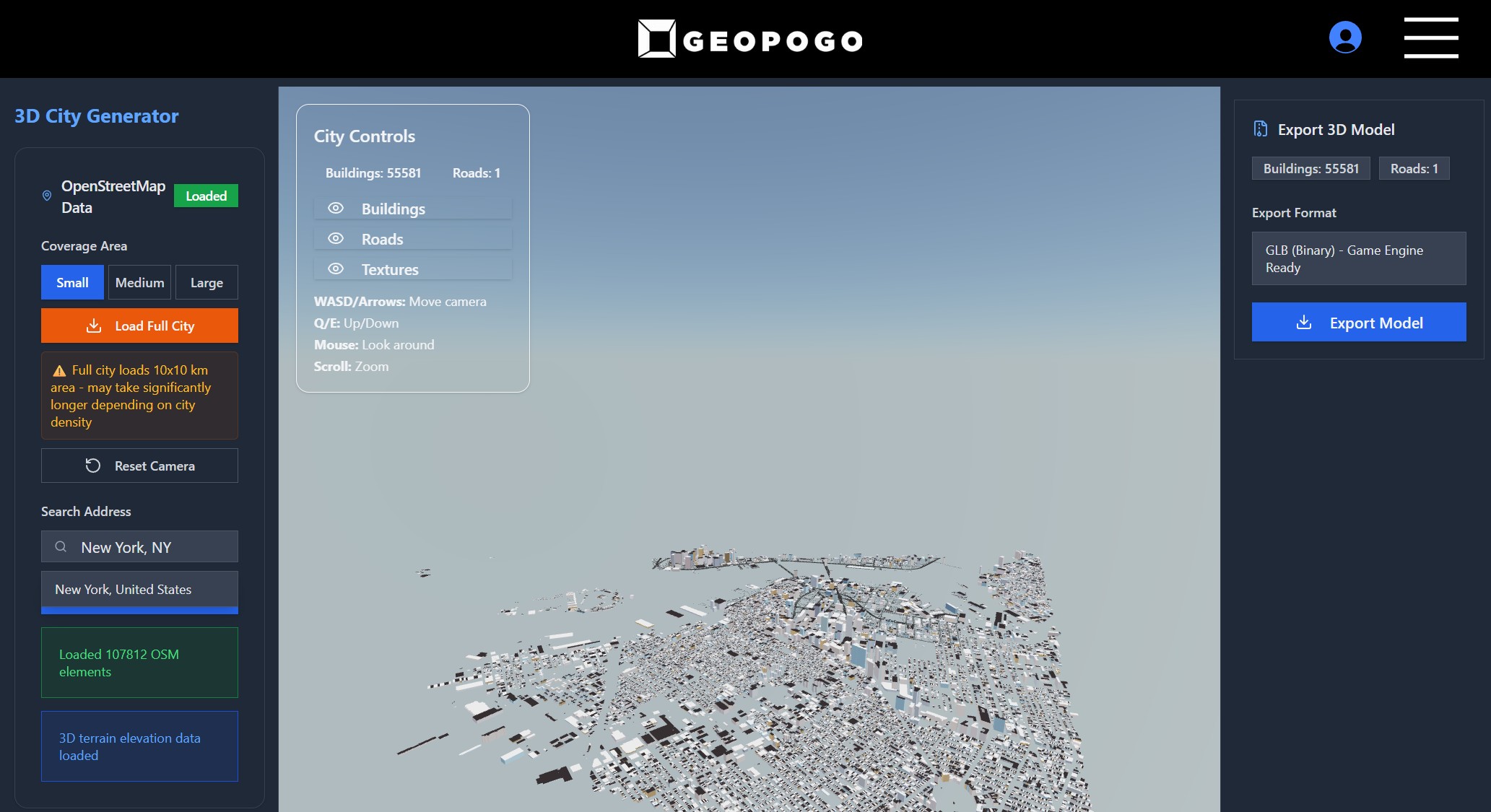
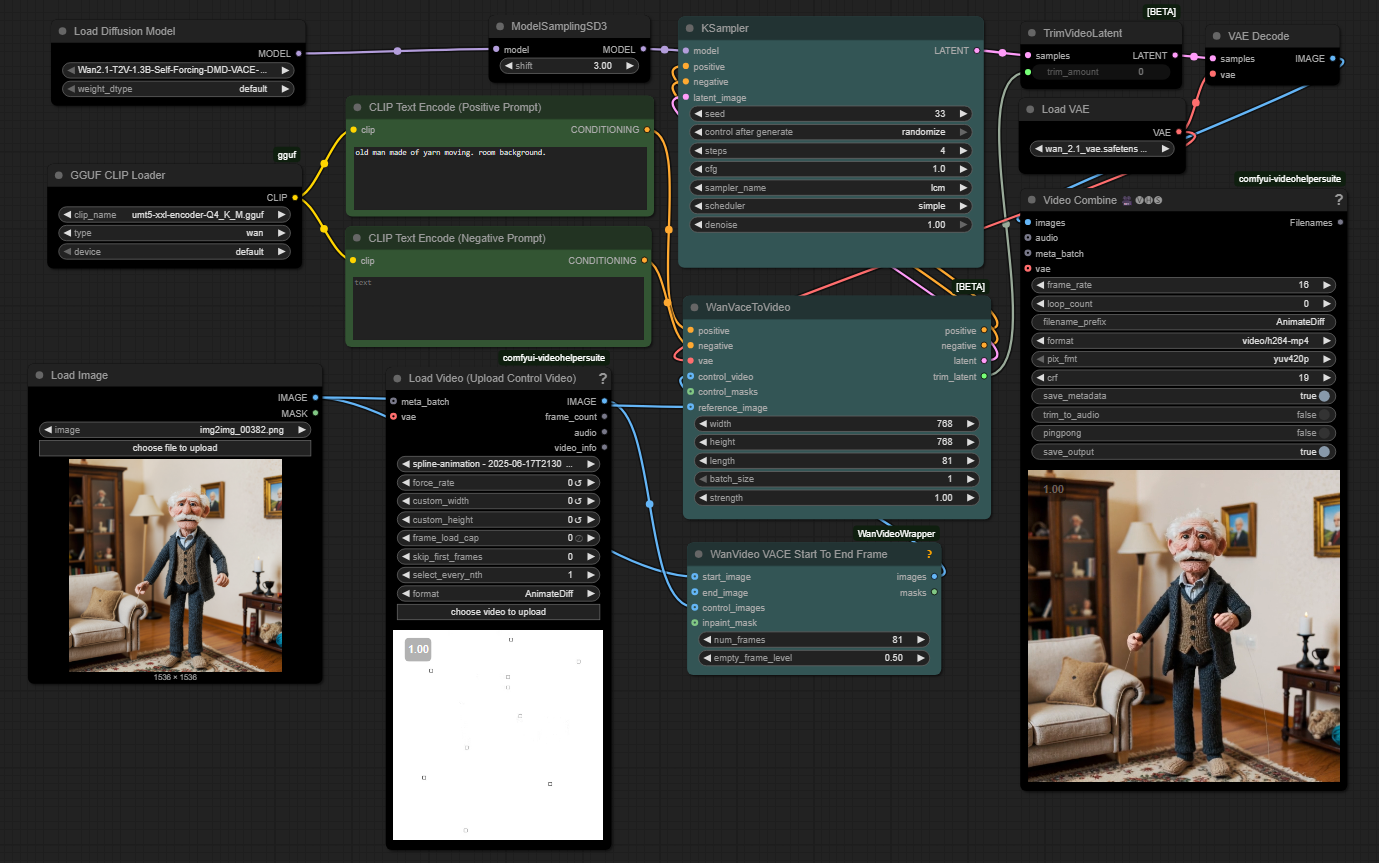
WhatDreamsCost Spline-Path-Control – Create motion controls for ComfyUI
https://github.com/WhatDreamsCost/Spline-Path-Control
https://whatdreamscost.github.io/Spline-Path-Control/
https://github.com/WhatDreamsCost/Spline-Path-Control/tree/main/example_workflows
Spline Path Control is a simple tool designed to make it easy to create motion controls. It allows you to create and animate shapes that follow splines, and then export the result as a
.webmvideo file.
This project was created to simplify the process of generating control videos for tools like VACE. Use it to control the motion of anything (camera movement, objects, humans etc) all without extra prompting.- Multi-Spline Editing: Create multiple, independent spline paths
- Easy To Use Controls: Quickly edit splines and points
- Full Control of Splines and Shapes:
- Start Frame: Set a delay before a spline’s animation begins.
- Duration: Control the speed of the shape along its path.
- Easing: Apply
Linear,Ease-in,Ease-out, andEase-in-outfunctions for smooth acceleration and deceleration. - Tension: Adjust the “curviness” of the spline path.
- Shape Customization: Change the shape (circle, square, triangle), size, fill color, and border.
- Reference Images: Drag and drop or upload a background image to trace paths over an existing image.
- WebM Export: Export your animation with a white background, perfect for use as a control video in VACE.
-
MiniMax-Remover – Taming Bad Noise Helps Video Object Removal Rotoscoping
https://github.com/zibojia/MiniMax-Remover
MiniMax-Remover is a fast and effective video object remover based on minimax optimization. It operates in two stages: the first stage trains a remover using a simplified DiT architecture, while the second stage distills a robust remover with CFG removal and fewer inference steps.
FEATURED POSTS
-
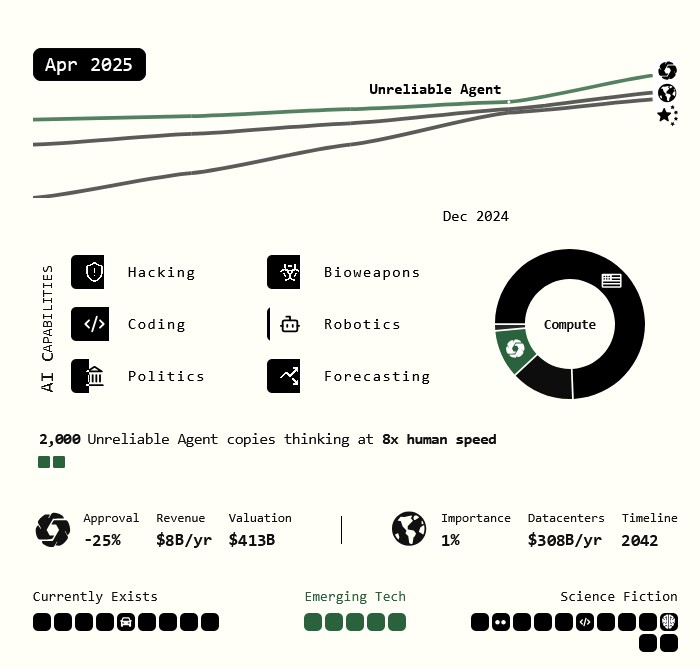
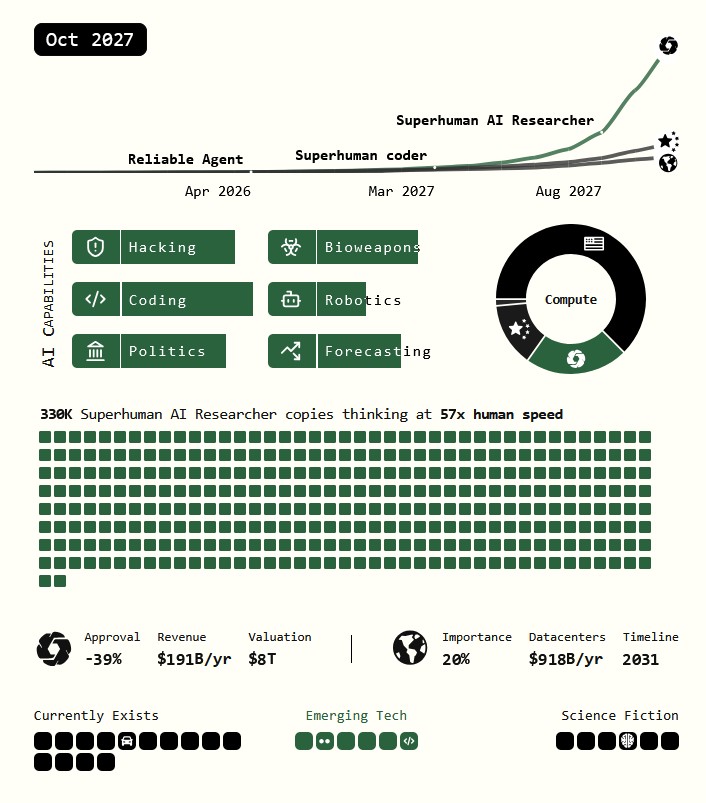
AI 2027 – Predicting the impact of superhuman AI over the next decade
We predict that the impact of superhuman AI over the next decade will be enormous, exceeding that of the Industrial Revolution.
We wrote a scenario that represents our best guess about what that might look like.1 It’s informed by trend extrapolations, wargames, expert feedback, experience at OpenAI, and previous forecasting successes.
-
Erik Winquist – The Definitive Weta Digital Guide to IBL hdri capture
www.fxguide.com/fxfeatured/the-definitive-weta-digital-guide-to-ibl
Notes:
- Camera type: full frame with exposure bracketing and an 8mm circular fish eye lens.
- Bracketing: 7 exposures at 2 stops increments.
- Tripod: supporting 120 degrees locked offsets
- Camera angle: should point up 7.5 degrees for better sky or upper dome coverage.
- Camera focus: set and tape locked to manual
- Start shooting looking towards the sun direction with and without the ND3 filter; The other angles will not require the ND3 filter.
- Documenting shooting with a slate (measure distance to slate, day, location, camera info, camera temperature, camera position)
NOTE: The goal is to clean the initial individual brackets before or at merging time as much as possible.
This means:- keeping original shooting metadata
- de-fringing
- removing aberration (through camera lens data or automatically)
- at 32 bit
- in ACEScg (or ACES) wherever possible
-
Tim Kang – calibrated white light values in sRGB color space
8bit sRGB encoded
2000K 255 139 22
2700K 255 172 89
3000K 255 184 109
3200K 255 190 122
4000K 255 211 165
4300K 255 219 178
D50 255 235 205
D55 255 243 224
D5600 255 244 227
D6000 255 249 240
D65 255 255 255
D10000 202 221 255
D20000 166 196 2558bit Rec709 Gamma 2.4
2000K 255 145 34
2700K 255 177 97
3000K 255 187 117
3200K 255 193 129
4000K 255 214 170
4300K 255 221 182
D50 255 236 208
D55 255 243 226
D5600 255 245 229
D6000 255 250 241
D65 255 255 255
D10000 204 222 255
D20000 170 199 2558bit Display P3 encoded
2000K 255 154 63
2700K 255 185 109
3000K 255 195 127
3200K 255 201 138
4000K 255 219 176
4300K 255 225 187
D50 255 239 212
D55 255 245 228
D5600 255 246 231
D6000 255 251 242
D65 255 255 255
D10000 208 223 255
D20000 175 199 25510bit Rec2020 PQ (100 nits)
2000K 520 435 273
2700K 520 466 358
3000K 520 475 384
3200K 520 480 399
4000K 520 495 446
4300K 520 500 458
D50 520 510 482
D55 520 514 497
D5600 520 514 500
D6000 520 517 509
D65 520 520 520
D10000 479 489 520
D20000 448 464 520