BREAKING NEWS
LATEST POSTS
-
VillageRoadShow production studio files for bankruptcy
Village Roadshow (prod company/financier: Wonka, the Matrix series, and Ocean’s 11) has filed for bankruptcy.
It’s a rough indicator of where we are in 2025 when one of the last independent production companies working with the studios goes under.
Here’s their balance sheet:
$400 M in library value of 100+ films (89 of which they co-own with Warner Bros.)
$500 M – $1bn total debt
$1.4 M in debt to WGA, whose members were told to stop working with Roadshow in December
$794 K owed to Bryan Cranston’s prod company
$250 K owed to Sony Pictures TV
$300 K/month overhead
The crowning expense that brought down this 36-year-old production company is the $18 M in (unpaid) legal fees from a lengthy and currently unresolved arbitration with their long-time partner Warner Bros, who they’ve had a co-financing arrangement since the late 90s.
Roadshow sued when WBD released their Matrix Resurrections (2021) film in theaters and on Max simultaneously, causing Roadshow to withhold their portion of the $190 M production costs.
Due to mounting financial pressures, Village Roadshow’s CEO, Steve Mosko, a veteran film and TV exec, left the company in January.
Now, this all falls on the shoulders of Jim Moore, CEO of Vine, an equity firm that owns Village Roadshow, as well as Luc Besson’s prod company EuropaCorp.
-
Google Gemini Robotics
For safety considerations, Google mentions a “layered, holistic approach” that maintains traditional robot safety measures like collision avoidance and force limitations. The company describes developing a “Robot Constitution” framework inspired by Isaac Asimov’s Three Laws of Robotics and releasing a dataset unsurprisingly called “ASIMOV” to help researchers evaluate safety implications of robotic actions.
This new ASIMOV dataset represents Google’s attempt to create standardized ways to assess robot safety beyond physical harm prevention. The dataset appears designed to help researchers test how well AI models understand the potential consequences of actions a robot might take in various scenarios. According to Google’s announcement, the dataset will “help researchers to rigorously measure the safety implications of robotic actions in real-world scenarios.”
-
Personalize Anything – For Free with Diffusion Transformer
https://fenghora.github.io/Personalize-Anything-Page
Customize any subject with advanced DiT without additional fine-tuning.

-
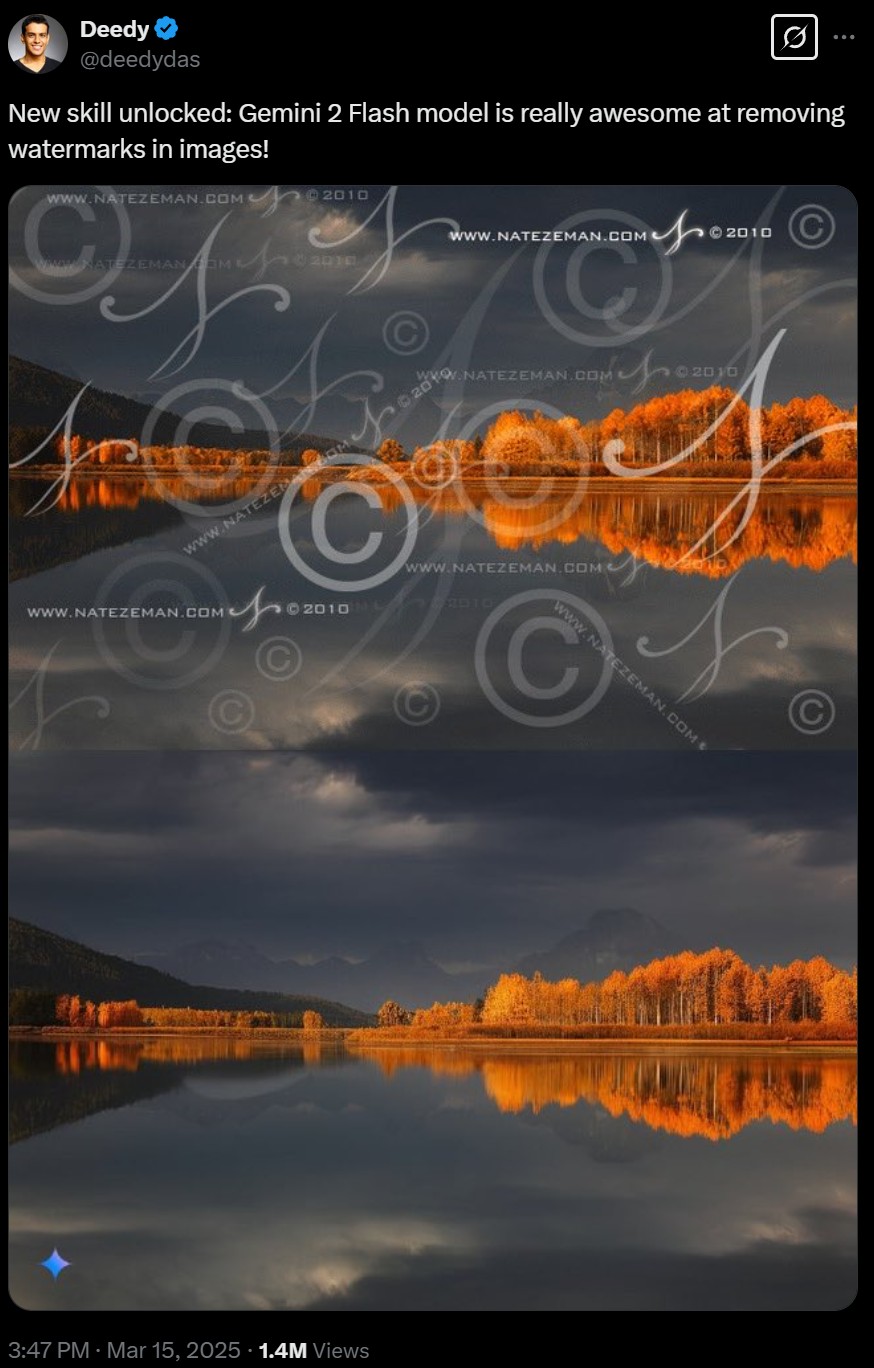
Google Gemini 2.0 Flash new AI model extremely proficient at removing watermarks from images
-
Stability.ai – Introducing Stable Virtual Camera: Multi-View Video Generation with 3D Camera Control
Capabilities
Stable Virtual Camera offers advanced capabilities for generating 3D videos, including:
- Dynamic Camera Control: Supports user-defined camera trajectories as well as multiple dynamic camera paths, including: 360°, Lemniscate (∞ shaped path), Spiral, Dolly Zoom In, Dolly Zoom Out, Zoom In, Zoom Out, Move Forward, Move Backward, Pan Up, Pan Down, Pan Left, Pan Right, and Roll.
- Flexible Inputs: Generates 3D videos from just one input image or up to 32.
- Multiple Aspect Ratios: Capable of producing videos in square (1:1), portrait (9:16), landscape (16:9), and other custom aspect ratios without additional training.
- Long Video Generation: Ensures 3D consistency in videos up to 1,000 frames, enabling seamless
Model limitations
In its initial version, Stable Virtual Camera may produce lower-quality results in certain scenarios. Input images featuring humans, animals, or dynamic textures like water often lead to degraded outputs. Additionally, highly ambiguous scenes, complex camera paths that intersect objects or surfaces, and irregularly shaped objects can cause flickering artifacts, especially when target viewpoints differ significantly from the input images.

FEATURED POSTS
-
SourceTree vs Github Desktop – Which one to use
Sourcetree and GitHub Desktop are both free, GUI-based Git clients aimed at simplifying version control for developers. While they share the same core purpose—making Git more accessible—they differ in features, UI design, integration options, and target audiences.
Installation & Setup
- Sourcetree
- Download: https://www.sourcetreeapp.com/
- Supported OS: Windows 10+, macOS 10.13+
- Prerequisites: Comes bundled with its own Git, or can be pointed to a system Git install.
- Initial Setup: Wizard guides SSH key generation, authentication with Bitbucket/GitHub/GitLab.
- GitHub Desktop
- Download: https://desktop.github.com/
- Supported OS: Windows 10+, macOS 10.15+
- Prerequisites: Bundled Git; seamless login with GitHub.com or GitHub Enterprise.
- Initial Setup: One-click sign-in with GitHub; auto-syncs repositories from your GitHub account.
Feature Comparison
(more…)Feature Sourcetree GitHub Desktop Branch Visualization Detailed graph view with drag-and-drop for rebasing/merging Linear graph, simpler but less configurable Staging & Commit File-by-file staging, inline diff view All-or-nothing staging, side-by-side diff Interactive Rebase Full support via UI Basic support via command line only Conflict Resolution Built-in merge tool integration (DiffMerge, Beyond Compare) Contextual conflict editor with choice panels Submodule Management Native submodule support Limited; requires CLI Custom Actions / Hooks Define custom actions (e.g., launch scripts) No UI for custom Git hooks Git Flow / Hg Flow Built-in support None Performance Can lag on very large repos Generally snappier on medium-sized repos Memory Footprint Higher RAM usage Lightweight Platform Integration Atlassian Bitbucket, Jira Deep GitHub.com / Enterprise integration Learning Curve Steeper for beginners Beginner-friendly - Sourcetree
-
Photography basics: Exposure Value vs Photographic Exposure vs Il/Luminance vs Pixel luminance measurements
Also see: https://www.pixelsham.com/2015/05/16/how-aperture-shutter-speed-and-iso-affect-your-photos/
In photography, exposure value (EV) is a number that represents a combination of a camera’s shutter speed and f-number, such that all combinations that yield the same exposure have the same EV (for any fixed scene luminance).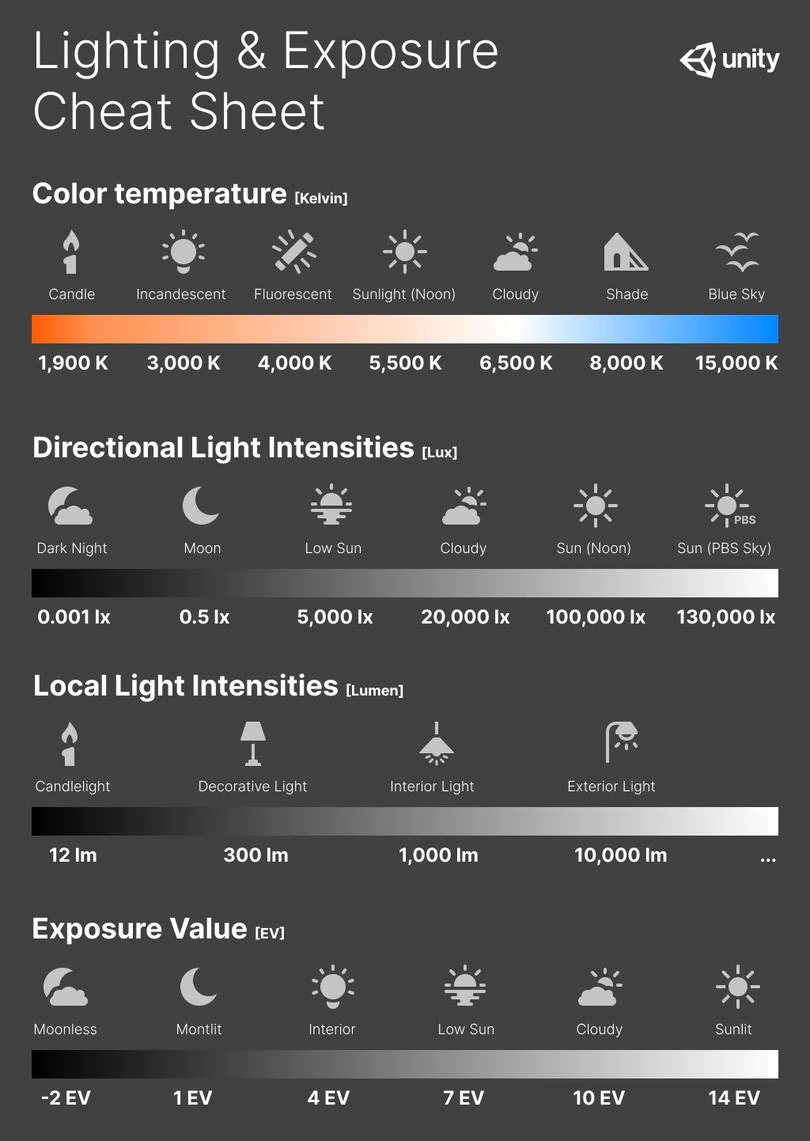
The EV concept was developed in an attempt to simplify choosing among combinations of equivalent camera settings. Although all camera settings with the same EV nominally give the same exposure, they do not necessarily give the same picture. EV is also used to indicate an interval on the photographic exposure scale. 1 EV corresponding to a standard power-of-2 exposure step, commonly referred to as a stop
EV 0 corresponds to an exposure time of 1 sec and a relative aperture of f/1.0. If the EV is known, it can be used to select combinations of exposure time and f-number.Note EV does not equal to photographic exposure. Photographic Exposure is defined as how much light hits the camera’s sensor. It depends on the camera settings mainly aperture and shutter speed. Exposure value (known as EV) is a number that represents the exposure setting of the camera.
Thus, strictly, EV is not a measure of luminance (indirect or reflected exposure) or illuminance (incidentl exposure); rather, an EV corresponds to a luminance (or illuminance) for which a camera with a given ISO speed would use the indicated EV to obtain the nominally correct exposure. Nonetheless, it is common practice among photographic equipment manufacturers to express luminance in EV for ISO 100 speed, as when specifying metering range or autofocus sensitivity.
The exposure depends on two things: how much light gets through the lenses to the camera’s sensor and for how long the sensor is exposed. The former is a function of the aperture value while the latter is a function of the shutter speed. Exposure value is a number that represents this potential amount of light that could hit the sensor. It is important to understand that exposure value is a measure of how exposed the sensor is to light and not a measure of how much light actually hits the sensor. The exposure value is independent of how lit the scene is. For example a pair of aperture value and shutter speed represents the same exposure value both if the camera is used during a very bright day or during a dark night.
Each exposure value number represents all the possible shutter and aperture settings that result in the same exposure. Although the exposure value is the same for different combinations of aperture values and shutter speeds the resulting photo can be very different (the aperture controls the depth of field while shutter speed controls how much motion is captured).
EV 0.0 is defined as the exposure when setting the aperture to f-number 1.0 and the shutter speed to 1 second. All other exposure values are relative to that number. Exposure values are on a base two logarithmic scale. This means that every single step of EV – plus or minus 1 – represents the exposure (actual light that hits the sensor) being halved or doubled.Formulas
(more…)
-
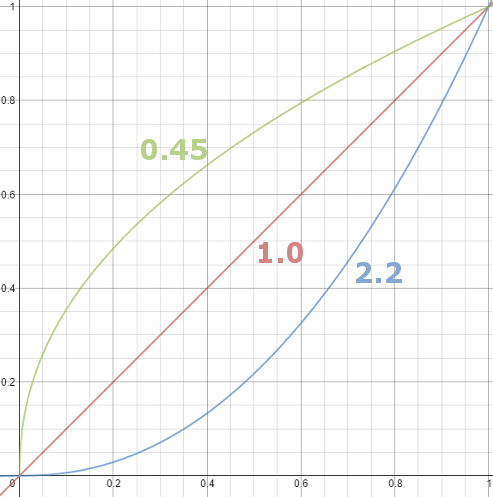
Gamma correction
http://www.normankoren.com/makingfineprints1A.html#Gammabox
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gamma_correction
http://www.photoscientia.co.uk/Gamma.htm
https://www.w3.org/Graphics/Color/sRGB.html
http://www.eizoglobal.com/library/basics/lcd_display_gamma/index.html
https://forum.reallusion.com/PrintTopic308094.aspx
Basically, gamma is the relationship between the brightness of a pixel as it appears on the screen, and the numerical value of that pixel. Generally Gamma is just about defining relationships.
Three main types:
– Image Gamma encoded in images
– Display Gammas encoded in hardware and/or viewing time
– System or Viewing Gamma which is the net effect of all gammas when you look back at a final image. In theory this should flatten back to 1.0 gamma.
(more…)
-
domeble – Hi-Resolution CGI Backplates and 360° HDRI
When collecting hdri make sure the data supports basic metadata, such as:
- Iso
- Aperture
- Exposure time or shutter time
- Color temperature
- Color space Exposure value (what the sensor receives of the sun intensity in lux)
- 7+ brackets (with 5 or 6 being the perceived balanced exposure)
In image processing, computer graphics, and photography, high dynamic range imaging (HDRI or just HDR) is a set of techniques that allow a greater dynamic range of luminances (a Photometry measure of the luminous intensity per unit area of light travelling in a given direction. It describes the amount of light that passes through or is emitted from a particular area, and falls within a given solid angle) between the lightest and darkest areas of an image than standard digital imaging techniques or photographic methods. This wider dynamic range allows HDR images to represent more accurately the wide range of intensity levels found in real scenes ranging from direct sunlight to faint starlight and to the deepest shadows.
The two main sources of HDR imagery are computer renderings and merging of multiple photographs, which in turn are known as low dynamic range (LDR) or standard dynamic range (SDR) images. Tone Mapping (Look-up) techniques, which reduce overall contrast to facilitate display of HDR images on devices with lower dynamic range, can be applied to produce images with preserved or exaggerated local contrast for artistic effect. Photography
In photography, dynamic range is measured in Exposure Values (in photography, exposure value denotes all combinations of camera shutter speed and relative aperture that give the same exposure. The concept was developed in Germany in the 1950s) differences or stops, between the brightest and darkest parts of the image that show detail. An increase of one EV or one stop is a doubling of the amount of light.
The human response to brightness is well approximated by a Steven’s power law, which over a reasonable range is close to logarithmic, as described by the Weber�Fechner law, which is one reason that logarithmic measures of light intensity are often used as well.
HDR is short for High Dynamic Range. It’s a term used to describe an image which contains a greater exposure range than the “black” to “white” that 8 or 16-bit integer formats (JPEG, TIFF, PNG) can describe. Whereas these Low Dynamic Range images (LDR) can hold perhaps 8 to 10 f-stops of image information, HDR images can describe beyond 30 stops and stored in 32 bit images.