BREAKING NEWS
LATEST POSTS
-
A Looming Threat to Bitcoin (and the financial world)- The Risk of a Quantum Hack
Advancements in quantum computing pose a potential threat to Bitcoin’s security. Google’s recent progress with its Willow quantum-computing chip has highlighted the possibility that future quantum computers could break the encryption protecting Bitcoin, enabling hackers to access secure digital wallets and potentially causing significant devaluation.
Researchers estimate that a quantum computer capable of such decryption is likely more than a decade away. Nonetheless, the Bitcoin developer community faces the complex task of upgrading the system to incorporate quantum-resistant encryption methods. Achieving consensus within the decentralized community may be a slow process, and users would eventually need to transfer their holdings to quantum-resistant addresses to safeguard their assets.
A quantum-powered attack on Bitcoin could also negatively impact traditional financial markets, possibly leading to substantial losses and a deep recession. To mitigate such threats, President-elect Donald Trump has proposed creating a strategic reserve for the government’s Bitcoin holdings.

-
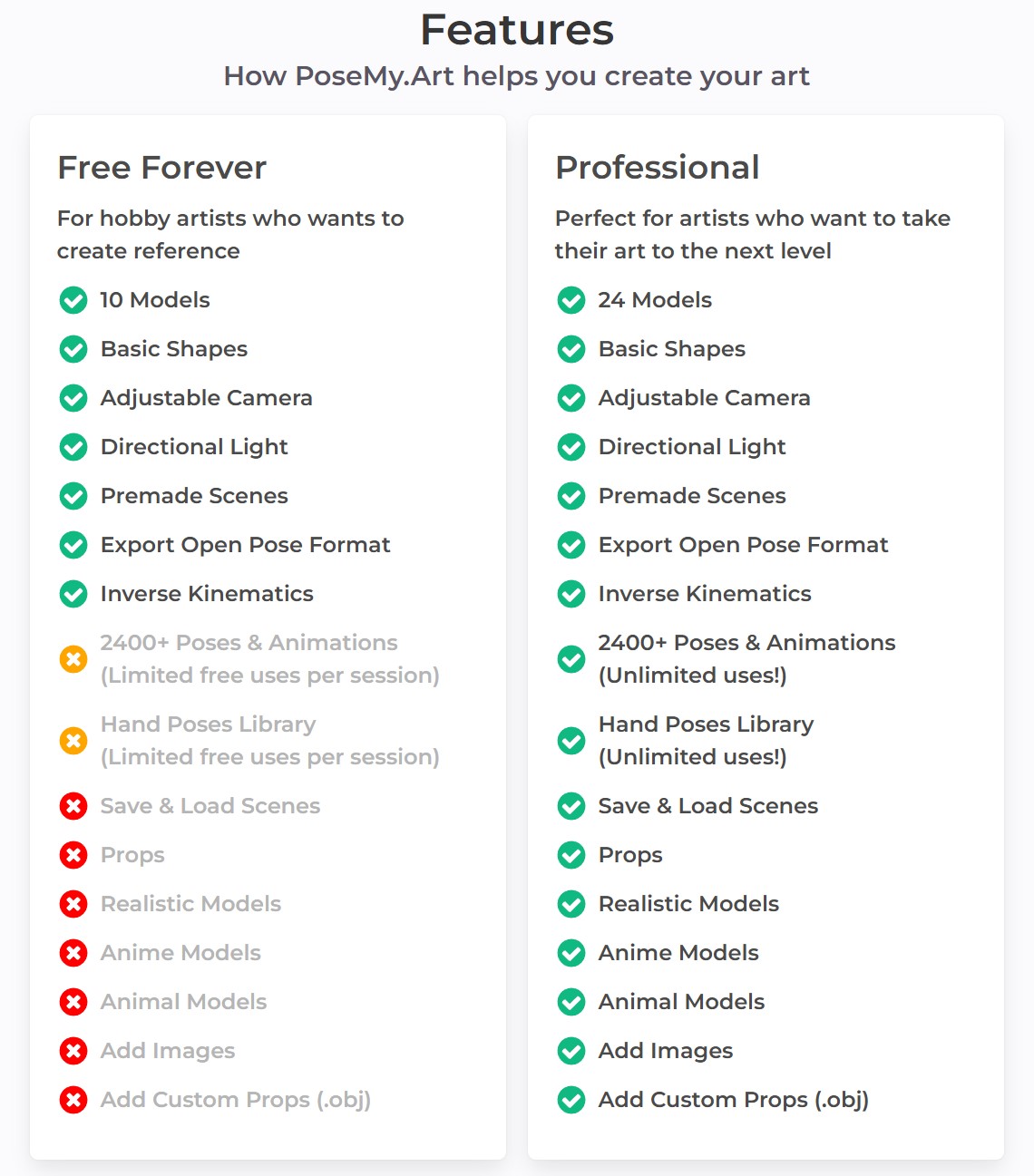
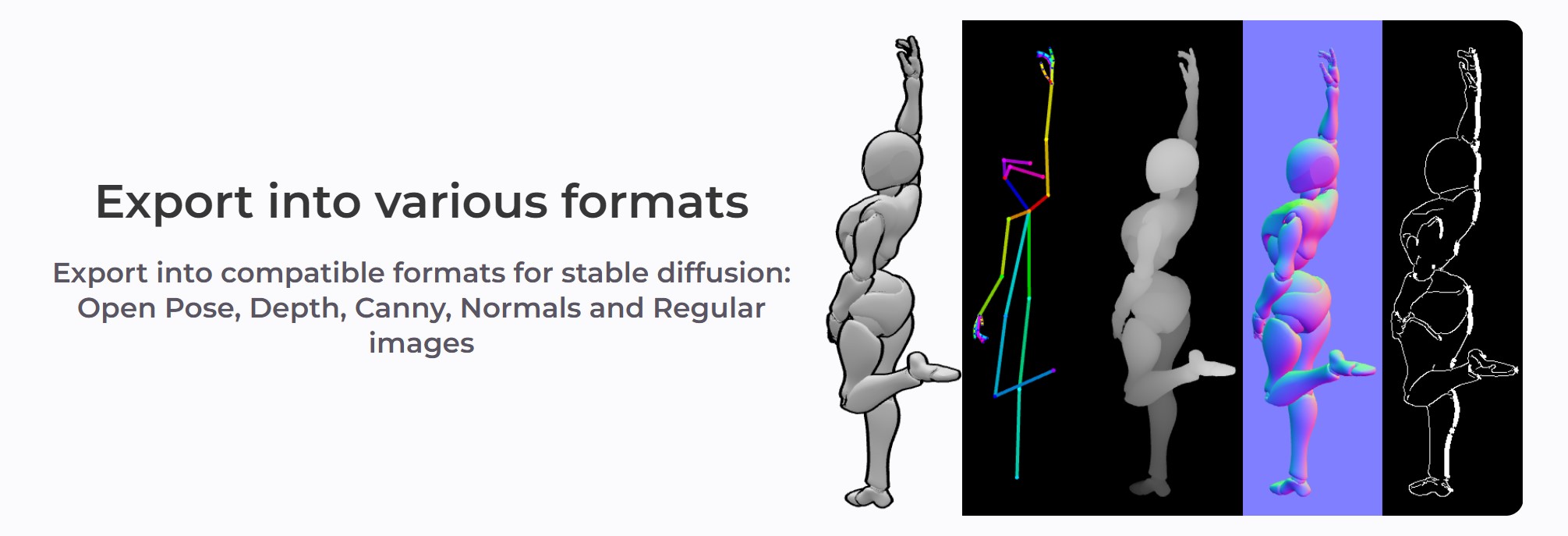
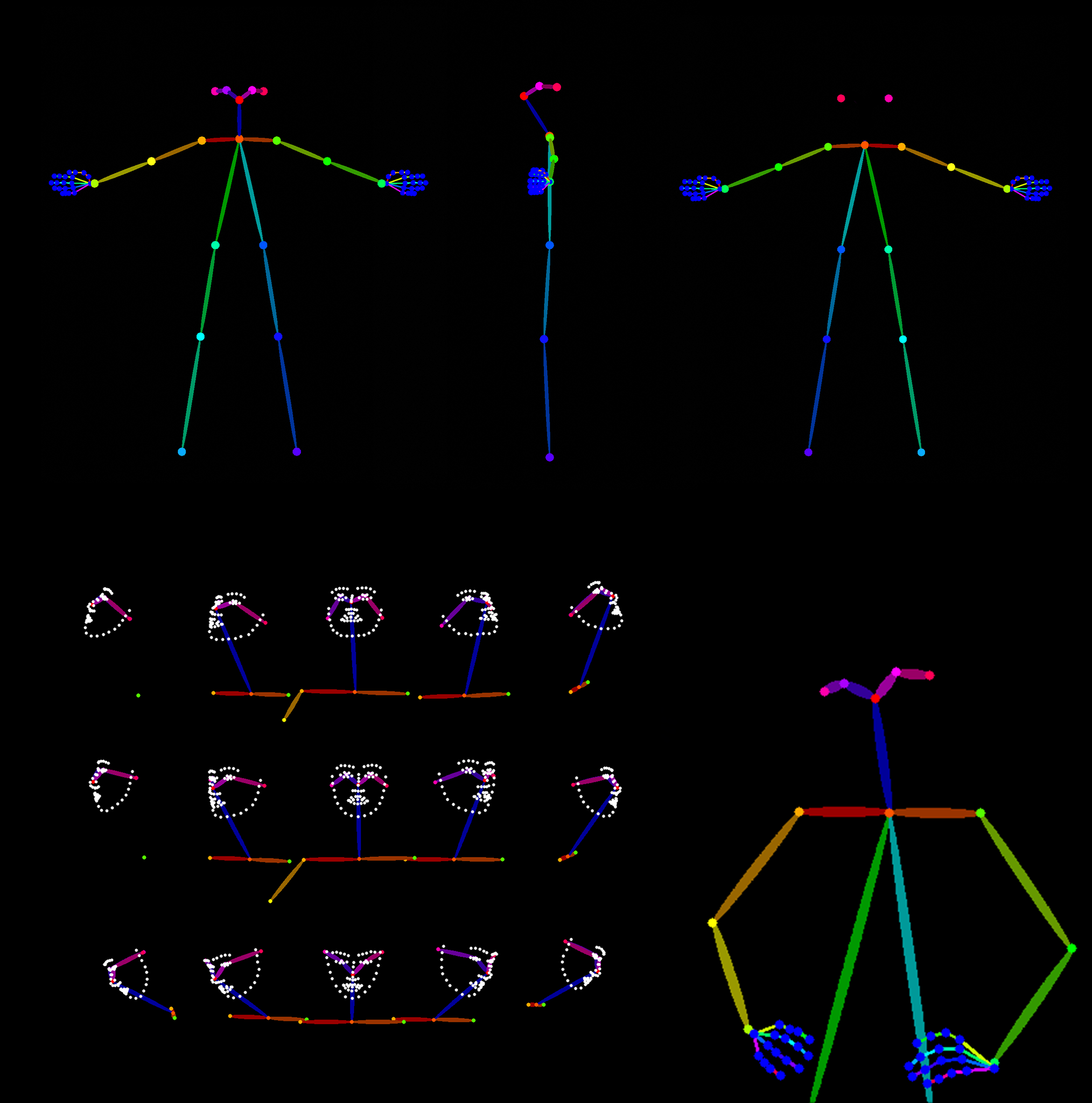
posemy.art – Create Poses for Drawing Reference and AI apps in Seconds for Free
-
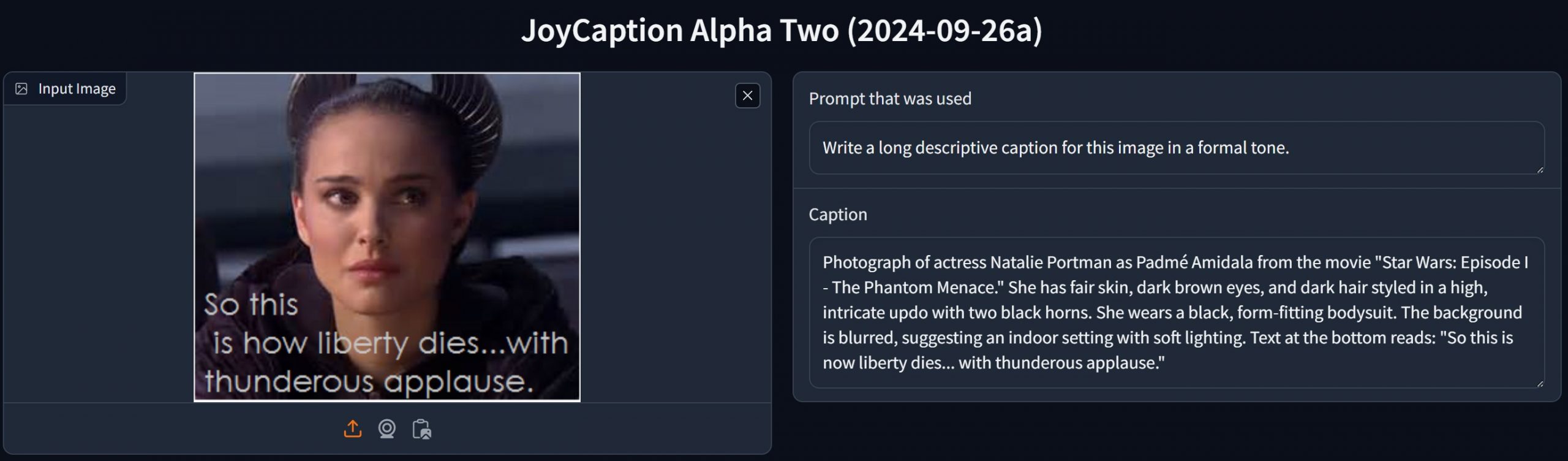
Mickmumpitz – Create CONSISTENT CHARACTERS from an INPUT IMAGE with FLUX and a character sheet! (ComfyUI Tutorial + Installation Guide + Lora training)
https://www.patreon.com/posts/create-from-with-115147229
Note: the image below is not from the workflow
Nodes:
Install missing nodes in the workflow through the manager.
Models:
Make sure not to mix SD1.5 and SDLX models.
Follow the details under the pdf below.
General suggesions:
– Comfy Org / Flux.1 [dev] Checkpoint model (fp8)
The manager will put it under checkpoints, which will not work.
Make sure to put it under the models/unet folder for the Load Diffusion Model node to work.
– same for realvisxlV50_v50LightningBakedvae.safetensors
it should go under models/vae
FEATURED POSTS
-
7 Commandments of Film Editing and composition
1. Watch every frame of raw footage twice. On the second time, take notes. If you don’t do this and try to start developing a scene premature, then it’s a big disservice to yourself and to the director, actors and production crew.
2. Nurture the relationships with the director. You are the secondary person in the relationship. Be calm and continually offer solutions. Get the main intention of the film as soon as possible from the director.
3. Organize your media so that you can find any shot instantly.
4. Factor in extra time for renders, exports, errors and crashes.
5. Attempt edits and ideas that shouldn’t work. It just might work. Until you do it and watch it, you won’t know. Don’t rule out ideas just because they don’t make sense in your mind.
6. Spend more time on your audio. It’s the glue of your edit. AUDIO SAVES EVERYTHING. Create fluid and seamless audio under your video.
7. Make cuts for the scene, but always in context for the whole film. Have a macro and a micro view at all times.
-
The Public Domain Is Working Again — No Thanks To Disney
www.cartoonbrew.com/law/the-public-domain-is-working-again-no-thanks-to-disney-169658.html
The law protects new works from unauthorized copying while allowing artists free rein on older works.
The Copyright Act of 1909 used to govern copyrights. Under that law, a creator had a copyright on his creation for 28 years from “publication,” which could then be renewed for another 28 years. Thus, after 56 years, a work would enter the public domain.
However, the Congress passed the Copyright Act of 1976, extending copyright protection for works made for hire to 75 years from publication.
Then again, in 1998, Congress passed the Sonny Bono Copyright Term Extension Act (derided as the “Mickey Mouse Protection Act” by some observers due to the Walt Disney Company’s intensive lobbying efforts), which added another twenty years to the term of copyright.
it is because Snow White was in the public domain that it was chosen to be Disney’s first animated feature.
Ironically, much of Disney’s legislative lobbying over the last several decades has been focused on preventing this same opportunity to other artists and filmmakers.The battle in the coming years will be to prevent further extensions to copyright law that benefit corporations at the expense of creators and society as a whole.
-
Photography basics: Color Temperature and White Balance
Color Temperature of a light source describes the spectrum of light which is radiated from a theoretical “blackbody” (an ideal physical body that absorbs all radiation and incident light – neither reflecting it nor allowing it to pass through) with a given surface temperature.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Color_temperature
Or. Most simply it is a method of describing the color characteristics of light through a numerical value that corresponds to the color emitted by a light source, measured in degrees of Kelvin (K) on a scale from 1,000 to 10,000.
More accurately. The color temperature of a light source is the temperature of an ideal backbody that radiates light of comparable hue to that of the light source.
(more…)
-
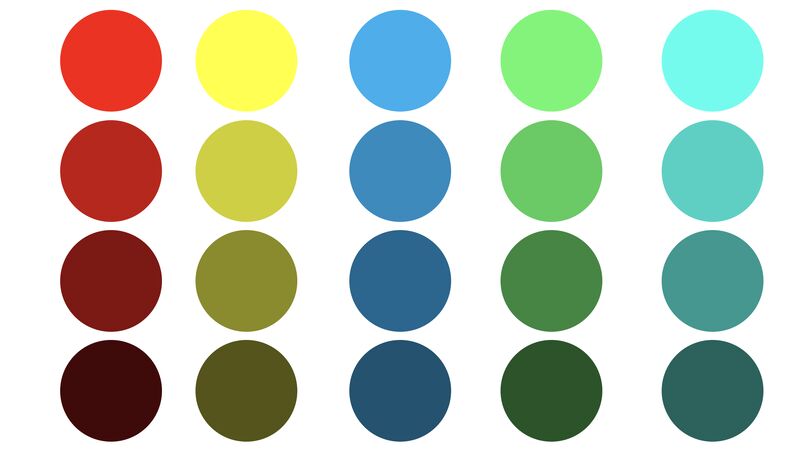
Is it possible to get a dark yellow
https://www.patreon.com/posts/102660674
https://www.linkedin.com/posts/stephenwestland_here-is-a-post-about-the-dark-yellow-problem-activity-7187131643764092929-7uCL
-
RawTherapee – a free, open source, cross-platform raw image and HDRi processing program
5.10 of this tool includes excellent tools to clean up cr2 and cr3 used on set to support HDRI processing.
Converting raw to AcesCG 32 bit tiffs with metadata.