BREAKING NEWS
LATEST POSTS
-
Lagoa Multiphysics new simulation solver for Autodesk Softimage
http://features.cgsociety.org/story_custom.php?story_id=5866
FEATURED POSTS
-
Aider.chat – A free, open-source AI pair-programming CLI tool
Aider enables developers to interactively generate, modify, and test code by leveraging both cloud-hosted and local LLMs directly from the terminal or within an IDE. Key capabilities include comprehensive codebase mapping, support for over 100 programming languages, automated git commit messages, voice-to-code interactions, and built-in linting and testing workflows. Installation is straightforward via pip or uv, and while the tool itself has no licensing cost, actual usage costs stem from the underlying LLM APIs, which are billed separately by providers like OpenAI or Anthropic.
Key Features
- Cloud & Local LLM Support
Connect to most major LLM providers out of the box, or run models locally for privacy and cost control aider.chat. - Codebase Mapping
Automatically indexes all project files so that even large repositories can be edited contextually aider.chat. - 100+ Language Support
Works with Python, JavaScript, Rust, Ruby, Go, C++, PHP, HTML, CSS, and dozens more aider.chat. - Git Integration
Generates sensible commit messages and automates diffs/undo operations through familiar git tooling aider.chat. - Voice-to-Code
Speak commands to Aider to request features, tests, or fixes without typing aider.chat. - Images & Web Pages
Attach screenshots, diagrams, or documentation URLs to provide visual context for edits aider.chat. - Linting & Testing
Runs lint and test suites automatically after each change, and can fix issues it detects
- Cloud & Local LLM Support
-
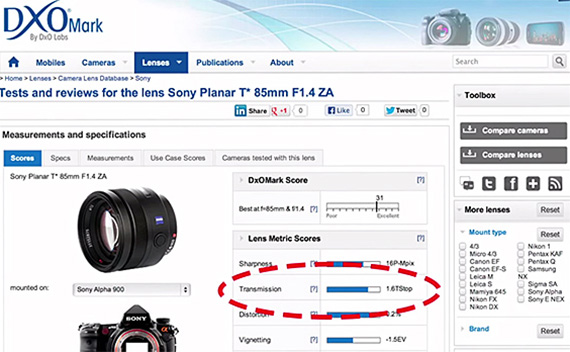
Photography basics: f-stop vs t-stop
https://www.premiumbeat.com/blog/understanding-lenses-aperture-f-stop-t-stop/
F-stops are the theoretical amount of light transmitted by the lens; t-stops, the actual amount. The difference is about 1/3 stop, often more with zooms.
f-stop is the measurement of the opening (aperture) of the lens in relation to its focal length (the distance between the lens and the sensor). The math is focal length / lens diameter.
It mainly controls depth of field, given a known amount of light.https://www.scantips.com/lights/fstop2.html
The smaller f-stop (larger aperture) the more depth of field and light.
Note that the numbers in an aperture—f/2.8, f/8—signify a certain amount of light, but that doesn’t necessarily mean that’s directly how much light is getting to your sensor.
T stop on the other hand is the measurement of how much light passes through aforementioned opening and actually makes it to the sensor. There is no such a lens which does not steal some light on the way to the sensor.
In short, is the corrected f-stop number you want to collect, based on the amount of light reaching the sensor after bouncing through all the lenses, to know exactly what is making it to film. The smaller, the more light.http://www.dxomark.com/Lenses/Ratings/Optical-Metric-Scores
Note that exposure stop is a measurement of sensibility to light not of lens capabilities.