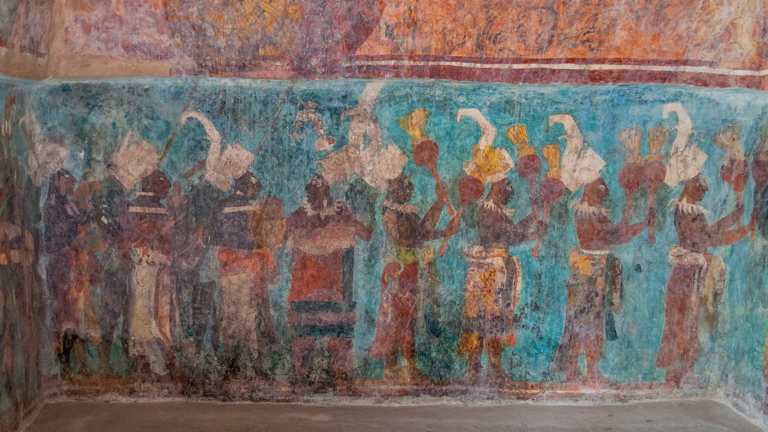BREAKING NEWS
LATEST POSTS
-
Narcis Calin’s Galaxy Engine – A free, open source simulation software
This 2025 I decided to start learning how to code, so I installed Visual Studio and I started looking into C++. After days of watching tutorials and guides about the basics of C++ and programming, I decided to make something physics-related. I started with a dot that fell to the ground and then I wanted to simulate gravitational attraction, so I made 2 circles attracting each other. I thought it was really cool to see something I made with code actually work, so I kept building on top of that small, basic program. And here we are after roughly 8 months of learning programming. This is Galaxy Engine, and it is a simulation software I have been making ever since I started my learning journey. It currently can simulate gravity, dark matter, galaxies, the Big Bang, temperature, fluid dynamics, breakable solids, planetary interactions, etc. The program can run many tens of thousands of particles in real time on the CPU thanks to the Barnes-Hut algorithm, mixed with Morton curves. It also includes its own PBR 2D path tracer with BVH optimizations. The path tracer can simulate a bunch of stuff like diffuse lighting, specular reflections, refraction, internal reflection, fresnel, emission, dispersion, roughness, IOR, nested IOR and more! I tried to make the path tracer closer to traditional 3D render engines like V-Ray. I honestly never imagined I would go this far with programming, and it has been an amazing learning experience so far. I think that mixing this knowledge with my 3D knowledge can unlock countless new possibilities. In case you are curious about Galaxy Engine, I made it completely free and Open-Source so that anyone can build and compile it locally! You can find the source code in GitHub
https://github.com/NarcisCalin/Galaxy-Engine
-
Introduction to BytesIO
When you’re working with binary data in Python—whether that’s image bytes, network payloads, or any in-memory binary stream—you often need a file-like interface without touching the disk. That’s where
BytesIOfrom the built-iniomodule comes in handy. It lets you treat a bytes buffer as if it were a file.What Is
BytesIO?- Module:
io - Class:
BytesIO - Purpose:
- Provides an in-memory binary stream.
- Acts like a file opened in binary mode (
'rb'/'wb'), but data lives in RAM rather than on disk.
from io import BytesIO
Why Use
BytesIO?- Speed
- No disk I/O—reads and writes happen in memory.
- Convenience
- Emulates file methods (
read(),write(),seek(), etc.). - Ideal for testing code that expects a file-like object.
- Emulates file methods (
- Safety
- No temporary files cluttering up your filesystem.
- Integration
- Libraries that accept file-like objects (e.g., PIL,
requests) will work withBytesIO.
- Libraries that accept file-like objects (e.g., PIL,
Basic Examples
1. Writing Bytes to a Buffer
(more…)from io import BytesIO # Create a BytesIO buffer buffer = BytesIO() # Write some binary data buffer.write(b'Hello, \xF0\x9F\x98\x8A') # includes a smiley emoji in UTF-8 # Retrieve the entire contents data = buffer.getvalue() print(data) # b'Hello, \xf0\x9f\x98\x8a' print(data.decode('utf-8')) # Hello, 😊 # Always close when done buffer.close() - Module:
-
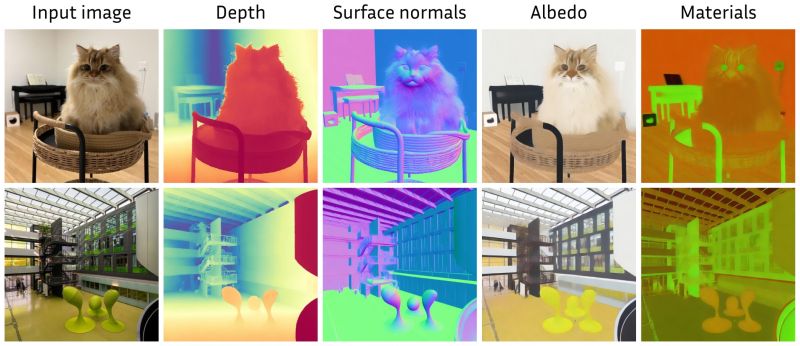
Marigold – repurposing diffusion-based image generators for dense predictions
Marigold repurposes Stable Diffusion for dense prediction tasks such as monocular depth estimation and surface normal prediction, delivering a level of detail often missing even in top discriminative models.
Key aspects that make it great:
– Reuses the original VAE and only lightly fine-tunes the denoising UNet
– Trained on just tens of thousands of synthetic image–modality pairs
– Runs on a single consumer GPU (e.g., RTX 4090)
– Zero-shot generalization to real-world, in-the-wild imageshttps://mlhonk.substack.com/p/31-marigold
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2505.09358
https://marigoldmonodepth.github.io/
-
Runway Aleph
https://runwayml.com/research/introducing-runway-aleph
Generate New Camera Angles
Generate the Next Shot
Use Any Style to Transfer to a Video
Change Environments, Locations, Seasons and Time of Day
Add Things to a Scene
Remove Things from a Scene
Change Objects in a Scene
Apply the Motion of a Video to an Image
Alter a Character’s Appearance
Recolor Elements of a Scene
Relight Shots
Green Screen Any Object, Person or Situation
FEATURED POSTS
-
AI Data Laundering: How Academic and Nonprofit Researchers Shield Tech Companies from Accountability
“Simon Willison created a Datasette browser to explore WebVid-10M, one of the two datasets used to train the video generation model, and quickly learned that all 10.7 million video clips were scraped from Shutterstock, watermarks and all.”
“In addition to the Shutterstock clips, Meta also used 10 million video clips from this 100M video dataset from Microsoft Research Asia. It’s not mentioned on their GitHub, but if you dig into the paper, you learn that every clip came from over 3 million YouTube videos.”
“It’s become standard practice for technology companies working with AI to commercially use datasets and models collected and trained by non-commercial research entities like universities or non-profits.”
“Like with the artists, photographers, and other creators found in the 2.3 billion images that trained Stable Diffusion, I can’t help but wonder how the creators of those 3 million YouTube videos feel about Meta using their work to train their new model.”
-
ComfyDock – The Easiest (Free) Way to Safely Run ComfyUI Sessions in a Boxed Container
https://www.reddit.com/r/comfyui/comments/1j2x4qv/comfydock_the_easiest_free_way_to_run_comfyui_in/
ComfyDock is a tool that allows you to easily manage your ComfyUI environments via Docker.
Common Challenges with ComfyUI
- Custom Node Installation Issues: Installing new custom nodes can inadvertently change settings across the whole installation, potentially breaking the environment.
- Workflow Compatibility: Workflows are often tested with specific custom nodes and ComfyUI versions. Running these workflows on different setups can lead to errors and frustration.
- Security Risks: Installing custom nodes directly on your host machine increases the risk of malicious code execution.
How ComfyDock Helps
- Environment Duplication: Easily duplicate your current environment before installing custom nodes. If something breaks, revert to the original environment effortlessly.
- Deployment and Sharing: Workflow developers can commit their environments to a Docker image, which can be shared with others and run on cloud GPUs to ensure compatibility.
- Enhanced Security: Containers help to isolate the environment, reducing the risk of malicious code impacting your host machine.

-
The Maya civilization and the color blue
Maya blue is a highly unusual pigment because it is a mix of organic indigo and an inorganic clay mineral called palygorskite.
Echoing the color of an azure sky, the indelible pigment was used to accentuate everything from ceramics to human sacrifices in the Late Preclassic period (300 B.C. to A.D. 300).
A team of researchers led by Dean Arnold, an adjunct curator of anthropology at the Field Museum in Chicago, determined that the key to Maya blue was actually a sacred incense called copal.
By heating the mixture of indigo, copal and palygorskite over a fire, the Maya produced the unique pigment, he reported at the time.