BREAKING NEWS
LATEST POSTS
-
Tencent Hunyuan3D 2.5 – Transform images and text into 3D models with ultra-high-definition precision
What makes it special?
• Massive 10B parameter geometric model with 10x more mesh faces.
• High-quality textures with industry-first multi-view PBR generation.
• Optimized skeletal rigging for streamlined animation workflows.
• Flexible pipeline for text-to-3D and image-to-3D generation.
They’re making it accessible to everyone:
• Open-source code and pre-trained models.
• Easy-to-use API and intuitive web interface.
• Free daily quota doubled to 20 generations! -
Alibaba 3DV-TON – A novel diffusion model for HQ and temporally consistent video
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2504.17414

Video try-on replaces clothing in videos with target garments. Existing methods struggle to generate high-quality and temporally consistent results when handling complex clothing patterns and diverse body poses. We present 3DV-TON, a novel diffusion-based framework for generating high-fidelity and temporally consistent video try-on results. Our approach employs generated animatable textured 3D meshes as explicit frame-level guidance, alleviating the issue of models over-focusing on appearance fidelity at the expanse of motion coherence. This is achieved by enabling direct reference to consistent garment texture movements throughout video sequences. The proposed method features an adaptive pipeline for generating dynamic 3D guidance: (1) selecting a keyframe for initial 2D image try-on, followed by (2) reconstructing and animating a textured 3D mesh synchronized with original video poses. We further introduce a robust rectangular masking strategy that successfully mitigates artifact propagation caused by leaking clothing information during dynamic human and garment movements. To advance video try-on research, we introduce HR-VVT, a high-resolution benchmark dataset containing 130 videos with diverse clothing types and scenarios. Quantitative and qualitative results demonstrate our superior performance over existing methods.
-
FramePack – Packing Input Frame Context in Next-Frame Prediction Models for Offline Video Generation With Low Resource Requirements
https://lllyasviel.github.io/frame_pack_gitpage/
- Diffuse thousands of frames at full fps-30 with 13B models using 6GB laptop GPU memory.
- Finetune 13B video model at batch size 64 on a single 8xA100/H100 node for personal/lab experiments.
- Personal RTX 4090 generates at speed 2.5 seconds/frame (unoptimized) or 1.5 seconds/frame (teacache).
- No timestep distillation.
- Video diffusion, but feels like image diffusion.
Image-to-5-Seconds (30fps, 150 frames)
-
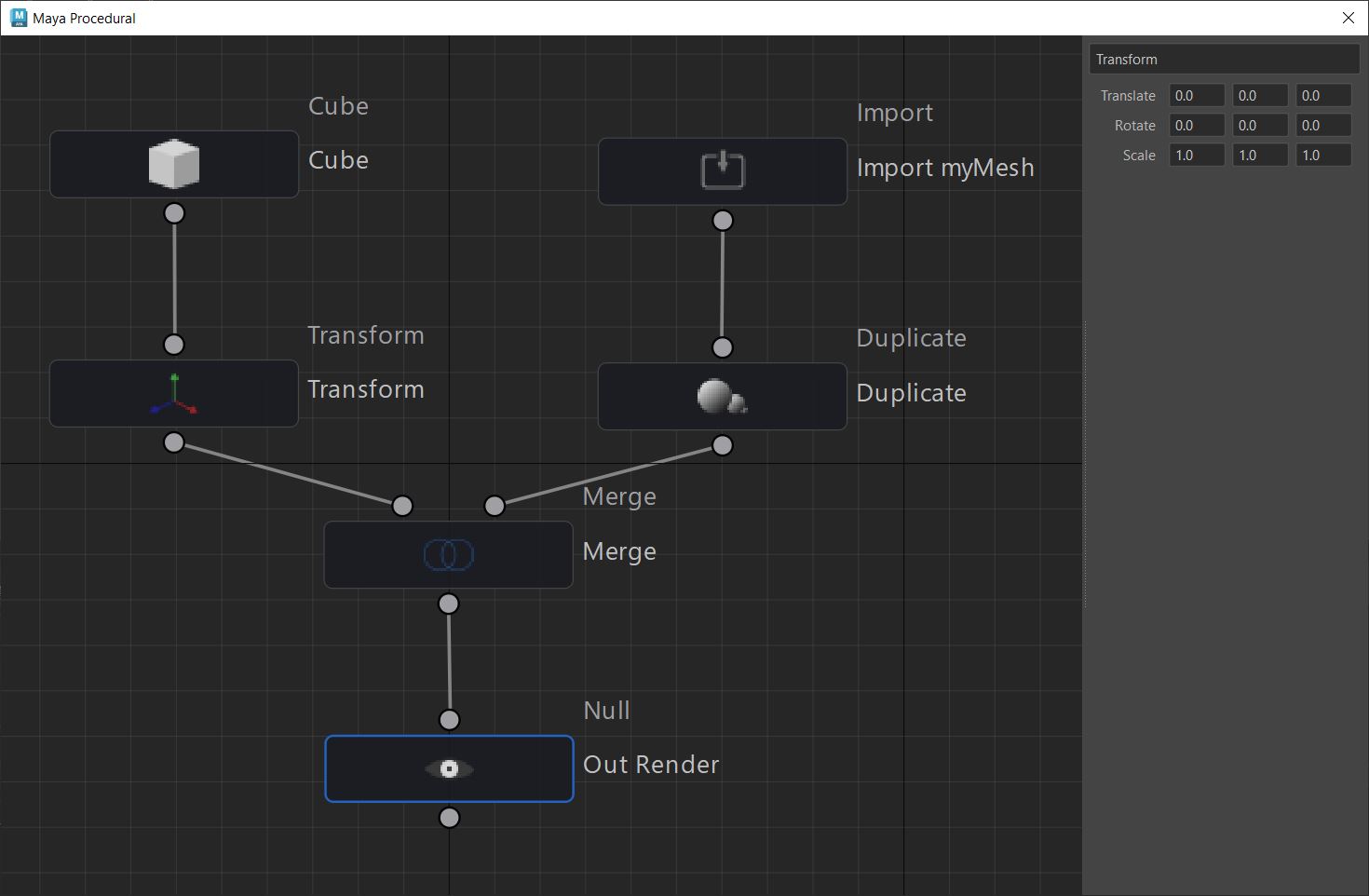
Anthony Sauzet – ProceduralMaya
A Maya script that introduces a node-based graph system for procedural modeling, like Houdini
https://github.com/AnthonySTZ/ProceduralMaya
-
11 Public Speaking Strategies

What do people report as their #1 greatest fear?
It’s not death….
It’s public speaking.
Glossophobia, the fear of public speaking, has been a daunting obstacle for me for years.
11 confidence-boosting tips
1/ The 5-5-5 Rule
→ Scan 5 faces; Hold each gaze for 5 seconds.
→ Repeat every 5 minutes.
→ Creates an authentic connection.
2/Power Pause
→ Dead silence for 3 seconds after key points.
→ Let your message land.
3/ The 3-Part Open
→ Hook with a question.
→ Share a story.
→ State your promise.
4/ Palm-Up Principle
→ Open palms when speaking = trustworthy.
→ Pointing fingers = confrontational.
5/ The 90-Second Reset
→ Feel nervous? Excuse yourself.
→ 90 seconds of deep breathing reset your nervous system.
6/ Rule of Three
→ Structure key points in threes.
→ Our brains love patterns.
7/ 2-Minute Story Rule
→ Keep stories under 2 minutes.
→ Any longer, you lose them.
8/ The Lighthouse Method
→ Plant “anchor points” around the room.
→ Rotate eye contact between them.
→ Looks natural, feels structured.
9/ The Power Position
→ Feet shoulder-width apart.
→ Hands relaxed at sides.
→ Projects confidence even when nervous.
10/ The Callback Technique
→ Reference earlier points later in your talk.
→ Creates a narrative thread.
→ Audiences love connections.
11/ The Rehearsal Truth
→ Practice the opening 3x more than the rest.
→ Nail the first 30 seconds; you’ll nail the talk. -
FreeCodeCamp – Train Your Own LLM
https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/train-your-own-llm
Ever wondered how large language models like ChatGPT are actually built? Behind these impressive AI tools lies a complex but fascinating process of data preparation, model training, and fine-tuning. While it might seem like something only experts with massive resources can do, it’s actually possible to learn how to build your own language model from scratch. And with the right guidance, you can go from loading raw text data to chatting with your very own AI assistant.
-
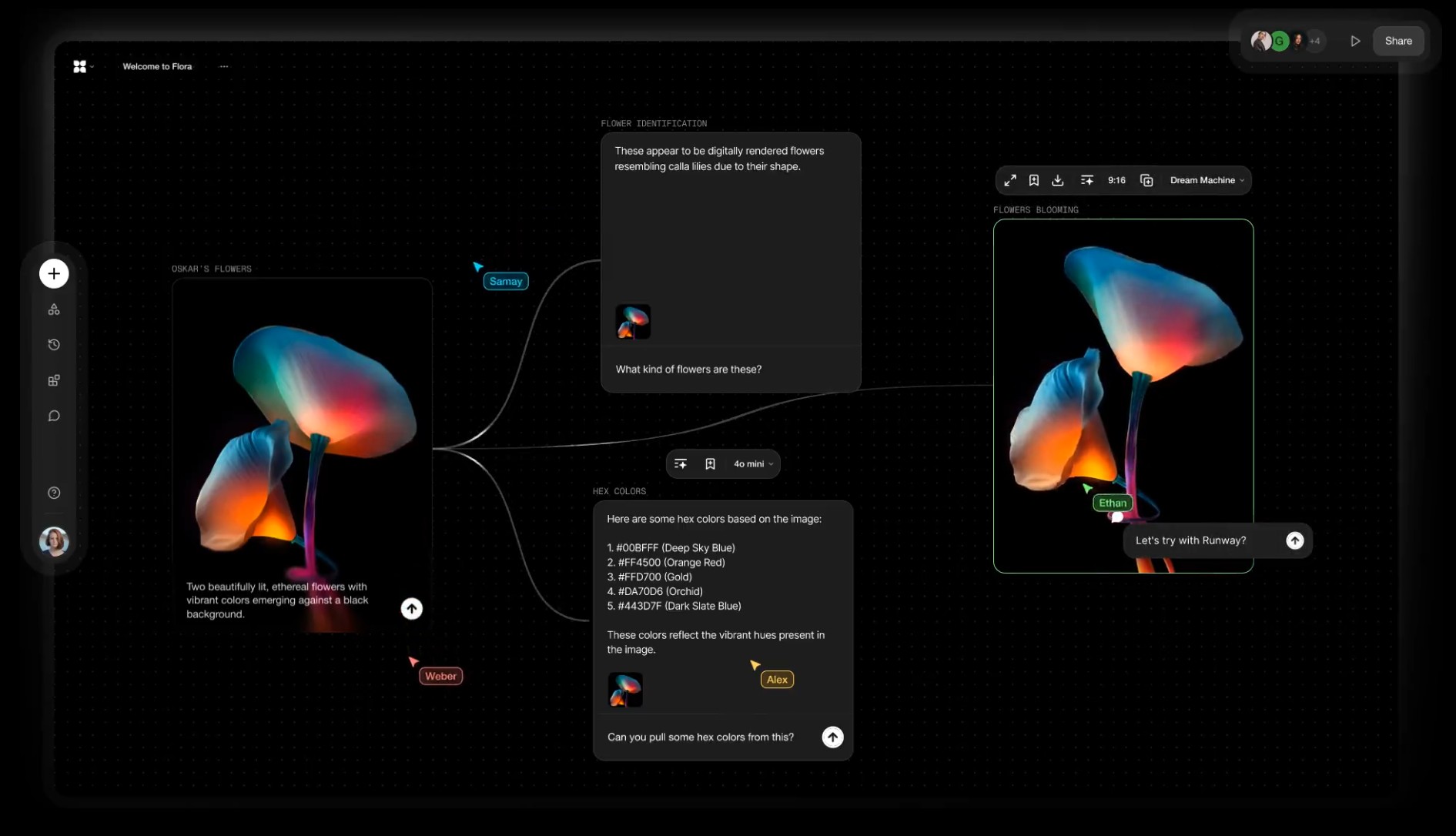
Alibaba FloraFauna.ai – AI Collaboration canvas
-
Runway introduces Gen-4 – Generate consistent elements by controlling input elements
https://runwayml.com/research/introducing-runway-gen-4
With Gen-4, you are now able to precisely generate consistent characters, locations and objects across scenes. Simply set your look and feel and the model will maintain coherent world environments while preserving the distinctive style, mood and cinematographic elements of each frame. Then, regenerate those elements from multiple perspectives and positions within your scenes.
𝗛𝗲𝗿𝗲’𝘀 𝘄𝗵𝘆 𝗚𝗲𝗻-𝟰 𝗰𝗵𝗮𝗻𝗴𝗲𝘀 𝗲𝘃𝗲𝗿𝘆𝘁𝗵𝗶𝗻𝗴:
✨ 𝗨𝗻𝘄𝗮𝘃𝗲𝗿𝗶𝗻𝗴 𝗖𝗵𝗮𝗿𝗮𝗰𝘁𝗲𝗿 𝗖𝗼𝗻𝘀𝗶𝘀𝘁𝗲𝗻𝗰𝘆
• Characters and environments 𝗻𝗼𝘄 𝘀𝘁𝗮𝘆 𝗳𝗹𝗮𝘄𝗹𝗲𝘀𝘀𝗹𝘆 𝗰𝗼𝗻𝘀𝗶𝘀𝘁𝗲𝗻𝘁 across shots—even as lighting shifts or angles pivot—all from one reference image. No more jarring transitions or mismatched details.
✨ 𝗗𝘆𝗻𝗮𝗺𝗶𝗰 𝗠𝘂𝗹𝘁𝗶-𝗔𝗻𝗴𝗹𝗲 𝗠𝗮𝘀𝘁𝗲𝗿𝘆
• Generate cohesive scenes from any perspective without manual tweaks. Gen-4 intuitively 𝗰𝗿𝗮𝗳𝘁𝘀 𝗺𝘂𝗹𝘁𝗶-𝗮𝗻𝗴𝗹𝗲 𝗰𝗼𝘃𝗲𝗿𝗮𝗴𝗲, 𝗮 𝗹𝗲𝗮𝗽 𝗽𝗮𝘀𝘁 𝗲𝗮𝗿𝗹𝗶𝗲𝗿 𝗺𝗼𝗱𝗲𝗹𝘀 that struggled with spatial continuity.
✨ 𝗣𝗵𝘆𝘀𝗶𝗰𝘀 𝗧𝗵𝗮𝘁 𝗙𝗲𝗲𝗹 𝗔𝗹𝗶𝘃𝗲
• Capes ripple, objects collide, and fabrics drape with startling realism. 𝗚𝗲𝗻-𝟰 𝘀𝗶𝗺𝘂𝗹𝗮𝘁𝗲𝘀 𝗿𝗲𝗮𝗹-𝘄𝗼𝗿𝗹𝗱 𝗽𝗵𝘆𝘀𝗶𝗰𝘀, breathing life into scenes that once demanded painstaking manual animation.
✨ 𝗦𝗲𝗮𝗺𝗹𝗲𝘀𝘀 𝗦𝘁𝘂𝗱𝗶𝗼 𝗜𝗻𝘁𝗲𝗴𝗿𝗮𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻
• Outputs now blend effortlessly with live-action footage or VFX pipelines. 𝗠𝗮𝗷𝗼𝗿 𝘀𝘁𝘂𝗱𝗶𝗼𝘀 𝗮𝗿𝗲 𝗮𝗹𝗿𝗲𝗮𝗱𝘆 𝗮𝗱𝗼𝗽𝘁𝗶𝗻𝗴 𝗚𝗲𝗻-𝟰 𝘁𝗼 𝗽𝗿𝗼𝘁𝗼𝘁𝘆𝗽𝗲 𝘀𝗰𝗲𝗻𝗲𝘀 𝗳𝗮𝘀𝘁𝗲𝗿 and slash production timelines.
• 𝗪𝗵𝘆 𝘁𝗵𝗶𝘀 𝗺𝗮𝘁𝘁𝗲𝗿𝘀: Gen-4 erases the line between AI experiments and professional filmmaking. 𝗗𝗶𝗿𝗲𝗰𝘁𝗼𝗿𝘀 𝗰𝗮𝗻 𝗶𝘁𝗲𝗿𝗮𝘁𝗲 𝗼𝗻 𝗰𝗶𝗻𝗲𝗺𝗮𝘁𝗶𝗰 𝘀𝗲𝗾𝘂𝗲𝗻𝗰𝗲𝘀 𝗶𝗻 𝗱𝗮𝘆𝘀, 𝗻𝗼𝘁 𝗺𝗼𝗻𝘁𝗵𝘀—democratizing access to tools that once required million-dollar budgets. -
Florent Poux – Top 10 Open Source Libraries and Software for 3D Point Cloud Processing
As point cloud processing becomes increasingly important across industries, I wanted to share the most powerful open-source tools I’ve used in my projects:
1️⃣ Open3D (http://www.open3d.org/)
The gold standard for point cloud processing in Python. Incredible visualization capabilities, efficient data structures, and comprehensive geometry processing functions. Perfect for both research and production.
2️⃣ PCL – Point Cloud Library (https://pointclouds.org/)
The C++ powerhouse of point cloud processing. Extensive algorithms for filtering, feature estimation, surface reconstruction, registration, and segmentation. Steep learning curve but unmatched performance.
3️⃣ PyTorch3D (https://pytorch3d.org/)
Facebook’s differentiable 3D library. Seamlessly integrates point cloud operations with deep learning. Essential if you’re building neural networks for 3D data.
4️⃣ PyTorch Geometric (https://lnkd.in/eCutwTuB)
Specializes in graph neural networks for point clouds. Implements cutting-edge architectures like PointNet, PointNet++, and DGCNN with optimized performance.
5️⃣ Kaolin (https://lnkd.in/eyj7QzCR)
NVIDIA’s 3D deep learning library. Offers differentiable renderers and accelerated GPU implementations of common point cloud operations.
6️⃣ CloudCompare (https://lnkd.in/emQtPz4d)
More than just visualization. This desktop application lets you perform complex processing without writing code. Perfect for quick exploration and comparison.
7️⃣ LAStools (https://lnkd.in/eRk5Bx7E)
The industry standard for LiDAR processing. Fast, scalable, and memory-efficient tools specifically designed for massive aerial and terrestrial LiDAR data.
8️⃣ PDAL – Point Data Abstraction Library (https://pdal.io/)
Think of it as “GDAL for point clouds.” Powerful for building processing pipelines and handling various file formats and coordinate transformations.
9️⃣ Open3D-ML (https://lnkd.in/eWnXufgG)
Extends Open3D with machine learning capabilities. Implementations of state-of-the-art 3D deep learning methods with consistent APIs.
🔟 MeshLab (https://www.meshlab.net/)
The Swiss Army knife for mesh processing. While primarily for meshes, its point cloud processing capabilities are excellent for cleanup, simplification, and reconstruction.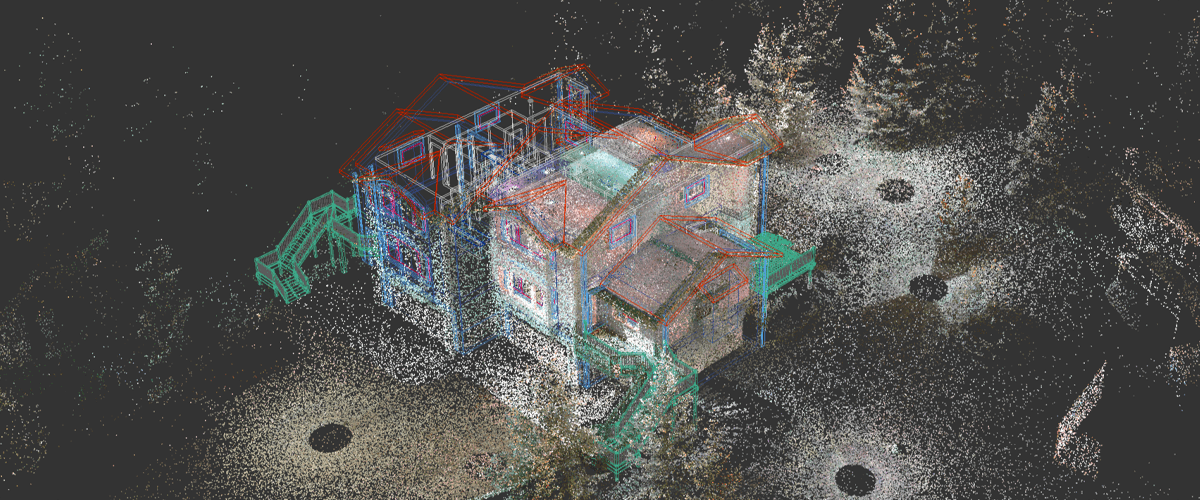
FEATURED POSTS
-
sRGB vs REC709 – An introduction and FFmpeg implementations
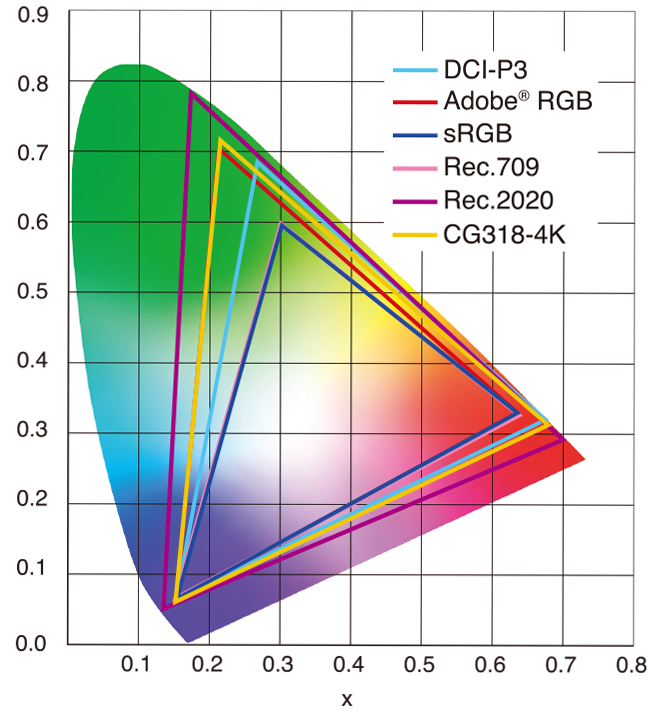
1. Basic Comparison
- What they are
- sRGB: A standard “web”/computer-display RGB color space defined by IEC 61966-2-1. It’s used for most monitors, cameras, printers, and the vast majority of images on the Internet.
- Rec. 709: An HD-video color space defined by ITU-R BT.709. It’s the go-to standard for HDTV broadcasts, Blu-ray discs, and professional video pipelines.
- Why they exist
- sRGB: Ensures consistent colors across different consumer devices (PCs, phones, webcams).
- Rec. 709: Ensures consistent colors across video production and playback chains (cameras → editing → broadcast → TV).
- What you’ll see
- On your desktop or phone, images tagged sRGB will look “right” without extra tweaking.
- On an HDTV or video-editing timeline, footage tagged Rec. 709 will display accurate contrast and hue on broadcast-grade monitors.
2. Digging Deeper
Feature sRGB Rec. 709 White point D65 (6504 K), same for both D65 (6504 K) Primaries (x,y) R: (0.640, 0.330) G: (0.300, 0.600) B: (0.150, 0.060) R: (0.640, 0.330) G: (0.300, 0.600) B: (0.150, 0.060) Gamut size Identical triangle on CIE 1931 chart Identical to sRGB Gamma / transfer Piecewise curve: approximate 2.2 with linear toe Pure power-law γ≈2.4 (often approximated as 2.2 in practice) Matrix coefficients N/A (pure RGB usage) Y = 0.2126 R + 0.7152 G + 0.0722 B (Rec. 709 matrix) Typical bit-depth 8-bit/channel (with 16-bit variants) 8-bit/channel (10-bit for professional video) Usage metadata Tagged as “sRGB” in image files (PNG, JPEG, etc.) Tagged as “bt709” in video containers (MP4, MOV) Color range Full-range RGB (0–255) Studio-range Y′CbCr (Y′ [16–235], Cb/Cr [16–240])
Why the Small Differences Matter
(more…) - What they are
-
Zibra.AI – Real-Time Volumetric Effects in Virtual Production. Now free for Indies!

A New Era for Volumetrics
For a long time, volumetric visual effects were viable only in high-end offline VFX workflows. Large data footprints and poor real-time rendering performance limited their use: most teams simply avoided volumetrics altogether. It’s similar to the early days of online video: limited computational power and low network bandwidth made video content hard to share or stream. Today, of course, we can’t imagine the internet without it, and we believe volumetrics are on a similar path.
With advanced data compression and real-time, GPU-driven decompression, anyone can now bring CGI-class visual effects into Unreal Engine.
From now on, it’s completely free for individual creators!
What it means for you?
(more…)