BREAKING NEWS
LATEST POSTS
-
Transformer Explainer -Interactive Learning of Text-Generative Models
https://github.com/poloclub/transformer-explainer
Transformer Explainer is an interactive visualization tool designed to help anyone learn how Transformer-based models like GPT work. It runs a live GPT-2 model right in your browser, allowing you to experiment with your own text and observe in real time how internal components and operations of the Transformer work together to predict the next tokens. Try Transformer Explainer at http://poloclub.github.io/transformer-explainer
-
Henry Daubrez – How to generate VR/ 360 videos directly with Google VEO
https://www.linkedin.com/posts/upskydown_vr-googleveo-veo3-activity-7334269406396461059-d8Da
If you prompt for a 360° video in VEO (like literally write “360°” ) it can generate a Monoscopic 360 video, then the next step is to inject the right metadata in your file so you can play it as an actual 360 video.
Once it’s saved with the right Metadata, it will be recognized as an actual 360/VR video, meaning you can just play it in VLC and drag your mouse to look around. -
Black Forest Labs released FLUX.1 Kontext
https://replicate.com/blog/flux-kontext
https://replicate.com/black-forest-labs/flux-kontext-pro
There are three models, two are available now, and a third open-weight version is coming soon:
- FLUX.1 Kontext [pro]: State-of-the-art performance for image editing. High-quality outputs, great prompt following, and consistent results.
- FLUX.1 Kontext [max]: A premium model that brings maximum performance, improved prompt adherence, and high-quality typography generation without compromise on speed.
- Coming soon: FLUX.1 Kontext [dev]: An open-weight, guidance-distilled version of Kontext.
We’re so excited with what Kontext can do, we’ve created a collection of models on Replicate to give you ideas:
- Multi-image kontext: Combine two images into one.
- Portrait series: Generate a series of portraits from a single image
- Change haircut: Change a person’s hair style and color
- Iconic locations: Put yourself in front of famous landmarks
- Professional headshot: Generate a professional headshot from any image
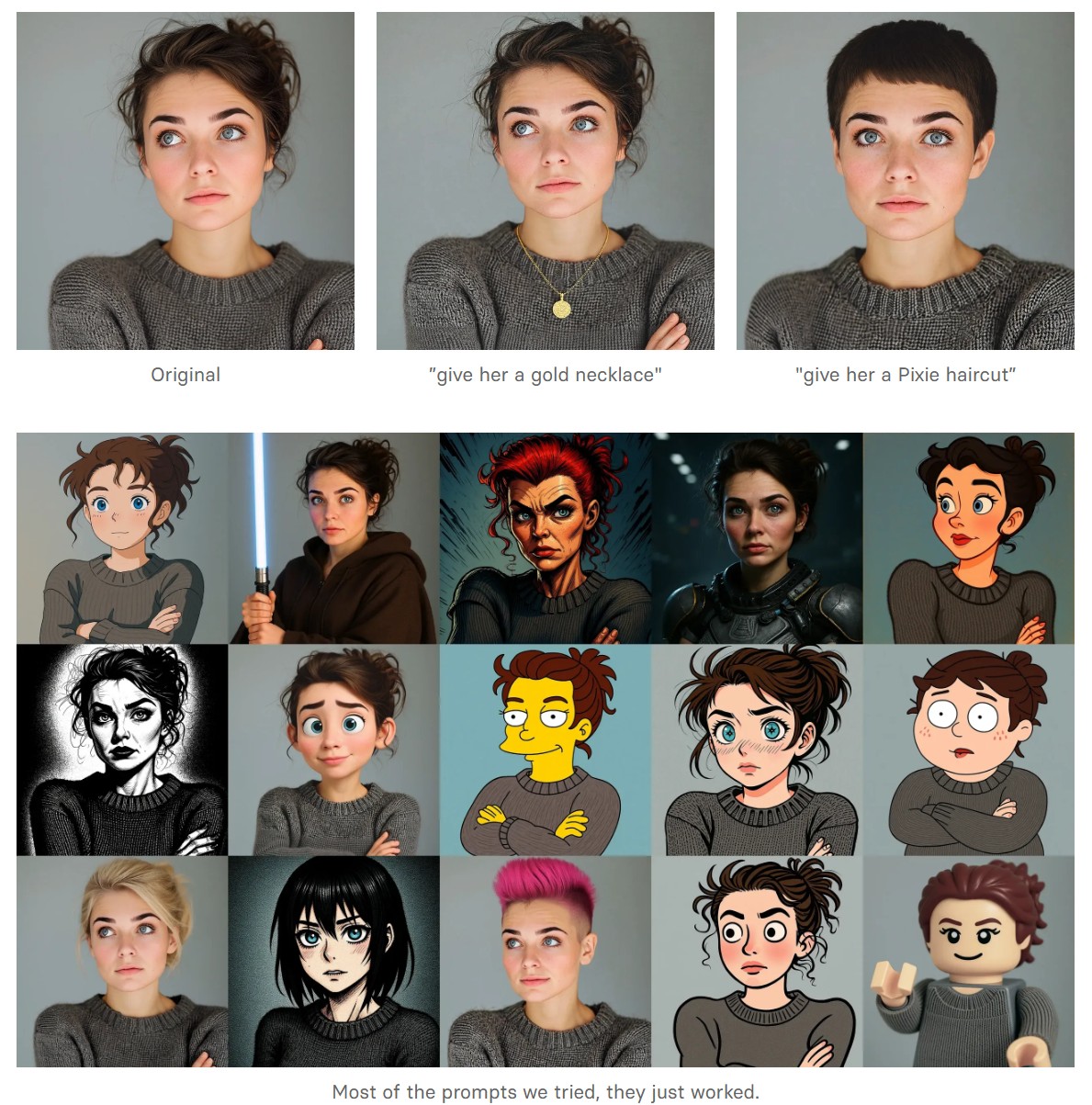

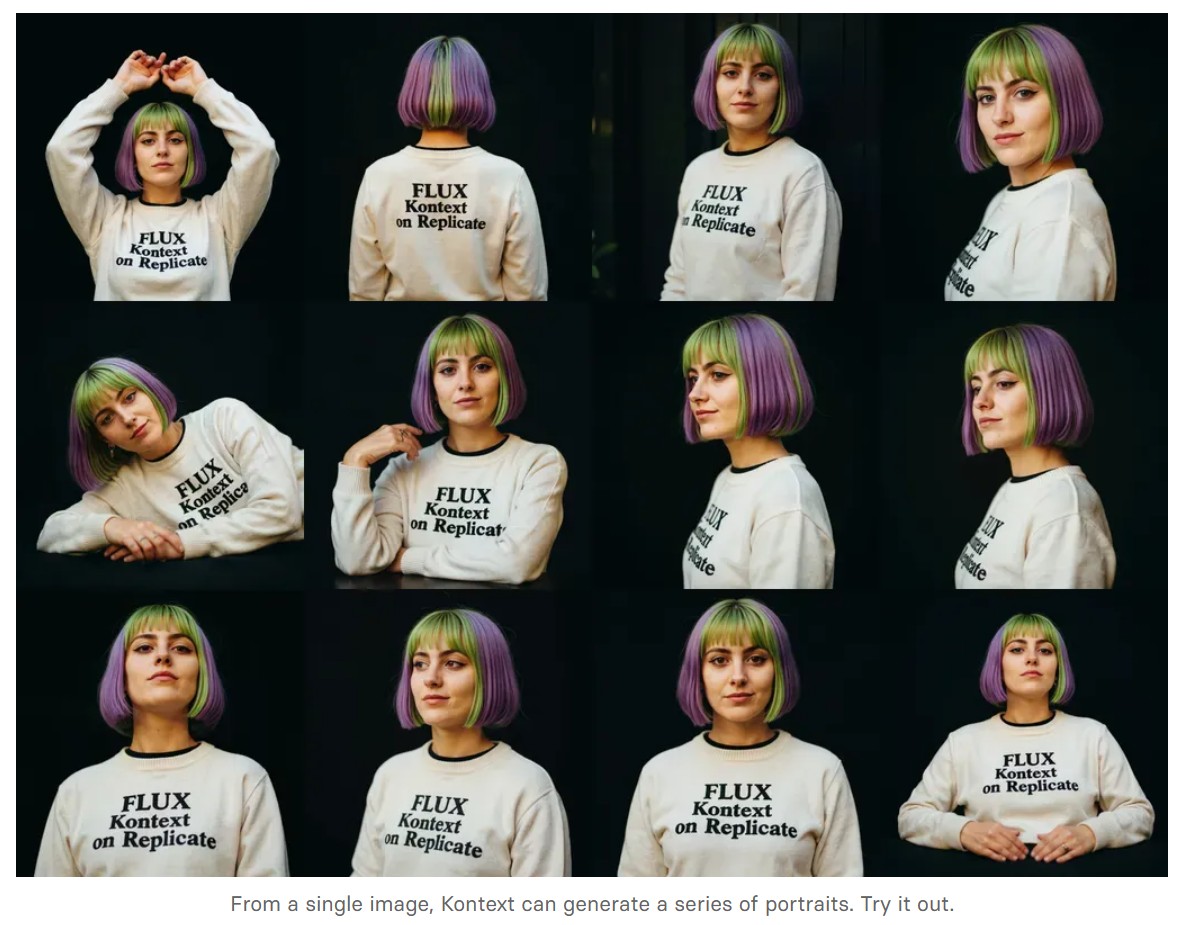
-
AI Models – A walkthrough by Andreas Horn
the 8 most important model types and what they’re actually built to do: ⬇️
1. 𝗟𝗟𝗠 – 𝗟𝗮𝗿𝗴𝗲 𝗟𝗮𝗻𝗴𝘂𝗮𝗴𝗲 𝗠𝗼𝗱𝗲𝗹
→ Your ChatGPT-style model.
Handles text, predicts the next token, and powers 90% of GenAI hype.
🛠 Use case: content, code, convos.
2. 𝗟𝗖𝗠 – 𝗟𝗮𝘁𝗲𝗻𝘁 𝗖𝗼𝗻𝘀𝗶𝘀𝘁𝗲𝗻𝗰𝘆 𝗠𝗼𝗱𝗲𝗹
→ Lightweight, diffusion-style models.
Fast, quantized, and efficient — perfect for real-time or edge deployment.
🛠 Use case: image generation, optimized inference.
3. 𝗟𝗔𝗠 – 𝗟𝗮𝗻𝗴𝘂𝗮𝗴𝗲 𝗔𝗰𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻 𝗠𝗼𝗱𝗲𝗹
→ Where LLM meets planning.
Adds memory, task breakdown, and intent recognition.
🛠 Use case: AI agents, tool use, step-by-step execution.
4. 𝗠𝗼𝗘 – 𝗠𝗶𝘅𝘁𝘂𝗿𝗲 𝗼𝗳 𝗘𝘅𝗽𝗲𝗿𝘁𝘀
→ One model, many minds.
Routes input to the right “expert” model slice — dynamic, scalable, efficient.
🛠 Use case: high-performance model serving at low compute cost.
5. 𝗩𝗟𝗠 – 𝗩𝗶𝘀𝗶𝗼𝗻 𝗟𝗮𝗻𝗴𝘂𝗮𝗴𝗲 𝗠𝗼𝗱𝗲𝗹
→ Multimodal beast.
Combines image + text understanding via shared embeddings.
🛠 Use case: Gemini, GPT-4o, search, robotics, assistive tech.
6. 𝗦𝗟𝗠 – 𝗦𝗺𝗮𝗹𝗹 𝗟𝗮𝗻𝗴𝘂𝗮𝗴𝗲 𝗠𝗼𝗱𝗲𝗹
→ Tiny but mighty.
Designed for edge use, fast inference, low latency, efficient memory.
🛠 Use case: on-device AI, chatbots, privacy-first GenAI.
7. 𝗠𝗟𝗠 – 𝗠𝗮𝘀𝗸𝗲𝗱 𝗟𝗮𝗻𝗴𝘂𝗮𝗴𝗲 𝗠𝗼𝗱𝗲𝗹
→ The OG foundation model.
Predicts masked tokens using bidirectional context.
🛠 Use case: search, classification, embeddings, pretraining.
8. 𝗦𝗔𝗠 – 𝗦𝗲𝗴𝗺𝗲𝗻𝘁 𝗔𝗻𝘆𝘁𝗵𝗶𝗻𝗴 𝗠𝗼𝗱𝗲𝗹
→ Vision model for pixel-level understanding.
Highlights, segments, and understands *everything* in an image.
🛠 Use case: medical imaging, AR, robotics, visual agents.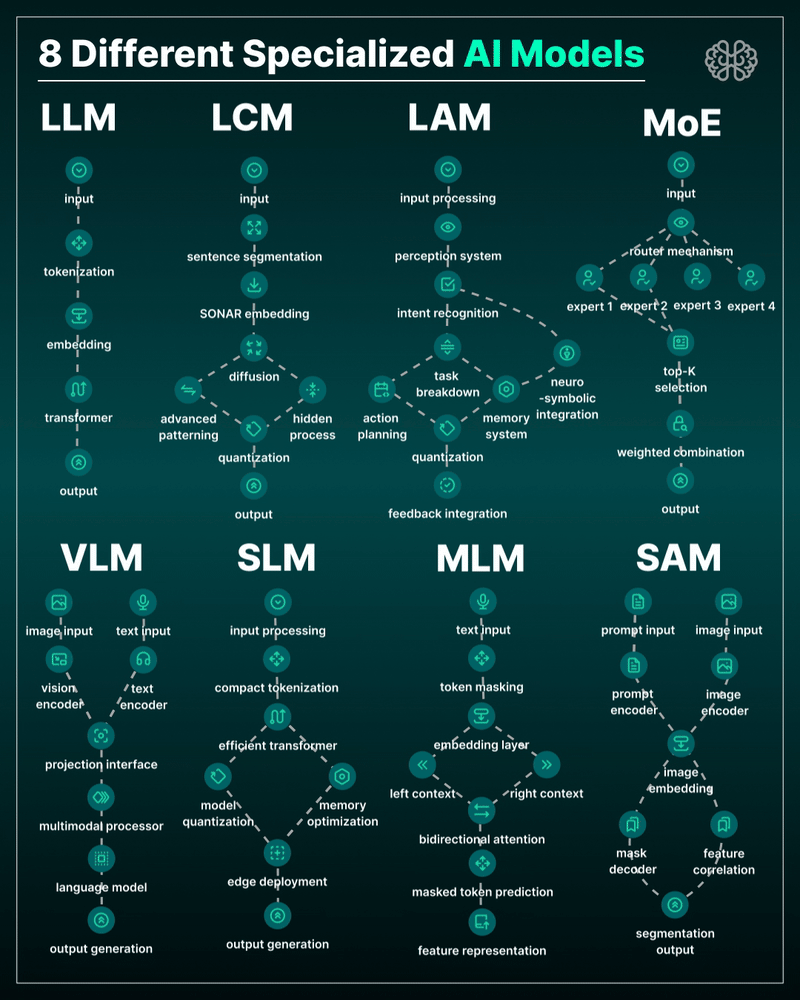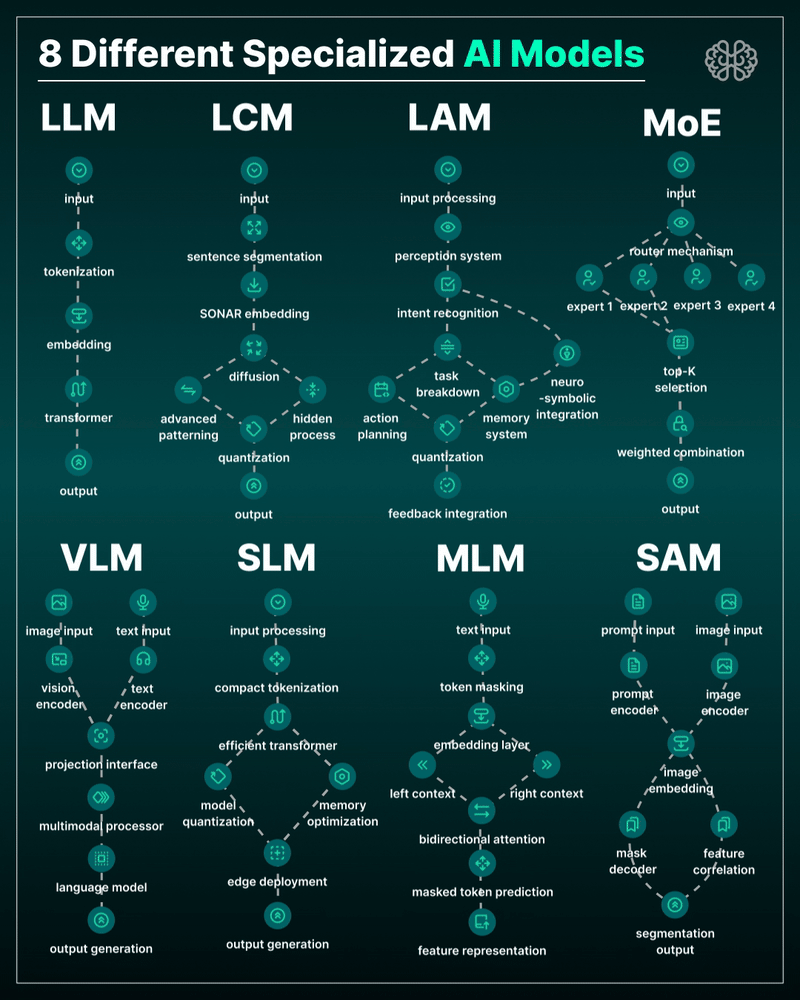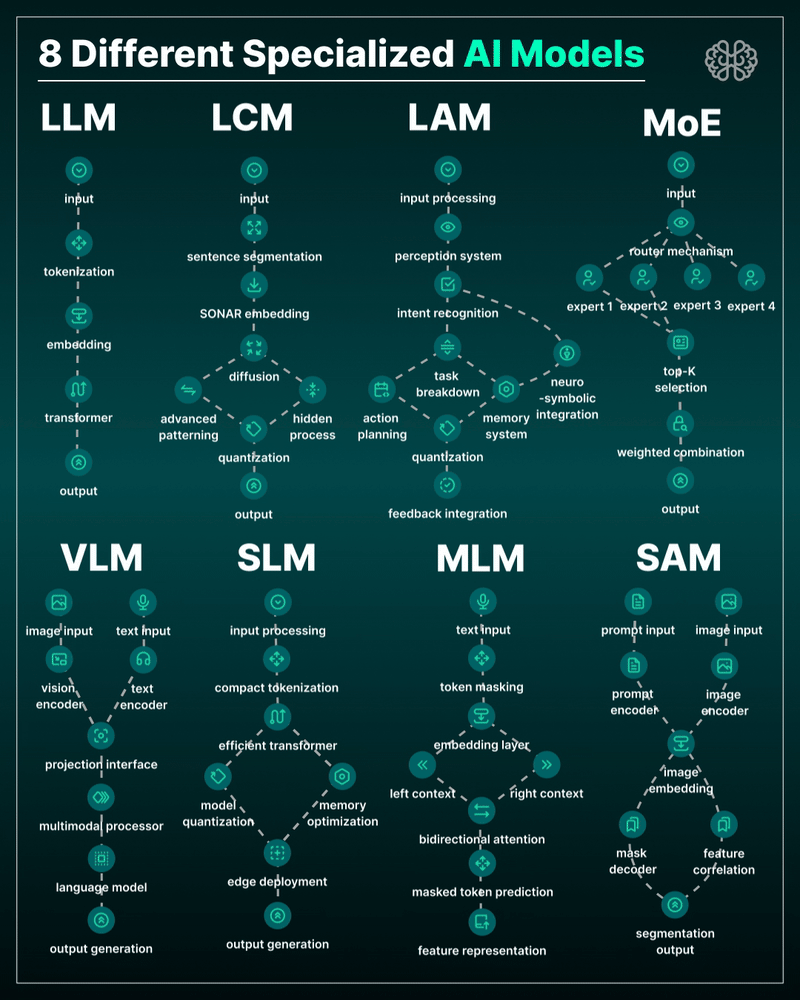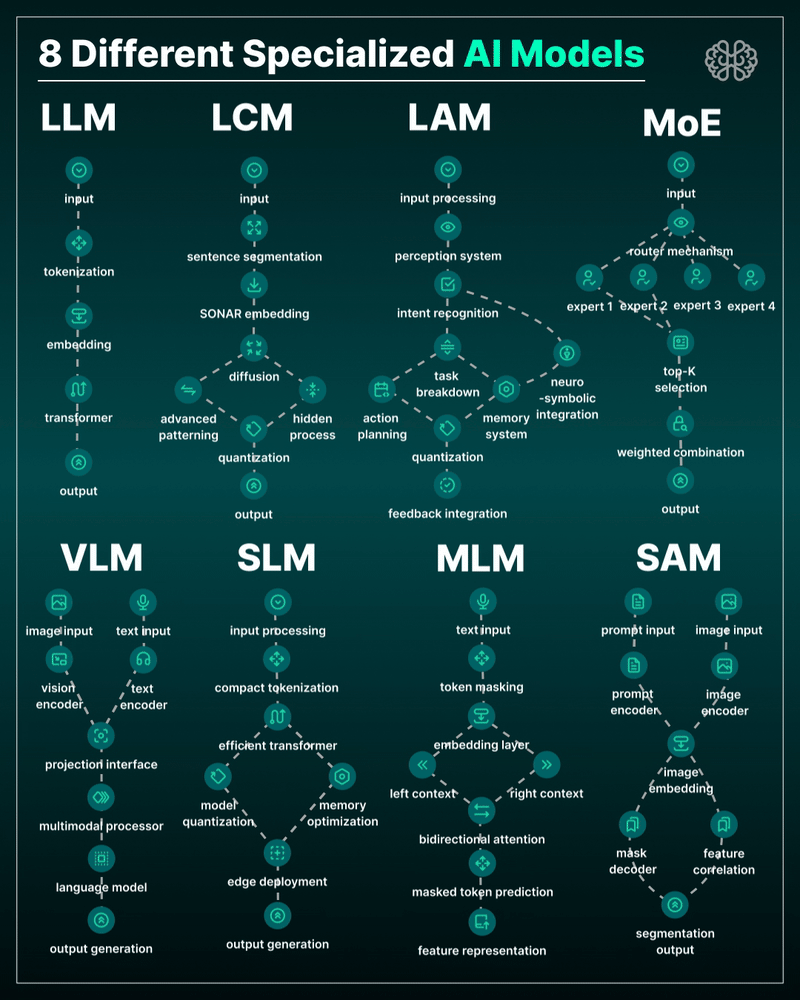
-
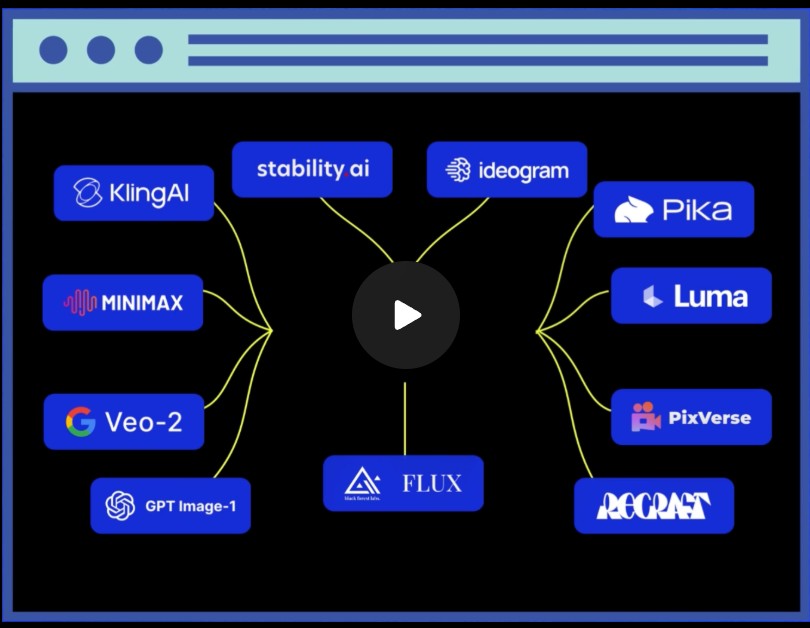
Introducting ComfyUI Native API Nodes
https://blog.comfy.org/p/comfyui-native-api-nodes
Models Supported
- Black Forest Labs Flux 1.1[pro] Ultra, Flux .1[pro]
- Kling 2.0, 1.6, 1.5 & Various Effects
- Luma Photon, Ray2, Ray1.6
- MiniMax Text-to-Video, Image-to-Video
- PixVerse V4 & Effects
- Recraft V3, V2 & Various Tools
- Stability AI Stable Image Ultra, Stable Diffusion 3.5 Large
- Google Veo2
- Ideogram V3, V2, V1
- OpenAI GPT4o image
- Pika 2.2
-
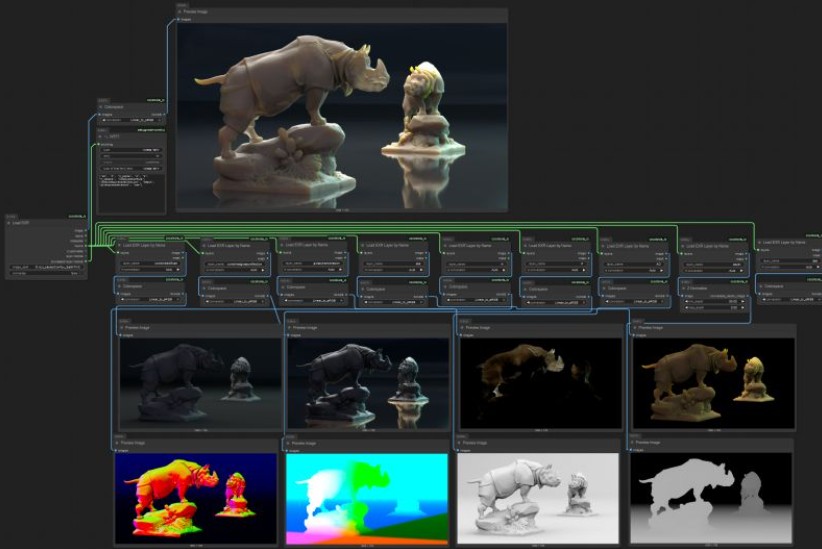
ComfyUI-CoCoTools_IO – A set of nodes focused on advanced image I/O operations, particularly for EXR file handling
https://github.com/Conor-Collins/ComfyUI-CoCoTools_IO
Features
- Advanced EXR image input with multilayer support
- EXR layer extraction and manipulation
- High-quality image saving with format-specific options
- Standard image format loading with bit depth awareness
Current Nodes
Image I/O
- Image Loader: Load standard image formats (PNG, JPG, WebP, etc.) with proper bit depth handling
- Load EXR: Comprehensive EXR file loading with support for multiple layers, channels, and cryptomatte data
- Load EXR Layer by Name: Extract specific layers from EXR files (similar to Nuke’s Shuffle node)
- Cryptomatte Layer: Specialized handling for cryptomatte layers in EXR files
- Image Saver: Save images in various formats with format-specific options (bit depth, compression, etc.)
Image Processing
- Colorspace: Convert between sRGB and Linear colorspaces
- Z Normalize: Normalize depth maps and other single-channel data
FEATURED POSTS
-
Top 3D Printing Website Resources
The Holy Grail – https://github.com/ad-si/awesome-3d-printing
- Thingiverse – https://www.thingiverse.com/
- Makerworld – https://makerworld.com/
- Printables – https://www.printables.com/
- Cults – https://cults3d.com/
- CG Trader – https://www.cgtrader.com/3d-print-models
- Sketchfab – https://sketchfab.com/store/3d-models/stl
- 3D Export – https://3dexport.com/
- MyMiniFactory – https://www.myminifactory.com/
- Thangs – https://thangs.com/
- Yeggi – https://www.yeggi.com/
- FAB365 – https://fab365.net/
- Gambody – https://www.gambody.com/
- All3DP News – https://all3dp.com/
- TCT Magazine – https://www.tctmagazine.com/topics/3D-printing-news/
- 3DPrint.com – https://3dprint.com/
- NASA 3D Models – https://nasa3d.arc.nasa.gov/models/printable
-
The Perils of Technical Debt – Understanding Its Impact on Security, Usability, and Stability
In software development, “technical debt” is a term used to describe the accumulation of shortcuts, suboptimal solutions, and outdated code that occur as developers rush to meet deadlines or prioritize immediate goals over long-term maintainability. While this concept initially seems abstract, its consequences are concrete and can significantly affect the security, usability, and stability of software systems.
The Nature of Technical Debt
Technical debt arises when software engineers choose a less-than-ideal implementation in the interest of saving time or reducing upfront effort. Much like financial debt, these decisions come with an interest rate: over time, the cost of maintaining and updating the system increases, and more effort is required to fix problems that stem from earlier choices. In extreme cases, technical debt can slow development to a crawl, causing future updates or improvements to become far more difficult than they would have been with cleaner, more scalable code.
Impact on Security
One of the most significant threats posed by technical debt is the vulnerability it creates in terms of software security. Outdated code often lacks the latest security patches or is built on legacy systems that are no longer supported. Attackers can exploit these weaknesses, leading to data breaches, ransomware, or other forms of cybercrime. Furthermore, as systems grow more complex and the debt compounds, identifying and fixing vulnerabilities becomes increasingly challenging. Failing to address technical debt leaves an organization exposed to security risks that may only become apparent after a costly incident.
Impact on Usability
Technical debt also affects the user experience. Systems burdened by outdated code often become clunky and slow, leading to poor usability. Engineers may find themselves continuously patching minor issues rather than implementing larger, user-centric improvements. Over time, this results in a product that feels antiquated, is difficult to use, or lacks modern functionality. In a competitive market, poor usability can alienate users, causing a loss of confidence and driving them to alternative products or services.
Impact on Stability
Stability is another critical area impacted by technical debt. As developers add features or make updates to systems weighed down by previous quick fixes, they run the risk of introducing bugs or causing system crashes. The tangled, fragile nature of code laden with technical debt makes troubleshooting difficult and increases the likelihood of cascading failures. Over time, instability in the software can erode both the trust of users and the efficiency of the development team, as more resources are dedicated to resolving recurring issues rather than innovating or expanding the system’s capabilities.
The Long-Term Costs of Ignoring Technical Debt
While technical debt can provide short-term gains by speeding up initial development, the long-term costs are much higher. Unaddressed technical debt can lead to project delays, escalating maintenance costs, and an ever-widening gap between current code and modern best practices. The more technical debt accumulates, the harder and more expensive it becomes to address. For many companies, failing to pay down this debt eventually results in a critical juncture: either invest heavily in refactoring the codebase or face an expensive overhaul to rebuild from the ground up.
Conclusion
Technical debt is an unavoidable aspect of software development, but understanding its perils is essential for minimizing its impact on security, usability, and stability. By actively managing technical debt—whether through regular refactoring, code audits, or simply prioritizing long-term quality over short-term expedience—organizations can avoid the most dangerous consequences and ensure their software remains robust and reliable in an ever-changing technological landscape.
-
Black Body color aka the Planckian Locus curve for white point eye perception
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Black-body_radiation
Black-body radiation is the type of electromagnetic radiation within or surrounding a body in thermodynamic equilibrium with its environment, or emitted by a black body (an opaque and non-reflective body) held at constant, uniform temperature. The radiation has a specific spectrum and intensity that depends only on the temperature of the body.
A black-body at room temperature appears black, as most of the energy it radiates is infra-red and cannot be perceived by the human eye. At higher temperatures, black bodies glow with increasing intensity and colors that range from dull red to blindingly brilliant blue-white as the temperature increases.
The Black Body Ultraviolet Catastrophe Experiment
In photography, color temperature describes the spectrum of light which is radiated from a “blackbody” with that surface temperature. A blackbody is an object which absorbs all incident light — neither reflecting it nor allowing it to pass through.
The Sun closely approximates a black-body radiator. Another rough analogue of blackbody radiation in our day to day experience might be in heating a metal or stone: these are said to become “red hot” when they attain one temperature, and then “white hot” for even higher temperatures. Similarly, black bodies at different temperatures also have varying color temperatures of “white light.”
Despite its name, light which may appear white does not necessarily contain an even distribution of colors across the visible spectrum.
Although planets and stars are neither in thermal equilibrium with their surroundings nor perfect black bodies, black-body radiation is used as a first approximation for the energy they emit. Black holes are near-perfect black bodies, and it is believed that they emit black-body radiation (called Hawking radiation), with a temperature that depends on the mass of the hole.






