BREAKING NEWS
LATEST POSTS
-
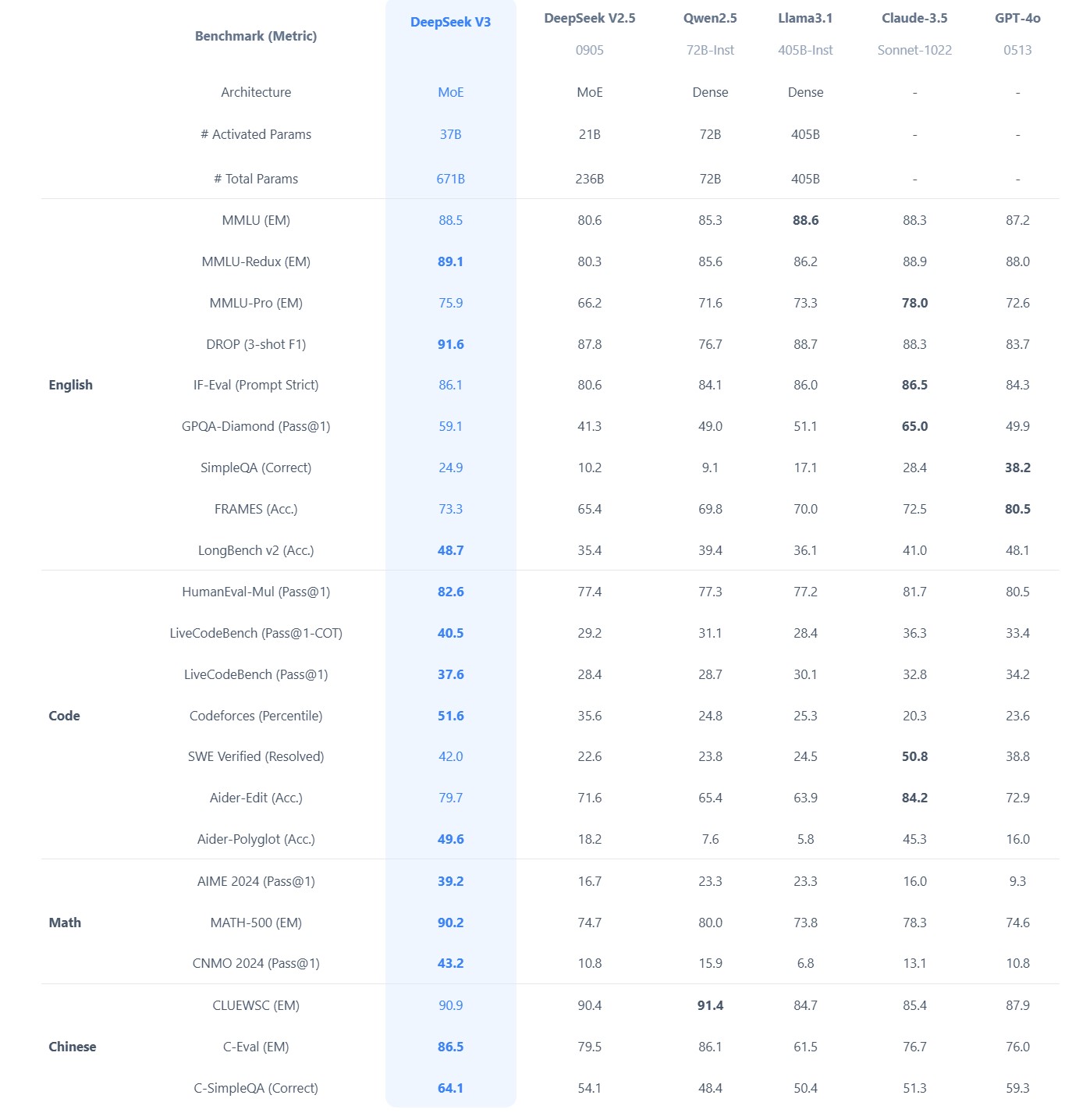
Brian Gallagher – Why Almost Everybody Is Wrong About DeepSeek vs. All the Other AI Companies
Benchmarks don’t capture real-world complexity like latency, domain-specific tasks, or edge cases. Enterprises often need more than raw performance, also needing reliability, ease of integration, and robust vendor support. Enterprise money will support the industries providing these services.
… it is also reasonable to assume that anything you put into the app or their website will be going to the Chinese government as well, so factor that in as well.
-
One-Prompt-One-Story – Free-Lunch Consistent Text-to-Image Generation Using a Single Prompt
https://byliutao.github.io/1Prompt1Story.github.io
Tneration models can create high-quality images from input prompts. However, they struggle to support the consistent generation of identity-preserving requirements for storytelling.
Our approach 1Prompt1Story concatenates all prompts into a single input for T2I diffusion models, initially preserving character identities.

-
What did DeepSeek figure out about reasoning with DeepSeek-R1?
https://www.seangoedecke.com/deepseek-r1
The Chinese AI lab DeepSeek recently released their new reasoning model R1, which is supposedly (a) better than the current best reasoning models (OpenAI’s o1- series), and (b) was trained on a GPU cluster a fraction the size of any of the big western AI labs.
DeepSeek uses a reinforcement learning approach, not a fine-tuning approach. There’s no need to generate a huge body of chain-of-thought data ahead of time, and there’s no need to run an expensive answer-checking model. Instead, the model generates its own chains-of-thought as it goes.
The secret behind their success? A bold move to train their models using FP8 (8-bit floating-point precision) instead of the standard FP32 (32-bit floating-point precision).
…
By using a clever system that applies high precision only when absolutely necessary, they achieved incredible efficiency without losing accuracy.
…
The impressive part? These multi-token predictions are about 85–90% accurate, meaning DeepSeek R1 can deliver high-quality answers at double the speed of its competitors.Chinese AI firm DeepSeek has 50,000 NVIDIA H100 AI GPUs

-
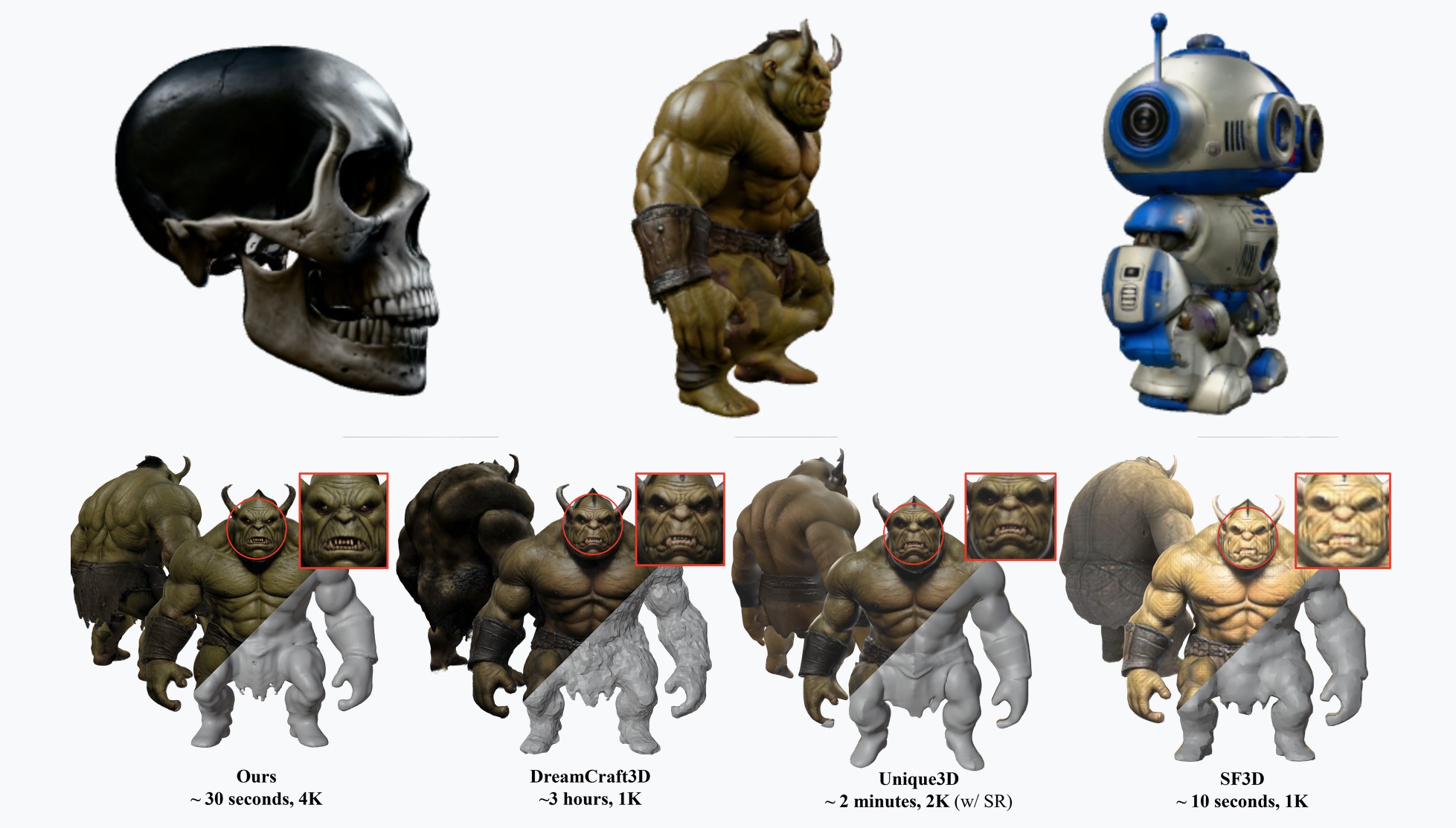
CaPa – Carve-n-Paint Synthesisfor Efficient 4K Textured Mesh Generation
https://github.com/ncsoft/CaPa
a novel method for generating hyper-quality 4K textured mesh under only 30 seconds, providing 3D assets ready for commercial applications such as games, movies, and VR/AR.

-
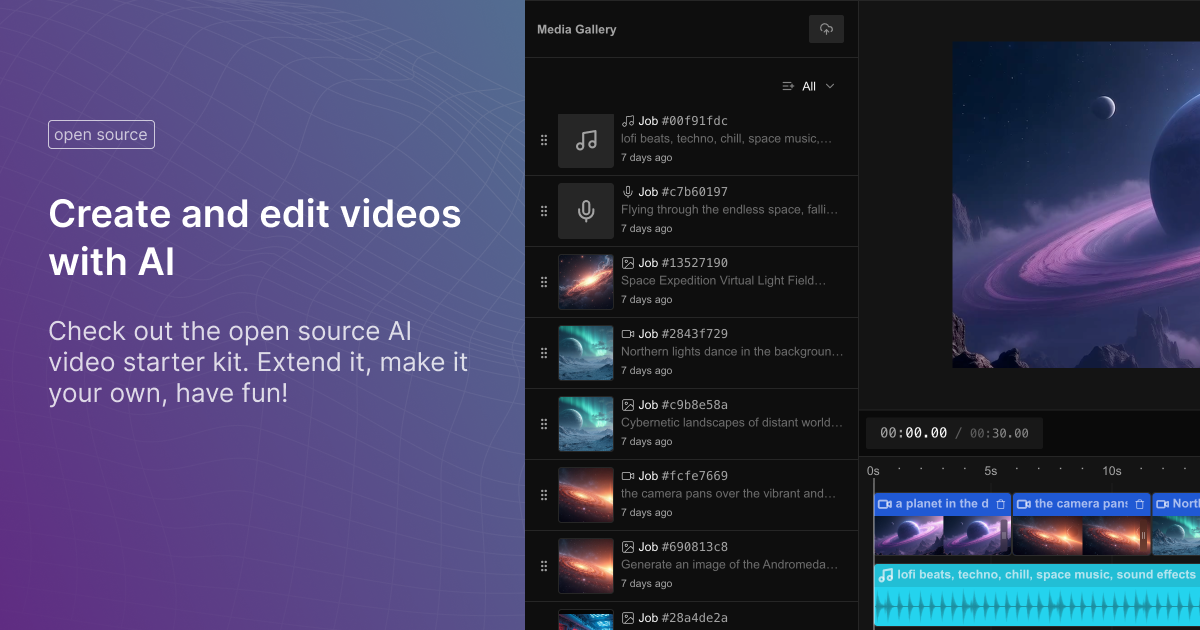
Fal Video Studio – The first open-source AI toolkit for video editing
https://github.com/fal-ai-community/video-starter-kit
https://fal-video-studio.vercel.app
- 🎬 Browser-Native Video Processing: Seamless video handling and composition in the browser
- 🤖 AI Model Integration: Direct access to state-of-the-art video models through fal.ai
- Minimax for video generation
- Hunyuan for visual synthesis
- LTX for video manipulation
- 🎵 Advanced Media Capabilities:
- Multi-clip video composition
- Audio track integration
- Voiceover support
- Extended video duration handling
- 🛠️ Developer Utilities:
- Metadata encoding
- Video processing pipeline
- Ready-to-use UI components
- TypeScript support
FEATURED POSTS
-
Embedding frame ranges into Quicktime movies with FFmpeg
QuickTime (.mov) files are fundamentally time-based, not frame-based, and so don’t have a built-in, uniform “first frame/last frame” field you can set as numeric frame IDs. Instead, tools like Shotgun Create rely on the timecode track and the movie’s duration to infer frame numbers. If you want Shotgun to pick up a non-default frame range (e.g. start at 1001, end at 1064), you must bake in an SMPTE timecode that corresponds to your desired start frame, and ensure the movie’s duration matches your clip length.
How Shotgun Reads Frame Ranges
- Default start frame is 1. If no timecode metadata is present, Shotgun assumes the movie begins at frame 1.
- Timecode ⇒ frame number. Shotgun Create “honors the timecodes of media sources,” mapping the embedded TC to frame IDs. For example, a 24 fps QuickTime tagged with a start timecode of 00:00:41:17 will be interpreted as beginning on frame 1001 (1001 ÷ 24 fps ≈ 41.71 s).
Embedding a Start Timecode
QuickTime uses a
tmcd(timecode) track. You can bake in an SMPTE track via FFmpeg’s-timecodeflag or via Compressor/encoder settings:- Compute your start TC.
- Desired start frame = 1001
- Frame 1001 at 24 fps ⇒ 1001 ÷ 24 ≈ 41.708 s ⇒ TC 00:00:41:17
- FFmpeg example:
ffmpeg -i input.mov \ -c copy \ -timecode 00:00:41:17 \ output.movThis adds a timecode track beginning at 00:00:41:17, which Shotgun maps to frame 1001.
Ensuring the Correct End Frame
Shotgun infers the last frame from the movie’s duration. To end on frame 1064:
- Frame count = 1064 – 1001 + 1 = 64 frames
- Duration = 64 ÷ 24 fps ≈ 2.667 s
FFmpeg trim example:
ffmpeg -i input.mov \ -c copy \ -timecode 00:00:41:17 \ -t 00:00:02.667 \ output_trimmed.movThis results in a 64-frame clip (1001→1064) at 24 fps.

-
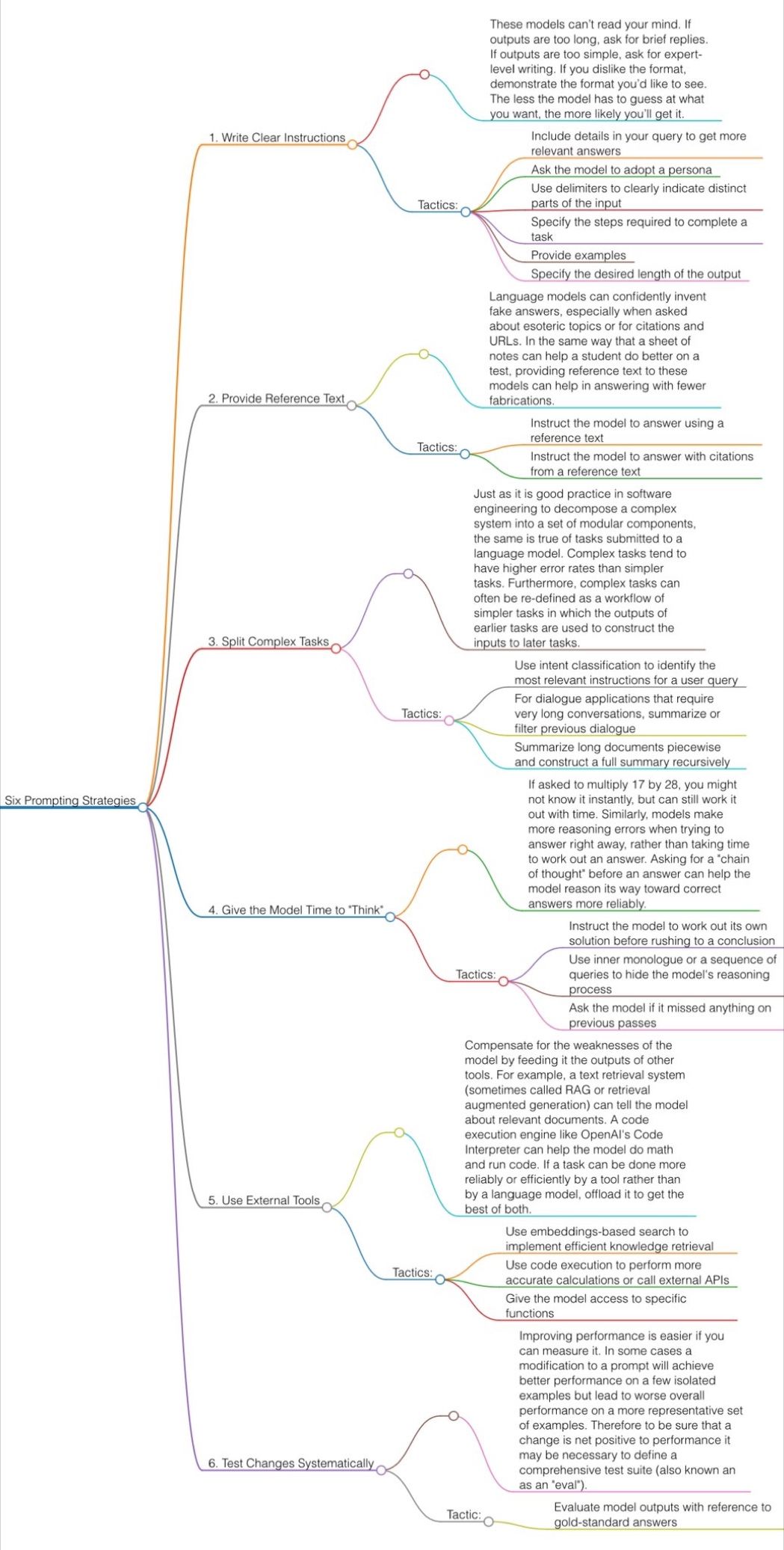
Guide to Prompt Engineering
The 10 most powerful techniques:
1. Communicate the Why
2. Explain the context (strategy, data)
3. Clearly state your objectives
4. Specify the key results (desired outcomes)
5. Provide an example or template
6. Define roles and use the thinking hats
7. Set constraints and limitations
8. Provide step-by-step instructions (CoT)
9. Ask to reverse-engineer the result to get a prompt
10. Use markdown or XML to clearly separate sections (e.g., examples)
Top 10 high-ROI use cases for PMs:
1. Get new product ideas
2. Identify hidden assumptions
3. Plan the right experiments
4. Summarize a customer interview
5. Summarize a meeting
6. Social listening (sentiment analysis)
7. Write user stories
8. Generate SQL queries for data analysis
9. Get help with PRD and other templates
10. Analyze your competitors
Quick prompting scheme:
1- pass an image to JoyCaption
https://www.pixelsham.com/2024/12/23/joy-caption-alpha-two-free-automatic-caption-of-images/
2- tune the caption with ChatGPT as suggested by Pixaroma:
Craft detailed prompts for Al (image/video) generation, avoiding quotation marks. When I provide a description or image, translate it into a prompt that captures a cinematic, movie-like quality, focusing on elements like scene, style, mood, lighting, and specific visual details. Ensure that the prompt evokes a rich, immersive atmosphere, emphasizing textures, depth, and realism. Always incorporate (static/slow) camera or cinematic movement to enhance the feeling of fluidity and visual storytelling. Keep the wording precise yet descriptive, directly usable, and designed to achieve a high-quality, film-inspired result.
https://www.reddit.com/r/ChatGPT/comments/139mxi3/chatgpt_created_this_guide_to_prompt_engineering/
1. Use the 80/20 principle to learn faster
Prompt: “I want to learn about [insert topic]. Identify and share the most important 20% of learnings from this topic that will help me understand 80% of it.”
2. Learn and develop any new skill
Prompt: “I want to learn/get better at [insert desired skill]. I am a complete beginner. Create a 30-day learning plan that will help a beginner like me learn and improve this skill.”
3. Summarize long documents and articles
Prompt: “Summarize the text below and give me a list of bullet points with key insights and the most important facts.” [Insert text]
4. Train ChatGPT to generate prompts for you
Prompt: “You are an AI designed to help [insert profession]. Generate a list of the 10 best prompts for yourself. The prompts should be about [insert topic].”
5. Master any new skill
Prompt: “I have 3 free days a week and 2 months. Design a crash study plan to master [insert desired skill].”
6. Simplify complex information
Prompt: “Break down [insert topic] into smaller, easier-to-understand parts. Use analogies and real-life examples to simplify the concept and make it more relatable.”
More suggestions under the post…
(more…)
-
HDRI shooting and editing by Xuan Prada and Greg Zaal
www.xuanprada.com/blog/2014/11/3/hdri-shooting
http://blog.gregzaal.com/2016/03/16/make-your-own-hdri/
http://blog.hdrihaven.com/how-to-create-high-quality-hdri/
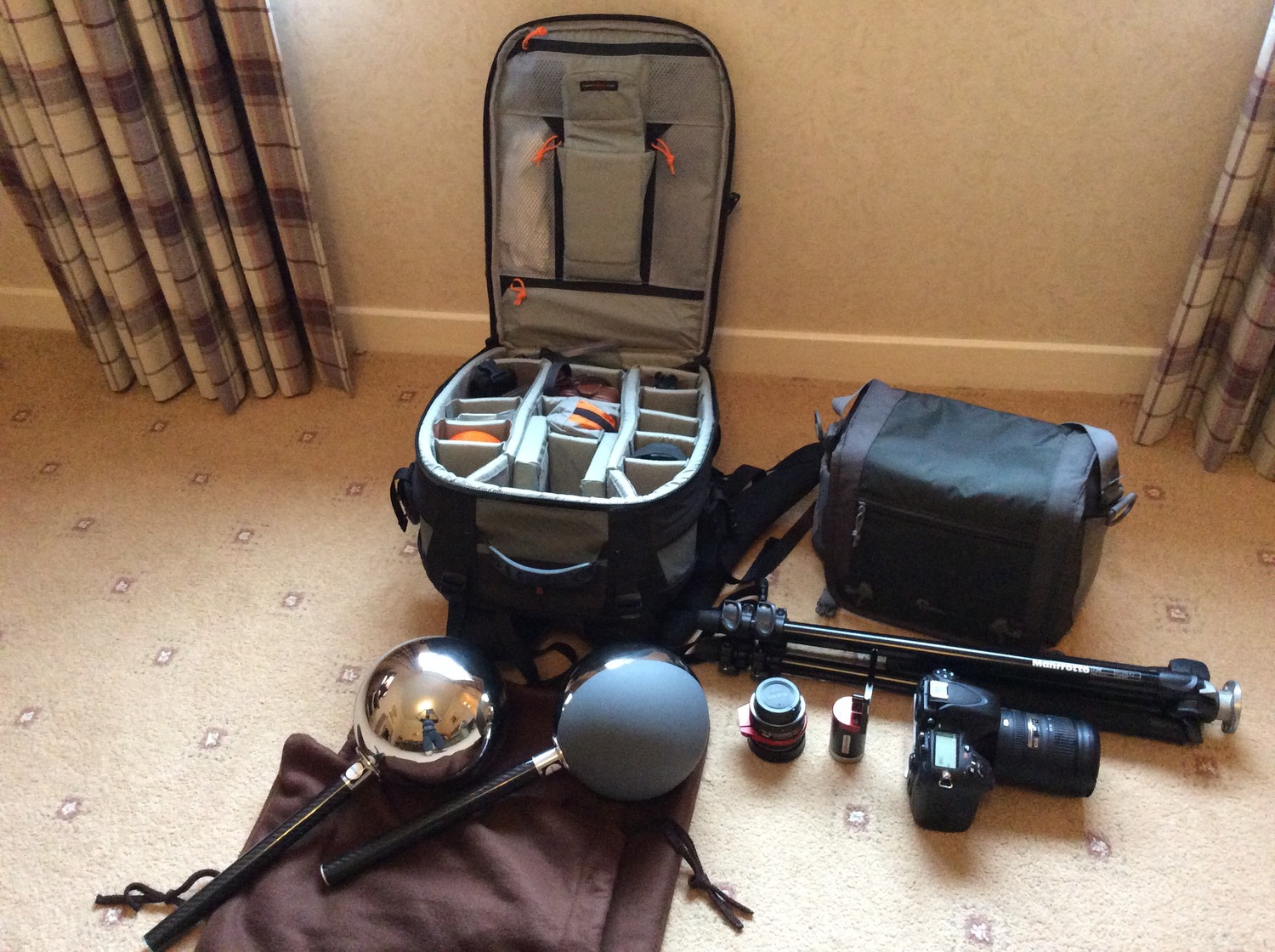

Shooting checklist
- Full coverage of the scene (fish-eye shots)
- Backplates for look-development (including ground or floor)
- Macbeth chart for white balance
- Grey ball for lighting calibration
- Chrome ball for lighting orientation
- Basic scene measurements
- Material samples
- Individual HDR artificial lighting sources if required
Methodology
(more…)





