BREAKING NEWS
LATEST POSTS
-
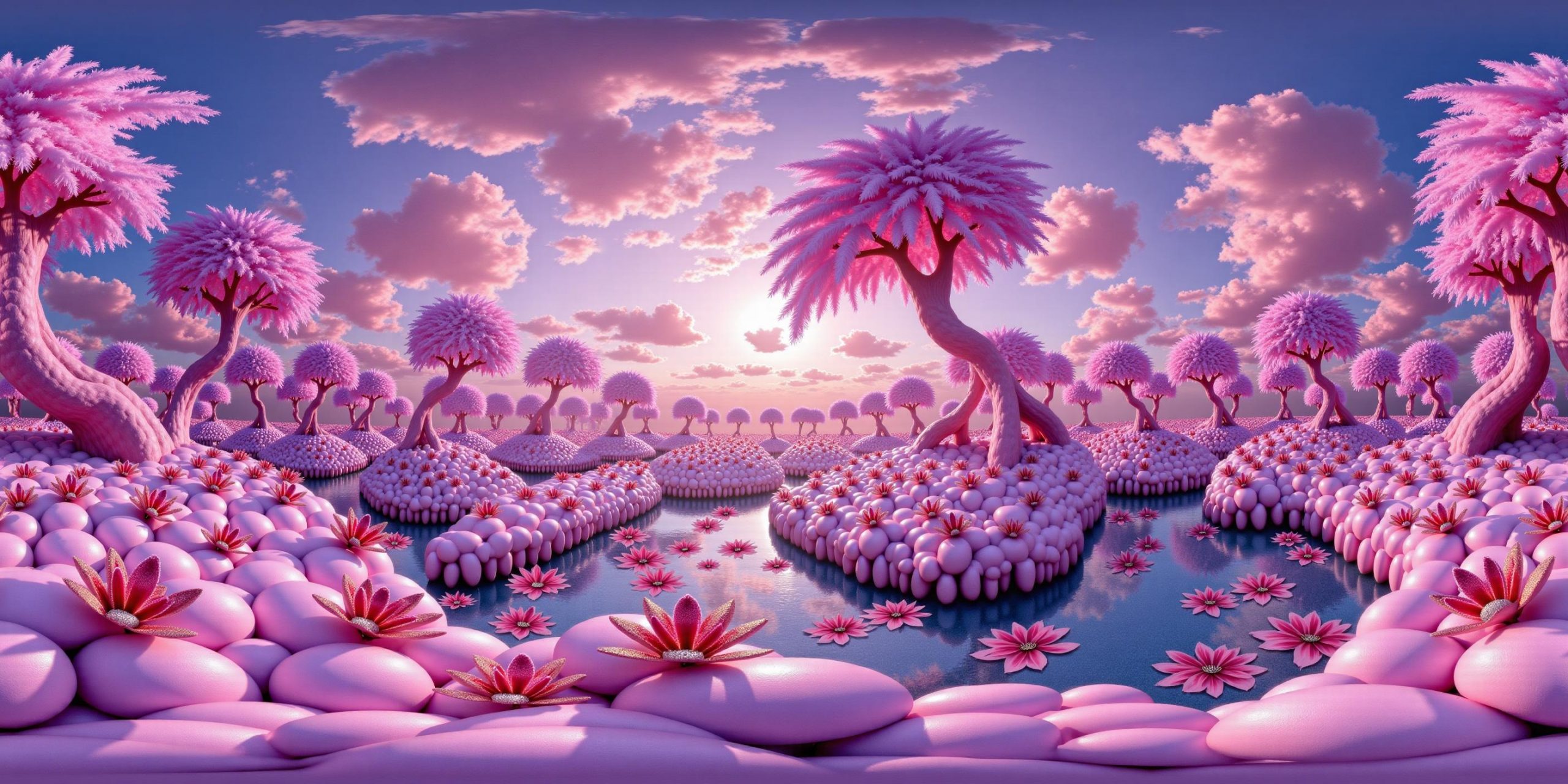
Arto T. – A workflow for creating photorealistic, equirectangular 360° panoramas in ComfyUI using Flux
https://civitai.com/models/735980/flux-equirectangular-360-panorama
https://civitai.com/models/745010?modelVersionId=833115
The trigger phrase is “equirectangular 360 degree panorama”. I would avoid saying “spherical projection” since that tends to result in non-equirectangular spherical images.
Image resolution should always be a 2:1 aspect ratio. 1024 x 512 or 1408 x 704 work quite well and were used in the training data. 2048 x 1024 also works.
I suggest using a weight of 0.5 – 1.5. If you are having issues with the image generating too flat instead of having the necessary spherical distortion, try increasing the weight above 1, though this could negatively impact small details of the image. For Flux guidance, I recommend a value of about 2.5 for realistic scenes.
8-bit output at the moment

-
Scientists claim to have discovered ‘new colour’ no one has seen before: Olo
https://www.bbc.com/news/articles/clyq0n3em41o
By stimulating specific cells in the retina, the participants claim to have witnessed a blue-green colour that scientists have called “olo”, but some experts have said the existence of a new colour is “open to argument”.
The findings, published in the journal Science Advances on Friday, have been described by the study’s co-author, Prof Ren Ng from the University of California, as “remarkable”.
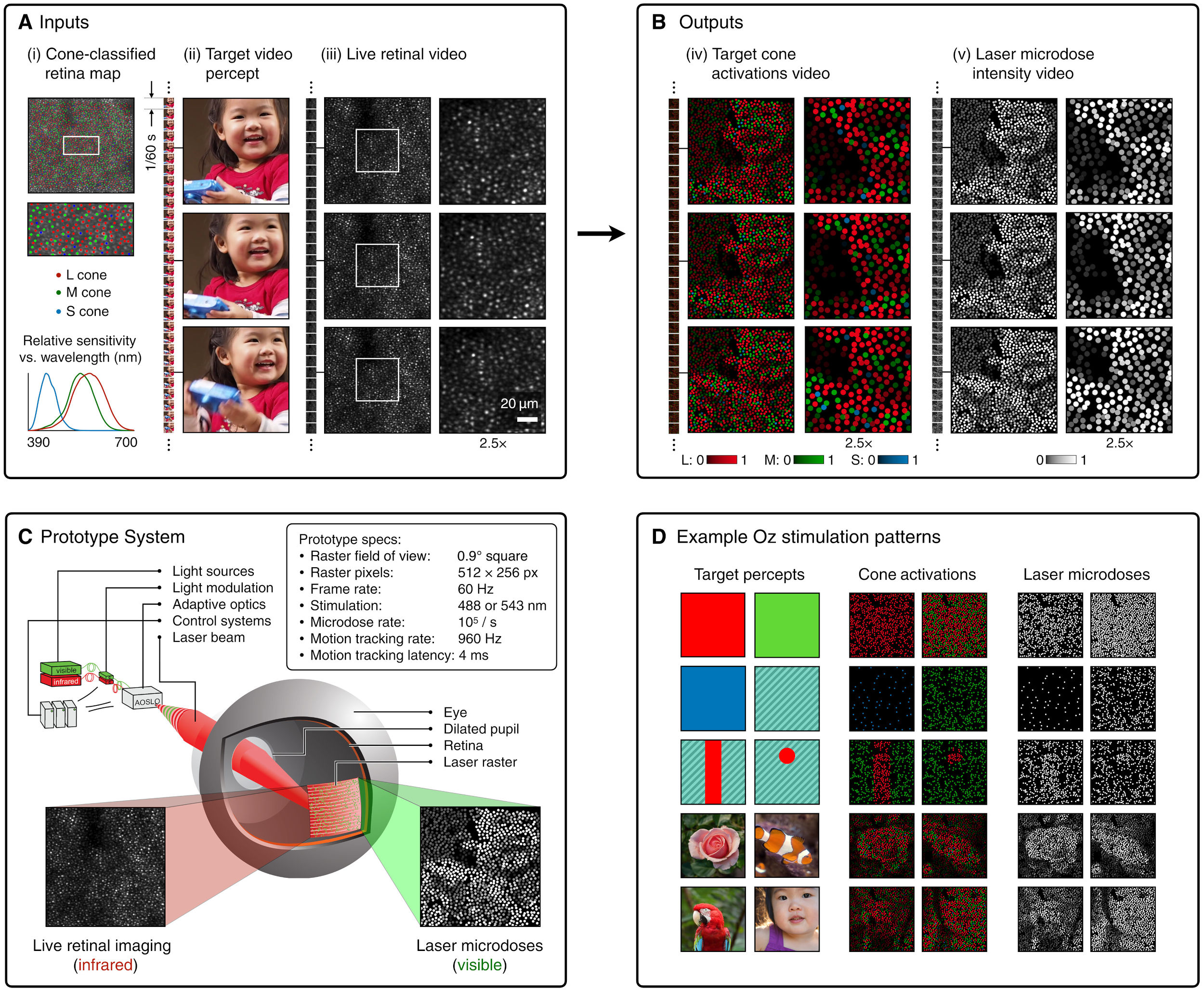
(A) System inputs. (i) Retina map of 103 cone cells preclassified by spectral type (7). (ii) Target visual percept (here, a video of a child, see movie S1 at 1:04). (iii) Infrared cellular-scale imaging of the retina with 60-frames-per-second rolling shutter. Fixational eye movement is visible over the three frames shown.
(B) System outputs. (iv) Real-time per-cone target activation levels to reproduce the target percept, computed by: extracting eye motion from the input video relative to the retina map; identifying the spectral type of every cone in the field of view; computing the per-cone activation the target percept would have produced. (v) Intensities of visible-wavelength 488-nm laser microdoses at each cone required to achieve its target activation level.
(C) Infrared imaging and visible-wavelength stimulation are physically accomplished in a raster scan across the retinal region using AOSLO. By modulating the visible-wavelength beam’s intensity, the laser microdoses shown in (v) are delivered. Drawing adapted with permission [Harmening and Sincich (54)].
(D) Examples of target percepts with corresponding cone activations and laser microdoses, ranging from colored squares to complex imagery. Teal-striped regions represent the color “olo” of stimulating only M cones.
-
-
Finn Jager – From HEIC (High Efficiency Image Container) iPhone to a Multichannel EXR
Finn Jäger has spent some time in making a sleeker tool for all you VFX nerds out there, it takes a HEIC iPhone still and exports a Multichannel EXR – the cool thing is it also converts it to acesCG and it merges the SDR base image with the gain map according to apples math hdr_rgb = sdr_rgb * (1.0 + (headroom – 1.0) * gainmap)
https://github.com/finnschi/heic-shenanigans

-
Mars Lewis on the Brandolini’s Law
Brandolini’s law (or the bullshit asymmetry principle) is an internet adage coined in 2013 by Italian programmer Alberto Brandolini. It compares the considerable effort of debunking misinformation to the relative ease of creating it in the first place.
The law states: “The amount of energy needed to refute bullshit is an order of magnitude bigger than to produce it.”
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Brandolini%27s_law
This is why every time you kill a lie, it feels like nothing changed. It’s why no matter how many facts you post, how many sources you cite, how many receipts you show—the swarm just keeps coming. Because while you’re out in the open doing surgery, the machine is behind the curtain spraying aerosol deceit into every vent.
The lie takes ten seconds. The truth takes ten paragraphs. And by the time you’ve written the tenth, the people you’re trying to reach have already scrolled past.
Every viral deception—the fake quote, the rigged video, the synthetic outrage—takes almost nothing to create. And once it’s out there, you’re not just correcting a fact—you’re prying it out of someone’s identity. Because people don’t adopt lies just for information. They adopt them for belonging. The lie becomes part of who they are, and your correction becomes an attack.
And still—you must correct it. Still, you must fight.
Because even if truth doesn’t spread as fast, it roots deeper. Even if it doesn’t go viral, it endures. And eventually, it makes people bulletproof to the next wave of narrative sewage.
You’re not here to win a one-day war. You’re here to outlast a never-ending invasion.
The lies are roaches. You kill one, and a hundred more scramble behind the drywall.The lies are Hydra heads. You cut one off, and two grow back. But you keep swinging anyway.
Because this isn’t about instant wins. It’s about making the cost of lying higher. It’s about being the resistance that doesn’t fold. You don’t fight because it’s easy. You fight because it’s right.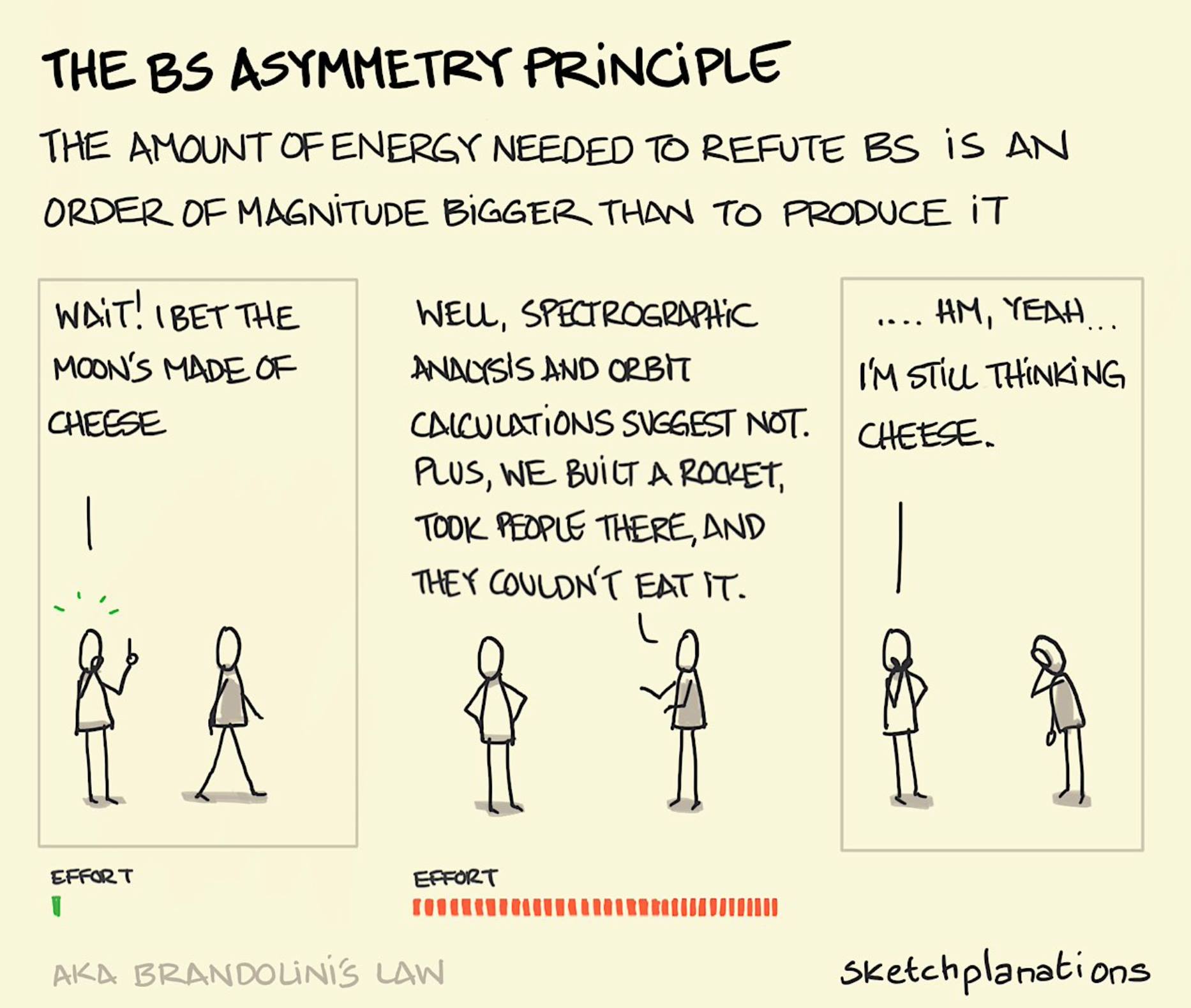
-
GenUE – Direct Prompt-to-Mesh Generation in Unreal Engine Integrated with ComfyUI
GenUE brings prompt-driven 3D asset creation directly into Unreal Engine using ComfyUI as a flexible backend. • Generate high-quality images from text prompts. • Choose from a catalog of batch-generated images – no style limitations. • Convert the selected image to a fully textured 3D mesh. • Automatically import and place the model into your Unreal Engine scene. This modular pipeline gives you full control over the image and 3D generation stages, with support for any ComfyUI workflow or model. Full generation (image + mesh + import) completes in under 2 minutes on a high-end consumer GPU.
-
Edward Ureña – Rig creator
https://edwardurena.gumroad.com/l/ramoo
What it offers:
• Base rigs for multiple character types
• Automatic weight application
• Built-in facial rigging system
• Bone generators with FK and IK options
• Streamlined constraint panel -
GPT-Image-1 API now available through ComfyUI with Dall-E integration
https://blog.comfy.org/p/comfyui-now-supports-gpt-image-1
https://docs.comfy.org/tutorials/api-nodes/openai/gpt-image-1
https://openai.com/index/image-generation-api
• Prompt GPT-Image-1 directly in ComfyUI using text or image inputs
• Set resolution and quality
• Supports image editing + transparent backgrounds
• Seamlessly mix with local workflows like WAN 2.1, FLUX Tools, and more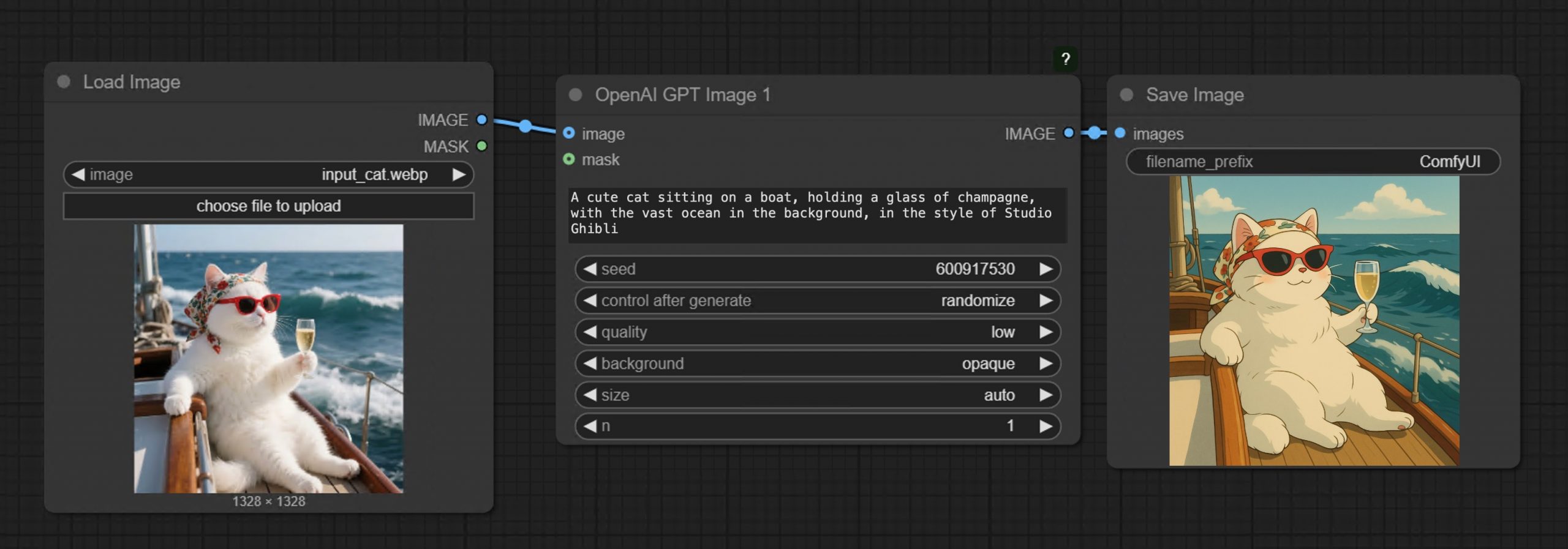
-
Tencent Hunyuan3D 2.5 – Transform images and text into 3D models with ultra-high-definition precision
What makes it special?
• Massive 10B parameter geometric model with 10x more mesh faces.
• High-quality textures with industry-first multi-view PBR generation.
• Optimized skeletal rigging for streamlined animation workflows.
• Flexible pipeline for text-to-3D and image-to-3D generation.
They’re making it accessible to everyone:
• Open-source code and pre-trained models.
• Easy-to-use API and intuitive web interface.
• Free daily quota doubled to 20 generations!
FEATURED POSTS
-
Cinematographers Blueprint 300dpi poster
The 300dpi digital poster is now available to all PixelSham.com subscribers.
If you have already subscribed and wish a copy, please send me a note through the contact page.
-
Want to build a start up company that lasts? Think three-layer cake
https://www.fastcompany.com/91131427/want-to-build-a-company-that-lasts-think-three-layer-cake
Building a successful business requires a focus on three key elements: product excellence, go-to-market strategy, and operational excellence. Neglecting any of these areas can lead to failure, as evidenced by the high percentage of startups that don’t make it past the five-year mark. Founders and CEOs must ensure a solid product foundation while also integrating effective sales, marketing, and management strategies to achieve sustainable growth and scale.
- Foundation: Product Excellence, Core Values and Mission
- Core Values: These are the guiding principles that dictate behavior and action within the company. They form the ethical foundation and are crucial for maintaining consistency in decision-making.
- Mission: This defines the company’s purpose and goals. A clear and compelling mission helps align the team and provides a sense of direction.
- Efficiency and Scalability: This layer focuses on creating efficient processes that can scale as the company grows. Streamlined operations reduce costs and increase productivity.
- Structure: Operational Excellence and Innovation
- Operational Excellence: Efficient processes, quality control, and continuous improvement fall into this layer. Ensuring that the company operates smoothly and effectively is crucial for sustainability.
- Innovation: Staying competitive requires innovation. This involves developing new products, services, or processes that add value and keep the company relevant in the market.
- Quality Control and Continuous Improvement: Ensuring that operational processes are of high quality and constantly improving helps maintain product excellence and customer satisfaction.
- Technology and Infrastructure: Investing in the right technology and infrastructure to support business operations is vital. This includes everything from manufacturing equipment to software systems that enhance operational efficiency.
- Strategy: Go-to-Market Strategy, Vision and Long-Term Planning
- Vision: A forward-looking vision inspires and motivates the team. It outlines where the company aims to be in the future and helps in setting long-term goals.
- Strategic Planning: This involves setting long-term goals and determining the actions and resources needed to achieve them. It includes market analysis, competitive strategy, and growth planning.
- Market Understanding: A deep understanding of the target market, including customer segments, competitors, and market trends, is essential. This knowledge helps in positioning the product effectively.
- Marketing and Sales Execution: This involves creating a robust marketing plan that includes branding, messaging, and advertising strategies to attract and retain customers. Additionally, building a strong sales strategy ensures that the product reaches the right customers through the right channels.
- Customer Acquisition and Retention: Effective strategies for acquiring new customers and retaining existing ones are critical. This includes loyalty programs, customer service excellence, and engagement initiatives.
- Foundation: Product Excellence, Core Values and Mission
-
What the Boeing 737 MAX’s crashes can teach us about production business – the effects of commoditisation
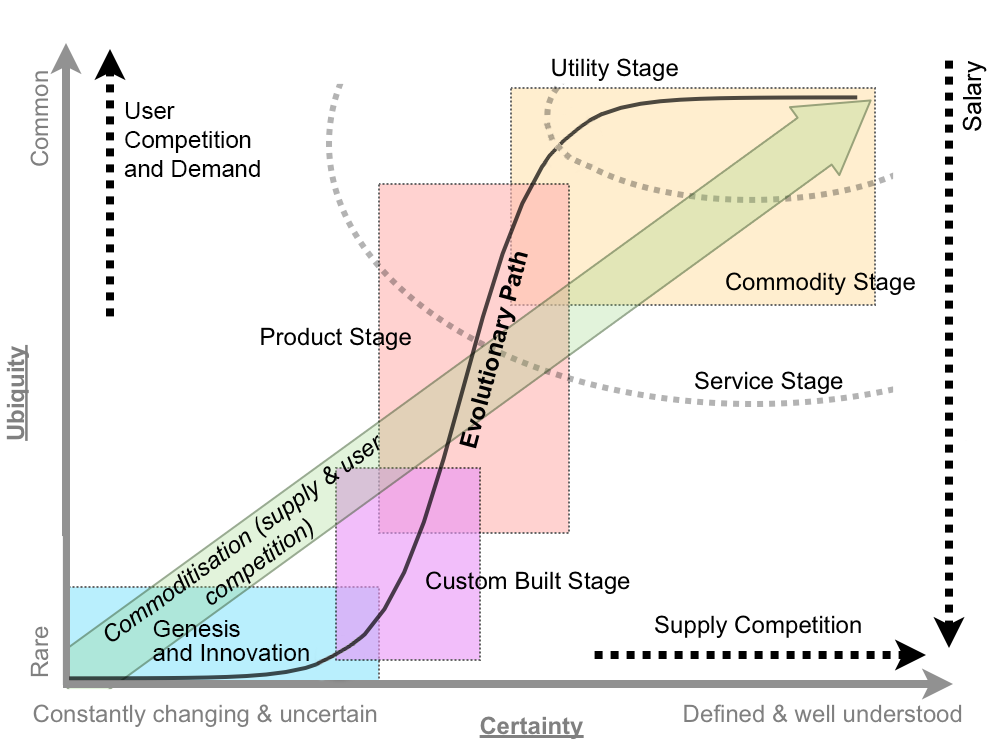
Airplane manufacturing is no different from mortgage lending or insulin distribution or make-believe blood analyzing software (or VFX?) —another cash cow for the one percent, bound inexorably for the slaughterhouse.
The beginning of the end was “Boeing’s 1997 acquisition of McDonnell Douglas, a dysfunctional firm with a dilapidated aircraft plant in Long Beach and a CEO (Harry Stonecipher) who liked to use what he called the “Hollywood model” for dealing with engineers: Hire them for a few months when project deadlines are nigh, fire them when you need to make numbers.” And all that came with it. “Stonecipher’s team had driven the last nail in the coffin of McDonnell’s flailing commercial jet business by trying to outsource everything but design, final assembly, and flight testing and sales.”
It is understood, now more than ever, that capitalism does half-assed things like that, especially in concert with computer software and oblivious regulators.
There was something unsettlingly familiar when the world first learned of MCAS in November, about two weeks after the system’s unthinkable stupidity drove the two-month-old plane and all 189 people on it to a horrific death. It smacked of the sort of screwup a 23-year-old intern might have made—and indeed, much of the software on the MAX had been engineered by recent grads of Indian software-coding academies making as little as $9 an hour, part of Boeing management’s endless war on the unions that once represented more than half its employees.
Down in South Carolina, a nonunion Boeing assembly line that opened in 2011 had for years churned out scores of whistle-blower complaints and wrongful termination lawsuits packed with scenes wherein quality-control documents were regularly forged, employees who enforced standards were sabotaged, and planes were routinely delivered to airlines with loose screws, scratched windows, and random debris everywhere.
Shockingly, another piece of the quality failure is Boeing securing investments from all airliners, starting with SouthWest above all, to guarantee Boeing’s production lines support in exchange for fair market prices and favorite treatments. Basically giving Boeing financial stability independently on the quality of their product. “Those partnerships were but one numbers-smoothing mechanism in a diversified tool kit Boeing had assembled over the previous generation for making its complex and volatile business more palatable to Wall Street.”
-
Photography Basics : Spectral Sensitivity Estimation Without a Camera
https://color-lab-eilat.github.io/Spectral-sensitivity-estimation-web/
A number of problems in computer vision and related fields would be mitigated if camera spectral sensitivities were known. As consumer cameras are not designed for high-precision visual tasks, manufacturers do not disclose spectral sensitivities. Their estimation requires a costly optical setup, which triggered researchers to come up with numerous indirect methods that aim to lower cost and complexity by using color targets. However, the use of color targets gives rise to new complications that make the estimation more difficult, and consequently, there currently exists no simple, low-cost, robust go-to method for spectral sensitivity estimation that non-specialized research labs can adopt. Furthermore, even if not limited by hardware or cost, researchers frequently work with imagery from multiple cameras that they do not have in their possession.
To provide a practical solution to this problem, we propose a framework for spectral sensitivity estimation that not only does not require any hardware (including a color target), but also does not require physical access to the camera itself. Similar to other work, we formulate an optimization problem that minimizes a two-term objective function: a camera-specific term from a system of equations, and a universal term that bounds the solution space.
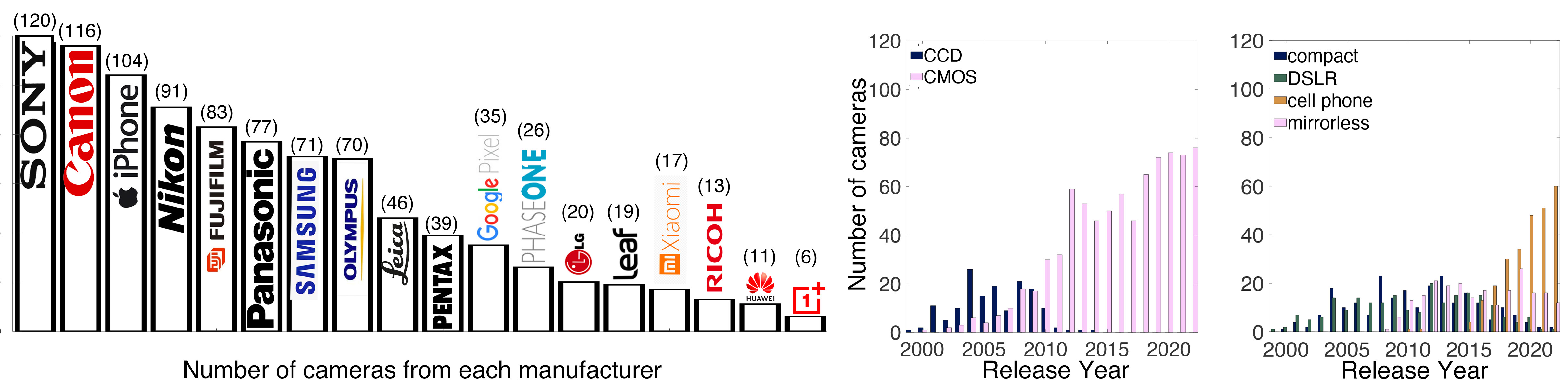
Different than other work, we utilize publicly available high-quality calibration data to construct both terms. We use the colorimetric mapping matrices provided by the Adobe DNG Converter to formulate the camera-specific system of equations, and constrain the solutions using an autoencoder trained on a database of ground-truth curves. On average, we achieve reconstruction errors as low as those that can arise due to manufacturing imperfections between two copies of the same camera. We provide predicted sensitivities for more than 1,000 cameras that the Adobe DNG Converter currently supports, and discuss which tasks can become trivial when camera responses are available.
-
The 7 key elements of brand identity design + 10 corporate identity examples
www.lucidpress.com/blog/the-7-key-elements-of-brand-identity-design
1. Clear brand purpose and positioning
2. Thorough market research
3. Likable brand personality
4. Memorable logo
5. Attractive color palette
6. Professional typography
7. On-brand supporting graphics