BREAKING NEWS
LATEST POSTS
-
Embedding frame ranges into Quicktime movies with FFmpeg
QuickTime (.mov) files are fundamentally time-based, not frame-based, and so don’t have a built-in, uniform “first frame/last frame” field you can set as numeric frame IDs. Instead, tools like Shotgun Create rely on the timecode track and the movie’s duration to infer frame numbers. If you want Shotgun to pick up a non-default frame range (e.g. start at 1001, end at 1064), you must bake in an SMPTE timecode that corresponds to your desired start frame, and ensure the movie’s duration matches your clip length.
How Shotgun Reads Frame Ranges
- Default start frame is 1. If no timecode metadata is present, Shotgun assumes the movie begins at frame 1.
- Timecode ⇒ frame number. Shotgun Create “honors the timecodes of media sources,” mapping the embedded TC to frame IDs. For example, a 24 fps QuickTime tagged with a start timecode of 00:00:41:17 will be interpreted as beginning on frame 1001 (1001 ÷ 24 fps ≈ 41.71 s).
Embedding a Start Timecode
QuickTime uses a
tmcd(timecode) track. You can bake in an SMPTE track via FFmpeg’s-timecodeflag or via Compressor/encoder settings:- Compute your start TC.
- Desired start frame = 1001
- Frame 1001 at 24 fps ⇒ 1001 ÷ 24 ≈ 41.708 s ⇒ TC 00:00:41:17
- FFmpeg example:
ffmpeg -i input.mov \ -c copy \ -timecode 00:00:41:17 \ output.movThis adds a timecode track beginning at 00:00:41:17, which Shotgun maps to frame 1001.
Ensuring the Correct End Frame
Shotgun infers the last frame from the movie’s duration. To end on frame 1064:
- Frame count = 1064 – 1001 + 1 = 64 frames
- Duration = 64 ÷ 24 fps ≈ 2.667 s
FFmpeg trim example:
ffmpeg -i input.mov \ -c copy \ -timecode 00:00:41:17 \ -t 00:00:02.667 \ output_trimmed.movThis results in a 64-frame clip (1001→1064) at 24 fps.

-
Aider.chat – A free, open-source AI pair-programming CLI tool
Aider enables developers to interactively generate, modify, and test code by leveraging both cloud-hosted and local LLMs directly from the terminal or within an IDE. Key capabilities include comprehensive codebase mapping, support for over 100 programming languages, automated git commit messages, voice-to-code interactions, and built-in linting and testing workflows. Installation is straightforward via pip or uv, and while the tool itself has no licensing cost, actual usage costs stem from the underlying LLM APIs, which are billed separately by providers like OpenAI or Anthropic.
Key Features
- Cloud & Local LLM Support
Connect to most major LLM providers out of the box, or run models locally for privacy and cost control aider.chat. - Codebase Mapping
Automatically indexes all project files so that even large repositories can be edited contextually aider.chat. - 100+ Language Support
Works with Python, JavaScript, Rust, Ruby, Go, C++, PHP, HTML, CSS, and dozens more aider.chat. - Git Integration
Generates sensible commit messages and automates diffs/undo operations through familiar git tooling aider.chat. - Voice-to-Code
Speak commands to Aider to request features, tests, or fixes without typing aider.chat. - Images & Web Pages
Attach screenshots, diagrams, or documentation URLs to provide visual context for edits aider.chat. - Linting & Testing
Runs lint and test suites automatically after each change, and can fix issues it detects
- Cloud & Local LLM Support
-
SourceTree vs Github Desktop – Which one to use
Sourcetree and GitHub Desktop are both free, GUI-based Git clients aimed at simplifying version control for developers. While they share the same core purpose—making Git more accessible—they differ in features, UI design, integration options, and target audiences.
Installation & Setup
- Sourcetree
- Download: https://www.sourcetreeapp.com/
- Supported OS: Windows 10+, macOS 10.13+
- Prerequisites: Comes bundled with its own Git, or can be pointed to a system Git install.
- Initial Setup: Wizard guides SSH key generation, authentication with Bitbucket/GitHub/GitLab.
- GitHub Desktop
- Download: https://desktop.github.com/
- Supported OS: Windows 10+, macOS 10.15+
- Prerequisites: Bundled Git; seamless login with GitHub.com or GitHub Enterprise.
- Initial Setup: One-click sign-in with GitHub; auto-syncs repositories from your GitHub account.
Feature Comparison
(more…)Feature Sourcetree GitHub Desktop Branch Visualization Detailed graph view with drag-and-drop for rebasing/merging Linear graph, simpler but less configurable Staging & Commit File-by-file staging, inline diff view All-or-nothing staging, side-by-side diff Interactive Rebase Full support via UI Basic support via command line only Conflict Resolution Built-in merge tool integration (DiffMerge, Beyond Compare) Contextual conflict editor with choice panels Submodule Management Native submodule support Limited; requires CLI Custom Actions / Hooks Define custom actions (e.g., launch scripts) No UI for custom Git hooks Git Flow / Hg Flow Built-in support None Performance Can lag on very large repos Generally snappier on medium-sized repos Memory Footprint Higher RAM usage Lightweight Platform Integration Atlassian Bitbucket, Jira Deep GitHub.com / Enterprise integration Learning Curve Steeper for beginners Beginner-friendly - Sourcetree
-
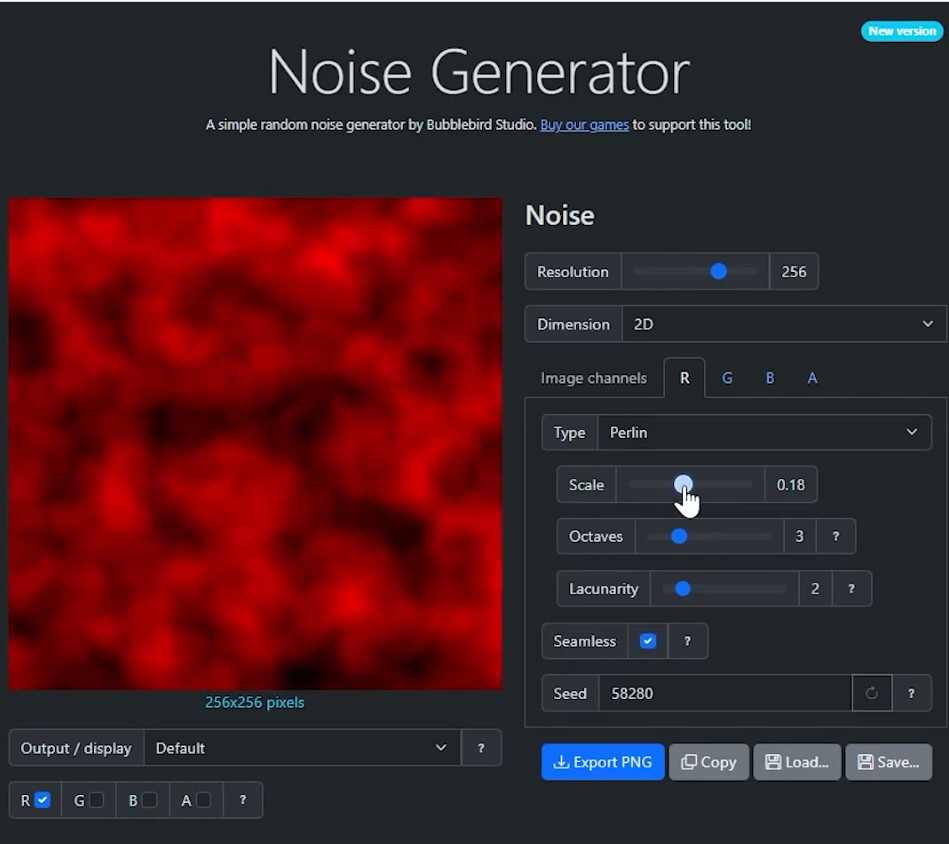
Bubblebird-Studio – Free NoiseGenerator
https://github.com/Bubblebird-Studio/NoiseGenerator
It currently support the following noise models:
Support for Blue Noise is planned.
You can freely use it here: https://noisegen.bubblebirdstudio.com/
-
Free 3DGS Render Addon for Blender 2.0
https://superhivemarket.com/products/3dgs-render-by-kiri-engine
https://github.com/Kiri-Innovation/3dgs-render-blender-addon
https://www.kiriengine.app/blender-addon/3dgs-render
The addon is a full 3DGS editing and rendering suite for Blender.3DGS scans can be created from .OBJ files, or 3DGS .PLY files can be imported as mesh objects, offering two distinct workflows. The created objects can be manipulated, animated and rendered inside Blender. Or Blender can be used as an intermediate editing and painting software – with the results being exportable to other 3DGS software and viewers.
FEATURED POSTS
-
ComfyDock – The Easiest (Free) Way to Safely Run ComfyUI Sessions in a Boxed Container
https://www.reddit.com/r/comfyui/comments/1j2x4qv/comfydock_the_easiest_free_way_to_run_comfyui_in/
ComfyDock is a tool that allows you to easily manage your ComfyUI environments via Docker.
Common Challenges with ComfyUI
- Custom Node Installation Issues: Installing new custom nodes can inadvertently change settings across the whole installation, potentially breaking the environment.
- Workflow Compatibility: Workflows are often tested with specific custom nodes and ComfyUI versions. Running these workflows on different setups can lead to errors and frustration.
- Security Risks: Installing custom nodes directly on your host machine increases the risk of malicious code execution.
How ComfyDock Helps
- Environment Duplication: Easily duplicate your current environment before installing custom nodes. If something breaks, revert to the original environment effortlessly.
- Deployment and Sharing: Workflow developers can commit their environments to a Docker image, which can be shared with others and run on cloud GPUs to ensure compatibility.
- Enhanced Security: Containers help to isolate the environment, reducing the risk of malicious code impacting your host machine.

-
Willem Zwarthoed – Aces gamut in VFX production pdf
https://www.provideocoalition.com/color-management-part-12-introducing-aces/
Local copy:
https://www.slideshare.net/hpduiker/acescg-a-common-color-encoding-for-visual-effects-applications