If you’re serious about AI Agents, this is the guide you’ve been waiting for. It’s packed with everything you need to build powerful AI agents. It follows a very hands-on approach that cuts down your time and avoids the common mistakes most developers make.
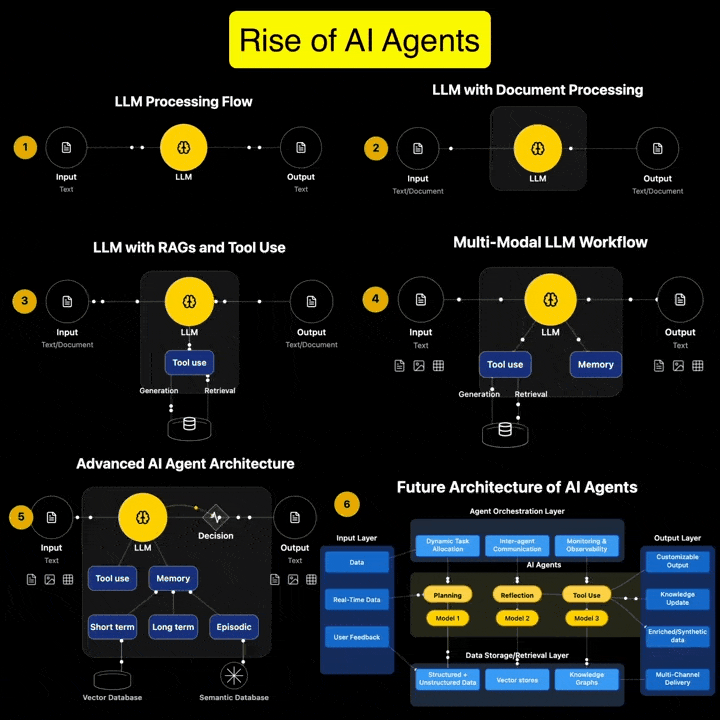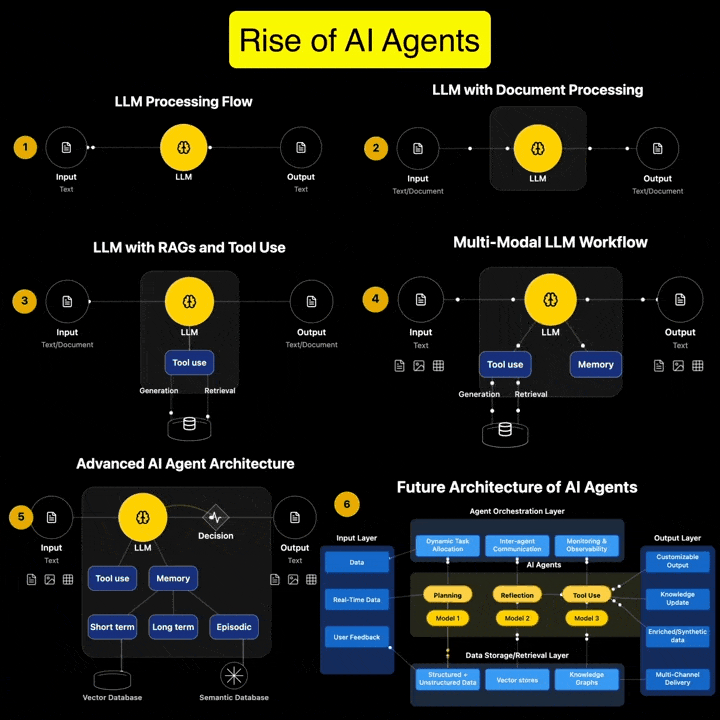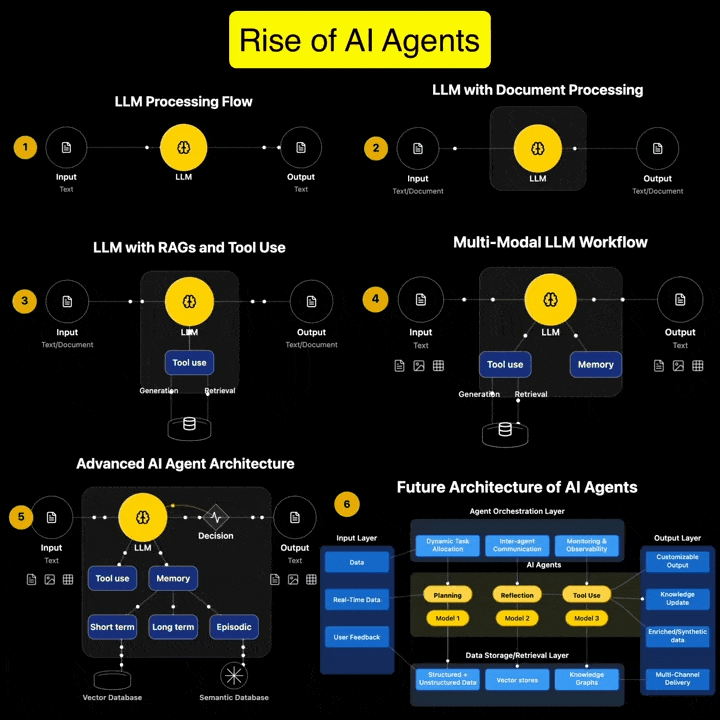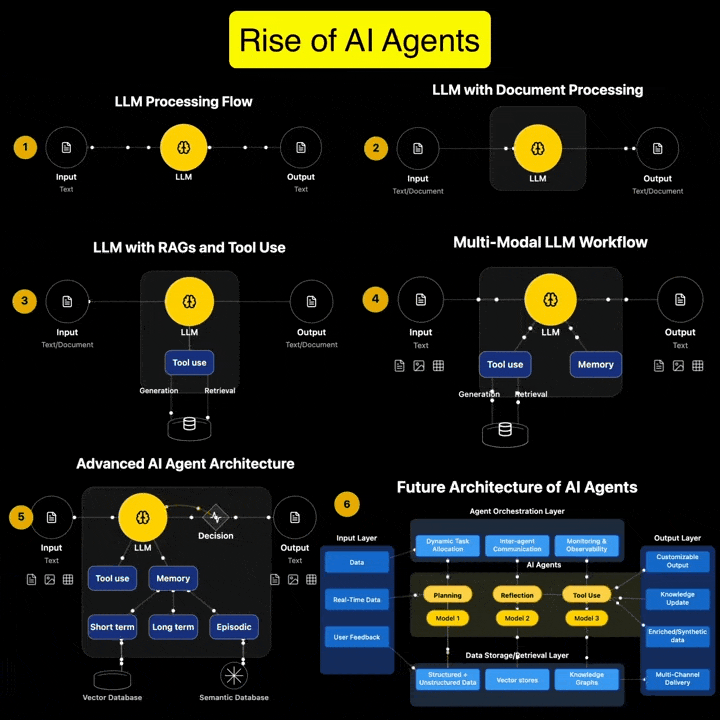
Andreas Horn on AI Agents vs Agentic AI
1. 𝗔𝗜 𝗔𝗴𝗲𝗻𝘁𝘀: 𝗧𝗼𝗼𝗹𝘀 𝘄𝗶𝘁𝗵 𝗔𝘂𝘁𝗼𝗻𝗼𝗺𝘆, 𝗪𝗶𝘁𝗵𝗶𝗻 𝗟𝗶𝗺𝗶𝘁𝘀
➜ AI agents are modular, goal-directed systems that operate within clearly defined boundaries. They’re built to:
* Use tools (APIs, browsers, databases)
* Execute specific, task-oriented workflows
* React to prompts or real-time inputs
* Plan short sequences and return actionable outputs
𝘛𝘩𝘦𝘺’𝘳𝘦 𝘦𝘹𝘤𝘦𝘭𝘭𝘦𝘯𝘵 𝘧𝘰𝘳 𝘵𝘢𝘳𝘨𝘦𝘵𝘦𝘥 𝘢𝘶𝘵𝘰𝘮𝘢𝘵𝘪𝘰𝘯, 𝘭𝘪𝘬𝘦: 𝘊𝘶𝘴𝘵𝘰𝘮𝘦𝘳 𝘴𝘶𝘱𝘱𝘰𝘳𝘵 𝘣𝘰𝘵𝘴, 𝘐𝘯𝘵𝘦𝘳𝘯𝘢𝘭 𝘬𝘯𝘰𝘸𝘭𝘦𝘥𝘨𝘦 𝘴𝘦𝘢𝘳𝘤𝘩, 𝘌𝘮𝘢𝘪𝘭 𝘵𝘳𝘪𝘢𝘨𝘦, 𝘔𝘦𝘦𝘵𝘪𝘯𝘨 𝘴𝘤𝘩𝘦𝘥𝘶𝘭𝘪𝘯𝘨, 𝘊𝘰𝘥𝘦 𝘴𝘶𝘨𝘨𝘦𝘴𝘵𝘪𝘰𝘯𝘴
But even the most advanced are limited by scope. They don’t initiate. They don’t collaborate. They execute what we ask!
2. 𝗔𝗴𝗲𝗻𝘁𝗶𝗰 𝗔𝗜: 𝗔 𝗦𝘆𝘀𝘁𝗲𝗺 𝗼𝗳 𝗦𝘆𝘀𝘁𝗲𝗺𝘀
➜ Agentic AI is an architectural leap. It’s not just one smarter agent — it’s multiple specialized agents working together toward shared goals. These systems exhibit:
* Multi-agent collaboration
* Goal decomposition and role assignment
* Inter-agent communication via memory or messaging
* Persistent context across time and tasks
* Recursive planning and error recovery
* Distributed orchestration and adaptive feedback
Agentic AI systems don’t just follow instructions. They coordinate. They adapt. They manage complexity.
𝘌𝘹𝘢𝘮𝘱𝘭𝘦𝘴 𝘪𝘯𝘤𝘭𝘶𝘥𝘦: 𝘳𝘦𝘴𝘦𝘢𝘳𝘤𝘩 𝘵𝘦𝘢𝘮𝘴 𝘱𝘰𝘸𝘦𝘳𝘦𝘥 𝘣𝘺 𝘢𝘨𝘦𝘯𝘵𝘴, 𝘴𝘮𝘢𝘳𝘵 𝘩𝘰𝘮𝘦 𝘦𝘤𝘰𝘴𝘺𝘴𝘵𝘦𝘮𝘴 𝘰𝘱𝘵𝘪𝘮𝘪𝘻𝘪𝘯𝘨 𝘦𝘯𝘦𝘳𝘨𝘺/𝘴𝘦𝘤𝘶𝘳𝘪𝘵𝘺, 𝘴𝘸𝘢𝘳𝘮𝘴 𝘰𝘧 𝘳𝘰𝘣𝘰𝘵𝘴 𝘪𝘯 𝘭𝘰𝘨𝘪𝘴𝘵𝘪𝘤𝘴 𝘰𝘳 𝘢𝘨𝘳𝘪𝘤𝘶𝘭𝘵𝘶𝘳𝘦 𝘮𝘢𝘯𝘢𝘨𝘪𝘯𝘨 𝘳𝘦𝘢𝘭-𝘵𝘪𝘮𝘦 𝘶𝘯𝘤𝘦𝘳𝘵𝘢𝘪𝘯𝘵𝘺
𝗧𝗵𝗲 𝗖𝗼𝗿𝗲 𝗗𝗶𝗳𝗳𝗲𝗿𝗲𝗻𝗰𝗲?
AI Agents = autonomous tools for single-task execution
Agentic AI = orchestrated ecosystems for workflow-level intelligence

Next, here 𝗮𝗿𝗲 𝘁𝗵𝗲 𝘁𝗼𝗽 10 𝗞𝗲𝘆 𝗧𝗮𝗸𝗲𝗮𝘄𝗮𝘆𝘀 𝗳𝗿𝗼𝗺 𝗢𝗽𝗲𝗻𝗔𝗜’𝘀 𝗚𝘂𝗶𝗱𝗲:
➜ Agents = Autonomy: Unlike simple chatbots, agents are autonomous systems that can handle complex tasks, make decisions, and manage workflows without constant human input. They go beyond pre-programmed responses.
➜ When Should You Build an Agent? If your task requires nuanced decision-making or complex data handling, like fraud detection, claims processing, or automated content moderation, building an agent is your solution.
➜ Key Components of an Agent: Every agent relies on three crucial elements: a reasoning model (for decision-making), tools (for action), and instructions (for guiding behavior). Ensure these components are designed robustly for efficiency.
➜ Tools Empower Agents: Tools allow agents to interact with the external world, whether querying databases, making API calls, or sending emails. They significantly expand an agent’s capabilities beyond just processing language.
➜ Clear Instructions Lead to Success: Avoid ambiguity in the instructions. The more specific and detailed your instructions are, the better the agent will perform, especially for complex tasks or edge cases.
➜ Start Simple, Then Scale: Start with a single-agent system to solve one task. Only expand to multi-agent systems when the complexity of the problem demands it. Managers can supervise multiple agents but start small for better control.
➜ Guardrails Are Essential: Build safety layers into your agents. Ensure they operate within desired parameters by setting up guardrails to prevent risky or undesirable behaviors—especially when dealing with sensitive data or high-stakes tasks.
➜ Incorporate Human Oversight: For high-risk operations, include human oversight. A “human-in-the-loop” approach allows for corrective actions before mistakes or undesirable outcomes occur, ensuring your agent stays on track.
➜ Iterate and Improve: Don’t expect perfection at first. Launch small, validate with real users, and continuously improve. Agents evolve and become more valuable with each iteration as they learn and adapt to new tasks.
𝗕𝘂𝗶𝗹𝗱𝗶𝗻𝗴 𝗔𝗜 𝗮𝗴𝗲𝗻𝘁𝘀 𝗶𝘀 𝗻𝗼 𝗹𝗼𝗻𝗴𝗲𝗿 𝗮 𝗳𝘂𝘁𝘂𝗿𝗲 𝗰𝗼𝗻𝗰𝗲𝗽𝘁—𝗶𝘁’𝘀 𝘁𝗵𝗲 𝗸𝗲𝘆 𝘁𝗼 𝗱𝗿𝗶𝘃𝗶𝗻𝗴 𝗶𝗻𝗻𝗼𝘃𝗮𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻 𝗮𝗻𝗱 𝗰𝗿𝗲𝗮𝘁𝗶𝗻𝗴 𝘀𝗰𝗮𝗹𝗮𝗯𝗹𝗲 𝘀𝗼𝗹𝘂𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻𝘀 𝘁𝗼𝗱𝗮𝘆.
➜ 𝗔𝗜 𝗔𝗴𝗲𝗻𝘁𝘀 𝗗𝗿𝗶𝘃𝗲 𝗕𝘂𝘀𝗶𝗻𝗲𝘀𝘀 𝗧𝗿𝗮𝗻𝘀𝗳𝗼𝗿𝗺𝗮𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻: AI agents are no longer just a tech trend; they are at the heart of reshaping business operations. The real challenge is how quickly companies can adapt their processes to leverage AI-driven automation and decision-making.
➜ 𝗖𝘂𝘀𝘁𝗼𝗺𝗶𝘇𝗮𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻 𝗳𝗼𝗿 𝗜𝗻𝗱𝘂𝘀𝘁𝗿𝘆-𝗦𝗽𝗲𝗰𝗶𝗳𝗶𝗰 𝗡𝗲𝗲𝗱𝘀: AI agents need to be tailored to the unique challenges of different industries. Whether it’s healthcare, finance, or manufacturing, customizing AI agents to solve specific industry problems can unlock higher efficiency and value.
➜ 𝗦𝘁𝗿𝗼𝗻𝗴 𝗚𝗼𝘃𝗲𝗿𝗻𝗮𝗻𝗰𝗲 𝗙𝗿𝗮𝗺𝗲𝘄𝗼𝗿𝗸𝘀 𝗔𝗿𝗲 𝗘𝘀𝘀𝗲𝗻𝘁𝗶𝗮𝗹: Unlike traditional automation, AI agents require robust governance to ensure ethical behavior and compliance with regulations. Businesses need to establish clear policies to mitigate risks and build trust in AI systems.
➜ 𝗖𝗼𝗹𝗹𝗮𝗯𝗼𝗿𝗮𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻 𝗕𝗲𝘁𝘄𝗲𝗲𝗻 𝗛𝘂𝗺𝗮𝗻𝘀 𝗮𝗻𝗱 𝗔𝗜: AI agents should enhance, not replace, human work. The real power lies in how AI agents can work alongside human expertise to free up employees for higher-level strategic tasks, making businesses more agile and competitive.
➜ 𝗗𝗮𝘁𝗮 𝗜𝗻𝘁𝗲𝗴𝗿𝗮𝘁𝗶𝗼𝗻 𝗮𝗻𝗱 𝗦𝗰𝗮𝗹𝗮𝗯𝗶𝗹𝗶𝘁𝘆 𝗔𝗿𝗲 𝗖𝗿𝗶𝘁𝗶𝗰𝗮𝗹: For AI agents to succeed, they must seamlessly integrate with existing data systems. Companies need to invest in scalable data infrastructure to handle the growing complexity of AI systems, ensuring they can expand as needed across various business functions.




