BREAKING NEWS
LATEST POSTS
-
Nike by Phil Schiller – The job is not done until the job is done
- Our business is change.
- We’re on offense. All the time.
- Perfect results count — not a perfect process. Break the rules: fight the law.
- This is as much about battle as about business.
- Assume nothing. Make sure people keep their promises. Push yourselves push others. Stretch the possible.
- Live off the land.
- Your job isn’t done until the job is done.
- Dangers
Bureaucracy
Personal ambition
Energy takers vs. energy givers
Knowing our weaknesses
Don’t get too many things on the platter - It won’t be pretty.
- If we do the right things we’ll make money damn near automatic.
-
How Good Is ChatGPT at Coding, Really?
https://spectrum.ieee.org/chatgpt-for-coding
ChatGPT has not been exposed yet to new problems and solutions. It lacks the critical thinking skills of a human and can only address problems it has previously encountered. This could explain why it is so much better at addressing older coding problems than newer ones.
“ChatGPT may generate incorrect code because it does not understand the meaning of algorithm problems, thus, simple error feedback information is not enough,”
-
Inside the Health Crisis of a Texas Bitcoin Town
https://time.com/6982015/bitcoin-mining-texas-health
This study explores the adverse effects of a Bitcoin mining facility on the health and environment of Granbury, Texas. Residents report significant disturbances due to noise pollution, resulting in sever vascular circulatory issues, migraines, sleep issues, and a decrease in local wildlife. Despite efforts to mitigate noise through sound barriers, the community continues to experience reduced quality of life. The rapid expansion of Bitcoin mining in Texas, driven by favorable political conditions, underscores the need for regulatory measures to balance economic benefits with community well-being.
-
Magnific.ai Relight – change the entire lighting of a scene
It’s a new Magnific spell that allows you to change the entire lighting of a scene and, optionally, the background with just:
1/ A prompt OR
2/ A reference image OR
3/ A light map (drawing your own lights)https://x.com/javilopen/status/1805274155065176489
-
Become a Master Negotiator Using These 7 Practical Negotiation Techniques
https://www.readtheprofile.com/p/negotiation-techniques
- Discover the other person’s need
- Get to ‘no’ fast
- Practice ‘mirroring’ and ‘labeling’
- Lead your counterpart to your desired destination
- Appeal to your counterpart’s emotions
- Maintain emotional control using the ‘Late Night FM DJ voice’
- Let your counterpart give you the answers to the test
Bonus video
FEATURED POSTS
-
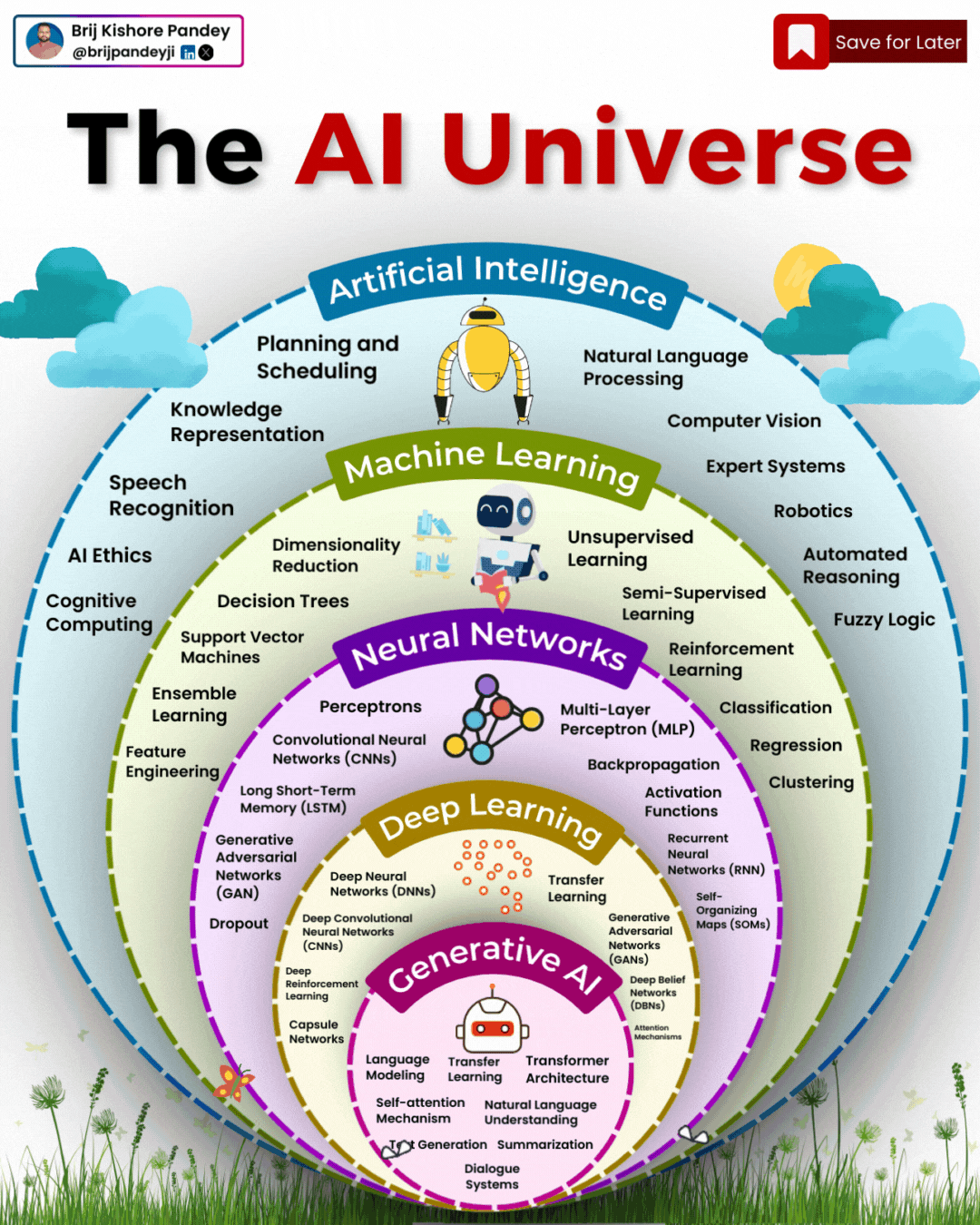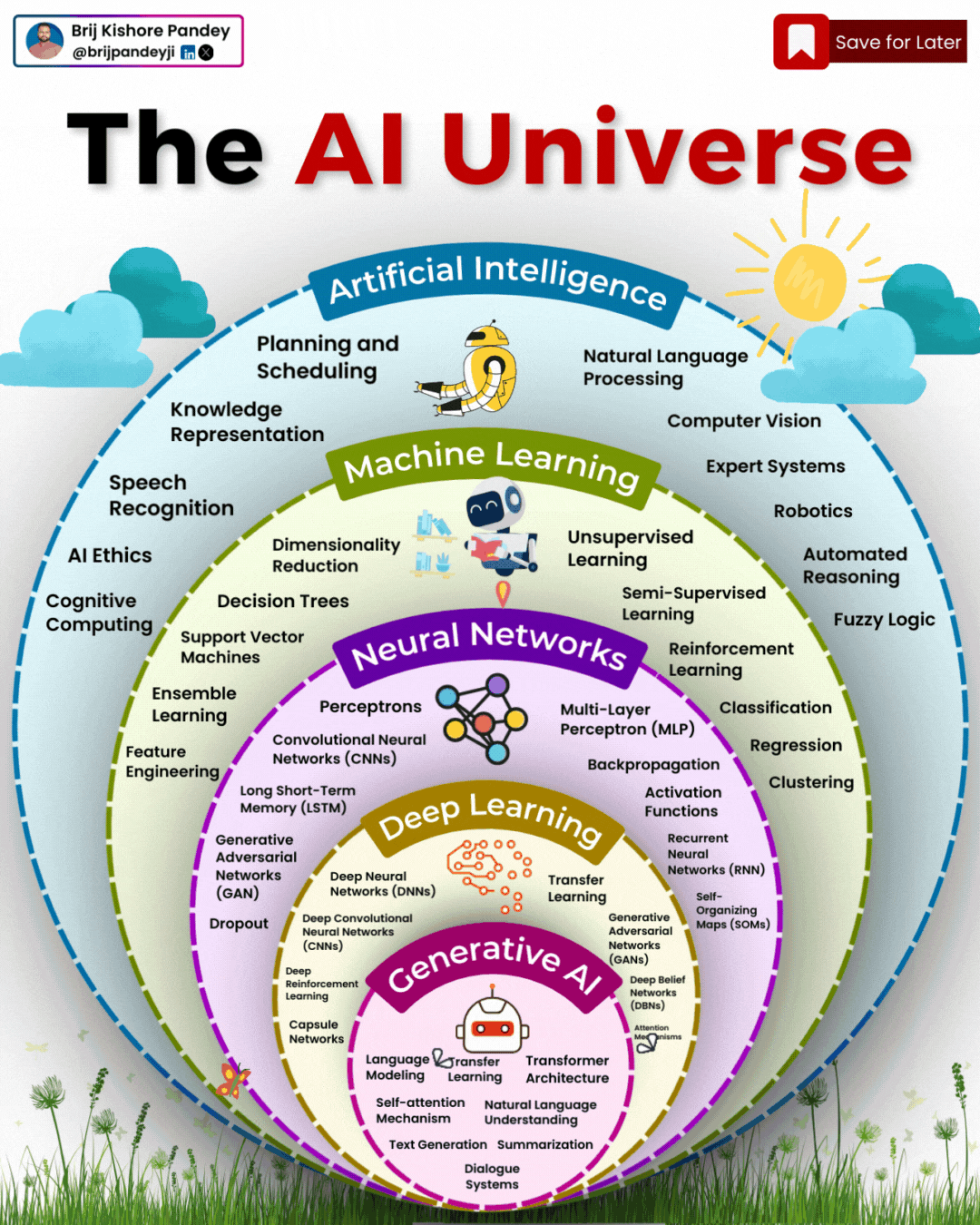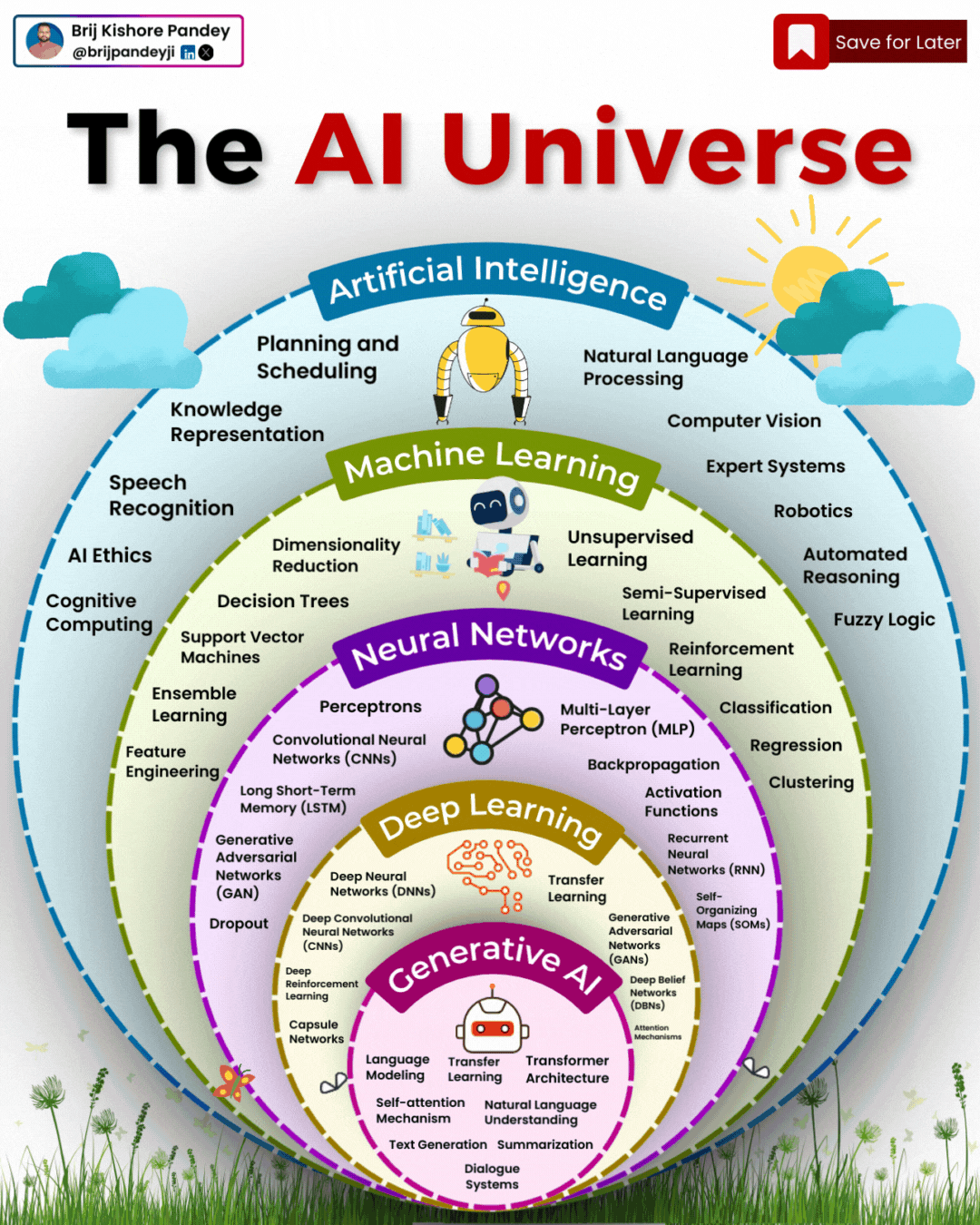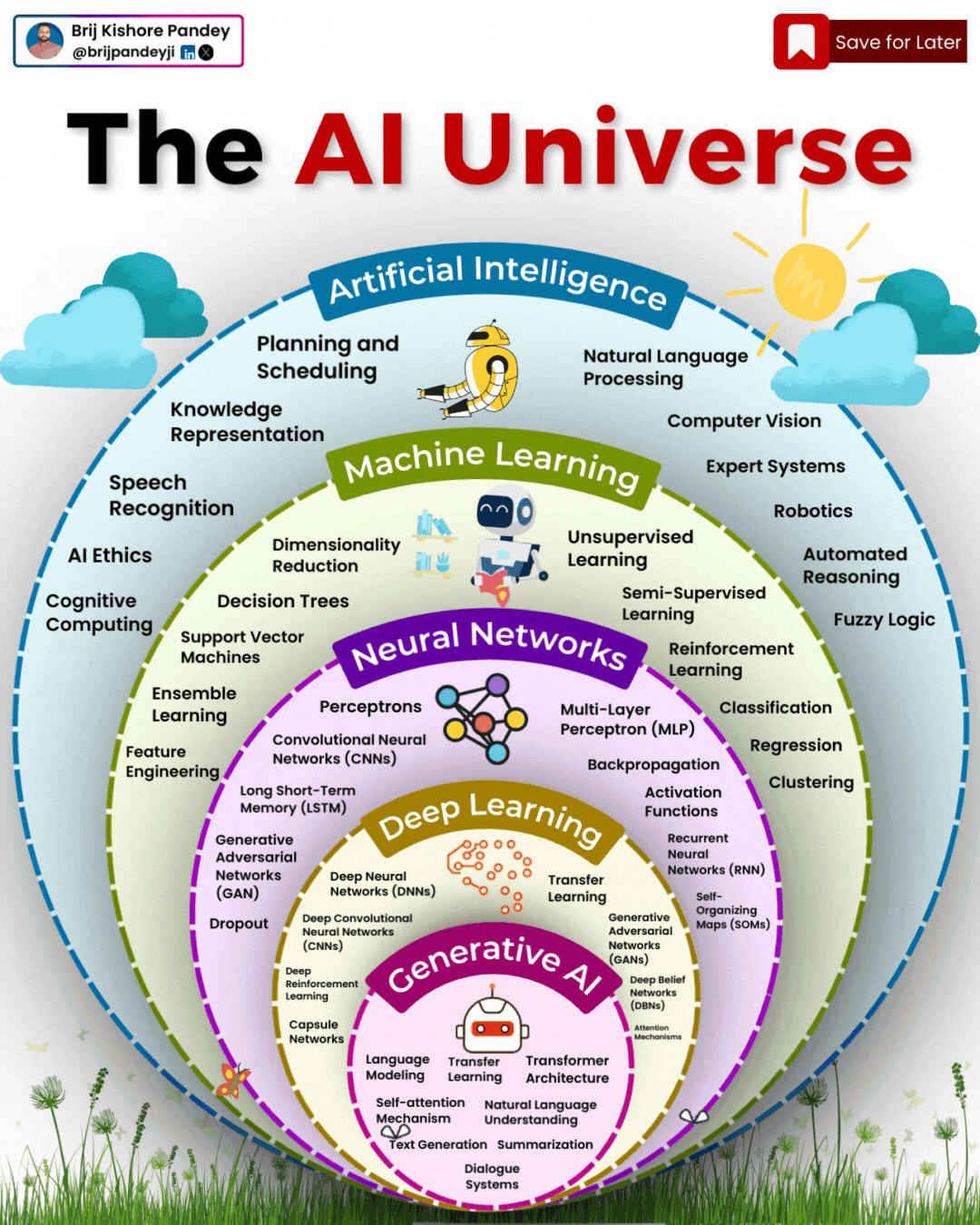
Types of AI Explained in a few Minutes – AI Glossary
1️⃣ 𝗔𝗿𝘁𝗶𝗳𝗶𝗰𝗶𝗮𝗹 𝗜𝗻𝘁𝗲𝗹𝗹𝗶𝗴𝗲𝗻𝗰𝗲 (𝗔𝗜) – The broadest category, covering automation, reasoning, and decision-making. Early AI was rule-based, but today, it’s mainly data-driven.
2️⃣ 𝗠𝗮𝗰𝗵𝗶𝗻𝗲 𝗟𝗲𝗮𝗿𝗻𝗶𝗻𝗴 (𝗠𝗟) – AI that learns patterns from data without explicit programming. Includes decision trees, clustering, and regression models.
3️⃣ 𝗡𝗲𝘂𝗿𝗮𝗹 𝗡𝗲𝘁𝘄𝗼𝗿𝗸𝘀 (𝗡𝗡) – A subset of ML, inspired by the human brain, designed for pattern recognition and feature extraction.
4️⃣ 𝗗𝗲𝗲𝗽 𝗟𝗲𝗮𝗿𝗻𝗶𝗻𝗴 (𝗗𝗟) – Multi-layered neural networks that drives a lot of modern AI advancements, for example enabling image recognition, speech processing, and more.
5️⃣ 𝗧𝗿𝗮𝗻𝘀𝗳𝗼𝗿𝗺𝗲𝗿𝘀 – A revolutionary deep learning architecture introduced by Google in 2017 that allows models to understand and generate language efficiently.
6️⃣ 𝗚𝗲𝗻𝗲𝗿𝗮𝘁𝗶𝘃𝗲 𝗔𝗜 (𝗚𝗲𝗻𝗔𝗜) – AI that doesn’t just analyze data—it creates. From text and images to music and code, this layer powers today’s most advanced AI models.
7️⃣ 𝗚𝗲𝗻𝗲𝗿𝗮𝘁𝗶𝘃𝗲 𝗣𝗿𝗲-𝗧𝗿𝗮𝗶𝗻𝗲𝗱 𝗧𝗿𝗮𝗻𝘀𝗳𝗼𝗿𝗺𝗲𝗿𝘀 (𝗚𝗣𝗧) – A specific subset of Generative AI that uses transformers for text generation.
8️⃣ 𝗟𝗮𝗿𝗴𝗲 𝗟𝗮𝗻𝗴𝘂𝗮𝗴𝗲 𝗠𝗼𝗱𝗲𝗹𝘀 (𝗟𝗟𝗠) – Massive AI models trained on extensive datasets to understand and generate human-like language.
9️⃣ 𝗚𝗣𝗧-4 – One of the most advanced LLMs, built on transformer architecture, trained on vast datasets to generate human-like responses.
🔟 𝗖𝗵𝗮𝘁𝗚𝗣𝗧 – A specific application of GPT-4, optimized for conversational AI and interactive use.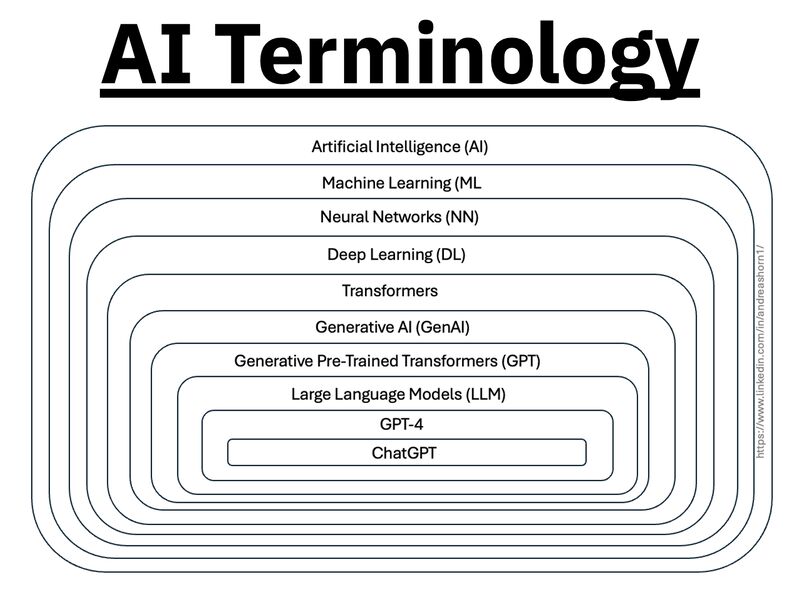
-
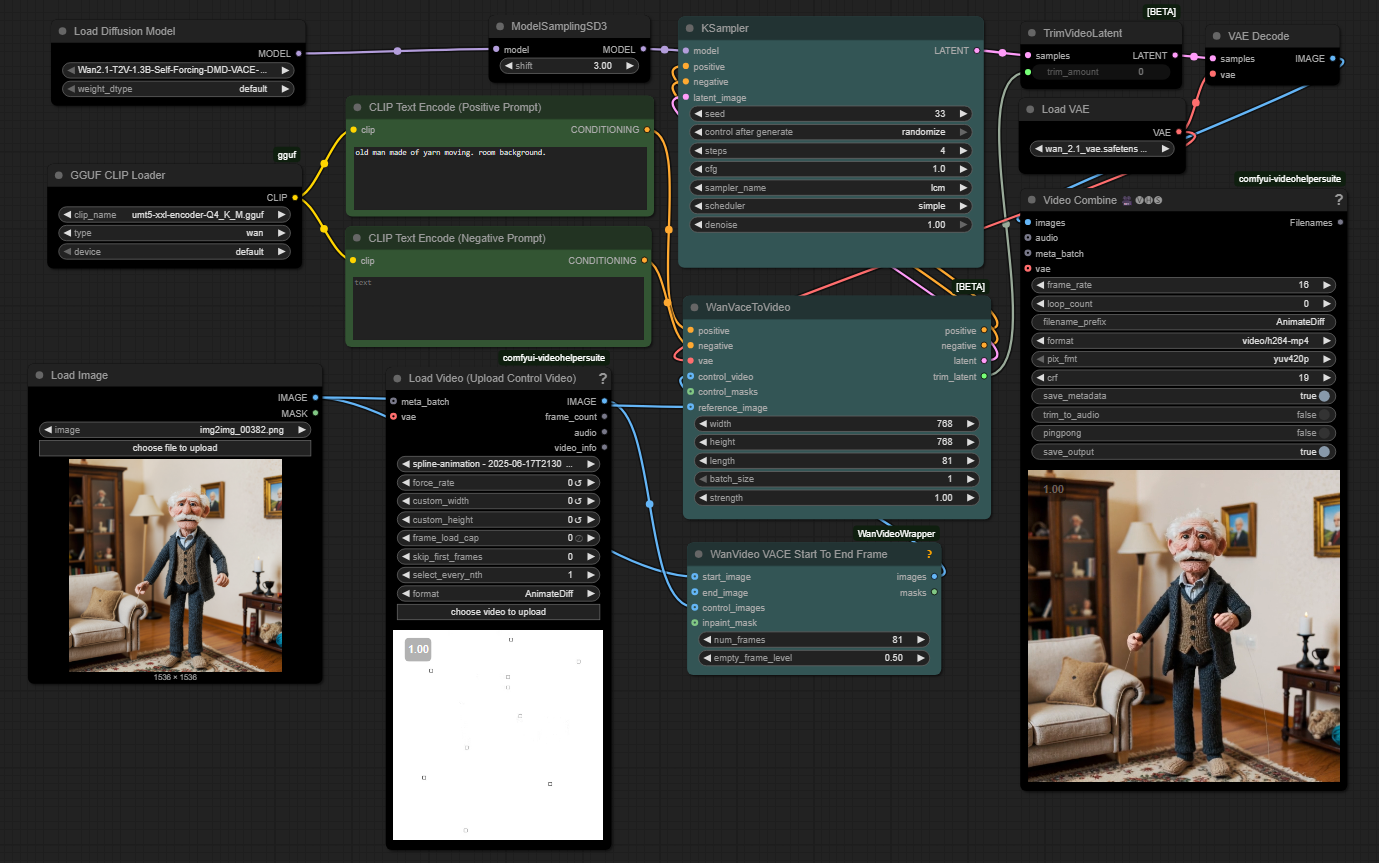
WhatDreamsCost Spline-Path-Control – Create motion controls for ComfyUI
https://github.com/WhatDreamsCost/Spline-Path-Control
https://whatdreamscost.github.io/Spline-Path-Control/
https://github.com/WhatDreamsCost/Spline-Path-Control/tree/main/example_workflows
Spline Path Control is a simple tool designed to make it easy to create motion controls. It allows you to create and animate shapes that follow splines, and then export the result as a
.webmvideo file.
This project was created to simplify the process of generating control videos for tools like VACE. Use it to control the motion of anything (camera movement, objects, humans etc) all without extra prompting.- Multi-Spline Editing: Create multiple, independent spline paths
- Easy To Use Controls: Quickly edit splines and points
- Full Control of Splines and Shapes:
- Start Frame: Set a delay before a spline’s animation begins.
- Duration: Control the speed of the shape along its path.
- Easing: Apply
Linear,Ease-in,Ease-out, andEase-in-outfunctions for smooth acceleration and deceleration. - Tension: Adjust the “curviness” of the spline path.
- Shape Customization: Change the shape (circle, square, triangle), size, fill color, and border.
- Reference Images: Drag and drop or upload a background image to trace paths over an existing image.
- WebM Export: Export your animation with a white background, perfect for use as a control video in VACE.
-
Scientists claim to have discovered ‘new colour’ no one has seen before: Olo
https://www.bbc.com/news/articles/clyq0n3em41o
By stimulating specific cells in the retina, the participants claim to have witnessed a blue-green colour that scientists have called “olo”, but some experts have said the existence of a new colour is “open to argument”.
The findings, published in the journal Science Advances on Friday, have been described by the study’s co-author, Prof Ren Ng from the University of California, as “remarkable”.
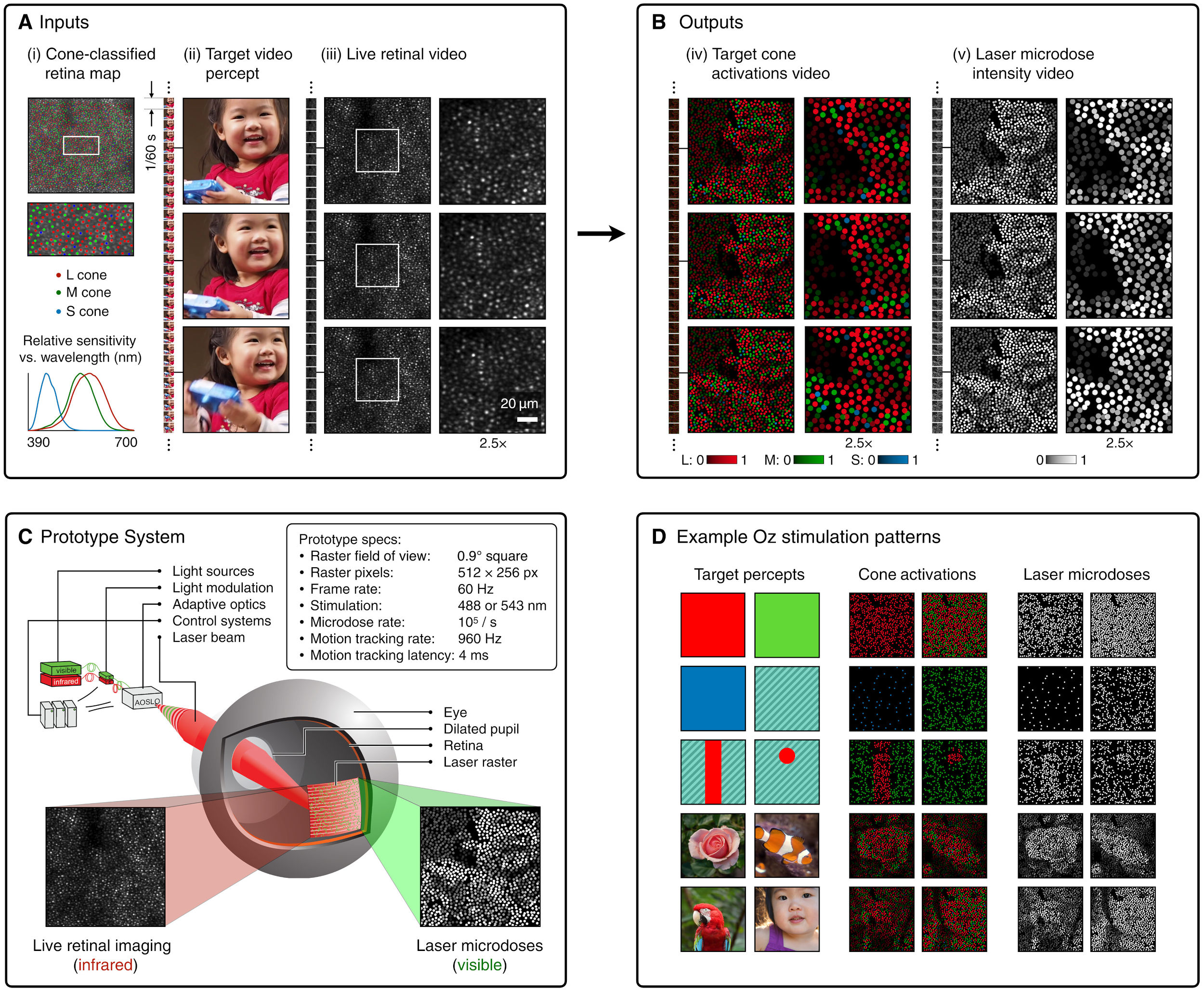
(A) System inputs. (i) Retina map of 103 cone cells preclassified by spectral type (7). (ii) Target visual percept (here, a video of a child, see movie S1 at 1:04). (iii) Infrared cellular-scale imaging of the retina with 60-frames-per-second rolling shutter. Fixational eye movement is visible over the three frames shown.
(B) System outputs. (iv) Real-time per-cone target activation levels to reproduce the target percept, computed by: extracting eye motion from the input video relative to the retina map; identifying the spectral type of every cone in the field of view; computing the per-cone activation the target percept would have produced. (v) Intensities of visible-wavelength 488-nm laser microdoses at each cone required to achieve its target activation level.
(C) Infrared imaging and visible-wavelength stimulation are physically accomplished in a raster scan across the retinal region using AOSLO. By modulating the visible-wavelength beam’s intensity, the laser microdoses shown in (v) are delivered. Drawing adapted with permission [Harmening and Sincich (54)].
(D) Examples of target percepts with corresponding cone activations and laser microdoses, ranging from colored squares to complex imagery. Teal-striped regions represent the color “olo” of stimulating only M cones.
-
Rendering – BRDF – Bidirectional reflectance distribution function
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bidirectional_reflectance_distribution_function
The bidirectional reflectance distribution function is a four-dimensional function that defines how light is reflected at an opaque surface
http://www.cs.ucla.edu/~zhu/tutorial/An_Introduction_to_BRDF-Based_Lighting.pdf
In general, when light interacts with matter, a complicated light-matter dynamic occurs. This interaction depends on the physical characteristics of the light as well as the physical composition and characteristics of the matter.
That is, some of the incident light is reflected, some of the light is transmitted, and another portion of the light is absorbed by the medium itself.
A BRDF describes how much light is reflected when light makes contact with a certain material. Similarly, a BTDF (Bi-directional Transmission Distribution Function) describes how much light is transmitted when light makes contact with a certain material
http://www.cs.princeton.edu/~smr/cs348c-97/surveypaper.html
It is difficult to establish exactly how far one should go in elaborating the surface model. A truly complete representation of the reflective behavior of a surface might take into account such phenomena as polarization, scattering, fluorescence, and phosphorescence, all of which might vary with position on the surface. Therefore, the variables in this complete function would be:
incoming and outgoing angle incoming and outgoing wavelength incoming and outgoing polarization (both linear and circular) incoming and outgoing position (which might differ due to subsurface scattering) time delay between the incoming and outgoing light ray






