COMPOSITION
-
SlowMoVideo – How to make a slow motion shot with the open source program
Read more: SlowMoVideo – How to make a slow motion shot with the open source programhttp://slowmovideo.granjow.net/
slowmoVideo is an OpenSource program that creates slow-motion videos from your footage.
Slow motion cinematography is the result of playing back frames for a longer duration than they were exposed. For example, if you expose 240 frames of film in one second, then play them back at 24 fps, the resulting movie is 10 times longer (slower) than the original filmed event….
Film cameras are relatively simple mechanical devices that allow you to crank up the speed to whatever rate the shutter and pull-down mechanism allow. Some film cameras can operate at 2,500 fps or higher (although film shot in these cameras often needs some readjustment in postproduction). Video, on the other hand, is always captured, recorded, and played back at a fixed rate, with a current limit around 60fps. This makes extreme slow motion effects harder to achieve (and less elegant) on video, because slowing down the video results in each frame held still on the screen for a long time, whereas with high-frame-rate film there are plenty of frames to fill the longer durations of time. On video, the slow motion effect is more like a slide show than smooth, continuous motion.
One obvious solution is to shoot film at high speed, then transfer it to video (a case where film still has a clear advantage, sorry George). Another possibility is to cross dissolve or blur from one frame to the next. This adds a smooth transition from one still frame to the next. The blur reduces the sharpness of the image, and compared to slowing down images shot at a high frame rate, this is somewhat of a cheat. However, there isn’t much you can do about it until video can be recorded at much higher rates. Of course, many film cameras can’t shoot at high frame rates either, so the whole super-slow-motion endeavor is somewhat specialized no matter what medium you are using. (There are some high speed digital cameras available now that allow you to capture lots of digital frames directly to your computer, so technology is starting to catch up with film. However, this feature isn’t going to appear in consumer camcorders any time soon.)
DESIGN
-
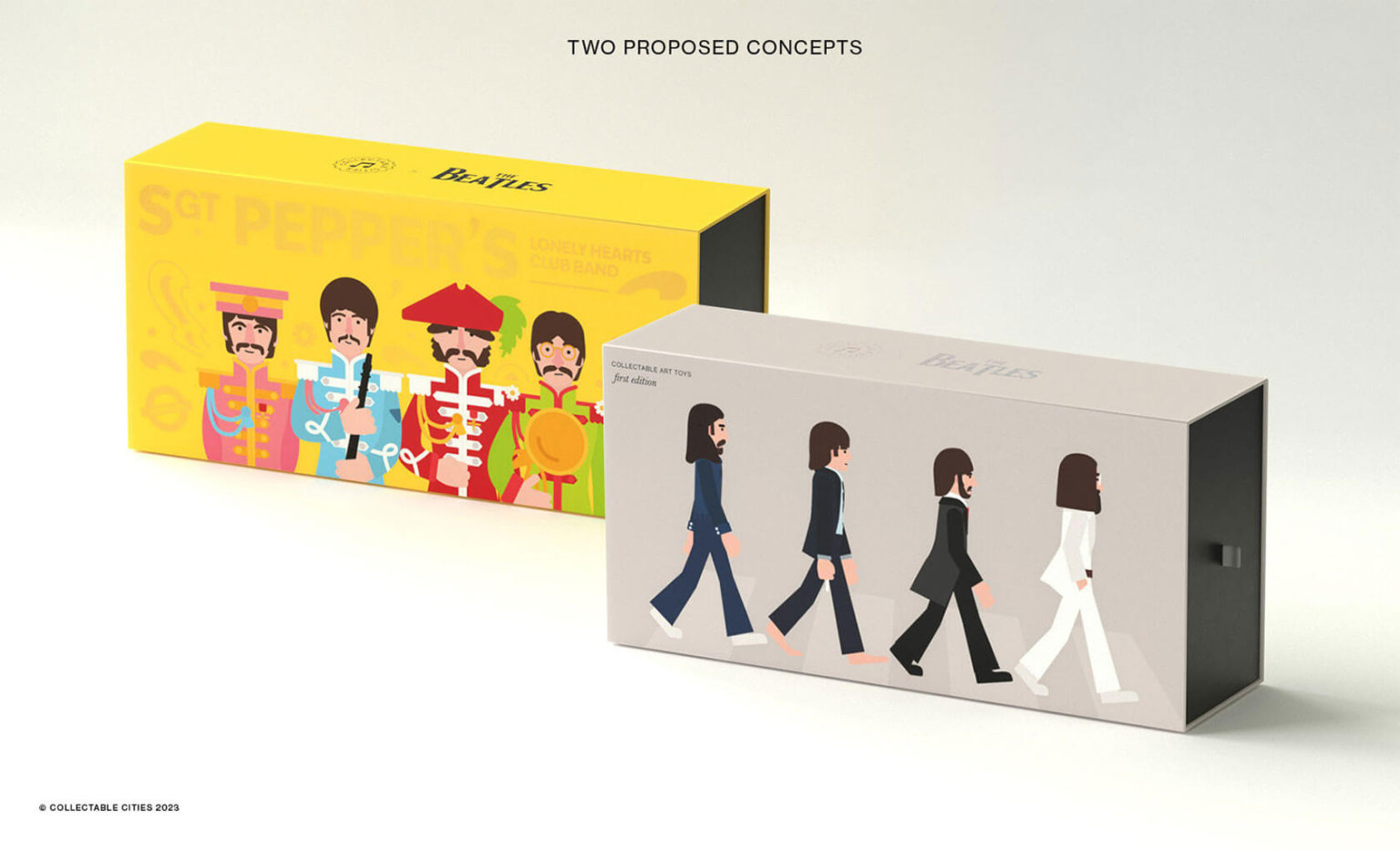
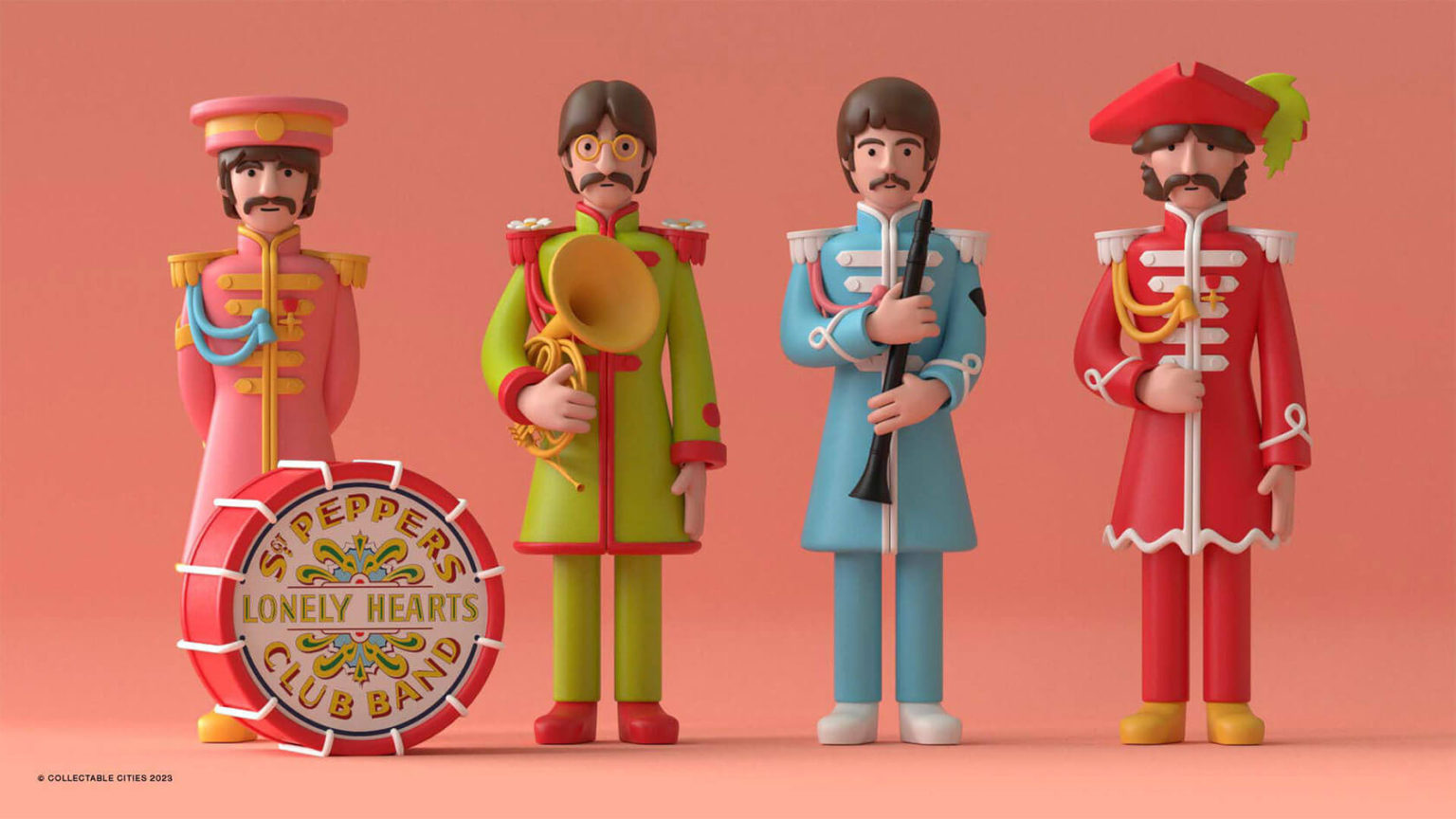
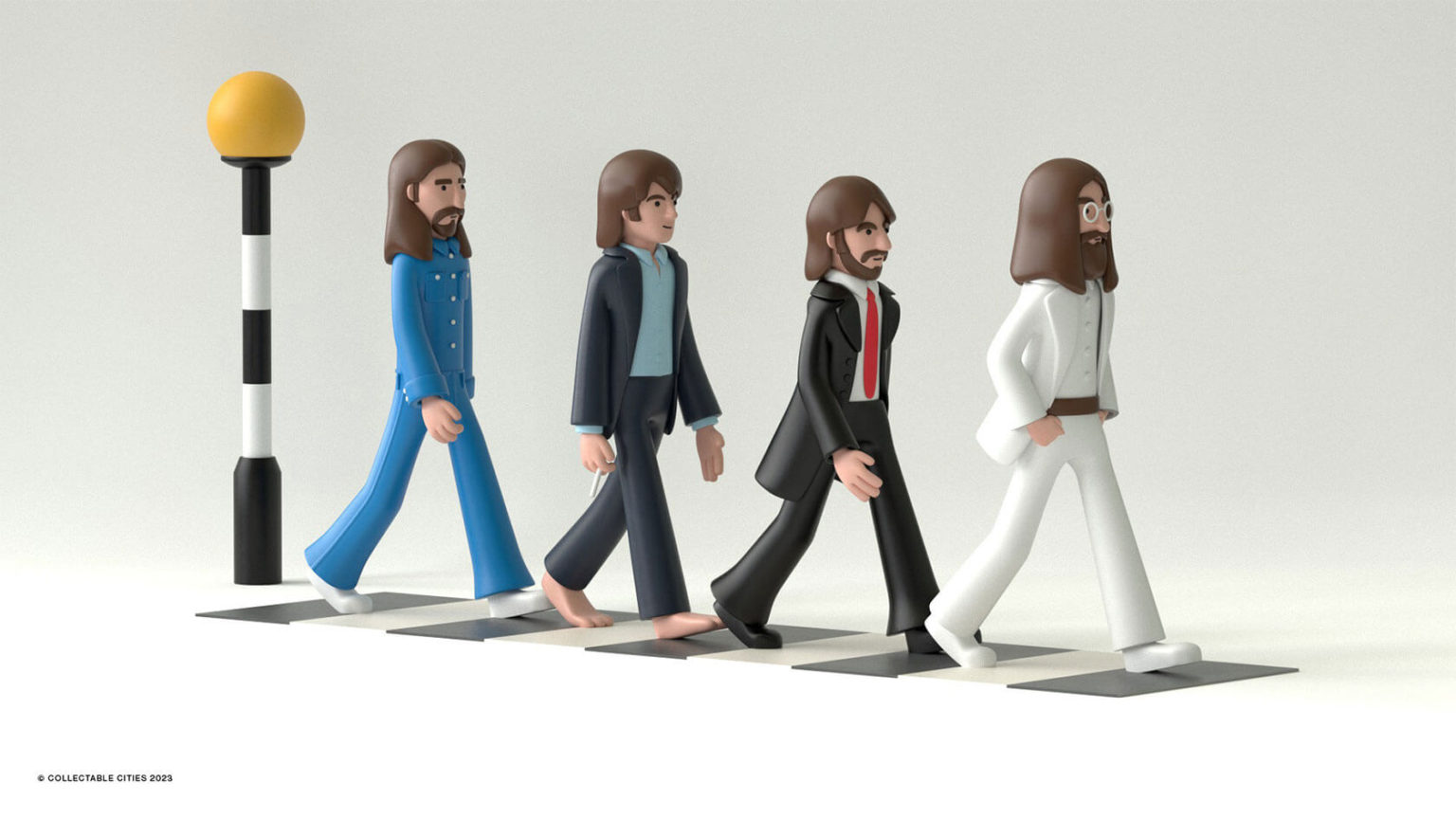
Creative duo Joseph Lattimer and Caitlin Derer Creates Absolutely Amazing The Beatles Collectable Toys
Read more: Creative duo Joseph Lattimer and Caitlin Derer Creates Absolutely Amazing The Beatles Collectable Toyshttps://designyoutrust.com/2024/11/artist-duo-creates-absolutely-amazing-the-beatles-collectable-toys



COLOR
-
The Maya civilization and the color blue
Read more: The Maya civilization and the color blueMaya blue is a highly unusual pigment because it is a mix of organic indigo and an inorganic clay mineral called palygorskite.
Echoing the color of an azure sky, the indelible pigment was used to accentuate everything from ceramics to human sacrifices in the Late Preclassic period (300 B.C. to A.D. 300).
A team of researchers led by Dean Arnold, an adjunct curator of anthropology at the Field Museum in Chicago, determined that the key to Maya blue was actually a sacred incense called copal.
By heating the mixture of indigo, copal and palygorskite over a fire, the Maya produced the unique pigment, he reported at the time.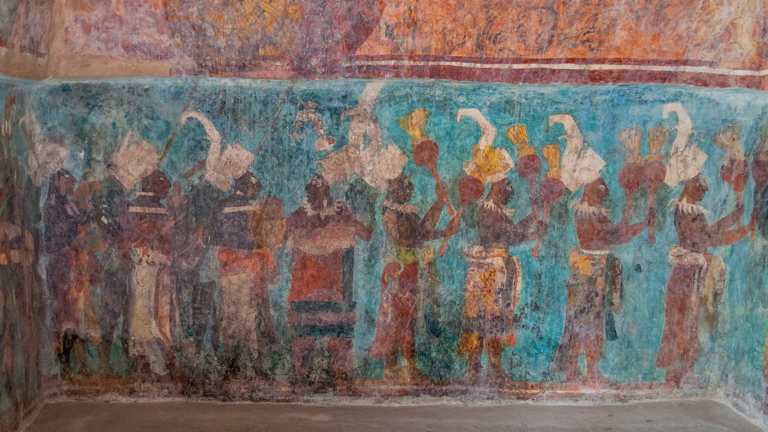
-
HDR and Color
Read more: HDR and Colorhttps://www.soundandvision.com/content/nits-and-bits-hdr-and-color
In HD we often refer to the range of available colors as a color gamut. Such a color gamut is typically plotted on a two-dimensional diagram, called a CIE chart, as shown in at the top of this blog. Each color is characterized by its x/y coordinates.
Good enough for government work, perhaps. But for HDR, with its higher luminance levels and wider color, the gamut becomes three-dimensional.
For HDR the color gamut therefore becomes a characteristic we now call the color volume. It isn’t easy to show color volume on a two-dimensional medium like the printed page or a computer screen, but one method is shown below. As the luminance becomes higher, the picture eventually turns to white. As it becomes darker, it fades to black. The traditional color gamut shown on the CIE chart is simply a slice through this color volume at a selected luminance level, such as 50%.
Three different color volumes—we still refer to them as color gamuts though their third dimension is important—are currently the most significant. The first is BT.709 (sometimes referred to as Rec.709), the color gamut used for pre-UHD/HDR formats, including standard HD.
The largest is known as BT.2020; it encompasses (roughly) the range of colors visible to the human eye (though ET might find it insufficient!).
Between these two is the color gamut used in digital cinema, known as DCI-P3.
sRGB
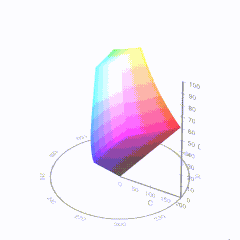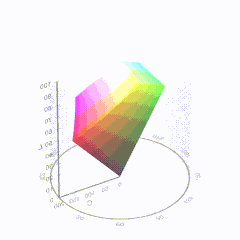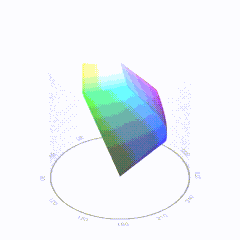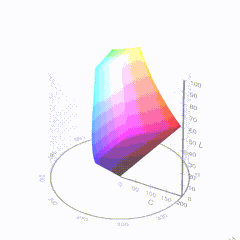
D65
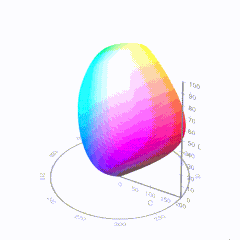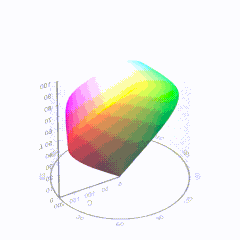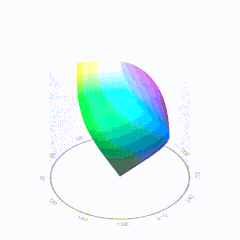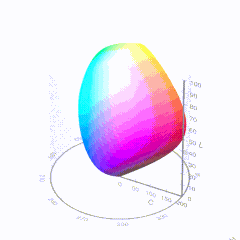
-
SecretWeapons MixBox – a practical library for paint-like digital color mixing
Read more: SecretWeapons MixBox – a practical library for paint-like digital color mixingInternally, Mixbox treats colors as real-life pigments using the Kubelka & Munk theory to predict realistic color behavior.
https://scrtwpns.com/mixbox/painter/
https://scrtwpns.com/mixbox.pdf
https://github.com/scrtwpns/mixbox
https://scrtwpns.com/mixbox/docs/
LIGHTING
-
Insta360-Research-Team DiT360 – High-Fidelity Panoramic Image Generation via Hybrid Training
Read more: Insta360-Research-Team DiT360 – High-Fidelity Panoramic Image Generation via Hybrid Traininghttps://github.com/Insta360-Research-Team/DiT360
DiT360 is a framework for high-quality panoramic image generation, leveraging both perspective and panoramic data in a hybrid training scheme. It adopts a two-level strategy—image-level cross-domain guidance and token-level hybrid supervision—to enhance perceptual realism and geometric fidelity.

-
Romain Chauliac – LightIt a lighting script for Maya and Arnold
Read more: Romain Chauliac – LightIt a lighting script for Maya and ArnoldLightIt is a script for Maya and Arnold that will help you and improve your lighting workflow.
Thanks to preset studio lighting components (lights, backdrop…), high quality studio scenes and HDRI library manager.https://www.artstation.com/artwork/393emJ
-
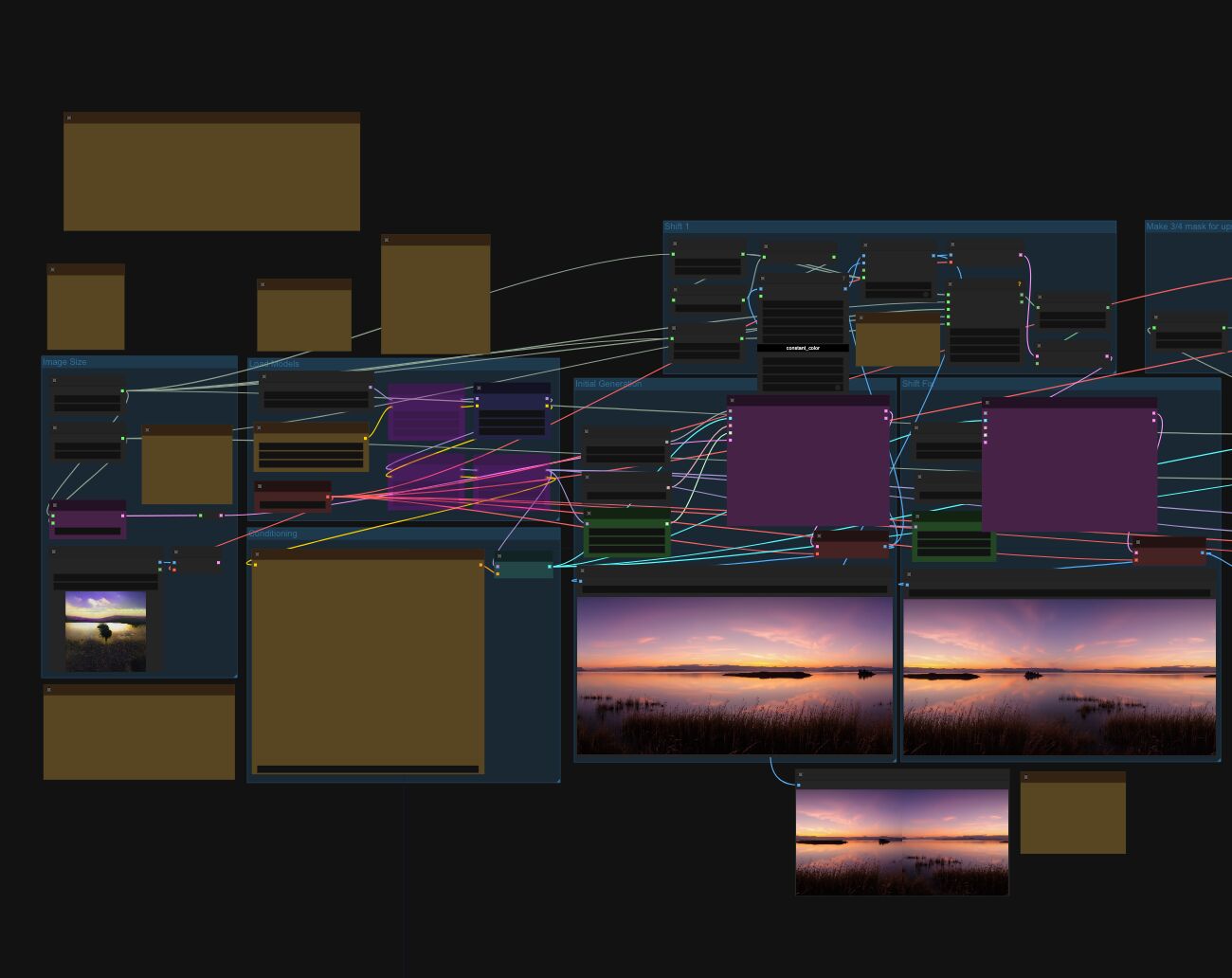
Arto T. – A workflow for creating photorealistic, equirectangular 360° panoramas in ComfyUI using Flux
Read more: Arto T. – A workflow for creating photorealistic, equirectangular 360° panoramas in ComfyUI using Fluxhttps://civitai.com/models/735980/flux-equirectangular-360-panorama
https://civitai.com/models/745010?modelVersionId=833115
The trigger phrase is “equirectangular 360 degree panorama”. I would avoid saying “spherical projection” since that tends to result in non-equirectangular spherical images.
Image resolution should always be a 2:1 aspect ratio. 1024 x 512 or 1408 x 704 work quite well and were used in the training data. 2048 x 1024 also works.
I suggest using a weight of 0.5 – 1.5. If you are having issues with the image generating too flat instead of having the necessary spherical distortion, try increasing the weight above 1, though this could negatively impact small details of the image. For Flux guidance, I recommend a value of about 2.5 for realistic scenes.
8-bit output at the moment

-
9 Best Hacks to Make a Cinematic Video with Any Camera
Read more: 9 Best Hacks to Make a Cinematic Video with Any Camerahttps://www.flexclip.com/learn/cinematic-video.html
- Frame Your Shots to Create Depth
- Create Shallow Depth of Field
- Avoid Shaky Footage and Use Flexible Camera Movements
- Properly Use Slow Motion
- Use Cinematic Lighting Techniques
- Apply Color Grading
- Use Cinematic Music and SFX
- Add Cinematic Fonts and Text Effects
- Create the Cinematic Bar at the Top and the Bottom

COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
-
Python and TCL: Tips and Tricks for Foundry Nuke
-
Steven Stahlberg – Perception and Composition
-
Methods for creating motion blur in Stop motion
-
WhatDreamsCost Spline-Path-Control – Create motion controls for ComfyUI
-
How do LLMs like ChatGPT (Generative Pre-Trained Transformer) work? Explained by Deep-Fake Ryan Gosling
-
AI Data Laundering: How Academic and Nonprofit Researchers Shield Tech Companies from Accountability
-
The Perils of Technical Debt – Understanding Its Impact on Security, Usability, and Stability
-
Embedding frame ranges into Quicktime movies with FFmpeg
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.