COMPOSITION
DESIGN
-
Interactive Maps of Earthquakes around the world
Read more: Interactive Maps of Earthquakes around the worldhttps://ralucanicola.github.io/JSAPI_demos/earthquakes
https://ralucanicola.github.io/JSAPI_demos/earthquakes-depth
https://ralucanicola.github.io/JSAPI_demos/ridgecrest-earthquake
https://ralucanicola.github.io/JSAPI_demos/last-earthquakes
COLOR
-
Virtual Production volumes study
Read more: Virtual Production volumes studyColor Fidelity in LED Volumes
https://theasc.com/articles/color-fidelity-in-led-volumesVirtual Production Glossary
https://vpglossary.com/What is Virtual Production – In depth analysis
https://www.leadingledtech.com/what-is-a-led-virtual-production-studio-in-depth-technical-analysis/A comparison of LED panels for use in Virtual Production:
Findings and recommendations
https://eprints.bournemouth.ac.uk/36826/1/LED_Comparison_White_Paper%281%29.pdf -
Mysterious animation wins best illusion of 2011 – Motion silencing illusion
Read more: Mysterious animation wins best illusion of 2011 – Motion silencing illusionThe 2011 Best Illusion of the Year uses motion to render color changes invisible, and so reveals a quirk in our visual systems that is new to scientists.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Motion_silencing_illusion
“It is a really beautiful effect, revealing something about how our visual system works that we didn’t know before,” said Daniel Simons, a professor at the University of Illinois, Champaign-Urbana. Simons studies visual cognition, and did not work on this illusion. Before its creation, scientists didn’t know that motion had this effect on perception, Simons said.
A viewer stares at a speck at the center of a ring of colored dots, which continuously change color. When the ring begins to rotate around the speck, the color changes appear to stop. But this is an illusion. For some reason, the motion causes our visual system to ignore the color changes. (You can, however, see the color changes if you follow the rotating circles with your eyes.)
-
SecretWeapons MixBox – a practical library for paint-like digital color mixing
Read more: SecretWeapons MixBox – a practical library for paint-like digital color mixingInternally, Mixbox treats colors as real-life pigments using the Kubelka & Munk theory to predict realistic color behavior.
https://scrtwpns.com/mixbox/painter/
https://scrtwpns.com/mixbox.pdf
https://github.com/scrtwpns/mixbox
https://scrtwpns.com/mixbox/docs/
-
Tobia Montanari – Memory Colors: an essential tool for Colorists
Read more: Tobia Montanari – Memory Colors: an essential tool for Coloristshttps://www.tobiamontanari.com/memory-colors-an-essential-tool-for-colorists/
“Memory colors are colors that are universally associated with specific objects, elements or scenes in our environment. They are the colors that we expect to see in specific situations: these colors are based on our expectation of how certain objects should look based on our past experiences and memories.
For instance, we associate specific hues, saturation and brightness values with human skintones and a slight variation can significantly affect the way we perceive a scene.
Similarly, we expect blue skies to have a particular hue, green trees to be a specific shade and so on.
Memory colors live inside of our brains and we often impose them onto what we see. By considering them during the grading process, the resulting image will be more visually appealing and won’t distract the viewer from the intended message of the story. Even a slight deviation from memory colors in a movie can create a sense of discordance, ultimately detracting from the viewer’s experience.”
LIGHTING
-
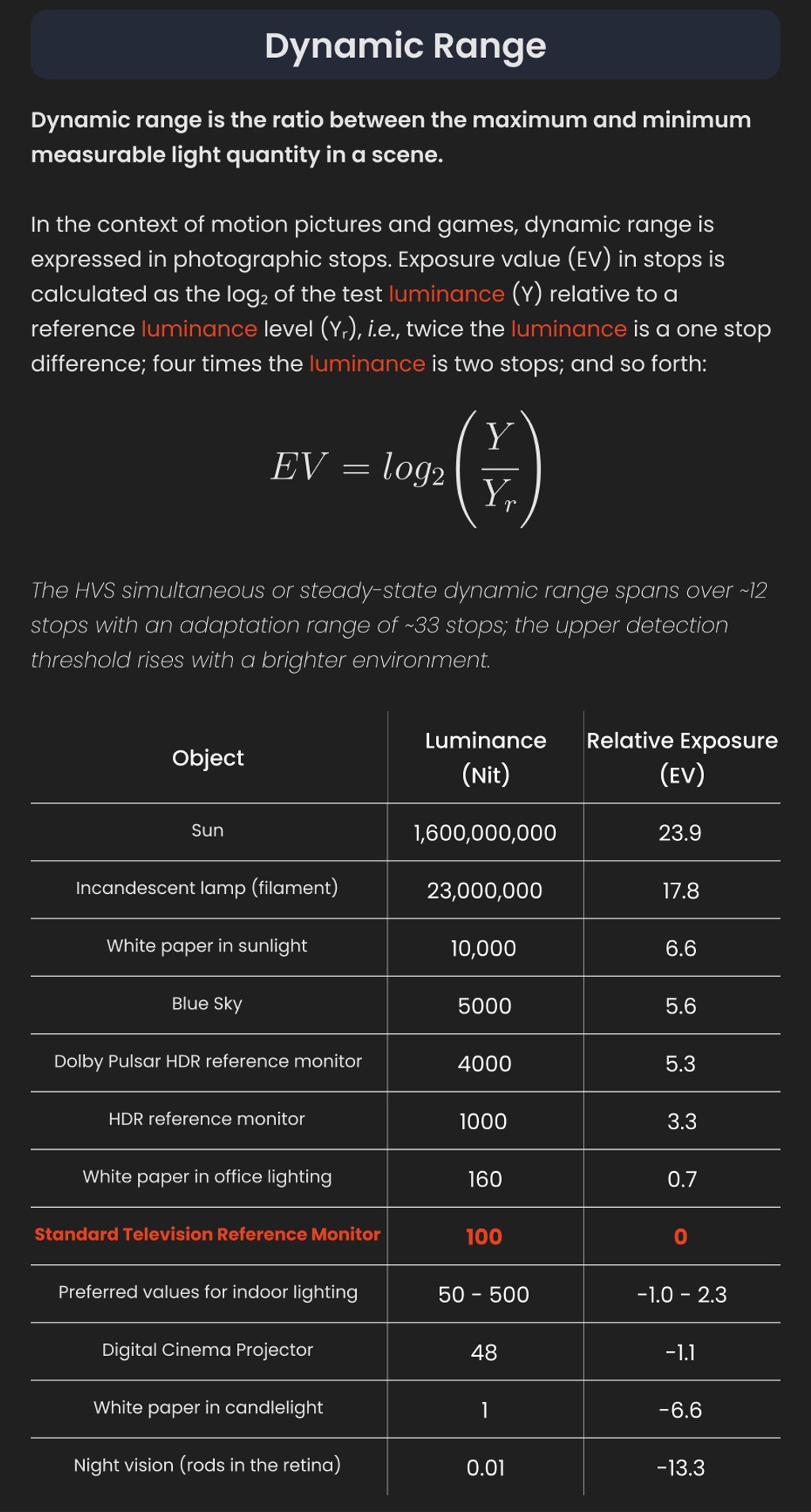
Rec-2020 – TVs new color gamut standard used by Dolby Vision?
Read more: Rec-2020 – TVs new color gamut standard used by Dolby Vision?https://www.hdrsoft.com/resources/dri.html#bit-depth
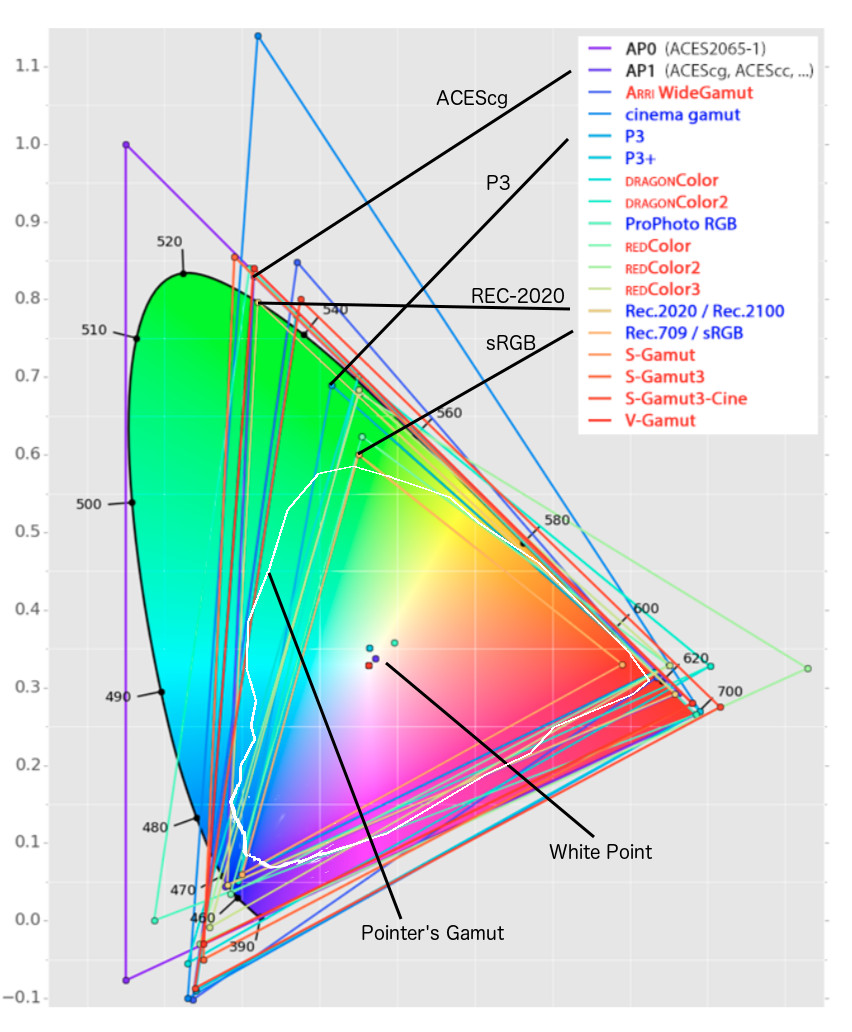
The dynamic range is a ratio between the maximum and minimum values of a physical measurement. Its definition depends on what the dynamic range refers to.
For a scene: Dynamic range is the ratio between the brightest and darkest parts of the scene.
For a camera: Dynamic range is the ratio of saturation to noise. More specifically, the ratio of the intensity that just saturates the camera to the intensity that just lifts the camera response one standard deviation above camera noise.
For a display: Dynamic range is the ratio between the maximum and minimum intensities emitted from the screen.
The Dynamic Range of real-world scenes can be quite high — ratios of 100,000:1 are common in the natural world. An HDR (High Dynamic Range) image stores pixel values that span the whole tonal range of real-world scenes. Therefore, an HDR image is encoded in a format that allows the largest range of values, e.g. floating-point values stored with 32 bits per color channel. Another characteristics of an HDR image is that it stores linear values. This means that the value of a pixel from an HDR image is proportional to the amount of light measured by the camera.
For TVs HDR is great, but it’s not the only new TV feature worth discussing.
(more…) -
What’s the Difference Between Ray Casting, Ray Tracing, Path Tracing and Rasterization? Physical light tracing…
Read more: What’s the Difference Between Ray Casting, Ray Tracing, Path Tracing and Rasterization? Physical light tracing…RASTERIZATION
Rasterisation (or rasterization) is the task of taking the information described in a vector graphics format OR the vertices of triangles making 3D shapes and converting them into a raster image (a series of pixels, dots or lines, which, when displayed together, create the image which was represented via shapes), or in other words “rasterizing” vectors or 3D models onto a 2D plane for display on a computer screen.For each triangle of a 3D shape, you project the corners of the triangle on the virtual screen with some math (projective geometry). Then you have the position of the 3 corners of the triangle on the pixel screen. Those 3 points have texture coordinates, so you know where in the texture are the 3 corners. The cost is proportional to the number of triangles, and is only a little bit affected by the screen resolution.
In computer graphics, a raster graphics or bitmap image is a dot matrix data structure that represents a generally rectangular grid of pixels (points of color), viewable via a monitor, paper, or other display medium.
With rasterization, objects on the screen are created from a mesh of virtual triangles, or polygons, that create 3D models of objects. A lot of information is associated with each vertex, including its position in space, as well as information about color, texture and its “normal,” which is used to determine the way the surface of an object is facing.
Computers then convert the triangles of the 3D models into pixels, or dots, on a 2D screen. Each pixel can be assigned an initial color value from the data stored in the triangle vertices.
Further pixel processing or “shading,” including changing pixel color based on how lights in the scene hit the pixel, and applying one or more textures to the pixel, combine to generate the final color applied to a pixel.
The main advantage of rasterization is its speed. However, rasterization is simply the process of computing the mapping from scene geometry to pixels and does not prescribe a particular way to compute the color of those pixels. So it cannot take shading, especially the physical light, into account and it cannot promise to get a photorealistic output. That’s a big limitation of rasterization.
There are also multiple problems:
If you have two triangles one is behind the other, you will draw twice all the pixels. you only keep the pixel from the triangle that is closer to you (Z-buffer), but you still do the work twice.
The borders of your triangles are jagged as it is hard to know if a pixel is in the triangle or out. You can do some smoothing on those, that is anti-aliasing.
You have to handle every triangles (including the ones behind you) and then see that they do not touch the screen at all. (we have techniques to mitigate this where we only look at triangles that are in the field of view)
Transparency is hard to handle (you can’t just do an average of the color of overlapping transparent triangles, you have to do it in the right order)
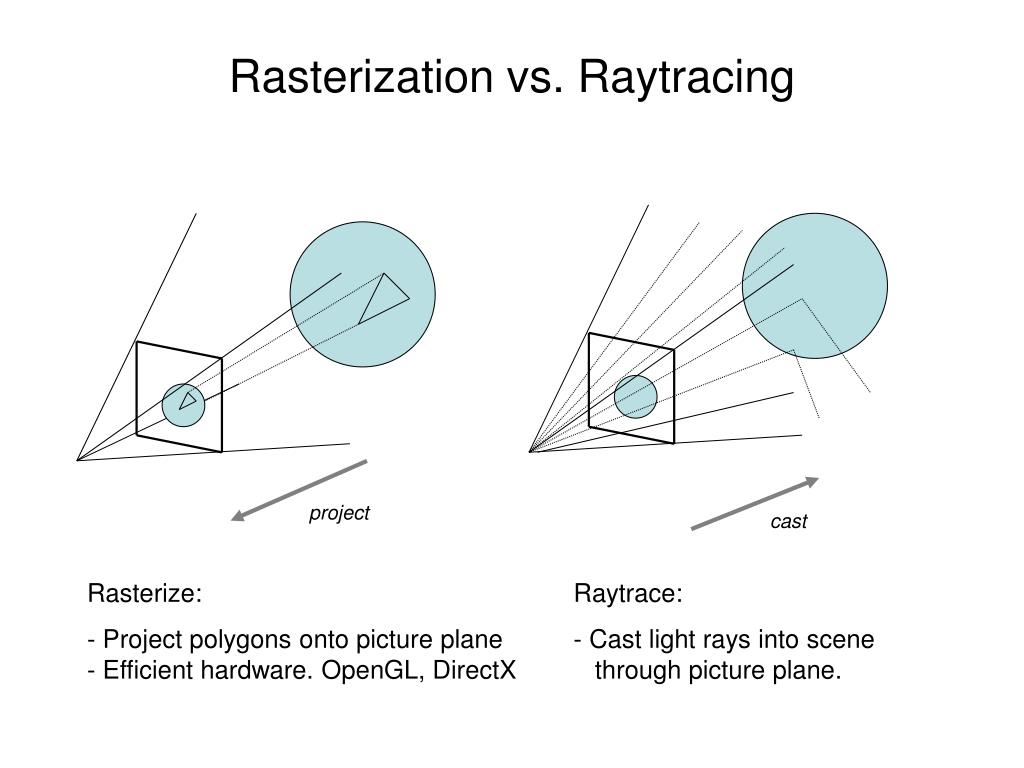
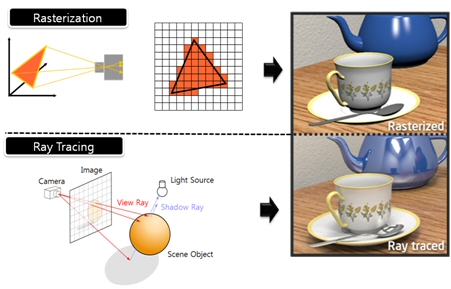
RAY CASTING
It is almost the exact reverse of rasterization: you start from the virtual screen instead of the vector or 3D shapes, and you project a ray, starting from each pixel of the screen, until it intersect with a triangle.The cost is directly correlated to the number of pixels in the screen and you need a really cheap way of finding the first triangle that intersect a ray. In the end, it is more expensive than rasterization but it will, by design, ignore the triangles that are out of the field of view.
You can use it to continue after the first triangle it hit, to take a little bit of the color of the next one, etc… This is useful to handle the border of the triangle cleanly (less jagged) and to handle transparency correctly.
RAYTRACING
Same idea as ray casting except once you hit a triangle you reflect on it and go into a different direction. The number of reflection you allow is the “depth” of your ray tracing. The color of the pixel can be calculated, based off the light source and all the polygons it had to reflect off of to get to that screen pixel.The easiest way to think of ray tracing is to look around you, right now. The objects you’re seeing are illuminated by beams of light. Now turn that around and follow the path of those beams backwards from your eye to the objects that light interacts with. That’s ray tracing.
Ray tracing is eye-oriented process that needs walking through each pixel looking for what object should be shown there, which is also can be described as a technique that follows a beam of light (in pixels) from a set point and simulates how it reacts when it encounters objects.
Compared with rasterization, ray tracing is hard to be implemented in real time, since even one ray can be traced and processed without much trouble, but after one ray bounces off an object, it can turn into 10 rays, and those 10 can turn into 100, 1000…The increase is exponential, and the the calculation for all these rays will be time consuming.
Historically, computer hardware hasn’t been fast enough to use these techniques in real time, such as in video games. Moviemakers can take as long as they like to render a single frame, so they do it offline in render farms. Video games have only a fraction of a second. As a result, most real-time graphics rely on the another technique called rasterization.
PATH TRACING
Path tracing can be used to solve more complex lighting situations.
Path tracing is a type of ray tracing. When using path tracing for rendering, the rays only produce a single ray per bounce. The rays do not follow a defined line per bounce (to a light, for example), but rather shoot off in a random direction. The path tracing algorithm then takes a random sampling of all of the rays to create the final image. This results in sampling a variety of different types of lighting.When a ray hits a surface it doesn’t trace a path to every light source, instead it bounces the ray off the surface and keeps bouncing it until it hits a light source or exhausts some bounce limit.
It then calculates the amount of light transferred all the way to the pixel, including any color information gathered from surfaces along the way.
It then averages out the values calculated from all the paths that were traced into the scene to get the final pixel color value.It requires a ton of computing power and if you don’t send out enough rays per pixel or don’t trace the paths far enough into the scene then you end up with a very spotty image as many pixels fail to find any light sources from their rays. So when you increase the the samples per pixel, you can see the image quality becomes better and better.
Ray tracing tends to be more efficient than path tracing. Basically, the render time of a ray tracer depends on the number of polygons in the scene. The more polygons you have, the longer it will take.
Meanwhile, the rendering time of a path tracer can be indifferent to the number of polygons, but it is related to light situation: If you add a light, transparency, translucence, or other shader effects, the path tracer will slow down considerably.blogs.nvidia.com/blog/2018/03/19/whats-difference-between-ray-tracing-rasterization/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rasterisation
https://www.quora.com/Whats-the-difference-between-ray-tracing-and-path-tracing
-
How to Direct and Edit a Fight Scene for Rhythm and Pacing
Read more: How to Direct and Edit a Fight Scene for Rhythm and Pacingwww.premiumbeat.com/blog/directing-fight-scene-cinematography/
1- Frame the action
2- Stage the action
3- Use camera movements
4- Set a rhythm
5- Control the speed of the action
-
HDRI shooting and editing by Xuan Prada and Greg Zaal
Read more: HDRI shooting and editing by Xuan Prada and Greg Zaalwww.xuanprada.com/blog/2014/11/3/hdri-shooting
http://blog.gregzaal.com/2016/03/16/make-your-own-hdri/
http://blog.hdrihaven.com/how-to-create-high-quality-hdri/

Shooting checklist
- Full coverage of the scene (fish-eye shots)
- Backplates for look-development (including ground or floor)
- Macbeth chart for white balance
- Grey ball for lighting calibration
- Chrome ball for lighting orientation
- Basic scene measurements
- Material samples
- Individual HDR artificial lighting sources if required
Methodology
(more…)
COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
-
Steven Stahlberg – Perception and Composition
-
Tencent Hunyuan3D 2.1 goes Open Source and adds MV (Multi-view) and MV Mini
-
MiniMax-Remover – Taming Bad Noise Helps Video Object Removal Rotoscoping
-
Photography basics: Exposure Value vs Photographic Exposure vs Il/Luminance vs Pixel luminance measurements
-
AI and the Law – Netflix : Using Generative AI in Content Production
-
AI Search – Find The Best AI Tools & Apps
-
Gamma correction
-
STOP FCC – SAVE THE FREE NET
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.