COMPOSITION
DESIGN
-
How to paint a boardgame miniatures
Read more: How to paint a boardgame miniaturesSteps:
- soap wash cleaning
- primer
- base-coat layer (black/white)
- detailing
- washing aka shade (could be done after highlighting)
- highlights aka dry brushing (could be done after washing)
- varnish (gloss/satin/matte)
COLOR
-
Yasuharu YOSHIZAWA – Comparison of sRGB vs ACREScg in Nuke
Read more: Yasuharu YOSHIZAWA – Comparison of sRGB vs ACREScg in NukeAnswering the question that is often asked, “Do I need to use ACEScg to display an sRGB monitor in the end?” (Demonstration shown at an in-house seminar)
Comparison of scanlineRender output with extreme color lights on color charts with sRGB/ACREScg in color – OCIO -working space in NukeDownload the Nuke script:
-
Mysterious animation wins best illusion of 2011 – Motion silencing illusion
Read more: Mysterious animation wins best illusion of 2011 – Motion silencing illusionThe 2011 Best Illusion of the Year uses motion to render color changes invisible, and so reveals a quirk in our visual systems that is new to scientists.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Motion_silencing_illusion
“It is a really beautiful effect, revealing something about how our visual system works that we didn’t know before,” said Daniel Simons, a professor at the University of Illinois, Champaign-Urbana. Simons studies visual cognition, and did not work on this illusion. Before its creation, scientists didn’t know that motion had this effect on perception, Simons said.
A viewer stares at a speck at the center of a ring of colored dots, which continuously change color. When the ring begins to rotate around the speck, the color changes appear to stop. But this is an illusion. For some reason, the motion causes our visual system to ignore the color changes. (You can, however, see the color changes if you follow the rotating circles with your eyes.)
-
colorhunt.co
Read more: colorhunt.coColor Hunt is a free and open platform for color inspiration with thousands of trendy hand-picked color palettes.
LIGHTING
-
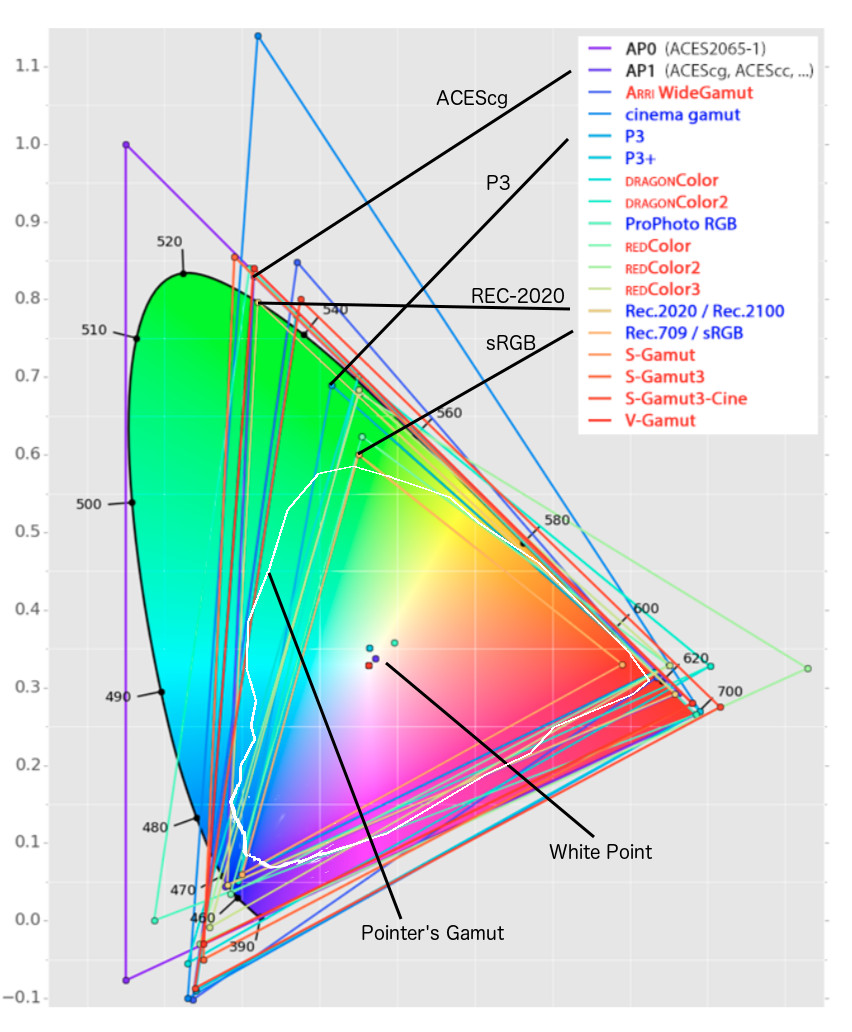
Rec-2020 – TVs new color gamut standard used by Dolby Vision?
Read more: Rec-2020 – TVs new color gamut standard used by Dolby Vision?https://www.hdrsoft.com/resources/dri.html#bit-depth
The dynamic range is a ratio between the maximum and minimum values of a physical measurement. Its definition depends on what the dynamic range refers to.
For a scene: Dynamic range is the ratio between the brightest and darkest parts of the scene.
For a camera: Dynamic range is the ratio of saturation to noise. More specifically, the ratio of the intensity that just saturates the camera to the intensity that just lifts the camera response one standard deviation above camera noise.
For a display: Dynamic range is the ratio between the maximum and minimum intensities emitted from the screen.
The Dynamic Range of real-world scenes can be quite high — ratios of 100,000:1 are common in the natural world. An HDR (High Dynamic Range) image stores pixel values that span the whole tonal range of real-world scenes. Therefore, an HDR image is encoded in a format that allows the largest range of values, e.g. floating-point values stored with 32 bits per color channel. Another characteristics of an HDR image is that it stores linear values. This means that the value of a pixel from an HDR image is proportional to the amount of light measured by the camera.
For TVs HDR is great, but it’s not the only new TV feature worth discussing.
(more…) -
Photography basics: Solid Angle measures
Read more: Photography basics: Solid Angle measureshttp://www.calculator.org/property.aspx?name=solid+angle
A measure of how large the object appears to an observer looking from that point. Thus. A measure for objects in the sky. Useful to retuen the size of the sun and moon… and in perspective, how much of their contribution to lighting. Solid angle can be represented in ‘angular diameter’ as well.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Solid_angle
http://www.mathsisfun.com/geometry/steradian.html
A solid angle is expressed in a dimensionless unit called a steradian (symbol: sr). By default in terms of the total celestial sphere and before atmospheric’s scattering, the Sun and the Moon subtend fractional areas of 0.000546% (Sun) and 0.000531% (Moon).
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Solid_angle#Sun_and_Moon
On earth the sun is likely closer to 0.00011 solid angle after athmospheric scattering. The sun as perceived from earth has a diameter of 0.53 degrees. This is about 0.000064 solid angle.
http://www.numericana.com/answer/angles.htm
The mean angular diameter of the full moon is 2q = 0.52° (it varies with time around that average, by about 0.009°). This translates into a solid angle of 0.0000647 sr, which means that the whole night sky covers a solid angle roughly one hundred thousand times greater than the full moon.
More info
http://lcogt.net/spacebook/using-angles-describe-positions-and-apparent-sizes-objects
http://amazing-space.stsci.edu/glossary/def.php.s=topic_astronomy
Angular Size
The apparent size of an object as seen by an observer; expressed in units of degrees (of arc), arc minutes, or arc seconds. The moon, as viewed from the Earth, has an angular diameter of one-half a degree.
The angle covered by the diameter of the full moon is about 31 arcmin or 1/2°, so astronomers would say the Moon’s angular diameter is 31 arcmin, or the Moon subtends an angle of 31 arcmin.
-
About green screens
Read more: About green screenshackaday.com/2015/02/07/how-green-screen-worked-before-computers/
www.newtek.com/blog/tips/best-green-screen-materials/
www.chromawall.com/blog//chroma-key-green
Chroma Key Green, the color of green screens is also known as Chroma Green and is valued at approximately 354C in the Pantone color matching system (PMS).
Chroma Green can be broken down in many different ways. Here is green screen green as other values useful for both physical and digital production:
Green Screen as RGB Color Value: 0, 177, 64
Green Screen as CMYK Color Value: 81, 0, 92, 0
Green Screen as Hex Color Value: #00b140
Green Screen as Websafe Color Value: #009933Chroma Key Green is reasonably close to an 18% gray reflectance.
Illuminate your green screen with an uniform source with less than 2/3 EV variation.
The level of brightness at any given f-stop should be equivalent to a 90% white card under the same lighting.
COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
-
Survivorship Bias: The error resulting from systematically focusing on successes and ignoring failures. How a young statistician saved his planes during WW2.
-
AI Search – Find The Best AI Tools & Apps
-
Advanced Computer Vision with Python OpenCV and Mediapipe
-
copypastecharacter.com – alphabets, special characters, alt codes and symbols library
-
Photography basics: Production Rendering Resolution Charts
-
AnimationXpress.com interviews Daniele Tosti for TheCgCareer.com channel
-
Game Development tips
-
Web vs Printing or digital RGB vs CMYK
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.