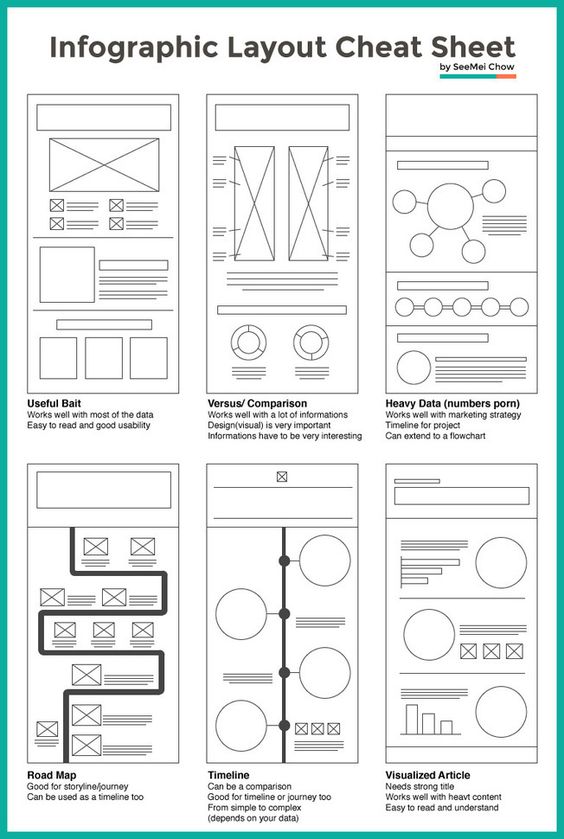
COMPOSITION
-
7 Commandments of Film Editing and composition
Read more: 7 Commandments of Film Editing and composition1. Watch every frame of raw footage twice. On the second time, take notes. If you don’t do this and try to start developing a scene premature, then it’s a big disservice to yourself and to the director, actors and production crew.
2. Nurture the relationships with the director. You are the secondary person in the relationship. Be calm and continually offer solutions. Get the main intention of the film as soon as possible from the director.
3. Organize your media so that you can find any shot instantly.
4. Factor in extra time for renders, exports, errors and crashes.
5. Attempt edits and ideas that shouldn’t work. It just might work. Until you do it and watch it, you won’t know. Don’t rule out ideas just because they don’t make sense in your mind.
6. Spend more time on your audio. It’s the glue of your edit. AUDIO SAVES EVERYTHING. Create fluid and seamless audio under your video.
7. Make cuts for the scene, but always in context for the whole film. Have a macro and a micro view at all times.
DESIGN
COLOR
-
No one could see the colour blue until modern times
Read more: No one could see the colour blue until modern timeshttps://www.businessinsider.com/what-is-blue-and-how-do-we-see-color-2015-2

The way humans see the world… until we have a way to describe something, even something so fundamental as a colour, we may not even notice that something it’s there.
Ancient languages didn’t have a word for blue — not Greek, not Chinese, not Japanese, not Hebrew, not Icelandic cultures. And without a word for the colour, there’s evidence that they may not have seen it at all.
https://www.wnycstudios.org/story/211119-colorsEvery language first had a word for black and for white, or dark and light. The next word for a colour to come into existence — in every language studied around the world — was red, the colour of blood and wine.
After red, historically, yellow appears, and later, green (though in a couple of languages, yellow and green switch places). The last of these colours to appear in every language is blue.The only ancient culture to develop a word for blue was the Egyptians — and as it happens, they were also the only culture that had a way to produce a blue dye.
https://mymodernmet.com/shades-of-blue-color-history/True blue hues are rare in the natural world because synthesizing pigments that absorb longer-wavelength light (reds and yellows) while reflecting shorter-wavelength blue light requires exceptionally elaborate molecular structures—biochemical feats that most plants and animals simply don’t undertake.
When you gaze at a blueberry’s deep blue surface, you’re actually seeing structural coloration rather than a true blue pigment. A fine, waxy bloom on the berry’s skin contains nanostructures that preferentially scatter blue and violet light, giving the fruit its signature blue sheen even though its inherent pigment is reddish.
Similarly, many of nature’s most striking blues—like those of blue jays and morpho butterflies—arise not from blue pigments but from microscopic architectures in feathers or wing scales. These tiny ridges and air pockets manipulate incoming light so that blue wavelengths emerge most prominently, creating vivid, angle-dependent colors through scattering rather than pigment alone.
(more…) -
Is it possible to get a dark yellow
Read more: Is it possible to get a dark yellowhttps://www.patreon.com/posts/102660674
https://www.linkedin.com/posts/stephenwestland_here-is-a-post-about-the-dark-yellow-problem-activity-7187131643764092929-7uCL
-
Christopher Butler – Understanding the Eye-Mind Connection – Vision is a mental process
Read more: Christopher Butler – Understanding the Eye-Mind Connection – Vision is a mental processhttps://www.chrbutler.com/understanding-the-eye-mind-connection
The intricate relationship between the eyes and the brain, often termed the eye-mind connection, reveals that vision is predominantly a cognitive process. This understanding has profound implications for fields such as design, where capturing and maintaining attention is paramount. This essay delves into the nuances of visual perception, the brain’s role in interpreting visual data, and how this knowledge can be applied to effective design strategies.
This cognitive aspect of vision is evident in phenomena such as optical illusions, where the brain interprets visual information in a way that contradicts physical reality. These illusions underscore that what we “see” is not merely a direct recording of the external world but a constructed experience shaped by cognitive processes.
Understanding the cognitive nature of vision is crucial for effective design. Designers must consider how the brain processes visual information to create compelling and engaging visuals. This involves several key principles:
- Attention and Engagement
- Visual Hierarchy
- Cognitive Load Management
- Context and Meaning
LIGHTING
-
What is physically correct lighting all about?
Read more: What is physically correct lighting all about?http://gamedev.stackexchange.com/questions/60638/what-is-physically-correct-lighting-all-about
2012-08 Nathan Reed wrote:
Physically-based shading means leaving behind phenomenological models, like the Phong shading model, which are simply built to “look good” subjectively without being based on physics in any real way, and moving to lighting and shading models that are derived from the laws of physics and/or from actual measurements of the real world, and rigorously obey physical constraints such as energy conservation.
For example, in many older rendering systems, shading models included separate controls for specular highlights from point lights and reflection of the environment via a cubemap. You could create a shader with the specular and the reflection set to wildly different values, even though those are both instances of the same physical process. In addition, you could set the specular to any arbitrary brightness, even if it would cause the surface to reflect more energy than it actually received.
In a physically-based system, both the point light specular and the environment reflection would be controlled by the same parameter, and the system would be set up to automatically adjust the brightness of both the specular and diffuse components to maintain overall energy conservation. Moreover you would want to set the specular brightness to a realistic value for the material you’re trying to simulate, based on measurements.
Physically-based lighting or shading includes physically-based BRDFs, which are usually based on microfacet theory, and physically correct light transport, which is based on the rendering equation (although heavily approximated in the case of real-time games).
It also includes the necessary changes in the art process to make use of these features. Switching to a physically-based system can cause some upsets for artists. First of all it requires full HDR lighting with a realistic level of brightness for light sources, the sky, etc. and this can take some getting used to for the lighting artists. It also requires texture/material artists to do some things differently (particularly for specular), and they can be frustrated by the apparent loss of control (e.g. locking together the specular highlight and environment reflection as mentioned above; artists will complain about this). They will need some time and guidance to adapt to the physically-based system.
On the plus side, once artists have adapted and gained trust in the physically-based system, they usually end up liking it better, because there are fewer parameters overall (less work for them to tweak). Also, materials created in one lighting environment generally look fine in other lighting environments too. This is unlike more ad-hoc models, where a set of material parameters might look good during daytime, but it comes out ridiculously glowy at night, or something like that.
Here are some resources to look at for physically-based lighting in games:
SIGGRAPH 2013 Physically Based Shading Course, particularly the background talk by Naty Hoffman at the beginning. You can also check out the previous incarnations of this course for more resources.
Sébastien Lagarde, Adopting a physically-based shading model and Feeding a physically-based shading model
And of course, I would be remiss if I didn’t mention Physically-Based Rendering by Pharr and Humphreys, an amazing reference on this whole subject and well worth your time, although it focuses on offline rather than real-time rendering.
-
3D Lighting Tutorial by Amaan Kram
Read more: 3D Lighting Tutorial by Amaan Kramhttp://www.amaanakram.com/lightingT/part1.htm
The goals of lighting in 3D computer graphics are more or less the same as those of real world lighting.
Lighting serves a basic function of bringing out, or pushing back the shapes of objects visible from the camera’s view.
It gives a two-dimensional image on the monitor an illusion of the third dimension-depth.But it does not just stop there. It gives an image its personality, its character. A scene lit in different ways can give a feeling of happiness, of sorrow, of fear etc., and it can do so in dramatic or subtle ways. Along with personality and character, lighting fills a scene with emotion that is directly transmitted to the viewer.
Trying to simulate a real environment in an artificial one can be a daunting task. But even if you make your 3D rendering look absolutely photo-realistic, it doesn’t guarantee that the image carries enough emotion to elicit a “wow” from the people viewing it.
Making 3D renderings photo-realistic can be hard. Putting deep emotions in them can be even harder. However, if you plan out your lighting strategy for the mood and emotion that you want your rendering to express, you make the process easier for yourself.
Each light source can be broken down in to 4 distinct components and analyzed accordingly.
· Intensity
· Direction
· Color
· SizeThe overall thrust of this writing is to produce photo-realistic images by applying good lighting techniques.
-
Photography basics: Color Temperature and White Balance
Read more: Photography basics: Color Temperature and White BalanceColor Temperature of a light source describes the spectrum of light which is radiated from a theoretical “blackbody” (an ideal physical body that absorbs all radiation and incident light – neither reflecting it nor allowing it to pass through) with a given surface temperature.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Color_temperature
Or. Most simply it is a method of describing the color characteristics of light through a numerical value that corresponds to the color emitted by a light source, measured in degrees of Kelvin (K) on a scale from 1,000 to 10,000.
More accurately. The color temperature of a light source is the temperature of an ideal backbody that radiates light of comparable hue to that of the light source.
(more…) -
Light and Matter : The 2018 theory of Physically-Based Rendering and Shading by Allegorithmic
Read more: Light and Matter : The 2018 theory of Physically-Based Rendering and Shading by Allegorithmicacademy.substance3d.com/courses/the-pbr-guide-part-1
academy.substance3d.com/courses/the-pbr-guide-part-2
Local copy:
COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
-
Zibra.AI – Real-Time Volumetric Effects in Virtual Production. Now free for Indies!
-
Blender VideoDepthAI – Turn any video into 3D Animated Scenes
-
Image rendering bit depth
-
GretagMacbeth Color Checker Numeric Values and Middle Gray
-
Principles of Animation with Alan Becker, Dermot OConnor and Shaun Keenan
-
Methods for creating motion blur in Stop motion
-
Matt Gray – How to generate a profitable business
-
Daniele Tosti Interview for the magazine InCG, Taiwan, Issue 28, 201609
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.