COMPOSITION
-
Photography basics: Camera Aspect Ratio, Sensor Size and Depth of Field – resolutions
Read more: Photography basics: Camera Aspect Ratio, Sensor Size and Depth of Field – resolutionshttp://www.shutterangle.com/2012/cinematic-look-aspect-ratio-sensor-size-depth-of-field/
http://www.shutterangle.com/2012/film-video-aspect-ratio-artistic-choice/
DESIGN
COLOR
-
Gamma correction
Read more: Gamma correction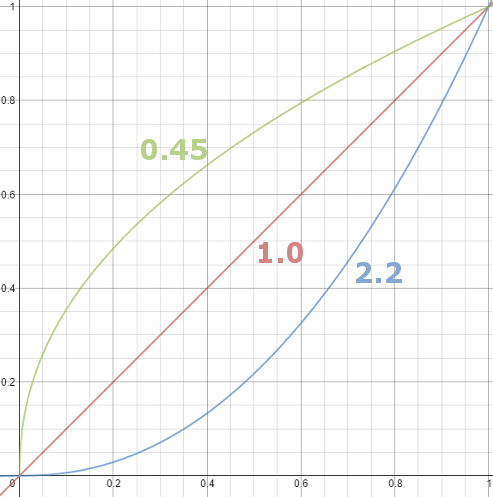
http://www.normankoren.com/makingfineprints1A.html#Gammabox
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gamma_correction
http://www.photoscientia.co.uk/Gamma.htm
https://www.w3.org/Graphics/Color/sRGB.html
http://www.eizoglobal.com/library/basics/lcd_display_gamma/index.html
https://forum.reallusion.com/PrintTopic308094.aspx
Basically, gamma is the relationship between the brightness of a pixel as it appears on the screen, and the numerical value of that pixel. Generally Gamma is just about defining relationships.
Three main types:
– Image Gamma encoded in images
– Display Gammas encoded in hardware and/or viewing time
– System or Viewing Gamma which is the net effect of all gammas when you look back at a final image. In theory this should flatten back to 1.0 gamma.
(more…) -
Björn Ottosson – OKlch color space
Read more: Björn Ottosson – OKlch color spaceBjörn Ottosson proposed OKlch in 2020 to create a color space that can closely mimic how color is perceived by the human eye, predicting perceived lightness, chroma, and hue.
The OK in OKLCH stands for Optimal Color.
- L: Lightness (the perceived brightness of the color)
- C: Chroma (the intensity or saturation of the color)
- H: Hue (the actual color, such as red, blue, green, etc.)

Also read:
-
The Color of Infinite Temperature
Read more: The Color of Infinite TemperatureThis is the color of something infinitely hot.

Of course you’d instantly be fried by gamma rays of arbitrarily high frequency, but this would be its spectrum in the visible range.
johncarlosbaez.wordpress.com/2022/01/16/the-color-of-infinite-temperature/
This is also the color of a typical neutron star. They’re so hot they look the same.
It’s also the color of the early Universe!This was worked out by David Madore.
The color he got is sRGB(148,177,255).
www.htmlcsscolor.com/hex/94B1FFAnd according to the experts who sip latte all day and make up names for colors, this color is called ‘Perano’.
-
About green screens
Read more: About green screenshackaday.com/2015/02/07/how-green-screen-worked-before-computers/
www.newtek.com/blog/tips/best-green-screen-materials/
www.chromawall.com/blog//chroma-key-green
Chroma Key Green, the color of green screens is also known as Chroma Green and is valued at approximately 354C in the Pantone color matching system (PMS).
Chroma Green can be broken down in many different ways. Here is green screen green as other values useful for both physical and digital production:
Green Screen as RGB Color Value: 0, 177, 64
Green Screen as CMYK Color Value: 81, 0, 92, 0
Green Screen as Hex Color Value: #00b140
Green Screen as Websafe Color Value: #009933Chroma Key Green is reasonably close to an 18% gray reflectance.
Illuminate your green screen with an uniform source with less than 2/3 EV variation.
The level of brightness at any given f-stop should be equivalent to a 90% white card under the same lighting. -
Is a MacBeth Colour Rendition Chart the Safest Way to Calibrate a Camera?
Read more: Is a MacBeth Colour Rendition Chart the Safest Way to Calibrate a Camera?www.colour-science.org/posts/the-colorchecker-considered-mostly-harmless/
“Unless you have all the relevant spectral measurements, a colour rendition chart should not be used to perform colour-correction of camera imagery but only for white balancing and relative exposure adjustments.”
“Using a colour rendition chart for colour-correction might dramatically increase error if the scene light source spectrum is different from the illuminant used to compute the colour rendition chart’s reference values.”
“other factors make using a colour rendition chart unsuitable for camera calibration:
– Uncontrolled geometry of the colour rendition chart with the incident illumination and the camera.
– Unknown sample reflectances and ageing as the colour of the samples vary with time.
– Low samples count.
– Camera noise and flare.
– Etc…“Those issues are well understood in the VFX industry, and when receiving plates, we almost exclusively use colour rendition charts to white balance and perform relative exposure adjustments, i.e. plate neutralisation.”
-
“Reality” is constructed by your brain. Here’s what that means, and why it matters.
Read more: “Reality” is constructed by your brain. Here’s what that means, and why it matters.“Fix your gaze on the black dot on the left side of this image. But wait! Finish reading this paragraph first. As you gaze at the left dot, try to answer this question: In what direction is the object on the right moving? Is it drifting diagonally, or is it moving up and down?”

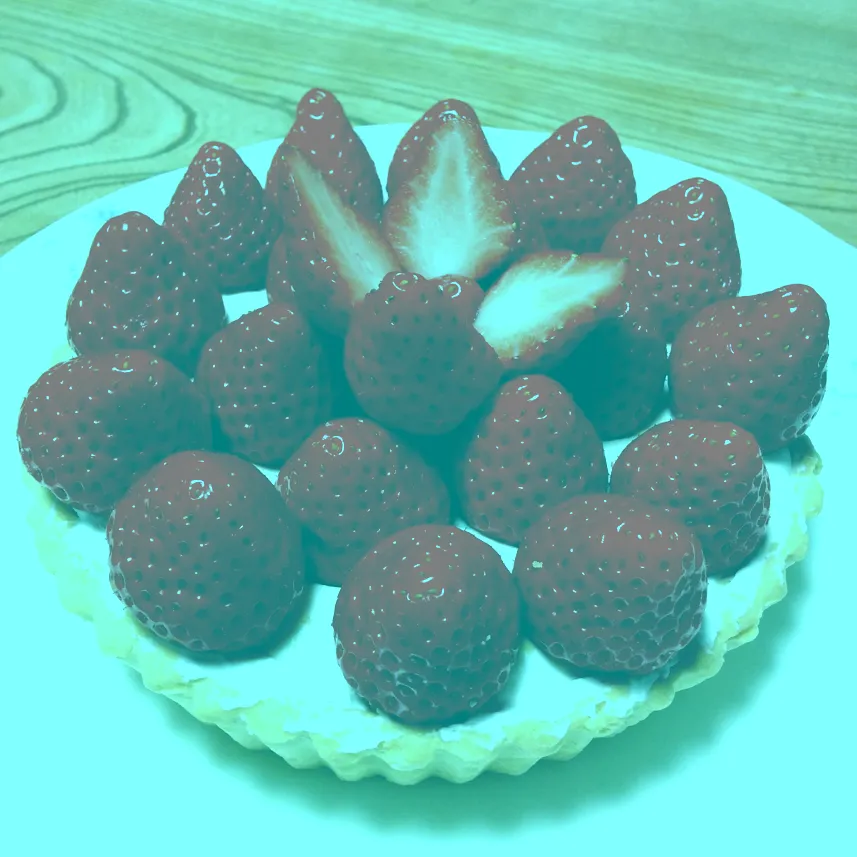
What color are these strawberries?

Are A and B the same gray?

LIGHTING
-
StudioBinder.com – CRI color rendering index
Read more: StudioBinder.com – CRI color rendering indexwww.studiobinder.com/blog/what-is-color-rendering-index
“The Color Rendering Index is a measurement of how faithfully a light source reveals the colors of whatever it illuminates, it describes the ability of a light source to reveal the color of an object, as compared to the color a natural light source would provide. The highest possible CRI is 100. A CRI of 100 generally refers to a perfect black body, like a tungsten light source or the sun. ”
www.pixelsham.com/2021/04/28/types-of-film-lights-and-their-efficiency
-
Cinematographers Blueprint 300dpi poster
Read more: Cinematographers Blueprint 300dpi posterThe 300dpi digital poster is now available to all PixelSham.com subscribers.
If you have already subscribed and wish a copy, please send me a note through the contact page.
COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
-
Eddie Yoon – There’s a big misconception about AI creative
-
Matt Gray – How to generate a profitable business
-
Embedding frame ranges into Quicktime movies with FFmpeg
-
Godot Cheat Sheets
-
Web vs Printing or digital RGB vs CMYK
-
AI Data Laundering: How Academic and Nonprofit Researchers Shield Tech Companies from Accountability
-
JavaScript how-to free resources
-
Advanced Computer Vision with Python OpenCV and Mediapipe
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.







