COMPOSITION
-
SlowMoVideo – How to make a slow motion shot with the open source program
Read more: SlowMoVideo – How to make a slow motion shot with the open source programhttp://slowmovideo.granjow.net/
slowmoVideo is an OpenSource program that creates slow-motion videos from your footage.
Slow motion cinematography is the result of playing back frames for a longer duration than they were exposed. For example, if you expose 240 frames of film in one second, then play them back at 24 fps, the resulting movie is 10 times longer (slower) than the original filmed event….
Film cameras are relatively simple mechanical devices that allow you to crank up the speed to whatever rate the shutter and pull-down mechanism allow. Some film cameras can operate at 2,500 fps or higher (although film shot in these cameras often needs some readjustment in postproduction). Video, on the other hand, is always captured, recorded, and played back at a fixed rate, with a current limit around 60fps. This makes extreme slow motion effects harder to achieve (and less elegant) on video, because slowing down the video results in each frame held still on the screen for a long time, whereas with high-frame-rate film there are plenty of frames to fill the longer durations of time. On video, the slow motion effect is more like a slide show than smooth, continuous motion.
One obvious solution is to shoot film at high speed, then transfer it to video (a case where film still has a clear advantage, sorry George). Another possibility is to cross dissolve or blur from one frame to the next. This adds a smooth transition from one still frame to the next. The blur reduces the sharpness of the image, and compared to slowing down images shot at a high frame rate, this is somewhat of a cheat. However, there isn’t much you can do about it until video can be recorded at much higher rates. Of course, many film cameras can’t shoot at high frame rates either, so the whole super-slow-motion endeavor is somewhat specialized no matter what medium you are using. (There are some high speed digital cameras available now that allow you to capture lots of digital frames directly to your computer, so technology is starting to catch up with film. However, this feature isn’t going to appear in consumer camcorders any time soon.)
-
StudioBinder – Roger Deakins on How to Choose a Camera Lens — Cinematography Composition Techniques
Read more: StudioBinder – Roger Deakins on How to Choose a Camera Lens — Cinematography Composition Techniqueshttps://www.studiobinder.com/blog/camera-lens-buying-guide/
https://www.studiobinder.com/blog/e-books/camera-lenses-explained-volume-1-ebook
DESIGN
COLOR
-
Space bodies’ components and light spectroscopy
Read more: Space bodies’ components and light spectroscopywww.plutorules.com/page-111-space-rocks.html
This help’s us understand the composition of components in/on solar system bodies.
Dips in the observed light spectrum, also known as, lines of absorption occur as gasses absorb energy from light at specific points along the light spectrum.
These dips or darkened zones (lines of absorption) leave a finger print which identify elements and compounds.
In this image the dark absorption bands appear as lines of emission which occur as the result of emitted not reflected (absorbed) light.
Lines of absorption
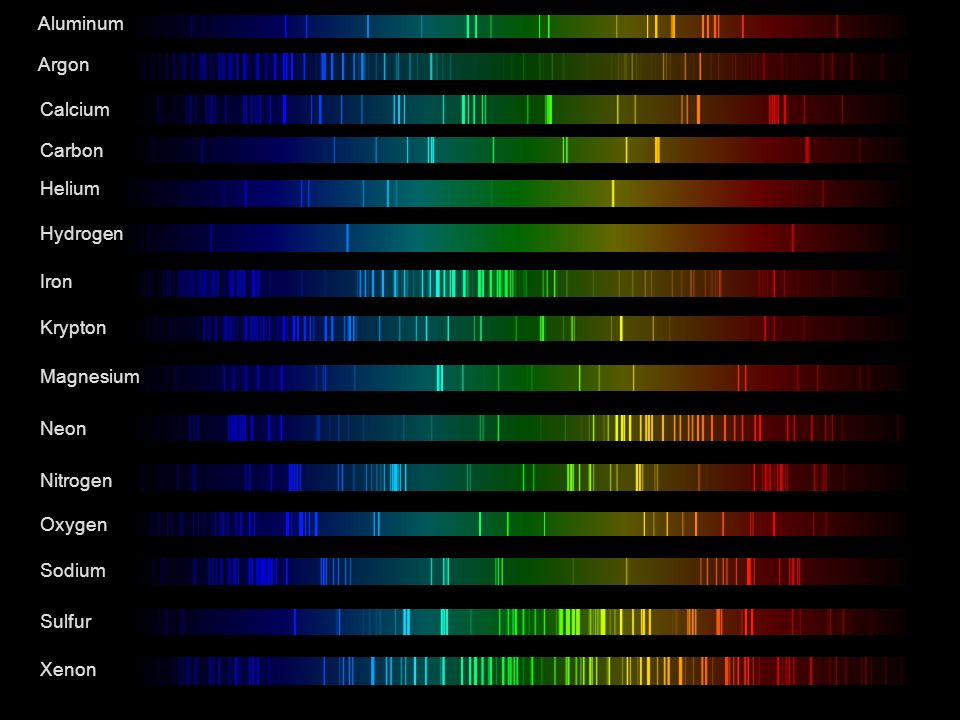 Lines of emission
Lines of emission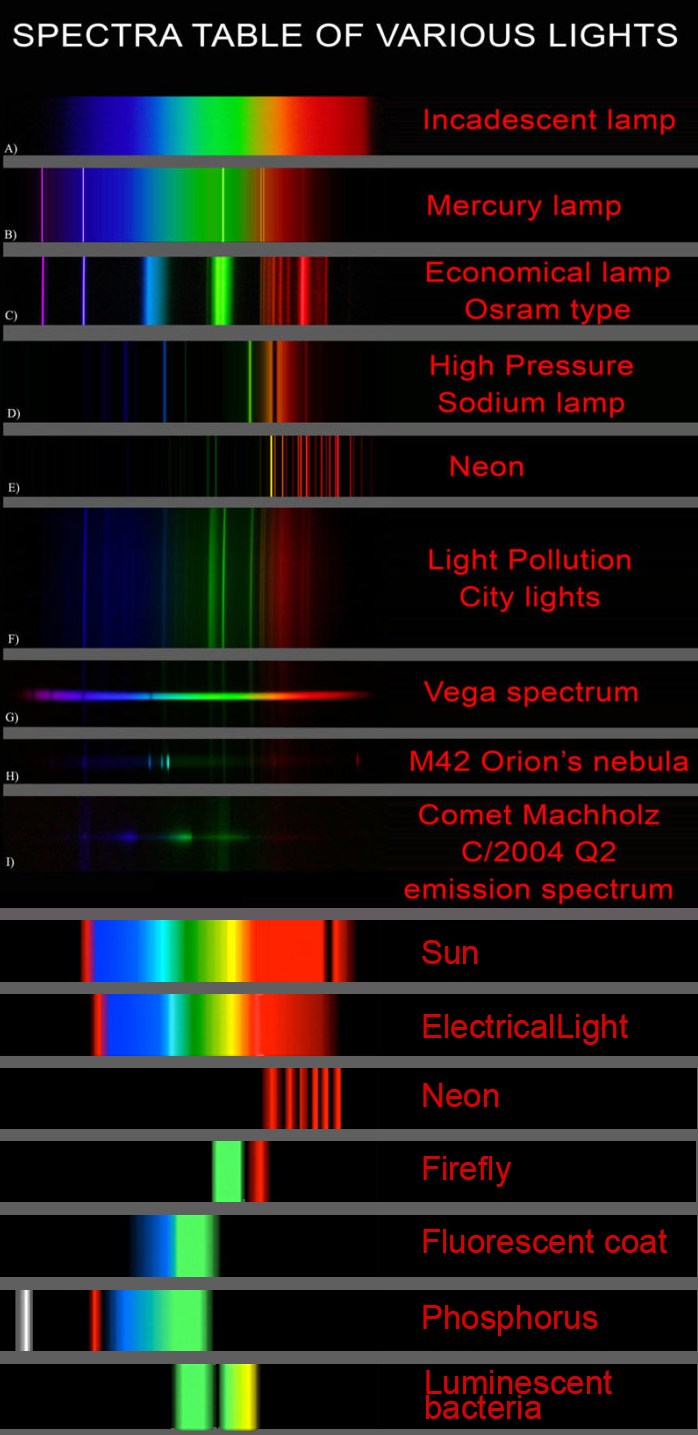
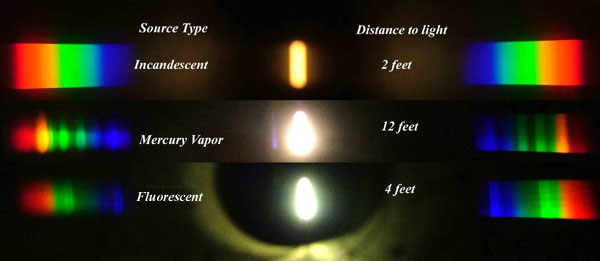

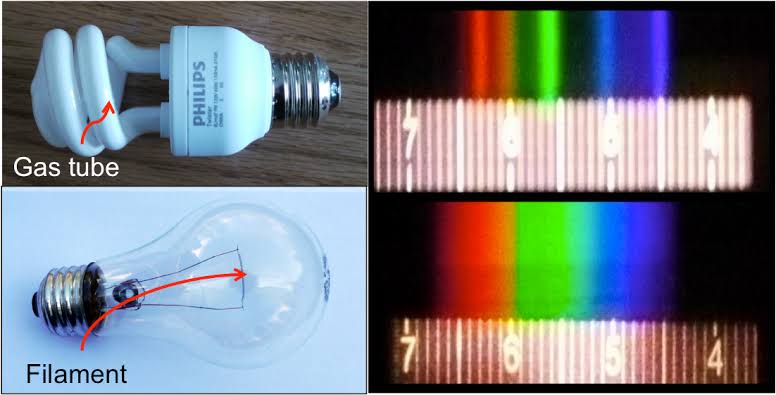
-
Capturing textures albedo
Read more: Capturing textures albedoBuilding a Portable PBR Texture Scanner by Stephane Lb
http://rtgfx.com/pbr-texture-scanner/How To Split Specular And Diffuse In Real Images, by John Hable
http://filmicworlds.com/blog/how-to-split-specular-and-diffuse-in-real-images/Capturing albedo using a Spectralon
https://www.activision.com/cdn/research/Real_World_Measurements_for_Call_of_Duty_Advanced_Warfare.pdfReal_World_Measurements_for_Call_of_Duty_Advanced_Warfare.pdf
Spectralon is a teflon-based pressed powderthat comes closest to being a pure Lambertian diffuse material that reflects 100% of all light. If we take an HDR photograph of the Spectralon alongside the material to be measured, we can derive thediffuse albedo of that material.
The process to capture diffuse reflectance is very similar to the one outlined by Hable.
1. We put a linear polarizing filter in front of the camera lens and a second linear polarizing filterin front of a modeling light or a flash such that the two filters are oriented perpendicular to eachother, i.e. cross polarized.
2. We place Spectralon close to and parallel with the material we are capturing and take brack-eted shots of the setup7. Typically, we’ll take nine photographs, from -4EV to +4EV in 1EVincrements.
3. We convert the bracketed shots to a linear HDR image. We found that many HDR packagesdo not produce an HDR image in which the pixel values are linear. PTGui is an example of apackage which does generate a linear HDR image. At this point, because of the cross polarization,the image is one of surface diffuse response.
4. We open the file in Photoshop and normalize the image by color picking the Spectralon, filling anew layer with that color and setting that layer to “Divide”. This sets the Spectralon to 1 in theimage. All other color values are relative to this so we can consider them as diffuse albedo.
-
SecretWeapons MixBox – a practical library for paint-like digital color mixing
Read more: SecretWeapons MixBox – a practical library for paint-like digital color mixingInternally, Mixbox treats colors as real-life pigments using the Kubelka & Munk theory to predict realistic color behavior.
https://scrtwpns.com/mixbox/painter/
https://scrtwpns.com/mixbox.pdf
https://github.com/scrtwpns/mixbox
https://scrtwpns.com/mixbox/docs/
-
GretagMacbeth Color Checker Numeric Values and Middle Gray
Read more: GretagMacbeth Color Checker Numeric Values and Middle GrayThe human eye perceives half scene brightness not as the linear 50% of the present energy (linear nature values) but as 18% of the overall brightness. We are biased to perceive more information in the dark and contrast areas. A Macbeth chart helps with calibrating back into a photographic capture into this “human perspective” of the world.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Middle_gray
In photography, painting, and other visual arts, middle gray or middle grey is a tone that is perceptually about halfway between black and white on a lightness scale in photography and printing, it is typically defined as 18% reflectance in visible light
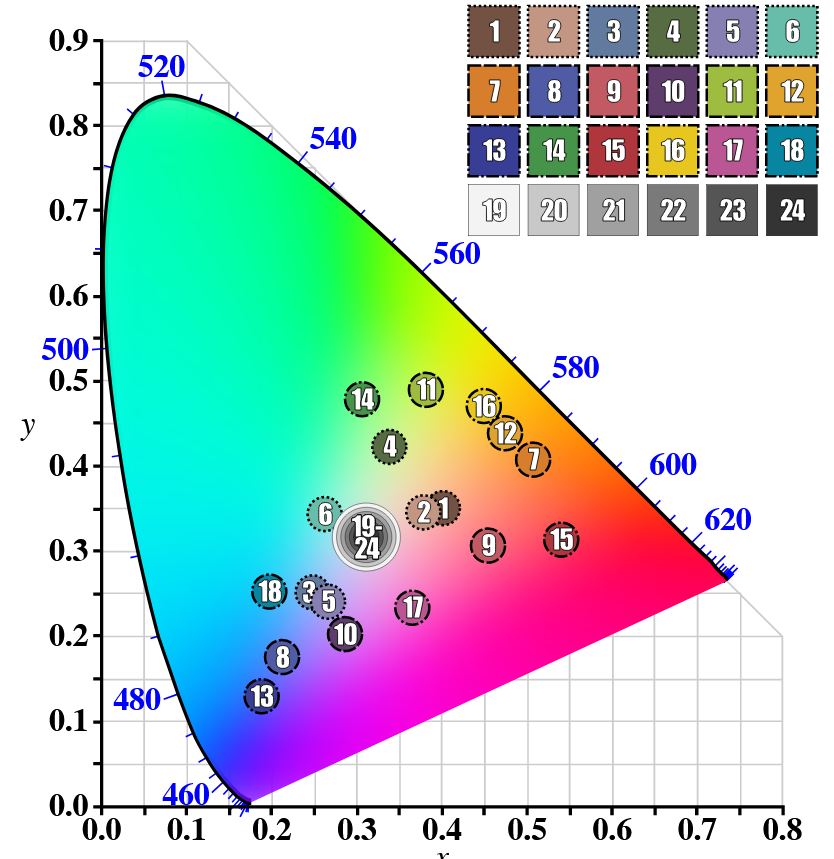
Light meters, cameras, and pictures are often calibrated using an 18% gray card[4][5][6] or a color reference card such as a ColorChecker. On the assumption that 18% is similar to the average reflectance of a scene, a grey card can be used to estimate the required exposure of the film.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ColorChecker
(more…)
LIGHTING
-
Rec-2020 – TVs new color gamut standard used by Dolby Vision?
Read more: Rec-2020 – TVs new color gamut standard used by Dolby Vision?https://www.hdrsoft.com/resources/dri.html#bit-depth
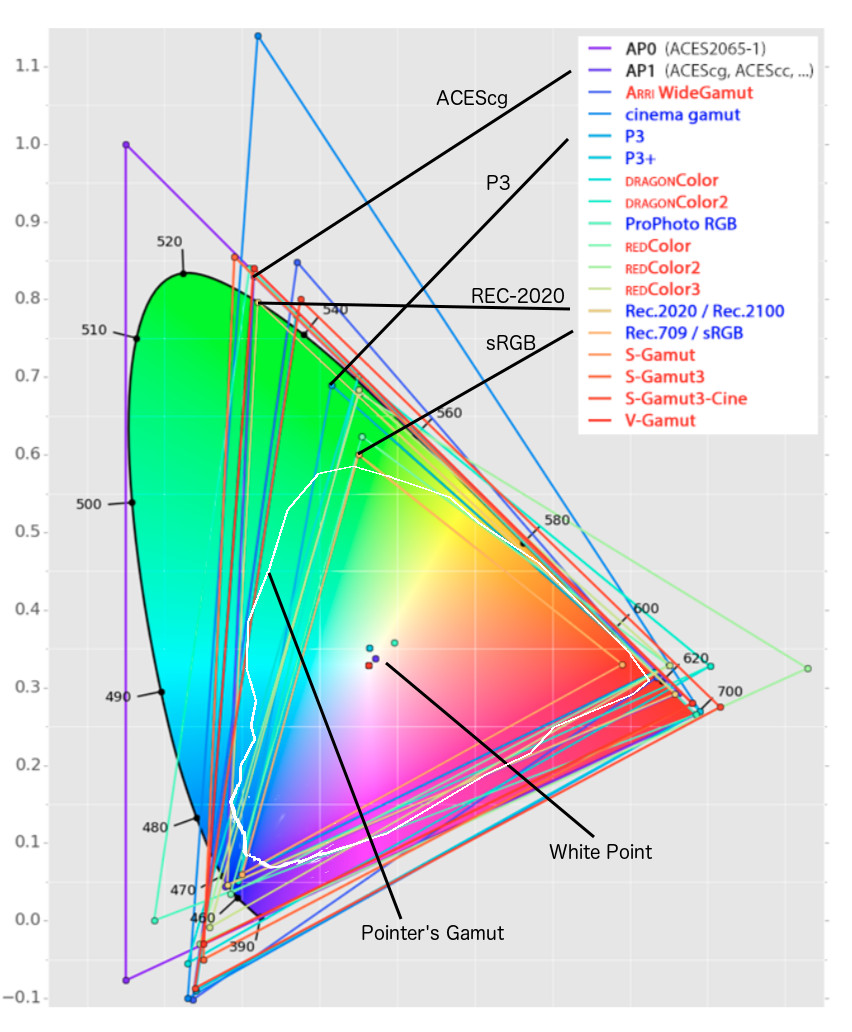
The dynamic range is a ratio between the maximum and minimum values of a physical measurement. Its definition depends on what the dynamic range refers to.
For a scene: Dynamic range is the ratio between the brightest and darkest parts of the scene.
For a camera: Dynamic range is the ratio of saturation to noise. More specifically, the ratio of the intensity that just saturates the camera to the intensity that just lifts the camera response one standard deviation above camera noise.
For a display: Dynamic range is the ratio between the maximum and minimum intensities emitted from the screen.
The Dynamic Range of real-world scenes can be quite high — ratios of 100,000:1 are common in the natural world. An HDR (High Dynamic Range) image stores pixel values that span the whole tonal range of real-world scenes. Therefore, an HDR image is encoded in a format that allows the largest range of values, e.g. floating-point values stored with 32 bits per color channel. Another characteristics of an HDR image is that it stores linear values. This means that the value of a pixel from an HDR image is proportional to the amount of light measured by the camera.
For TVs HDR is great, but it’s not the only new TV feature worth discussing.
(more…) -
DiffusionLight: HDRI Light Probes for Free by Painting a Chrome Ball
Read more: DiffusionLight: HDRI Light Probes for Free by Painting a Chrome Ballhttps://diffusionlight.github.io/
https://github.com/DiffusionLight/DiffusionLight
https://github.com/DiffusionLight/DiffusionLight?tab=MIT-1-ov-file#readme
https://colab.research.google.com/drive/15pC4qb9mEtRYsW3utXkk-jnaeVxUy-0S
“a simple yet effective technique to estimate lighting in a single input image. Current techniques rely heavily on HDR panorama datasets to train neural networks to regress an input with limited field-of-view to a full environment map. However, these approaches often struggle with real-world, uncontrolled settings due to the limited diversity and size of their datasets. To address this problem, we leverage diffusion models trained on billions of standard images to render a chrome ball into the input image. Despite its simplicity, this task remains challenging: the diffusion models often insert incorrect or inconsistent objects and cannot readily generate images in HDR format. Our research uncovers a surprising relationship between the appearance of chrome balls and the initial diffusion noise map, which we utilize to consistently generate high-quality chrome balls. We further fine-tune an LDR difusion model (Stable Diffusion XL) with LoRA, enabling it to perform exposure bracketing for HDR light estimation. Our method produces convincing light estimates across diverse settings and demonstrates superior generalization to in-the-wild scenarios.”

-
PTGui 13 beta adds control through a Patch Editor
Read more: PTGui 13 beta adds control through a Patch EditorAdditions:
- Patch Editor (PTGui Pro)
- DNG output
- Improved RAW / DNG handling
- JPEG 2000 support
- Performance improvements
-
7 Easy Portrait Lighting Setups
Read more: 7 Easy Portrait Lighting SetupsButterfly
Loop
Rembrandt
Split
Rim
Broad
Short
COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
-
Animation/VFX/Game Industry JOB POSTINGS by Chris Mayne
-
Ross Pettit on The Agile Manager – How tech firms went for prioritizing cash flow instead of talent (and artists)
-
White Balance is Broken!
-
AI and the Law – Netflix : Using Generative AI in Content Production
-
Free fonts
-
Zibra.AI – Real-Time Volumetric Effects in Virtual Production. Now free for Indies!
-
Yann Lecun: Meta AI, Open Source, Limits of LLMs, AGI & the Future of AI | Lex Fridman Podcast #416
-
Photography basics: Exposure Value vs Photographic Exposure vs Il/Luminance vs Pixel luminance measurements
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.