COMPOSITION
DESIGN
-
boldtron – 𝗗𝗘𝗣𝗜𝗖𝗧𝗜𝗡𝗚 𝗪𝗔𝗧𝗘𝗥𝗚𝗨𝗡𝗦
Read more: boldtron – 𝗗𝗘𝗣𝗜𝗖𝗧𝗜𝗡𝗚 𝗪𝗔𝗧𝗘𝗥𝗚𝗨𝗡𝗦See this Instagram post by @boldtron using ComfyUI + Krea
https://www.instagram.com/p/C5v-H0PNYYg/?utm_source=ig_web_button_share_sheet
COLOR
-
Björn Ottosson – How software gets color wrong
Read more: Björn Ottosson – How software gets color wronghttps://bottosson.github.io/posts/colorwrong/
Most software around us today are decent at accurately displaying colors. Processing of colors is another story unfortunately, and is often done badly.
To understand what the problem is, let’s start with an example of three ways of blending green and magenta:
- Perceptual blend – A smooth transition using a model designed to mimic human perception of color. The blending is done so that the perceived brightness and color varies smoothly and evenly.
- Linear blend – A model for blending color based on how light behaves physically. This type of blending can occur in many ways naturally, for example when colors are blended together by focus blur in a camera or when viewing a pattern of two colors at a distance.
- sRGB blend – This is how colors would normally be blended in computer software, using sRGB to represent the colors.
Let’s look at some more examples of blending of colors, to see how these problems surface more practically. The examples use strong colors since then the differences are more pronounced. This is using the same three ways of blending colors as the first example.
Instead of making it as easy as possible to work with color, most software make it unnecessarily hard, by doing image processing with representations not designed for it. Approximating the physical behavior of light with linear RGB models is one easy thing to do, but more work is needed to create image representations tailored for image processing and human perception.
Also see:
-
Photography basics: Color Temperature and White Balance
Read more: Photography basics: Color Temperature and White BalanceColor Temperature of a light source describes the spectrum of light which is radiated from a theoretical “blackbody” (an ideal physical body that absorbs all radiation and incident light – neither reflecting it nor allowing it to pass through) with a given surface temperature.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Color_temperature
Or. Most simply it is a method of describing the color characteristics of light through a numerical value that corresponds to the color emitted by a light source, measured in degrees of Kelvin (K) on a scale from 1,000 to 10,000.
More accurately. The color temperature of a light source is the temperature of an ideal backbody that radiates light of comparable hue to that of the light source.
(more…) -
GretagMacbeth Color Checker Numeric Values and Middle Gray
Read more: GretagMacbeth Color Checker Numeric Values and Middle GrayThe human eye perceives half scene brightness not as the linear 50% of the present energy (linear nature values) but as 18% of the overall brightness. We are biased to perceive more information in the dark and contrast areas. A Macbeth chart helps with calibrating back into a photographic capture into this “human perspective” of the world.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Middle_gray
In photography, painting, and other visual arts, middle gray or middle grey is a tone that is perceptually about halfway between black and white on a lightness scale in photography and printing, it is typically defined as 18% reflectance in visible light
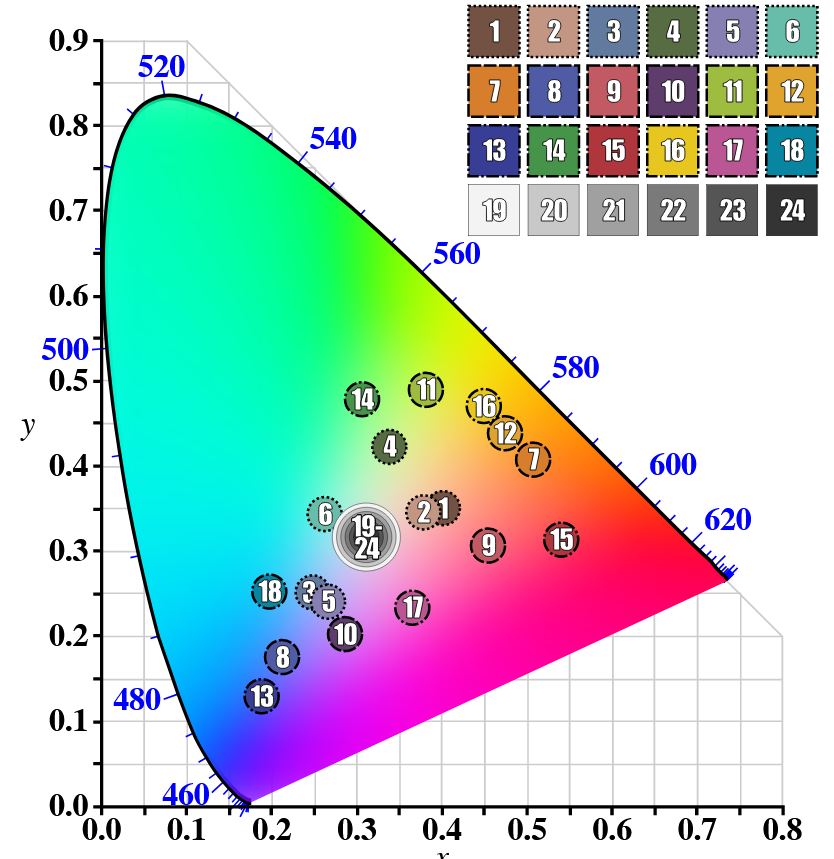
Light meters, cameras, and pictures are often calibrated using an 18% gray card[4][5][6] or a color reference card such as a ColorChecker. On the assumption that 18% is similar to the average reflectance of a scene, a grey card can be used to estimate the required exposure of the film.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ColorChecker
(more…) -
HDR and Color
Read more: HDR and Colorhttps://www.soundandvision.com/content/nits-and-bits-hdr-and-color
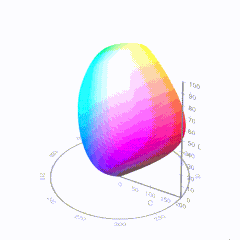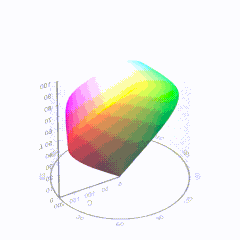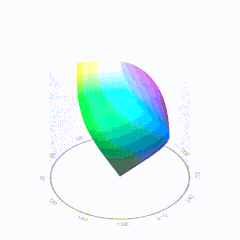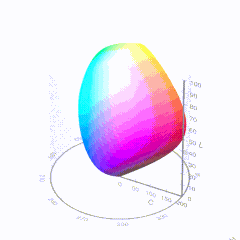
In HD we often refer to the range of available colors as a color gamut. Such a color gamut is typically plotted on a two-dimensional diagram, called a CIE chart, as shown in at the top of this blog. Each color is characterized by its x/y coordinates.
Good enough for government work, perhaps. But for HDR, with its higher luminance levels and wider color, the gamut becomes three-dimensional.
For HDR the color gamut therefore becomes a characteristic we now call the color volume. It isn’t easy to show color volume on a two-dimensional medium like the printed page or a computer screen, but one method is shown below. As the luminance becomes higher, the picture eventually turns to white. As it becomes darker, it fades to black. The traditional color gamut shown on the CIE chart is simply a slice through this color volume at a selected luminance level, such as 50%.
Three different color volumes—we still refer to them as color gamuts though their third dimension is important—are currently the most significant. The first is BT.709 (sometimes referred to as Rec.709), the color gamut used for pre-UHD/HDR formats, including standard HD.
The largest is known as BT.2020; it encompasses (roughly) the range of colors visible to the human eye (though ET might find it insufficient!).
Between these two is the color gamut used in digital cinema, known as DCI-P3.
sRGB
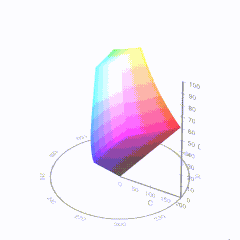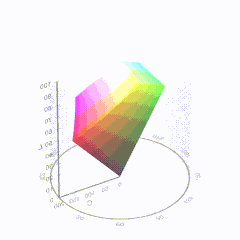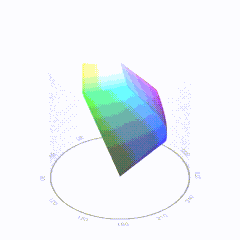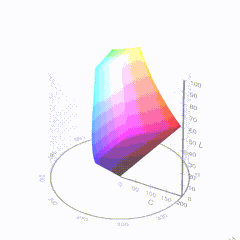
D65
-
Tobia Montanari – Memory Colors: an essential tool for Colorists
Read more: Tobia Montanari – Memory Colors: an essential tool for Coloristshttps://www.tobiamontanari.com/memory-colors-an-essential-tool-for-colorists/
“Memory colors are colors that are universally associated with specific objects, elements or scenes in our environment. They are the colors that we expect to see in specific situations: these colors are based on our expectation of how certain objects should look based on our past experiences and memories.
For instance, we associate specific hues, saturation and brightness values with human skintones and a slight variation can significantly affect the way we perceive a scene.
Similarly, we expect blue skies to have a particular hue, green trees to be a specific shade and so on.
Memory colors live inside of our brains and we often impose them onto what we see. By considering them during the grading process, the resulting image will be more visually appealing and won’t distract the viewer from the intended message of the story. Even a slight deviation from memory colors in a movie can create a sense of discordance, ultimately detracting from the viewer’s experience.”
LIGHTING
-
Simulon – a Hollywood production studio app in the hands of an independent creator with access to consumer hardware, LDRi to HDRi through ML
Read more: Simulon – a Hollywood production studio app in the hands of an independent creator with access to consumer hardware, LDRi to HDRi through MLDivesh Naidoo: The video below was made with a live in-camera preview and auto-exposure matching, no camera solve, no HDRI capture and no manual compositing setup. Using the new Simulon phone app.
LDR to HDR through ML
https://simulon.typeform.com/betatest
(more…)Process example
-
Photography basics: Color Temperature and White Balance
Read more: Photography basics: Color Temperature and White BalanceColor Temperature of a light source describes the spectrum of light which is radiated from a theoretical “blackbody” (an ideal physical body that absorbs all radiation and incident light – neither reflecting it nor allowing it to pass through) with a given surface temperature.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Color_temperature
Or. Most simply it is a method of describing the color characteristics of light through a numerical value that corresponds to the color emitted by a light source, measured in degrees of Kelvin (K) on a scale from 1,000 to 10,000.
More accurately. The color temperature of a light source is the temperature of an ideal backbody that radiates light of comparable hue to that of the light source.
(more…)
COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.