COMPOSITION
-
Christopher Butler – Understanding the Eye-Mind Connection – Vision is a mental process
Read more: Christopher Butler – Understanding the Eye-Mind Connection – Vision is a mental processhttps://www.chrbutler.com/understanding-the-eye-mind-connection
The intricate relationship between the eyes and the brain, often termed the eye-mind connection, reveals that vision is predominantly a cognitive process. This understanding has profound implications for fields such as design, where capturing and maintaining attention is paramount. This essay delves into the nuances of visual perception, the brain’s role in interpreting visual data, and how this knowledge can be applied to effective design strategies.
This cognitive aspect of vision is evident in phenomena such as optical illusions, where the brain interprets visual information in a way that contradicts physical reality. These illusions underscore that what we “see” is not merely a direct recording of the external world but a constructed experience shaped by cognitive processes.
Understanding the cognitive nature of vision is crucial for effective design. Designers must consider how the brain processes visual information to create compelling and engaging visuals. This involves several key principles:
- Attention and Engagement
- Visual Hierarchy
- Cognitive Load Management
- Context and Meaning

-
Types of Film Lights and their efficiency – CRI, Color Temperature and Luminous Efficacy
Read more: Types of Film Lights and their efficiency – CRI, Color Temperature and Luminous Efficacynofilmschool.com/types-of-film-lights
“Not every light performs the same way. Lights and lighting are tricky to handle. You have to plan for every circumstance. But the good news is, lighting can be adjusted. Let’s look at different factors that affect lighting in every scene you shoot. “
Use CRI, Luminous Efficacy and color temperature controls to match your needs.Color Temperature
Color temperature describes the “color” of white light by a light source radiated by a perfect black body at a given temperature measured in degrees Kelvinhttps://www.pixelsham.com/2019/10/18/color-temperature/
CRI
“The Color Rendering Index is a measurement of how faithfully a light source reveals the colors of whatever it illuminates, it describes the ability of a light source to reveal the color of an object, as compared to the color a natural light source would provide. The highest possible CRI is 100. A CRI of 100 generally refers to a perfect black body, like a tungsten light source or the sun. “https://www.studiobinder.com/blog/what-is-color-rendering-index
(more…) -
7 Commandments of Film Editing and composition
Read more: 7 Commandments of Film Editing and composition1. Watch every frame of raw footage twice. On the second time, take notes. If you don’t do this and try to start developing a scene premature, then it’s a big disservice to yourself and to the director, actors and production crew.
2. Nurture the relationships with the director. You are the secondary person in the relationship. Be calm and continually offer solutions. Get the main intention of the film as soon as possible from the director.
3. Organize your media so that you can find any shot instantly.
4. Factor in extra time for renders, exports, errors and crashes.
5. Attempt edits and ideas that shouldn’t work. It just might work. Until you do it and watch it, you won’t know. Don’t rule out ideas just because they don’t make sense in your mind.
6. Spend more time on your audio. It’s the glue of your edit. AUDIO SAVES EVERYTHING. Create fluid and seamless audio under your video.
7. Make cuts for the scene, but always in context for the whole film. Have a macro and a micro view at all times.
DESIGN
-
AI Dresses by MaryAnna
Read more: AI Dresses by MaryAnnahttps://www.linkedin.com/feed/update/urn:li:activity:7015985798567067648
Created by Discord user: @MaryAnna
COLOR
-
Composition – cinematography Cheat Sheet
Read more: Composition – cinematography Cheat Sheet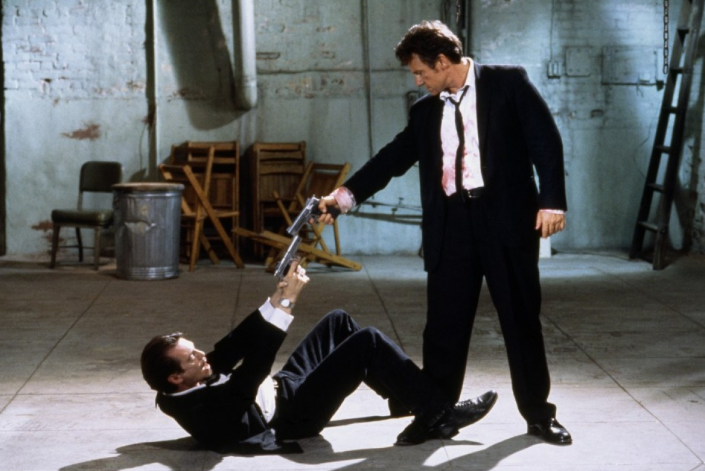
Where is our eye attracted first? Why?
Size. Focus. Lighting. Color.
Size. Mr. White (Harvey Keitel) on the right.
Focus. He’s one of the two objects in focus.
Lighting. Mr. White is large and in focus and Mr. Pink (Steve Buscemi) is highlighted by
a shaft of light.
Color. Both are black and white but the read on Mr. White’s shirt now really stands out.
(more…)
What type of lighting? -
Tim Kang – calibrated white light values in sRGB color space
Read more: Tim Kang – calibrated white light values in sRGB color space8bit sRGB encoded
2000K 255 139 22
2700K 255 172 89
3000K 255 184 109
3200K 255 190 122
4000K 255 211 165
4300K 255 219 178
D50 255 235 205
D55 255 243 224
D5600 255 244 227
D6000 255 249 240
D65 255 255 255
D10000 202 221 255
D20000 166 196 2558bit Rec709 Gamma 2.4
2000K 255 145 34
2700K 255 177 97
3000K 255 187 117
3200K 255 193 129
4000K 255 214 170
4300K 255 221 182
D50 255 236 208
D55 255 243 226
D5600 255 245 229
D6000 255 250 241
D65 255 255 255
D10000 204 222 255
D20000 170 199 2558bit Display P3 encoded
2000K 255 154 63
2700K 255 185 109
3000K 255 195 127
3200K 255 201 138
4000K 255 219 176
4300K 255 225 187
D50 255 239 212
D55 255 245 228
D5600 255 246 231
D6000 255 251 242
D65 255 255 255
D10000 208 223 255
D20000 175 199 25510bit Rec2020 PQ (100 nits)
2000K 520 435 273
2700K 520 466 358
3000K 520 475 384
3200K 520 480 399
4000K 520 495 446
4300K 520 500 458
D50 520 510 482
D55 520 514 497
D5600 520 514 500
D6000 520 517 509
D65 520 520 520
D10000 479 489 520
D20000 448 464 520 -
No one could see the colour blue until modern times
Read more: No one could see the colour blue until modern timeshttps://www.businessinsider.com/what-is-blue-and-how-do-we-see-color-2015-2

The way humans see the world… until we have a way to describe something, even something so fundamental as a colour, we may not even notice that something it’s there.
Ancient languages didn’t have a word for blue — not Greek, not Chinese, not Japanese, not Hebrew, not Icelandic cultures. And without a word for the colour, there’s evidence that they may not have seen it at all.
https://www.wnycstudios.org/story/211119-colorsEvery language first had a word for black and for white, or dark and light. The next word for a colour to come into existence — in every language studied around the world — was red, the colour of blood and wine.
After red, historically, yellow appears, and later, green (though in a couple of languages, yellow and green switch places). The last of these colours to appear in every language is blue.The only ancient culture to develop a word for blue was the Egyptians — and as it happens, they were also the only culture that had a way to produce a blue dye.
https://mymodernmet.com/shades-of-blue-color-history/True blue hues are rare in the natural world because synthesizing pigments that absorb longer-wavelength light (reds and yellows) while reflecting shorter-wavelength blue light requires exceptionally elaborate molecular structures—biochemical feats that most plants and animals simply don’t undertake.
When you gaze at a blueberry’s deep blue surface, you’re actually seeing structural coloration rather than a true blue pigment. A fine, waxy bloom on the berry’s skin contains nanostructures that preferentially scatter blue and violet light, giving the fruit its signature blue sheen even though its inherent pigment is reddish.
Similarly, many of nature’s most striking blues—like those of blue jays and morpho butterflies—arise not from blue pigments but from microscopic architectures in feathers or wing scales. These tiny ridges and air pockets manipulate incoming light so that blue wavelengths emerge most prominently, creating vivid, angle-dependent colors through scattering rather than pigment alone.
(more…) -
Anders Langlands – Render Color Spaces
Read more: Anders Langlands – Render Color Spaceshttps://www.colour-science.org/anders-langlands/
This page compares images rendered in Arnold using spectral rendering and different sets of colourspace primaries: Rec.709, Rec.2020, ACES and DCI-P3. The SPD data for the GretagMacbeth Color Checker are the measurements of Noburu Ohta, taken from Mansencal, Mauderer and Parsons (2014) colour-science.org.
-
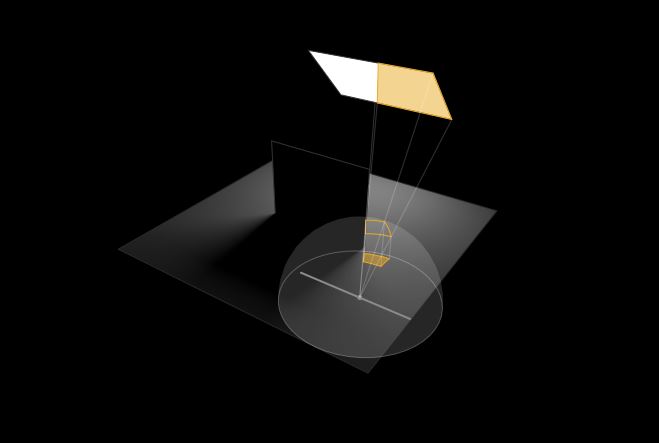
Brett Jones / Phil Reyneri (Lightform) / Philipp7pc: The study of Projection Mapping through Projectors
Read more: Brett Jones / Phil Reyneri (Lightform) / Philipp7pc: The study of Projection Mapping through ProjectorsVideo Projection Tool Software
https://hcgilje.wordpress.com/vpt/https://www.projectorpoint.co.uk/news/how-bright-should-my-projector-be/
http://www.adwindowscreens.com/the_calculator/
heavym
https://heavym.net/en/MadMapper
https://madmapper.com/
LIGHTING
-
HDRI Median Cut plugin
Read more: HDRI Median Cut pluginwww.hdrlabs.com/picturenaut/plugins.html
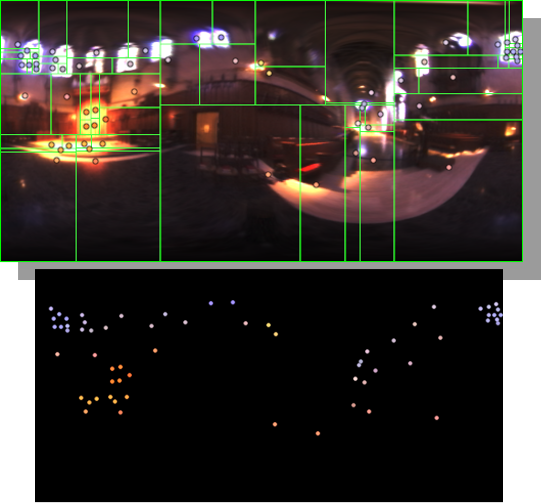
Note. The Median Cut algorithm is typically used for color quantization, which involves reducing the number of colors in an image while preserving its visual quality. It doesn’t directly provide a way to identify the brightest areas in an image. However, if you’re interested in identifying the brightest areas, you might want to look into other methods like thresholding, histogram analysis, or edge detection, through openCV for example.
Here is an openCV example:
(more…) -
Capturing the world in HDR for real time projects – Call of Duty: Advanced Warfare
Read more: Capturing the world in HDR for real time projects – Call of Duty: Advanced WarfareReal-World Measurements for Call of Duty: Advanced Warfare
www.activision.com/cdn/research/Real_World_Measurements_for_Call_of_Duty_Advanced_Warfare.pdf
Local version
Real_World_Measurements_for_Call_of_Duty_Advanced_Warfare.pdf
COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
-
sRGB vs REC709 – An introduction and FFmpeg implementations
-
Animation/VFX/Game Industry JOB POSTINGS by Chris Mayne
-
Top 3D Printing Website Resources
-
Sensitivity of human eye
-
AI and the Law – Netflix : Using Generative AI in Content Production
-
Canva bought Affinity – Now Affinity Photo and Affinity Designer are… GONE?!
-
Most common ways to smooth 3D prints
-
N8N.io – From Zero to Your First AI Agent in 25 Minutes
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.









![sRGB gamma correction test [gamma correction test]](http://www.madore.org/~david/misc/color/gammatest.png)