COMPOSITION
DESIGN
COLOR
-
SecretWeapons MixBox – a practical library for paint-like digital color mixing
Read more: SecretWeapons MixBox – a practical library for paint-like digital color mixingInternally, Mixbox treats colors as real-life pigments using the Kubelka & Munk theory to predict realistic color behavior.
https://scrtwpns.com/mixbox/painter/
https://scrtwpns.com/mixbox.pdf
https://github.com/scrtwpns/mixbox
https://scrtwpns.com/mixbox/docs/
-
FXGuide – ACES 2.0 with ILM’s Alex Fry
Read more: FXGuide – ACES 2.0 with ILM’s Alex Fryhttps://draftdocs.acescentral.com/background/whats-new/
ACES 2.0 is the second major release of the components that make up the ACES system. The most significant change is a new suite of rendering transforms whose design was informed by collected feedback and requests from users of ACES 1. The changes aim to improve the appearance of perceived artifacts and to complete previously unfinished components of the system, resulting in a more complete, robust, and consistent product.
Highlights of the key changes in ACES 2.0 are as follows:
- New output transforms, including:
- A less aggressive tone scale
- More intuitive controls to create custom outputs to non-standard displays
- Robust gamut mapping to improve perceptual uniformity
- Improved performance of the inverse transforms
- Enhanced AMF specification
- An updated specification for ACES Transform IDs
- OpenEXR compression recommendations
- Enhanced tools for generating Input Transforms and recommended procedures for characterizing prosumer cameras
- Look Transform Library
- Expanded documentation
Rendering Transform
The most substantial change in ACES 2.0 is a complete redesign of the rendering transform.
ACES 2.0 was built as a unified system, rather than through piecemeal additions. Different deliverable outputs “match” better and making outputs to display setups other than the provided presets is intended to be user-driven. The rendering transforms are less likely to produce undesirable artifacts “out of the box”, which means less time can be spent fixing problematic images and more time making pictures look the way you want.
Key design goals
- Improve consistency of tone scale and provide an easy to use parameter to allow for outputs between preset dynamic ranges
- Minimize hue skews across exposure range in a region of same hue
- Unify for structural consistency across transform type
- Easy to use parameters to create outputs other than the presets
- Robust gamut mapping to improve harsh clipping artifacts
- Fill extents of output code value cube (where appropriate and expected)
- Invertible – not necessarily reversible, but Output > ACES > Output round-trip should be possible
- Accomplish all of the above while maintaining an acceptable “out-of-the box” rendering
- New output transforms, including:
-
HDR and Color
Read more: HDR and Colorhttps://www.soundandvision.com/content/nits-and-bits-hdr-and-color
In HD we often refer to the range of available colors as a color gamut. Such a color gamut is typically plotted on a two-dimensional diagram, called a CIE chart, as shown in at the top of this blog. Each color is characterized by its x/y coordinates.
Good enough for government work, perhaps. But for HDR, with its higher luminance levels and wider color, the gamut becomes three-dimensional.
For HDR the color gamut therefore becomes a characteristic we now call the color volume. It isn’t easy to show color volume on a two-dimensional medium like the printed page or a computer screen, but one method is shown below. As the luminance becomes higher, the picture eventually turns to white. As it becomes darker, it fades to black. The traditional color gamut shown on the CIE chart is simply a slice through this color volume at a selected luminance level, such as 50%.
Three different color volumes—we still refer to them as color gamuts though their third dimension is important—are currently the most significant. The first is BT.709 (sometimes referred to as Rec.709), the color gamut used for pre-UHD/HDR formats, including standard HD.
The largest is known as BT.2020; it encompasses (roughly) the range of colors visible to the human eye (though ET might find it insufficient!).
Between these two is the color gamut used in digital cinema, known as DCI-P3.
sRGB
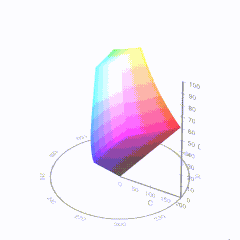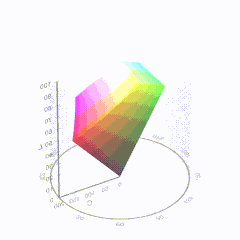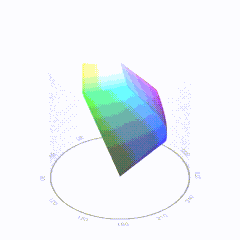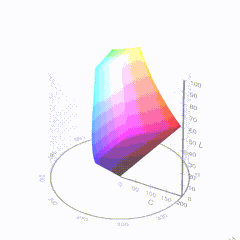
D65
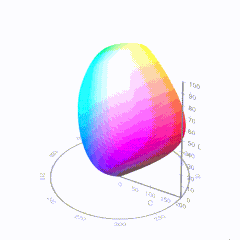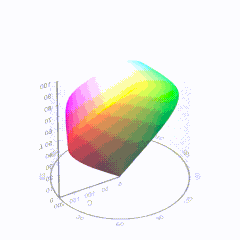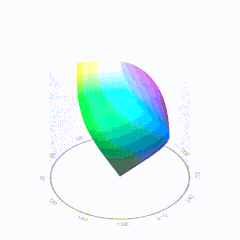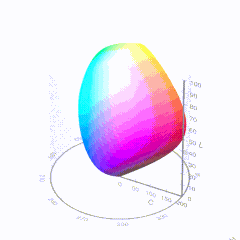
-
3D Lighting Tutorial by Amaan Kram
Read more: 3D Lighting Tutorial by Amaan Kramhttp://www.amaanakram.com/lightingT/part1.htm
The goals of lighting in 3D computer graphics are more or less the same as those of real world lighting.
Lighting serves a basic function of bringing out, or pushing back the shapes of objects visible from the camera’s view.
It gives a two-dimensional image on the monitor an illusion of the third dimension-depth.But it does not just stop there. It gives an image its personality, its character. A scene lit in different ways can give a feeling of happiness, of sorrow, of fear etc., and it can do so in dramatic or subtle ways. Along with personality and character, lighting fills a scene with emotion that is directly transmitted to the viewer.
Trying to simulate a real environment in an artificial one can be a daunting task. But even if you make your 3D rendering look absolutely photo-realistic, it doesn’t guarantee that the image carries enough emotion to elicit a “wow” from the people viewing it.
Making 3D renderings photo-realistic can be hard. Putting deep emotions in them can be even harder. However, if you plan out your lighting strategy for the mood and emotion that you want your rendering to express, you make the process easier for yourself.
Each light source can be broken down in to 4 distinct components and analyzed accordingly.
· Intensity
· Direction
· Color
· SizeThe overall thrust of this writing is to produce photo-realistic images by applying good lighting techniques.
-
What is OLED and what can it do for your TV
Read more: What is OLED and what can it do for your TVhttps://www.cnet.com/news/what-is-oled-and-what-can-it-do-for-your-tv/
OLED stands for Organic Light Emitting Diode. Each pixel in an OLED display is made of a material that glows when you jab it with electricity. Kind of like the heating elements in a toaster, but with less heat and better resolution. This effect is called electroluminescence, which is one of those delightful words that is big, but actually makes sense: “electro” for electricity, “lumin” for light and “escence” for, well, basically “essence.”
OLED TV marketing often claims “infinite” contrast ratios, and while that might sound like typical hyperbole, it’s one of the extremely rare instances where such claims are actually true. Since OLED can produce a perfect black, emitting no light whatsoever, its contrast ratio (expressed as the brightest white divided by the darkest black) is technically infinite.
OLED is the only technology capable of absolute blacks and extremely bright whites on a per-pixel basis. LCD definitely can’t do that, and even the vaunted, beloved, dearly departed plasma couldn’t do absolute blacks.
-
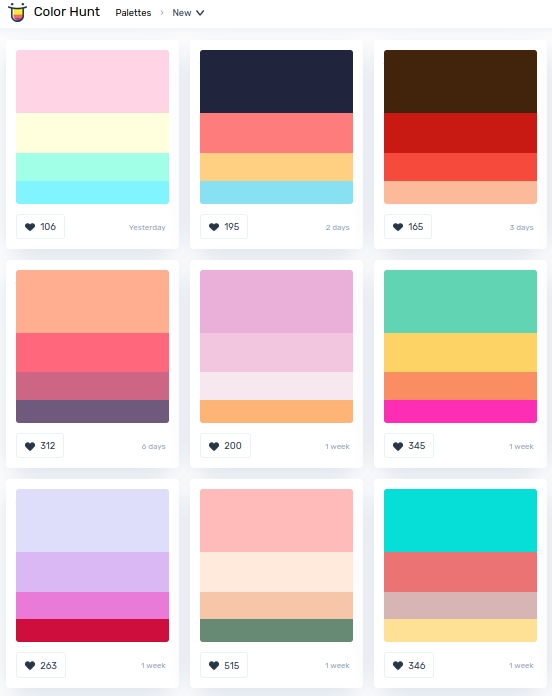
colorhunt.co
Read more: colorhunt.coColor Hunt is a free and open platform for color inspiration with thousands of trendy hand-picked color palettes.
-
PTGui 13 beta adds control through a Patch Editor
Read more: PTGui 13 beta adds control through a Patch EditorAdditions:
- Patch Editor (PTGui Pro)
- DNG output
- Improved RAW / DNG handling
- JPEG 2000 support
- Performance improvements
-
GretagMacbeth Color Checker Numeric Values and Middle Gray
Read more: GretagMacbeth Color Checker Numeric Values and Middle GrayThe human eye perceives half scene brightness not as the linear 50% of the present energy (linear nature values) but as 18% of the overall brightness. We are biased to perceive more information in the dark and contrast areas. A Macbeth chart helps with calibrating back into a photographic capture into this “human perspective” of the world.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Middle_gray
In photography, painting, and other visual arts, middle gray or middle grey is a tone that is perceptually about halfway between black and white on a lightness scale in photography and printing, it is typically defined as 18% reflectance in visible light
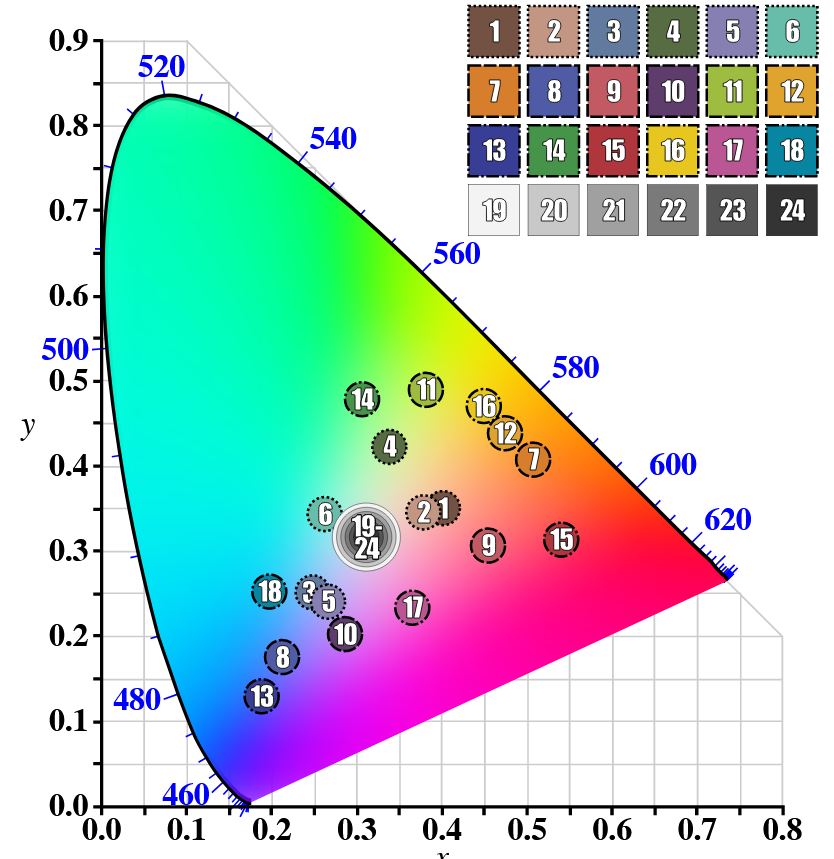
Light meters, cameras, and pictures are often calibrated using an 18% gray card[4][5][6] or a color reference card such as a ColorChecker. On the assumption that 18% is similar to the average reflectance of a scene, a grey card can be used to estimate the required exposure of the film.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ColorChecker
(more…)
LIGHTING
-
Composition – cinematography Cheat Sheet
Read more: Composition – cinematography Cheat Sheet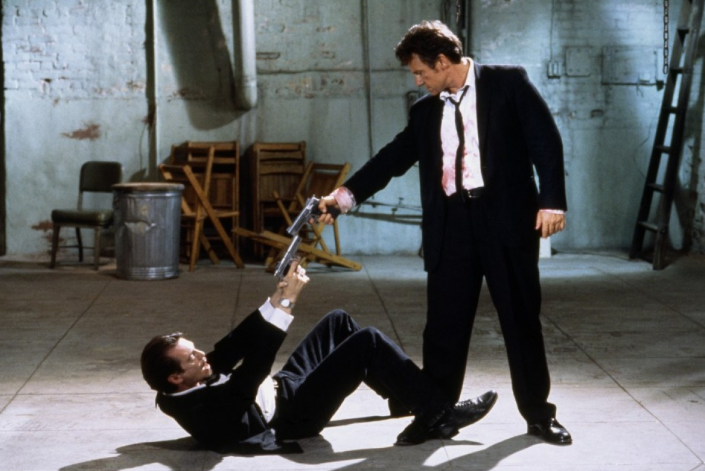
Where is our eye attracted first? Why?
Size. Focus. Lighting. Color.
Size. Mr. White (Harvey Keitel) on the right.
Focus. He’s one of the two objects in focus.
Lighting. Mr. White is large and in focus and Mr. Pink (Steve Buscemi) is highlighted by
a shaft of light.
Color. Both are black and white but the read on Mr. White’s shirt now really stands out.
(more…)
What type of lighting? -
About green screens
Read more: About green screenshackaday.com/2015/02/07/how-green-screen-worked-before-computers/
www.newtek.com/blog/tips/best-green-screen-materials/
www.chromawall.com/blog//chroma-key-green
Chroma Key Green, the color of green screens is also known as Chroma Green and is valued at approximately 354C in the Pantone color matching system (PMS).
Chroma Green can be broken down in many different ways. Here is green screen green as other values useful for both physical and digital production:
Green Screen as RGB Color Value: 0, 177, 64
Green Screen as CMYK Color Value: 81, 0, 92, 0
Green Screen as Hex Color Value: #00b140
Green Screen as Websafe Color Value: #009933Chroma Key Green is reasonably close to an 18% gray reflectance.
Illuminate your green screen with an uniform source with less than 2/3 EV variation.
The level of brightness at any given f-stop should be equivalent to a 90% white card under the same lighting. -
7 Easy Portrait Lighting Setups
Read more: 7 Easy Portrait Lighting SetupsButterfly
Loop
Rembrandt
Split
Rim
Broad
Short
-
NVidia DiffusionRenderer – Neural Inverse and Forward Rendering with Video Diffusion Models. How NVIDIA reimagined relighting
Read more: NVidia DiffusionRenderer – Neural Inverse and Forward Rendering with Video Diffusion Models. How NVIDIA reimagined relightinghttps://www.fxguide.com/quicktakes/diffusing-reality-how-nvidia-reimagined-relighting/
https://research.nvidia.com/labs/toronto-ai/DiffusionRenderer/
-
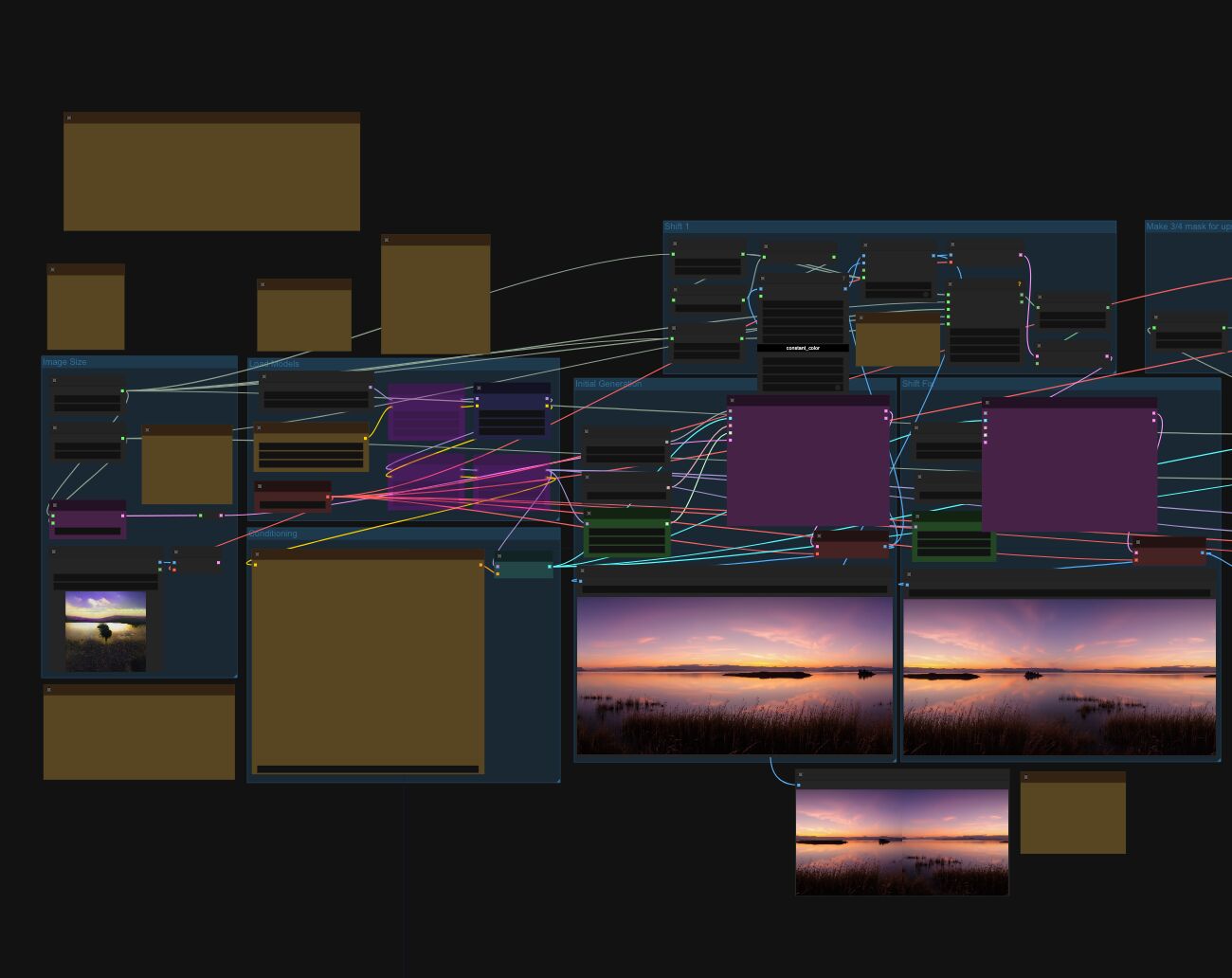
Arto T. – A workflow for creating photorealistic, equirectangular 360° panoramas in ComfyUI using Flux
Read more: Arto T. – A workflow for creating photorealistic, equirectangular 360° panoramas in ComfyUI using Fluxhttps://civitai.com/models/735980/flux-equirectangular-360-panorama
https://civitai.com/models/745010?modelVersionId=833115
The trigger phrase is “equirectangular 360 degree panorama”. I would avoid saying “spherical projection” since that tends to result in non-equirectangular spherical images.
Image resolution should always be a 2:1 aspect ratio. 1024 x 512 or 1408 x 704 work quite well and were used in the training data. 2048 x 1024 also works.
I suggest using a weight of 0.5 – 1.5. If you are having issues with the image generating too flat instead of having the necessary spherical distortion, try increasing the weight above 1, though this could negatively impact small details of the image. For Flux guidance, I recommend a value of about 2.5 for realistic scenes.
8-bit output at the moment

-
PTGui 13 beta adds control through a Patch Editor
Read more: PTGui 13 beta adds control through a Patch EditorAdditions:
- Patch Editor (PTGui Pro)
- DNG output
- Improved RAW / DNG handling
- JPEG 2000 support
- Performance improvements
COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.