COMPOSITION
-
7 Commandments of Film Editing and composition
Read more: 7 Commandments of Film Editing and composition1. Watch every frame of raw footage twice. On the second time, take notes. If you don’t do this and try to start developing a scene premature, then it’s a big disservice to yourself and to the director, actors and production crew.
2. Nurture the relationships with the director. You are the secondary person in the relationship. Be calm and continually offer solutions. Get the main intention of the film as soon as possible from the director.
3. Organize your media so that you can find any shot instantly.
4. Factor in extra time for renders, exports, errors and crashes.
5. Attempt edits and ideas that shouldn’t work. It just might work. Until you do it and watch it, you won’t know. Don’t rule out ideas just because they don’t make sense in your mind.
6. Spend more time on your audio. It’s the glue of your edit. AUDIO SAVES EVERYTHING. Create fluid and seamless audio under your video.
7. Make cuts for the scene, but always in context for the whole film. Have a macro and a micro view at all times.
DESIGN
-
Principles of Interior Design – Balance
Read more: Principles of Interior Design – Balancehttps://www.yankodesign.com/2024/09/18/principles-of-interior-design-balance
The three types of balance include:
- Symmetrical Balance
- Asymmetrical Balance
- Radial Balance
-
Goga Tandashvili – bas-relief master
Read more: Goga Tandashvili – bas-relief master@moltenimmersiveart Goga Tandashvili is a master of the art of Bas-Relief. Using this technique, he creates stunning figures that are slightly raised from a flat surface, bringing scenes inspired by the natural world to life. #Art #Artists #GogaTandashvili #BasReliefSculpture #ArtInspiredByNature #ImpressionistArt #BasRelief #Sculptures #Sculptor #Molten #MoltenArt #MoltenImmersiveArt #MoltenAffect #Curation #Curator #ArtCuration #ArtCurator #DorothyDiStefano ♬ original sound – Molten Immersive Art
COLOR
-
Paul Debevec, Chloe LeGendre, Lukas Lepicovsky – Jointly Optimizing Color Rendition and In-Camera Backgrounds in an RGB Virtual Production Stage
Read more: Paul Debevec, Chloe LeGendre, Lukas Lepicovsky – Jointly Optimizing Color Rendition and In-Camera Backgrounds in an RGB Virtual Production Stagehttps://arxiv.org/pdf/2205.12403.pdf
RGB LEDs vs RGBWP (RGB + lime + phospor converted amber) LEDs
Local copy:
-
HDR and Color
Read more: HDR and Colorhttps://www.soundandvision.com/content/nits-and-bits-hdr-and-color
In HD we often refer to the range of available colors as a color gamut. Such a color gamut is typically plotted on a two-dimensional diagram, called a CIE chart, as shown in at the top of this blog. Each color is characterized by its x/y coordinates.
Good enough for government work, perhaps. But for HDR, with its higher luminance levels and wider color, the gamut becomes three-dimensional.
For HDR the color gamut therefore becomes a characteristic we now call the color volume. It isn’t easy to show color volume on a two-dimensional medium like the printed page or a computer screen, but one method is shown below. As the luminance becomes higher, the picture eventually turns to white. As it becomes darker, it fades to black. The traditional color gamut shown on the CIE chart is simply a slice through this color volume at a selected luminance level, such as 50%.
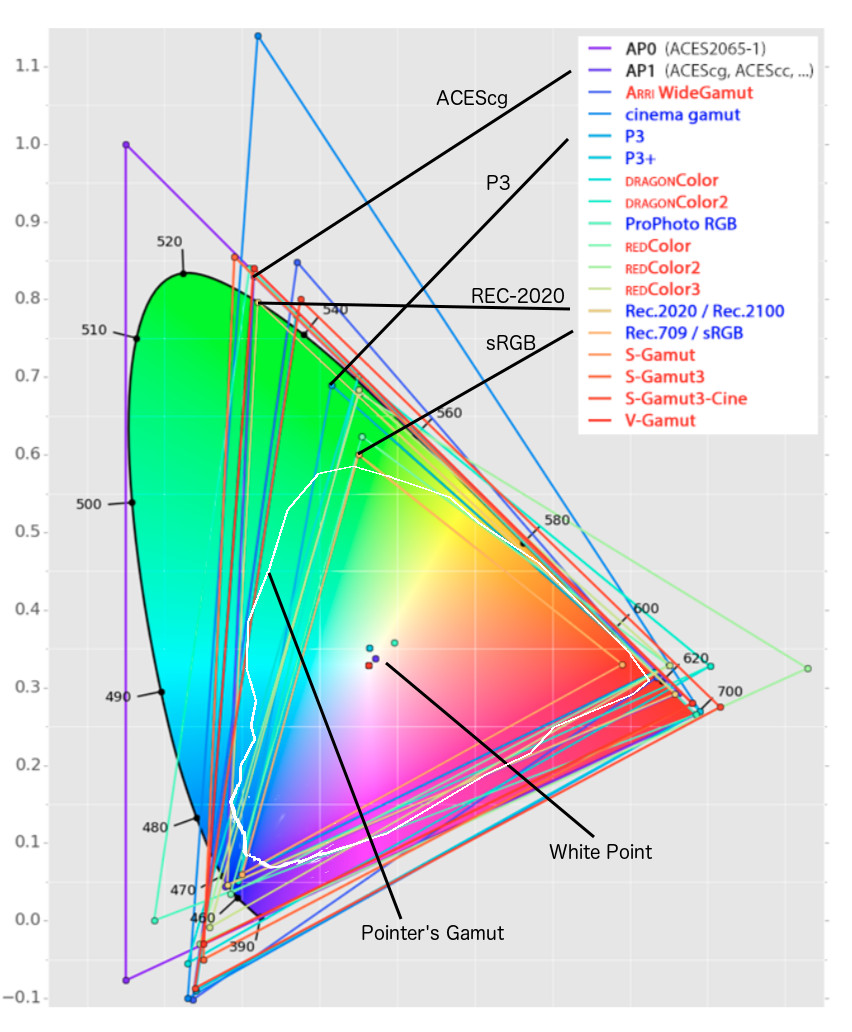
Three different color volumes—we still refer to them as color gamuts though their third dimension is important—are currently the most significant. The first is BT.709 (sometimes referred to as Rec.709), the color gamut used for pre-UHD/HDR formats, including standard HD.
The largest is known as BT.2020; it encompasses (roughly) the range of colors visible to the human eye (though ET might find it insufficient!).
Between these two is the color gamut used in digital cinema, known as DCI-P3.
sRGB
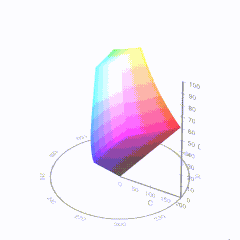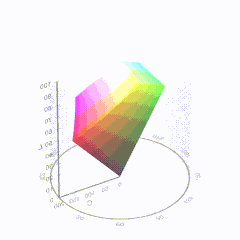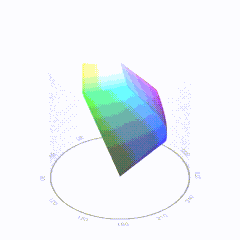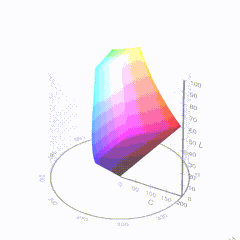
D65
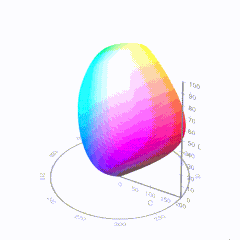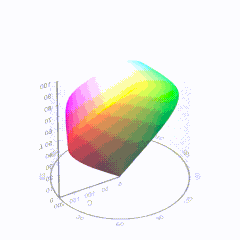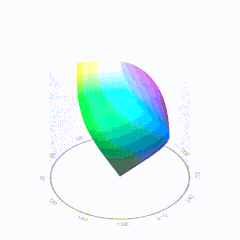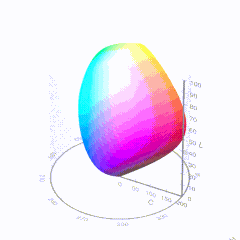
-
Practical Aspects of Spectral Data and LEDs in Digital Content Production and Virtual Production – SIGGRAPH 2022
Read more: Practical Aspects of Spectral Data and LEDs in Digital Content Production and Virtual Production – SIGGRAPH 2022Comparison to the commercial side

https://www.ecolorled.com/blog/detail/what-is-rgb-rgbw-rgbic-strip-lights
RGBW (RGB + White) LED strip uses a 4-in-1 LED chip made up of red, green, blue, and white.
RGBWW (RGB + White + Warm White) LED strip uses either a 5-in-1 LED chip with red, green, blue, white, and warm white for color mixing. The only difference between RGBW and RGBWW is the intensity of the white color. The term RGBCCT consists of RGB and CCT. CCT (Correlated Color Temperature) means that the color temperature of the led strip light can be adjusted to change between warm white and white. Thus, RGBWW strip light is another name of RGBCCT strip.
RGBCW is the acronym for Red, Green, Blue, Cold, and Warm. These 5-in-1 chips are used in supper bright smart LED lighting products
-
Rec-2020 – TVs new color gamut standard used by Dolby Vision?
Read more: Rec-2020 – TVs new color gamut standard used by Dolby Vision?https://www.hdrsoft.com/resources/dri.html#bit-depth
The dynamic range is a ratio between the maximum and minimum values of a physical measurement. Its definition depends on what the dynamic range refers to.
For a scene: Dynamic range is the ratio between the brightest and darkest parts of the scene.
For a camera: Dynamic range is the ratio of saturation to noise. More specifically, the ratio of the intensity that just saturates the camera to the intensity that just lifts the camera response one standard deviation above camera noise.
For a display: Dynamic range is the ratio between the maximum and minimum intensities emitted from the screen.
The Dynamic Range of real-world scenes can be quite high — ratios of 100,000:1 are common in the natural world. An HDR (High Dynamic Range) image stores pixel values that span the whole tonal range of real-world scenes. Therefore, an HDR image is encoded in a format that allows the largest range of values, e.g. floating-point values stored with 32 bits per color channel. Another characteristics of an HDR image is that it stores linear values. This means that the value of a pixel from an HDR image is proportional to the amount of light measured by the camera.
For TVs HDR is great, but it’s not the only new TV feature worth discussing.
(more…) -
GretagMacbeth Color Checker Numeric Values and Middle Gray
Read more: GretagMacbeth Color Checker Numeric Values and Middle GrayThe human eye perceives half scene brightness not as the linear 50% of the present energy (linear nature values) but as 18% of the overall brightness. We are biased to perceive more information in the dark and contrast areas. A Macbeth chart helps with calibrating back into a photographic capture into this “human perspective” of the world.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Middle_gray
In photography, painting, and other visual arts, middle gray or middle grey is a tone that is perceptually about halfway between black and white on a lightness scale in photography and printing, it is typically defined as 18% reflectance in visible light
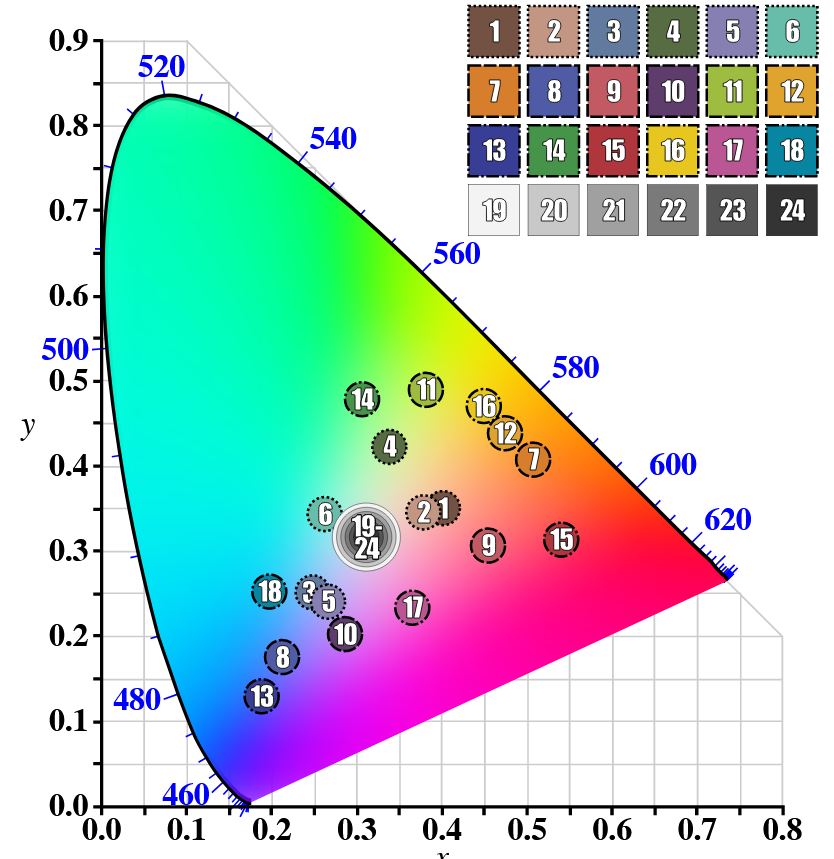
Light meters, cameras, and pictures are often calibrated using an 18% gray card[4][5][6] or a color reference card such as a ColorChecker. On the assumption that 18% is similar to the average reflectance of a scene, a grey card can be used to estimate the required exposure of the film.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ColorChecker
(more…)
LIGHTING
-
Custom bokeh in a raytraced DOF render
Read more: Custom bokeh in a raytraced DOF renderTo achieve a custom pinhole camera effect with a custom bokeh in Arnold Raytracer, you can follow these steps:
- Set the render camera with a focal length around 50 (or as needed)
- Set the F-Stop to a high value (e.g., 22).
- Set the focus distance as you require
- Turn on DOF
- Place a plane a few cm in front of the camera.
- Texture the plane with a transparent shape at the center of it. (Transmission with no specular roughness)
-
studiobinder.com – What is Tenebrism and Hard Lighting — The Art of Light and Shadow and chiaroscuro Explained
Read more: studiobinder.com – What is Tenebrism and Hard Lighting — The Art of Light and Shadow and chiaroscuro Explainedhttps://www.studiobinder.com/blog/what-is-tenebrism-art-definition/
https://www.studiobinder.com/blog/what-is-hard-light-photography/
-
How to Direct and Edit a Fight Scene for Rhythm and Pacing
Read more: How to Direct and Edit a Fight Scene for Rhythm and Pacingwww.premiumbeat.com/blog/directing-fight-scene-cinematography/
1- Frame the action
2- Stage the action
3- Use camera movements
4- Set a rhythm
5- Control the speed of the action
COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
-
Types of AI Explained in a few Minutes – AI Glossary
-
sRGB vs REC709 – An introduction and FFmpeg implementations
-
Blender VideoDepthAI – Turn any video into 3D Animated Scenes
-
Guide to Prompt Engineering
-
Web vs Printing or digital RGB vs CMYK
-
ComfyUI FLOAT – A container for FLOAT Generative Motion Latent Flow Matching for Audio-driven Talking Portrait – lip sync
-
QR code logos
-
NVidia – High-Fidelity 3D Mesh Generation at Scale with Meshtron
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.