COMPOSITION
DESIGN
COLOR
-
PBR Color Reference List for Materials – by Grzegorz Baran
Read more: PBR Color Reference List for Materials – by Grzegorz Baran“The list should be helpful for every material artist who work on PBR materials as it contains over 200 color values measured with PCE-RGB2 1002 Color Spectrometer device and presented in linear and sRGB (2.2) gamma space.
All color values, HUE and Saturation in this list come from measurements taken with PCE-RGB2 1002 Color Spectrometer device and are presented in linear and sRGB (2.2) gamma space (more info at the end of this video) I calculated Relative Luminance and Luminance values based on captured color using my own equation which takes color based luminance perception into consideration. Bare in mind that there is no ‘one’ color per substance as nothing in nature is even 100% uniform and any value in +/-10% range from these should be considered as correct one. Therefore this list should be always considered as a color reference for material’s albedos, not ulitimate and absolute truth.“
-
PTGui 13 beta adds control through a Patch Editor
Read more: PTGui 13 beta adds control through a Patch EditorAdditions:
- Patch Editor (PTGui Pro)
- DNG output
- Improved RAW / DNG handling
- JPEG 2000 support
- Performance improvements
-
OLED vs QLED – What TV is better?
Read more: OLED vs QLED – What TV is better?Supported by LG, Philips, Panasonic and Sony sell the OLED system TVs.
OLED stands for “organic light emitting diode.”
It is a fundamentally different technology from LCD, the major type of TV today.
OLED is “emissive,” meaning the pixels emit their own light.Samsung is branding its best TVs with a new acronym: “QLED”
QLED (according to Samsung) stands for “quantum dot LED TV.”
It is a variation of the common LED LCD, adding a quantum dot film to the LCD “sandwich.”
QLED, like LCD, is, in its current form, “transmissive” and relies on an LED backlight.OLED is the only technology capable of absolute blacks and extremely bright whites on a per-pixel basis. LCD definitely can’t do that, and even the vaunted, beloved, dearly departed plasma couldn’t do absolute blacks.
QLED, as an improvement over OLED, significantly improves the picture quality. QLED can produce an even wider range of colors than OLED, which says something about this new tech. QLED is also known to produce up to 40% higher luminance efficiency than OLED technology. Further, many tests conclude that QLED is far more efficient in terms of power consumption than its predecessor, OLED.
(more…) -
If a blind person gained sight, could they recognize objects previously touched?
Read more: If a blind person gained sight, could they recognize objects previously touched?Blind people who regain their sight may find themselves in a world they don’t immediately comprehend. “It would be more like a sighted person trying to rely on tactile information,” Moore says.
Learning to see is a developmental process, just like learning language, Prof Cathleen Moore continues. “As far as vision goes, a three-and-a-half year old child is already a well-calibrated system.”
-
Pattern generators
Read more: Pattern generatorshttp://qrohlf.com/trianglify-generator/
https://halftonepro.com/app/polygons#
https://mattdesl.svbtle.com/generative-art-with-nodejs-and-canvas
https://www.patterncooler.com/
http://permadi.com/java/spaint/spaint.html
https://dribbble.com/shots/1847313-Kaleidoscope-Generator-PSD
http://eskimoblood.github.io/gerstnerizer/
http://www.stripegenerator.com/
http://btmills.github.io/geopattern/geopattern.html
http://fractalarchitect.net/FA4-Random-Generator.html
https://sciencevsmagic.net/fractal/#0605,0000,3,2,0,1,2
https://sites.google.com/site/mandelbulber/home
-
The Color of Infinite Temperature
Read more: The Color of Infinite TemperatureThis is the color of something infinitely hot.

Of course you’d instantly be fried by gamma rays of arbitrarily high frequency, but this would be its spectrum in the visible range.
johncarlosbaez.wordpress.com/2022/01/16/the-color-of-infinite-temperature/
This is also the color of a typical neutron star. They’re so hot they look the same.
It’s also the color of the early Universe!This was worked out by David Madore.
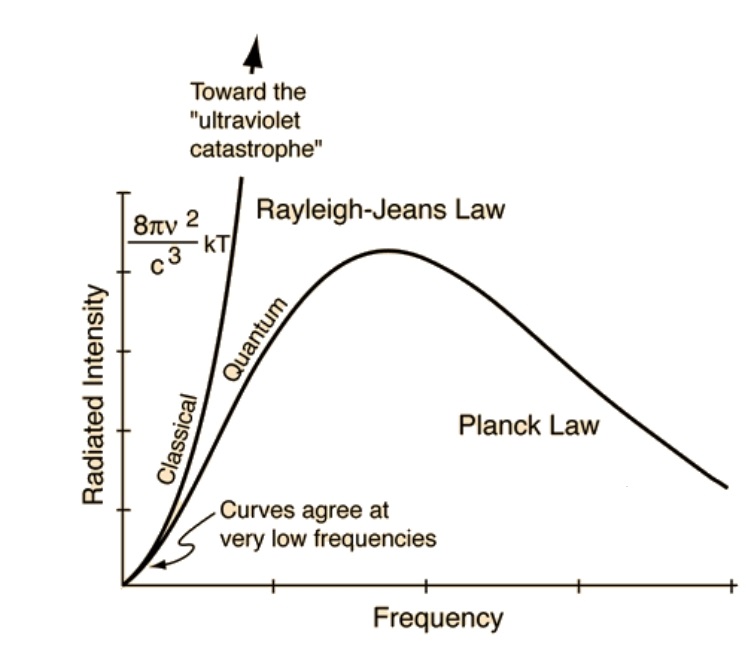
The color he got is sRGB(148,177,255).
www.htmlcsscolor.com/hex/94B1FFAnd according to the experts who sip latte all day and make up names for colors, this color is called ‘Perano’.
-
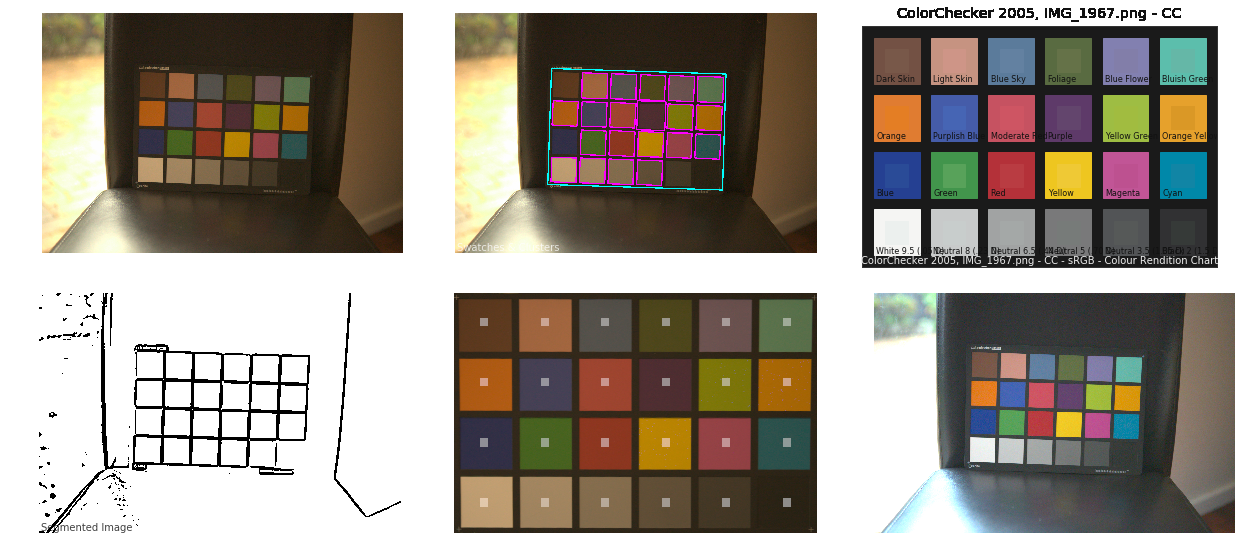
Colour – MacBeth Chart Checker Detection
Read more: Colour – MacBeth Chart Checker Detectiongithub.com/colour-science/colour-checker-detection
A Python package implementing various colour checker detection algorithms and related utilities.
-
Scientists claim to have discovered ‘new colour’ no one has seen before: Olo
Read more: Scientists claim to have discovered ‘new colour’ no one has seen before: Olohttps://www.bbc.com/news/articles/clyq0n3em41o
By stimulating specific cells in the retina, the participants claim to have witnessed a blue-green colour that scientists have called “olo”, but some experts have said the existence of a new colour is “open to argument”.
The findings, published in the journal Science Advances on Friday, have been described by the study’s co-author, Prof Ren Ng from the University of California, as “remarkable”.
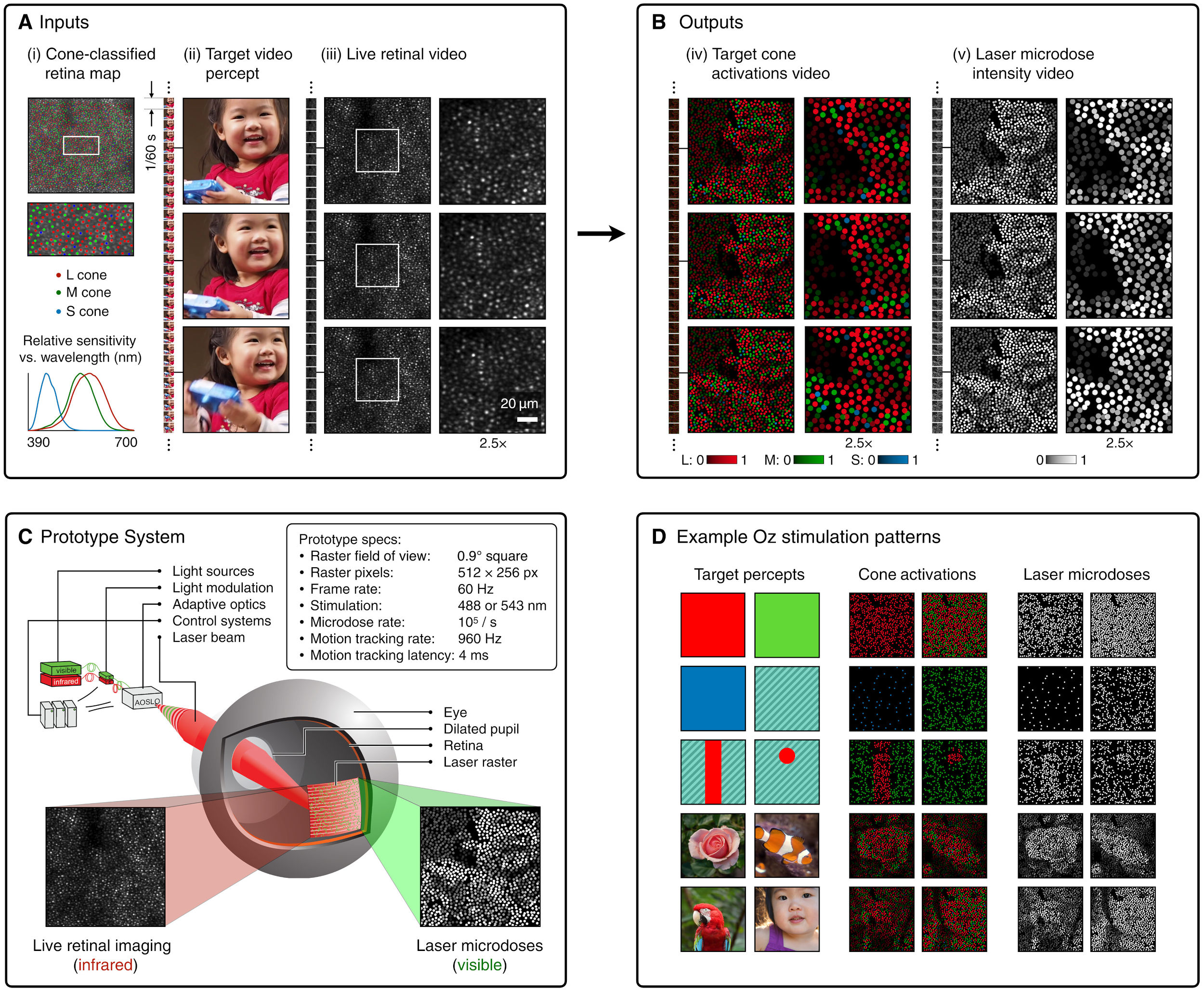
(A) System inputs. (i) Retina map of 103 cone cells preclassified by spectral type (7). (ii) Target visual percept (here, a video of a child, see movie S1 at 1:04). (iii) Infrared cellular-scale imaging of the retina with 60-frames-per-second rolling shutter. Fixational eye movement is visible over the three frames shown.
(B) System outputs. (iv) Real-time per-cone target activation levels to reproduce the target percept, computed by: extracting eye motion from the input video relative to the retina map; identifying the spectral type of every cone in the field of view; computing the per-cone activation the target percept would have produced. (v) Intensities of visible-wavelength 488-nm laser microdoses at each cone required to achieve its target activation level.
(C) Infrared imaging and visible-wavelength stimulation are physically accomplished in a raster scan across the retinal region using AOSLO. By modulating the visible-wavelength beam’s intensity, the laser microdoses shown in (v) are delivered. Drawing adapted with permission [Harmening and Sincich (54)].
(D) Examples of target percepts with corresponding cone activations and laser microdoses, ranging from colored squares to complex imagery. Teal-striped regions represent the color “olo” of stimulating only M cones.
-
A Brief History of Color in Art
Read more: A Brief History of Color in Artwww.artsy.net/article/the-art-genome-project-a-brief-history-of-color-in-art
Of all the pigments that have been banned over the centuries, the color most missed by painters is likely Lead White.
This hue could capture and reflect a gleam of light like no other, though its production was anything but glamorous. The 17th-century Dutch method for manufacturing the pigment involved layering cow and horse manure over lead and vinegar. After three months in a sealed room, these materials would combine to create flakes of pure white. While scientists in the late 19th century identified lead as poisonous, it wasn’t until 1978 that the United States banned the production of lead white paint.
More reading:
www.canva.com/learn/color-meanings/https://www.infogrades.com/history-events-infographics/bizarre-history-of-colors/
LIGHTING
-
Terminators and Iron Men: HDRI, Image-based lighting and physical shading at ILM – Siggraph 2010
Read more: Terminators and Iron Men: HDRI, Image-based lighting and physical shading at ILM – Siggraph 2010 -
Arto T. – A workflow for creating photorealistic, equirectangular 360° panoramas in ComfyUI using Flux
Read more: Arto T. – A workflow for creating photorealistic, equirectangular 360° panoramas in ComfyUI using Fluxhttps://civitai.com/models/735980/flux-equirectangular-360-panorama
https://civitai.com/models/745010?modelVersionId=833115
The trigger phrase is “equirectangular 360 degree panorama”. I would avoid saying “spherical projection” since that tends to result in non-equirectangular spherical images.
Image resolution should always be a 2:1 aspect ratio. 1024 x 512 or 1408 x 704 work quite well and were used in the training data. 2048 x 1024 also works.
I suggest using a weight of 0.5 – 1.5. If you are having issues with the image generating too flat instead of having the necessary spherical distortion, try increasing the weight above 1, though this could negatively impact small details of the image. For Flux guidance, I recommend a value of about 2.5 for realistic scenes.
8-bit output at the moment

-
Willem Zwarthoed – Aces gamut in VFX production pdf
Read more: Willem Zwarthoed – Aces gamut in VFX production pdfhttps://www.provideocoalition.com/color-management-part-12-introducing-aces/
Local copy:
https://www.slideshare.net/hpduiker/acescg-a-common-color-encoding-for-visual-effects-applications
-
What is physically correct lighting all about?
Read more: What is physically correct lighting all about?http://gamedev.stackexchange.com/questions/60638/what-is-physically-correct-lighting-all-about
2012-08 Nathan Reed wrote:
Physically-based shading means leaving behind phenomenological models, like the Phong shading model, which are simply built to “look good” subjectively without being based on physics in any real way, and moving to lighting and shading models that are derived from the laws of physics and/or from actual measurements of the real world, and rigorously obey physical constraints such as energy conservation.
For example, in many older rendering systems, shading models included separate controls for specular highlights from point lights and reflection of the environment via a cubemap. You could create a shader with the specular and the reflection set to wildly different values, even though those are both instances of the same physical process. In addition, you could set the specular to any arbitrary brightness, even if it would cause the surface to reflect more energy than it actually received.
In a physically-based system, both the point light specular and the environment reflection would be controlled by the same parameter, and the system would be set up to automatically adjust the brightness of both the specular and diffuse components to maintain overall energy conservation. Moreover you would want to set the specular brightness to a realistic value for the material you’re trying to simulate, based on measurements.
Physically-based lighting or shading includes physically-based BRDFs, which are usually based on microfacet theory, and physically correct light transport, which is based on the rendering equation (although heavily approximated in the case of real-time games).
It also includes the necessary changes in the art process to make use of these features. Switching to a physically-based system can cause some upsets for artists. First of all it requires full HDR lighting with a realistic level of brightness for light sources, the sky, etc. and this can take some getting used to for the lighting artists. It also requires texture/material artists to do some things differently (particularly for specular), and they can be frustrated by the apparent loss of control (e.g. locking together the specular highlight and environment reflection as mentioned above; artists will complain about this). They will need some time and guidance to adapt to the physically-based system.
On the plus side, once artists have adapted and gained trust in the physically-based system, they usually end up liking it better, because there are fewer parameters overall (less work for them to tweak). Also, materials created in one lighting environment generally look fine in other lighting environments too. This is unlike more ad-hoc models, where a set of material parameters might look good during daytime, but it comes out ridiculously glowy at night, or something like that.
Here are some resources to look at for physically-based lighting in games:
SIGGRAPH 2013 Physically Based Shading Course, particularly the background talk by Naty Hoffman at the beginning. You can also check out the previous incarnations of this course for more resources.
Sébastien Lagarde, Adopting a physically-based shading model and Feeding a physically-based shading model
And of course, I would be remiss if I didn’t mention Physically-Based Rendering by Pharr and Humphreys, an amazing reference on this whole subject and well worth your time, although it focuses on offline rather than real-time rendering.
-
Unity 3D resources
Read more: Unity 3D resources
http://answers.unity3d.com/questions/12321/how-can-i-start-learning-unity-fast-list-of-tutori.html
If you have no previous experience with Unity, start with these six video tutorials which give a quick overview of the Unity interface and some important features http://unity3d.com/support/documentation/video/
COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.




