COMPOSITION
-
Photography basics: Depth of Field and composition
Read more: Photography basics: Depth of Field and compositionDepth of field is the range within which focusing is resolved in a photo.
Aperture has a huge affect on to the depth of field.Changing the f-stops (f/#) of a lens will change aperture and as such the DOF.
f-stops are a just certain number which is telling you the size of the aperture. That’s how f-stop is related to aperture (and DOF).
If you increase f-stops, it will increase DOF, the area in focus (and decrease the aperture). On the other hand, decreasing the f-stop it will decrease DOF (and increase the aperture).
The red cone in the figure is an angular representation of the resolution of the system. Versus the dotted lines, which indicate the aperture coverage. Where the lines of the two cones intersect defines the total range of the depth of field.
This image explains why the longer the depth of field, the greater the range of clarity.
DESIGN
-
Turn Yourself Into an Action Figure Using ChatGPT
Read more: Turn Yourself Into an Action Figure Using ChatGPTChatGPT Action Figure Prompts:
Create an action figure from the photo. It must be visualised in a realistic way. There should be accessories next to the figure like a UX designer have, Macbook Pro, a camera, drawing tablet, headset etc. Add a hole to the top of the box in the action figure. Also write the text “UX Mate” and below it “Keep Learning! Keep Designing
Use this image to create a picture of a action figure toy of a construction worker in a blister package from head to toe with accessories including a hammer, a staple gun and a ladder. The package should read “Kirk The Handy Man”
Create a realistic image of a toy action figure box. The box should be designed in a toy-equipment/action-figure style, with a cut-out window at the top like classic action figure packaging. The main color of the box and moleskine notebook should match the color of my jacket (referenced visually). Add colorful Mexican skull decorations across the box for a vibrant and artistic flair. Inside the box, include a “Your name” action figure, posed heroically. Next to the figure, arrange the following “equipment” in a stylized layout: • item 1 • item 2 … On the box, write: “Your name” (bold title font) Underneath: “Your role or anything else” The entire scene should look like a real product mockup, highly realistic, lit like a studio product photo. On the box, write: “Your name” (bold title font) Underneath: “Your role or description” The entire scene should look like a real product mockup, highly realistic, lit like a studio product photo. Prompt on Kling AI The figure steps out of its toy packaging and begins walking forward. As he continues to walk, the camera gradually zooms out in sync with his movement.
“Create image. Create a toy of the person in the photo. Let it be an action figure. Next to the figure, there should be the toy’s equipment, each in its individual blisters. 1) a book called “Tecnoforma”. 2) A 3-headed dog with a tag that says “Troika” and a bone at its feet with word “austerity” written on it. 3) a three-headed Hydra with with a tag called “Geringonça”. 4) a book titled “D. Sebastião”. Don’t repeat the equipment under any circumstance. The card holding the blister should be strong orange. Also, on top of the box, write ‘Pedro Passos Coelho’ and underneath it, ‘PSD action figure’. The figure and equipment must all be inside blisters. Visualize this in a realistic way.”
-
Kristina Kashtanova – “This is how GPT-4 sees and hears itself”
Read more: Kristina Kashtanova – “This is how GPT-4 sees and hears itself”“I used GPT-4 to describe itself. Then I used its description to generate an image, a video based on this image and a soundtrack.
Tools I used: GPT-4, Midjourney, Kaiber AI, Mubert, RunwayML
This is the description I used that GPT-4 had of itself as a prompt to text-to-image, image-to-video, and text-to-music. I put the video and sound together in RunwayML.
GPT-4 described itself as: “Imagine a sleek, metallic sphere with a smooth surface, representing the vast knowledge contained within the model. The sphere emits a soft, pulsating glow that shifts between various colors, symbolizing the dynamic nature of the AI as it processes information and generates responses. The sphere appears to float in a digital environment, surrounded by streams of data and code, reflecting the complex algorithms and computing power behind the AI”
COLOR
-
Practical Aspects of Spectral Data and LEDs in Digital Content Production and Virtual Production – SIGGRAPH 2022
Read more: Practical Aspects of Spectral Data and LEDs in Digital Content Production and Virtual Production – SIGGRAPH 2022Comparison to the commercial side

https://www.ecolorled.com/blog/detail/what-is-rgb-rgbw-rgbic-strip-lights
RGBW (RGB + White) LED strip uses a 4-in-1 LED chip made up of red, green, blue, and white.
RGBWW (RGB + White + Warm White) LED strip uses either a 5-in-1 LED chip with red, green, blue, white, and warm white for color mixing. The only difference between RGBW and RGBWW is the intensity of the white color. The term RGBCCT consists of RGB and CCT. CCT (Correlated Color Temperature) means that the color temperature of the led strip light can be adjusted to change between warm white and white. Thus, RGBWW strip light is another name of RGBCCT strip.
RGBCW is the acronym for Red, Green, Blue, Cold, and Warm. These 5-in-1 chips are used in supper bright smart LED lighting products
-
3D Lighting Tutorial by Amaan Kram
Read more: 3D Lighting Tutorial by Amaan Kramhttp://www.amaanakram.com/lightingT/part1.htm
The goals of lighting in 3D computer graphics are more or less the same as those of real world lighting.
Lighting serves a basic function of bringing out, or pushing back the shapes of objects visible from the camera’s view.
It gives a two-dimensional image on the monitor an illusion of the third dimension-depth.But it does not just stop there. It gives an image its personality, its character. A scene lit in different ways can give a feeling of happiness, of sorrow, of fear etc., and it can do so in dramatic or subtle ways. Along with personality and character, lighting fills a scene with emotion that is directly transmitted to the viewer.
Trying to simulate a real environment in an artificial one can be a daunting task. But even if you make your 3D rendering look absolutely photo-realistic, it doesn’t guarantee that the image carries enough emotion to elicit a “wow” from the people viewing it.
Making 3D renderings photo-realistic can be hard. Putting deep emotions in them can be even harder. However, if you plan out your lighting strategy for the mood and emotion that you want your rendering to express, you make the process easier for yourself.
Each light source can be broken down in to 4 distinct components and analyzed accordingly.
· Intensity
· Direction
· Color
· SizeThe overall thrust of this writing is to produce photo-realistic images by applying good lighting techniques.
-
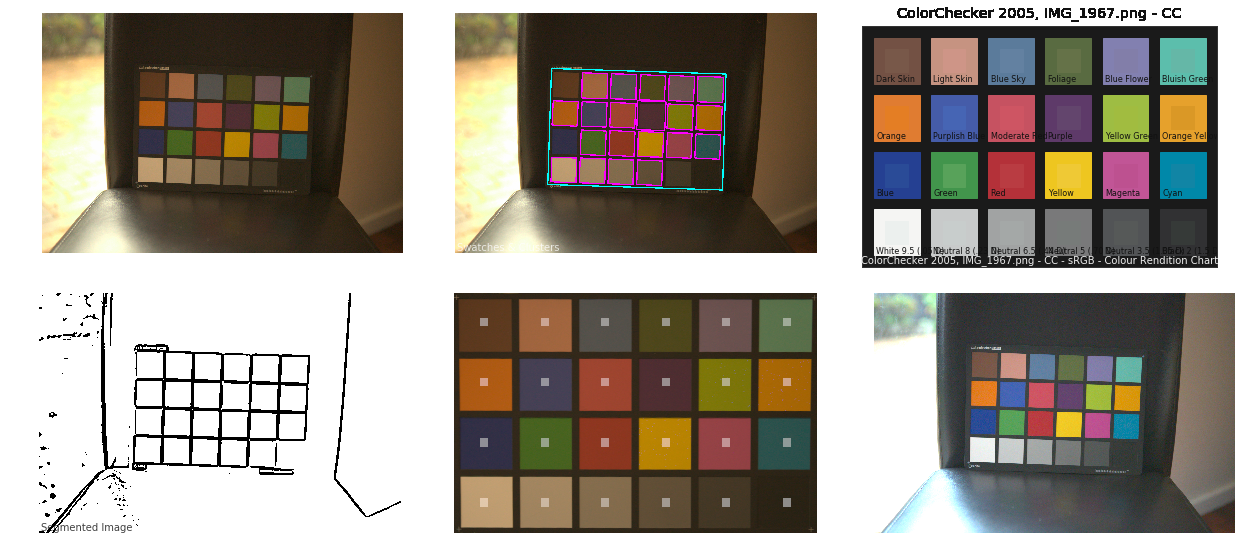
GretagMacbeth Color Checker Numeric Values and Middle Gray
Read more: GretagMacbeth Color Checker Numeric Values and Middle GrayThe human eye perceives half scene brightness not as the linear 50% of the present energy (linear nature values) but as 18% of the overall brightness. We are biased to perceive more information in the dark and contrast areas. A Macbeth chart helps with calibrating back into a photographic capture into this “human perspective” of the world.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Middle_gray
In photography, painting, and other visual arts, middle gray or middle grey is a tone that is perceptually about halfway between black and white on a lightness scale in photography and printing, it is typically defined as 18% reflectance in visible light
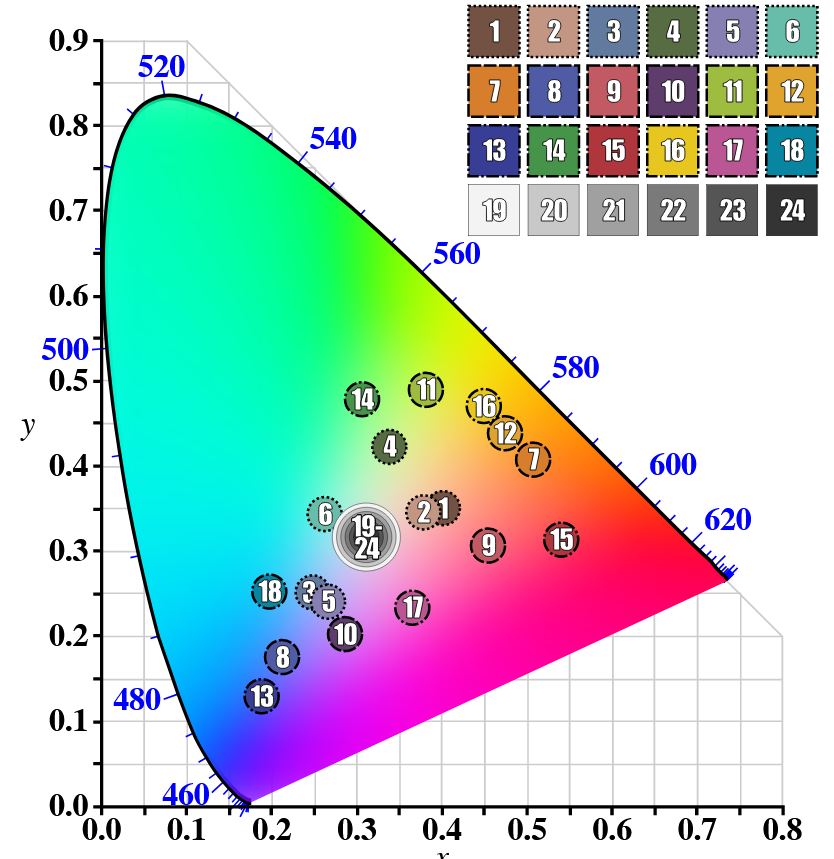
Light meters, cameras, and pictures are often calibrated using an 18% gray card[4][5][6] or a color reference card such as a ColorChecker. On the assumption that 18% is similar to the average reflectance of a scene, a grey card can be used to estimate the required exposure of the film.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ColorChecker
(more…) -
Colour – MacBeth Chart Checker Detection
Read more: Colour – MacBeth Chart Checker Detectiongithub.com/colour-science/colour-checker-detection
A Python package implementing various colour checker detection algorithms and related utilities.
LIGHTING
-
Composition – These are the basic lighting techniques you need to know for photography and film
Read more: Composition – These are the basic lighting techniques you need to know for photography and filmhttp://www.diyphotography.net/basic-lighting-techniques-need-know-photography-film/
Amongst the basic techniques, there’s…
1- Side lighting – Literally how it sounds, lighting a subject from the side when they’re faced toward you
2- Rembrandt lighting – Here the light is at around 45 degrees over from the front of the subject, raised and pointing down at 45 degrees
3- Back lighting – Again, how it sounds, lighting a subject from behind. This can help to add drama with silouettes
4- Rim lighting – This produces a light glowing outline around your subject
5- Key light – The main light source, and it’s not necessarily always the brightest light source
6- Fill light – This is used to fill in the shadows and provide detail that would otherwise be blackness
7- Cross lighting – Using two lights placed opposite from each other to light two subjects
-
Practical Aspects of Spectral Data and LEDs in Digital Content Production and Virtual Production – SIGGRAPH 2022
Read more: Practical Aspects of Spectral Data and LEDs in Digital Content Production and Virtual Production – SIGGRAPH 2022Comparison to the commercial side

https://www.ecolorled.com/blog/detail/what-is-rgb-rgbw-rgbic-strip-lights
RGBW (RGB + White) LED strip uses a 4-in-1 LED chip made up of red, green, blue, and white.
RGBWW (RGB + White + Warm White) LED strip uses either a 5-in-1 LED chip with red, green, blue, white, and warm white for color mixing. The only difference between RGBW and RGBWW is the intensity of the white color. The term RGBCCT consists of RGB and CCT. CCT (Correlated Color Temperature) means that the color temperature of the led strip light can be adjusted to change between warm white and white. Thus, RGBWW strip light is another name of RGBCCT strip.
RGBCW is the acronym for Red, Green, Blue, Cold, and Warm. These 5-in-1 chips are used in supper bright smart LED lighting products
COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
-
WhatDreamsCost Spline-Path-Control – Create motion controls for ComfyUI
-
Top 3D Printing Website Resources
-
FFmpeg – examples and convenience lines
-
Scene Referred vs Display Referred color workflows
-
Photography basics: Lumens vs Candelas (candle) vs Lux vs FootCandle vs Watts vs Irradiance vs Illuminance
-
JavaScript how-to free resources
-
The Perils of Technical Debt – Understanding Its Impact on Security, Usability, and Stability
-
What’s the Difference Between Ray Casting, Ray Tracing, Path Tracing and Rasterization? Physical light tracing…
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.