COMPOSITION
-
Christopher Butler – Understanding the Eye-Mind Connection – Vision is a mental process
Read more: Christopher Butler – Understanding the Eye-Mind Connection – Vision is a mental processhttps://www.chrbutler.com/understanding-the-eye-mind-connection
The intricate relationship between the eyes and the brain, often termed the eye-mind connection, reveals that vision is predominantly a cognitive process. This understanding has profound implications for fields such as design, where capturing and maintaining attention is paramount. This essay delves into the nuances of visual perception, the brain’s role in interpreting visual data, and how this knowledge can be applied to effective design strategies.
This cognitive aspect of vision is evident in phenomena such as optical illusions, where the brain interprets visual information in a way that contradicts physical reality. These illusions underscore that what we “see” is not merely a direct recording of the external world but a constructed experience shaped by cognitive processes.
Understanding the cognitive nature of vision is crucial for effective design. Designers must consider how the brain processes visual information to create compelling and engaging visuals. This involves several key principles:
- Attention and Engagement
- Visual Hierarchy
- Cognitive Load Management
- Context and Meaning

DESIGN
COLOR
-
Brett Jones / Phil Reyneri (Lightform) / Philipp7pc: The study of Projection Mapping through Projectors
Read more: Brett Jones / Phil Reyneri (Lightform) / Philipp7pc: The study of Projection Mapping through ProjectorsVideo Projection Tool Software
https://hcgilje.wordpress.com/vpt/https://www.projectorpoint.co.uk/news/how-bright-should-my-projector-be/
http://www.adwindowscreens.com/the_calculator/
heavym
https://heavym.net/en/MadMapper
https://madmapper.com/ -
What light is best to illuminate gems for resale
Read more: What light is best to illuminate gems for resalewww.palagems.com/gem-lighting2
Artificial light sources, not unlike the diverse phases of natural light, vary considerably in their properties. As a result, some lamps render an object’s color better than others do.
The most important criterion for assessing the color-rendering ability of any lamp is its spectral power distribution curve.
Natural daylight varies too much in strength and spectral composition to be taken seriously as a lighting standard for grading and dealing colored stones. For anything to be a standard, it must be constant in its properties, which natural light is not.
For dealers in particular to make the transition from natural light to an artificial light source, that source must offer:
1- A degree of illuminance at least as strong as the common phases of natural daylight.
2- Spectral properties identical or comparable to a phase of natural daylight.A source combining these two things makes gems appear much the same as when viewed under a given phase of natural light. From the viewpoint of many dealers, this corresponds to a naturalappearance.
The 6000° Kelvin xenon short-arc lamp appears closest to meeting the criteria for a standard light source. Besides the strong illuminance this lamp affords, its spectrum is very similar to CIE standard illuminants of similar color temperature.
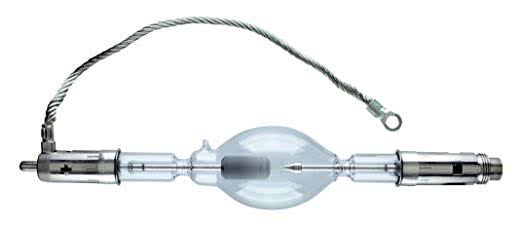

-
Tim Kang – calibrated white light values in sRGB color space
Read more: Tim Kang – calibrated white light values in sRGB color space8bit sRGB encoded
2000K 255 139 22
2700K 255 172 89
3000K 255 184 109
3200K 255 190 122
4000K 255 211 165
4300K 255 219 178
D50 255 235 205
D55 255 243 224
D5600 255 244 227
D6000 255 249 240
D65 255 255 255
D10000 202 221 255
D20000 166 196 2558bit Rec709 Gamma 2.4
2000K 255 145 34
2700K 255 177 97
3000K 255 187 117
3200K 255 193 129
4000K 255 214 170
4300K 255 221 182
D50 255 236 208
D55 255 243 226
D5600 255 245 229
D6000 255 250 241
D65 255 255 255
D10000 204 222 255
D20000 170 199 2558bit Display P3 encoded
2000K 255 154 63
2700K 255 185 109
3000K 255 195 127
3200K 255 201 138
4000K 255 219 176
4300K 255 225 187
D50 255 239 212
D55 255 245 228
D5600 255 246 231
D6000 255 251 242
D65 255 255 255
D10000 208 223 255
D20000 175 199 25510bit Rec2020 PQ (100 nits)
2000K 520 435 273
2700K 520 466 358
3000K 520 475 384
3200K 520 480 399
4000K 520 495 446
4300K 520 500 458
D50 520 510 482
D55 520 514 497
D5600 520 514 500
D6000 520 517 509
D65 520 520 520
D10000 479 489 520
D20000 448 464 520 -
FXGuide – ACES 2.0 with ILM’s Alex Fry
Read more: FXGuide – ACES 2.0 with ILM’s Alex Fryhttps://draftdocs.acescentral.com/background/whats-new/
ACES 2.0 is the second major release of the components that make up the ACES system. The most significant change is a new suite of rendering transforms whose design was informed by collected feedback and requests from users of ACES 1. The changes aim to improve the appearance of perceived artifacts and to complete previously unfinished components of the system, resulting in a more complete, robust, and consistent product.
Highlights of the key changes in ACES 2.0 are as follows:
- New output transforms, including:
- A less aggressive tone scale
- More intuitive controls to create custom outputs to non-standard displays
- Robust gamut mapping to improve perceptual uniformity
- Improved performance of the inverse transforms
- Enhanced AMF specification
- An updated specification for ACES Transform IDs
- OpenEXR compression recommendations
- Enhanced tools for generating Input Transforms and recommended procedures for characterizing prosumer cameras
- Look Transform Library
- Expanded documentation
Rendering Transform
The most substantial change in ACES 2.0 is a complete redesign of the rendering transform.
ACES 2.0 was built as a unified system, rather than through piecemeal additions. Different deliverable outputs “match” better and making outputs to display setups other than the provided presets is intended to be user-driven. The rendering transforms are less likely to produce undesirable artifacts “out of the box”, which means less time can be spent fixing problematic images and more time making pictures look the way you want.
Key design goals
- Improve consistency of tone scale and provide an easy to use parameter to allow for outputs between preset dynamic ranges
- Minimize hue skews across exposure range in a region of same hue
- Unify for structural consistency across transform type
- Easy to use parameters to create outputs other than the presets
- Robust gamut mapping to improve harsh clipping artifacts
- Fill extents of output code value cube (where appropriate and expected)
- Invertible – not necessarily reversible, but Output > ACES > Output round-trip should be possible
- Accomplish all of the above while maintaining an acceptable “out-of-the box” rendering
- New output transforms, including:
-
Gamma correction
Read more: Gamma correction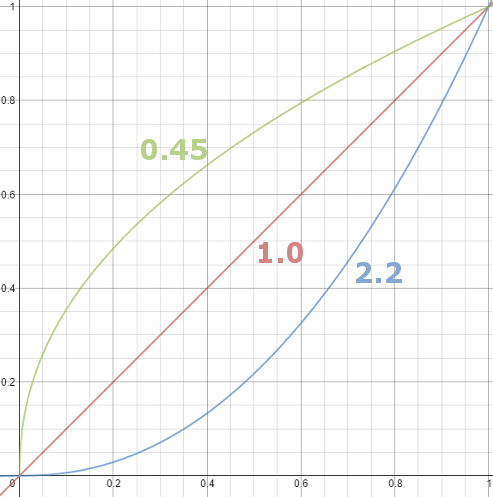
http://www.normankoren.com/makingfineprints1A.html#Gammabox
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gamma_correction
http://www.photoscientia.co.uk/Gamma.htm
https://www.w3.org/Graphics/Color/sRGB.html
http://www.eizoglobal.com/library/basics/lcd_display_gamma/index.html
https://forum.reallusion.com/PrintTopic308094.aspx
Basically, gamma is the relationship between the brightness of a pixel as it appears on the screen, and the numerical value of that pixel. Generally Gamma is just about defining relationships.
Three main types:
– Image Gamma encoded in images
– Display Gammas encoded in hardware and/or viewing time
– System or Viewing Gamma which is the net effect of all gammas when you look back at a final image. In theory this should flatten back to 1.0 gamma.
(more…) -
OpenColorIO standard
Read more: OpenColorIO standardhttps://www.provideocoalition.com/color-management-part-11-introducing-opencolorio/
OpenColorIO (OCIO) is a new open source project from Sony Imageworks.
Based on development started in 2003, OCIO enables color transforms and image display to be handled in a consistent manner across multiple graphics applications. Unlike other color management solutions, OCIO is geared towards motion-picture post production, with an emphasis on visual effects and animation color pipelines.
-
GretagMacbeth Color Checker Numeric Values and Middle Gray
Read more: GretagMacbeth Color Checker Numeric Values and Middle GrayThe human eye perceives half scene brightness not as the linear 50% of the present energy (linear nature values) but as 18% of the overall brightness. We are biased to perceive more information in the dark and contrast areas. A Macbeth chart helps with calibrating back into a photographic capture into this “human perspective” of the world.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Middle_gray
In photography, painting, and other visual arts, middle gray or middle grey is a tone that is perceptually about halfway between black and white on a lightness scale in photography and printing, it is typically defined as 18% reflectance in visible light
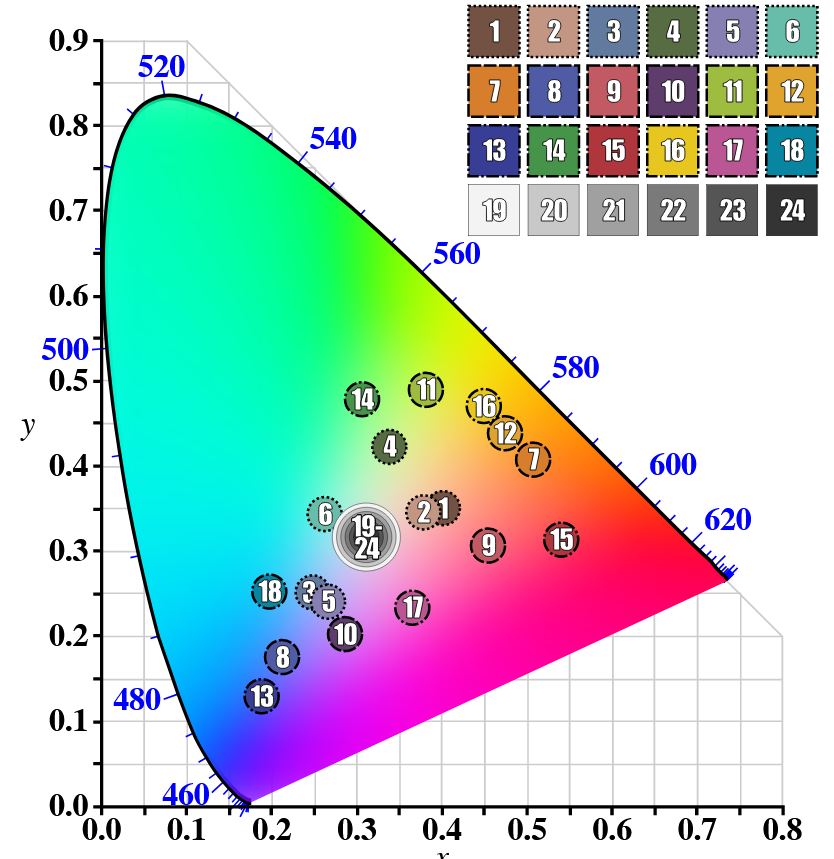
Light meters, cameras, and pictures are often calibrated using an 18% gray card[4][5][6] or a color reference card such as a ColorChecker. On the assumption that 18% is similar to the average reflectance of a scene, a grey card can be used to estimate the required exposure of the film.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ColorChecker
(more…) -
The Color of Infinite Temperature
Read more: The Color of Infinite TemperatureThis is the color of something infinitely hot.

Of course you’d instantly be fried by gamma rays of arbitrarily high frequency, but this would be its spectrum in the visible range.
johncarlosbaez.wordpress.com/2022/01/16/the-color-of-infinite-temperature/
This is also the color of a typical neutron star. They’re so hot they look the same.
It’s also the color of the early Universe!This was worked out by David Madore.
The color he got is sRGB(148,177,255).
www.htmlcsscolor.com/hex/94B1FFAnd according to the experts who sip latte all day and make up names for colors, this color is called ‘Perano’.
-
Björn Ottosson – OKlch color space
Read more: Björn Ottosson – OKlch color spaceBjörn Ottosson proposed OKlch in 2020 to create a color space that can closely mimic how color is perceived by the human eye, predicting perceived lightness, chroma, and hue.
The OK in OKLCH stands for Optimal Color.
- L: Lightness (the perceived brightness of the color)
- C: Chroma (the intensity or saturation of the color)
- H: Hue (the actual color, such as red, blue, green, etc.)

Also read:
LIGHTING
-
HDRI Median Cut plugin
Read more: HDRI Median Cut pluginwww.hdrlabs.com/picturenaut/plugins.html
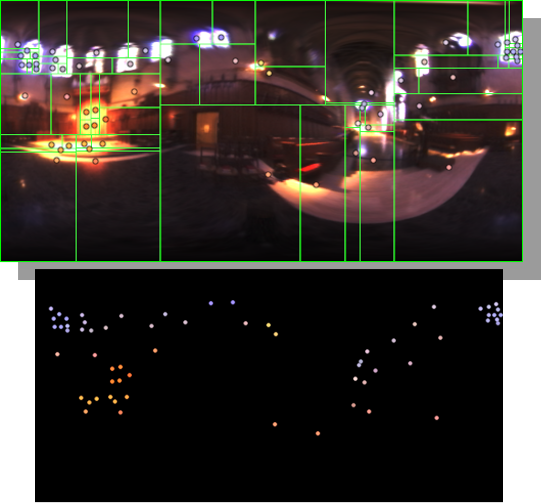
Note. The Median Cut algorithm is typically used for color quantization, which involves reducing the number of colors in an image while preserving its visual quality. It doesn’t directly provide a way to identify the brightest areas in an image. However, if you’re interested in identifying the brightest areas, you might want to look into other methods like thresholding, histogram analysis, or edge detection, through openCV for example.
Here is an openCV example:
(more…) -
Bella – Fast Spectral Rendering
Read more: Bella – Fast Spectral RenderingBella works in spectral space, allowing effects such as BSDF wavelength dependency, diffraction, or atmosphere to be modeled far more accurately than in color space.
https://superrendersfarm.com/blog/uncategorized/bella-a-new-spectral-physically-based-renderer/
-
Is a MacBeth Colour Rendition Chart the Safest Way to Calibrate a Camera?
Read more: Is a MacBeth Colour Rendition Chart the Safest Way to Calibrate a Camera?www.colour-science.org/posts/the-colorchecker-considered-mostly-harmless/
“Unless you have all the relevant spectral measurements, a colour rendition chart should not be used to perform colour-correction of camera imagery but only for white balancing and relative exposure adjustments.”
“Using a colour rendition chart for colour-correction might dramatically increase error if the scene light source spectrum is different from the illuminant used to compute the colour rendition chart’s reference values.”
“other factors make using a colour rendition chart unsuitable for camera calibration:
– Uncontrolled geometry of the colour rendition chart with the incident illumination and the camera.
– Unknown sample reflectances and ageing as the colour of the samples vary with time.
– Low samples count.
– Camera noise and flare.
– Etc…“Those issues are well understood in the VFX industry, and when receiving plates, we almost exclusively use colour rendition charts to white balance and perform relative exposure adjustments, i.e. plate neutralisation.”
COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
-
Photography basics: How Exposure Stops (Aperture, Shutter Speed, and ISO) Affect Your Photos – cheat sheet cards
-
Want to build a start up company that lasts? Think three-layer cake
-
Photography basics: Color Temperature and White Balance
-
Python and TCL: Tips and Tricks for Foundry Nuke
-
Matt Hallett – WAN 2.1 VACE Total Video Control in ComfyUI
-
GretagMacbeth Color Checker Numeric Values and Middle Gray
-
59 AI Filmmaking Tools For Your Workflow
-
Methods for creating motion blur in Stop motion
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.




