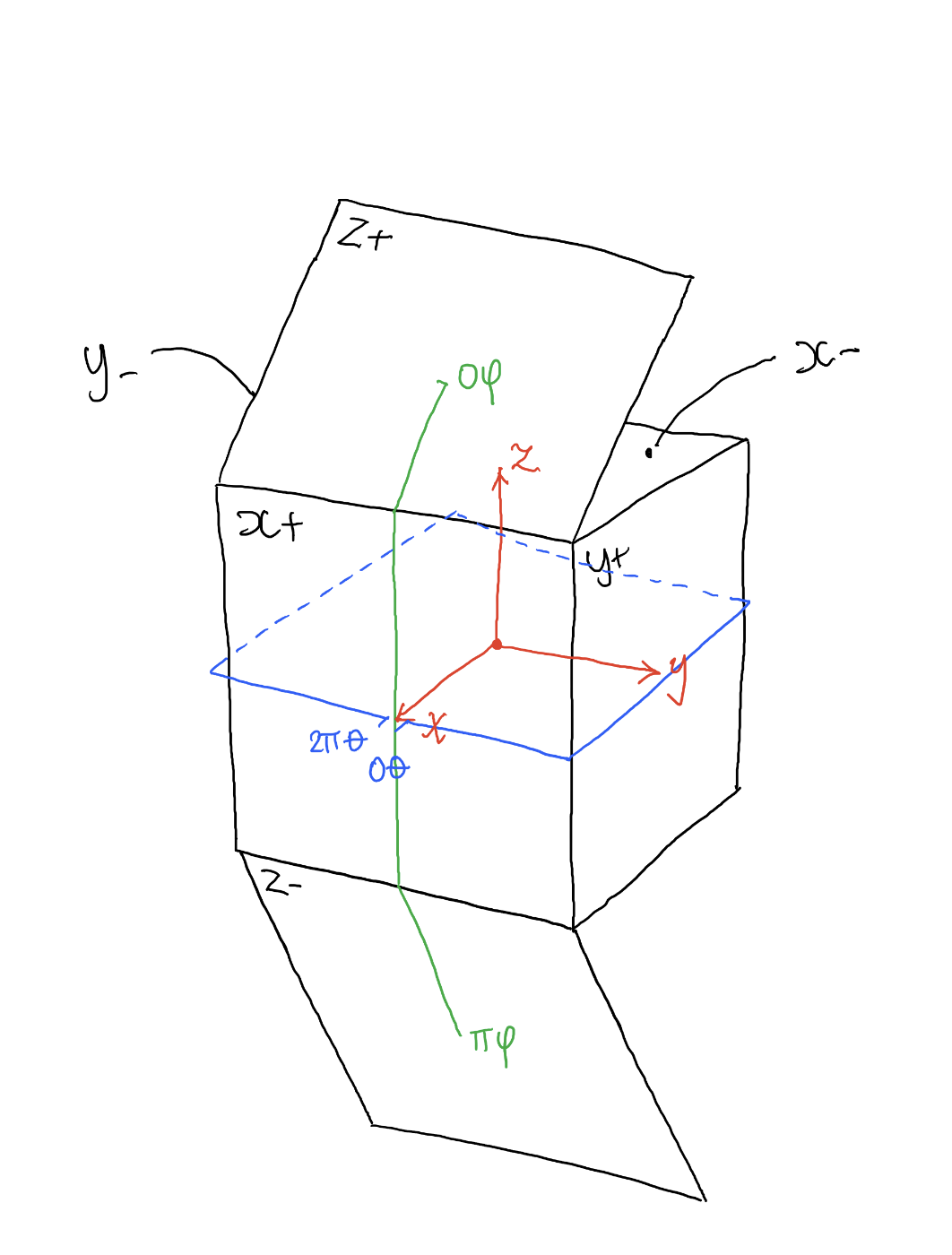
COMPOSITION
DESIGN
-
How to paint a boardgame miniatures
Read more: How to paint a boardgame miniaturesSteps:
- soap wash cleaning
- primer
- base-coat layer (black/white)
- detailing
- washing aka shade (could be done after highlighting)
- highlights aka dry brushing (could be done after washing)
- varnish (gloss/satin/matte)
COLOR
-
Gamma correction
Read more: Gamma correction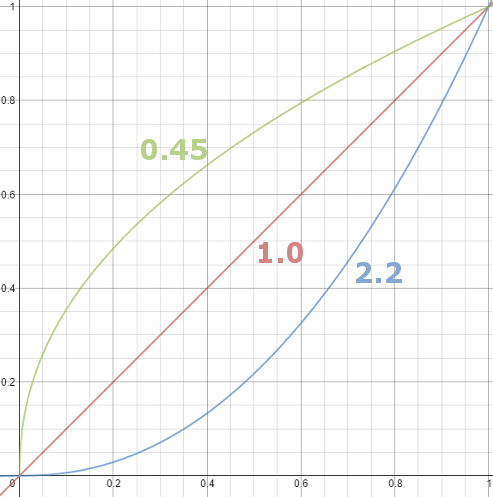
http://www.normankoren.com/makingfineprints1A.html#Gammabox
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gamma_correction
http://www.photoscientia.co.uk/Gamma.htm
https://www.w3.org/Graphics/Color/sRGB.html
http://www.eizoglobal.com/library/basics/lcd_display_gamma/index.html
https://forum.reallusion.com/PrintTopic308094.aspx
Basically, gamma is the relationship between the brightness of a pixel as it appears on the screen, and the numerical value of that pixel. Generally Gamma is just about defining relationships.
Three main types:
– Image Gamma encoded in images
– Display Gammas encoded in hardware and/or viewing time
– System or Viewing Gamma which is the net effect of all gammas when you look back at a final image. In theory this should flatten back to 1.0 gamma.
(more…)
LIGHTING
-
What’s the Difference Between Ray Casting, Ray Tracing, Path Tracing and Rasterization? Physical light tracing…
Read more: What’s the Difference Between Ray Casting, Ray Tracing, Path Tracing and Rasterization? Physical light tracing…RASTERIZATION
Rasterisation (or rasterization) is the task of taking the information described in a vector graphics format OR the vertices of triangles making 3D shapes and converting them into a raster image (a series of pixels, dots or lines, which, when displayed together, create the image which was represented via shapes), or in other words “rasterizing” vectors or 3D models onto a 2D plane for display on a computer screen.For each triangle of a 3D shape, you project the corners of the triangle on the virtual screen with some math (projective geometry). Then you have the position of the 3 corners of the triangle on the pixel screen. Those 3 points have texture coordinates, so you know where in the texture are the 3 corners. The cost is proportional to the number of triangles, and is only a little bit affected by the screen resolution.
In computer graphics, a raster graphics or bitmap image is a dot matrix data structure that represents a generally rectangular grid of pixels (points of color), viewable via a monitor, paper, or other display medium.
With rasterization, objects on the screen are created from a mesh of virtual triangles, or polygons, that create 3D models of objects. A lot of information is associated with each vertex, including its position in space, as well as information about color, texture and its “normal,” which is used to determine the way the surface of an object is facing.
Computers then convert the triangles of the 3D models into pixels, or dots, on a 2D screen. Each pixel can be assigned an initial color value from the data stored in the triangle vertices.
Further pixel processing or “shading,” including changing pixel color based on how lights in the scene hit the pixel, and applying one or more textures to the pixel, combine to generate the final color applied to a pixel.
The main advantage of rasterization is its speed. However, rasterization is simply the process of computing the mapping from scene geometry to pixels and does not prescribe a particular way to compute the color of those pixels. So it cannot take shading, especially the physical light, into account and it cannot promise to get a photorealistic output. That’s a big limitation of rasterization.
There are also multiple problems:
If you have two triangles one is behind the other, you will draw twice all the pixels. you only keep the pixel from the triangle that is closer to you (Z-buffer), but you still do the work twice.
The borders of your triangles are jagged as it is hard to know if a pixel is in the triangle or out. You can do some smoothing on those, that is anti-aliasing.
You have to handle every triangles (including the ones behind you) and then see that they do not touch the screen at all. (we have techniques to mitigate this where we only look at triangles that are in the field of view)
Transparency is hard to handle (you can’t just do an average of the color of overlapping transparent triangles, you have to do it in the right order)
-
Gamma correction
Read more: Gamma correction
http://www.normankoren.com/makingfineprints1A.html#Gammabox
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gamma_correction
http://www.photoscientia.co.uk/Gamma.htm
https://www.w3.org/Graphics/Color/sRGB.html
http://www.eizoglobal.com/library/basics/lcd_display_gamma/index.html
https://forum.reallusion.com/PrintTopic308094.aspx
Basically, gamma is the relationship between the brightness of a pixel as it appears on the screen, and the numerical value of that pixel. Generally Gamma is just about defining relationships.
Three main types:
– Image Gamma encoded in images
– Display Gammas encoded in hardware and/or viewing time
– System or Viewing Gamma which is the net effect of all gammas when you look back at a final image. In theory this should flatten back to 1.0 gamma.
(more…) -
Rec-2020 – TVs new color gamut standard used by Dolby Vision?
Read more: Rec-2020 – TVs new color gamut standard used by Dolby Vision?https://www.hdrsoft.com/resources/dri.html#bit-depth
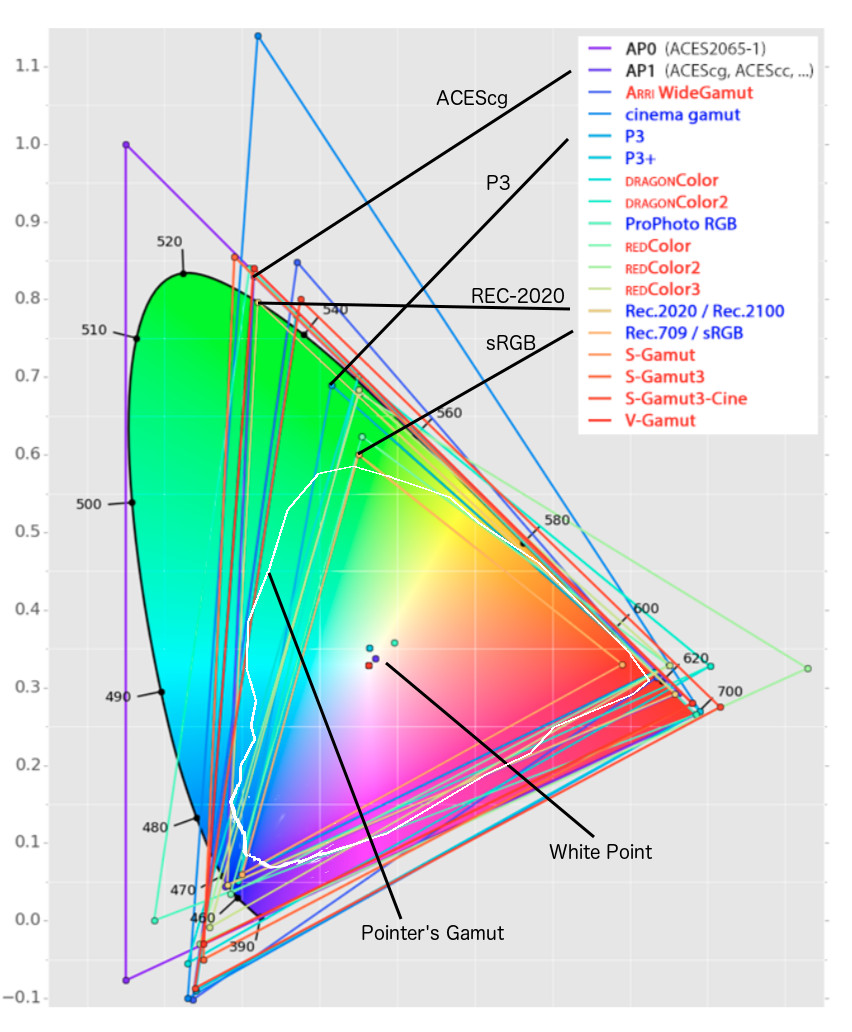
The dynamic range is a ratio between the maximum and minimum values of a physical measurement. Its definition depends on what the dynamic range refers to.
For a scene: Dynamic range is the ratio between the brightest and darkest parts of the scene.
For a camera: Dynamic range is the ratio of saturation to noise. More specifically, the ratio of the intensity that just saturates the camera to the intensity that just lifts the camera response one standard deviation above camera noise.
For a display: Dynamic range is the ratio between the maximum and minimum intensities emitted from the screen.
The Dynamic Range of real-world scenes can be quite high — ratios of 100,000:1 are common in the natural world. An HDR (High Dynamic Range) image stores pixel values that span the whole tonal range of real-world scenes. Therefore, an HDR image is encoded in a format that allows the largest range of values, e.g. floating-point values stored with 32 bits per color channel. Another characteristics of an HDR image is that it stores linear values. This means that the value of a pixel from an HDR image is proportional to the amount of light measured by the camera.
For TVs HDR is great, but it’s not the only new TV feature worth discussing.
(more…) -
Narcis Calin’s Galaxy Engine – A free, open source simulation software
Read more: Narcis Calin’s Galaxy Engine – A free, open source simulation softwareThis 2025 I decided to start learning how to code, so I installed Visual Studio and I started looking into C++. After days of watching tutorials and guides about the basics of C++ and programming, I decided to make something physics-related. I started with a dot that fell to the ground and then I wanted to simulate gravitational attraction, so I made 2 circles attracting each other. I thought it was really cool to see something I made with code actually work, so I kept building on top of that small, basic program. And here we are after roughly 8 months of learning programming. This is Galaxy Engine, and it is a simulation software I have been making ever since I started my learning journey. It currently can simulate gravity, dark matter, galaxies, the Big Bang, temperature, fluid dynamics, breakable solids, planetary interactions, etc. The program can run many tens of thousands of particles in real time on the CPU thanks to the Barnes-Hut algorithm, mixed with Morton curves. It also includes its own PBR 2D path tracer with BVH optimizations. The path tracer can simulate a bunch of stuff like diffuse lighting, specular reflections, refraction, internal reflection, fresnel, emission, dispersion, roughness, IOR, nested IOR and more! I tried to make the path tracer closer to traditional 3D render engines like V-Ray. I honestly never imagined I would go this far with programming, and it has been an amazing learning experience so far. I think that mixing this knowledge with my 3D knowledge can unlock countless new possibilities. In case you are curious about Galaxy Engine, I made it completely free and Open-Source so that anyone can build and compile it locally! You can find the source code in GitHub
https://github.com/NarcisCalin/Galaxy-Engine
COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
-
sRGB vs REC709 – An introduction and FFmpeg implementations
-
Daniele Tosti Interview for the magazine InCG, Taiwan, Issue 28, 201609
-
Black Forest Labs released FLUX.1 Kontext
-
Want to build a start up company that lasts? Think three-layer cake
-
NVidia – High-Fidelity 3D Mesh Generation at Scale with Meshtron
-
Generative AI Glossary / AI Dictionary / AI Terminology
-
copypastecharacter.com – alphabets, special characters, alt codes and symbols library
-
How to paint a boardgame miniatures
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.