COMPOSITION
-
Composition – cinematography Cheat Sheet
Read more: Composition – cinematography Cheat Sheet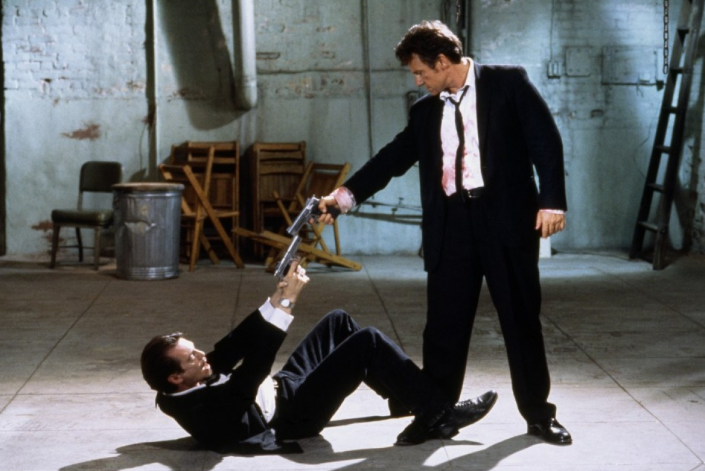
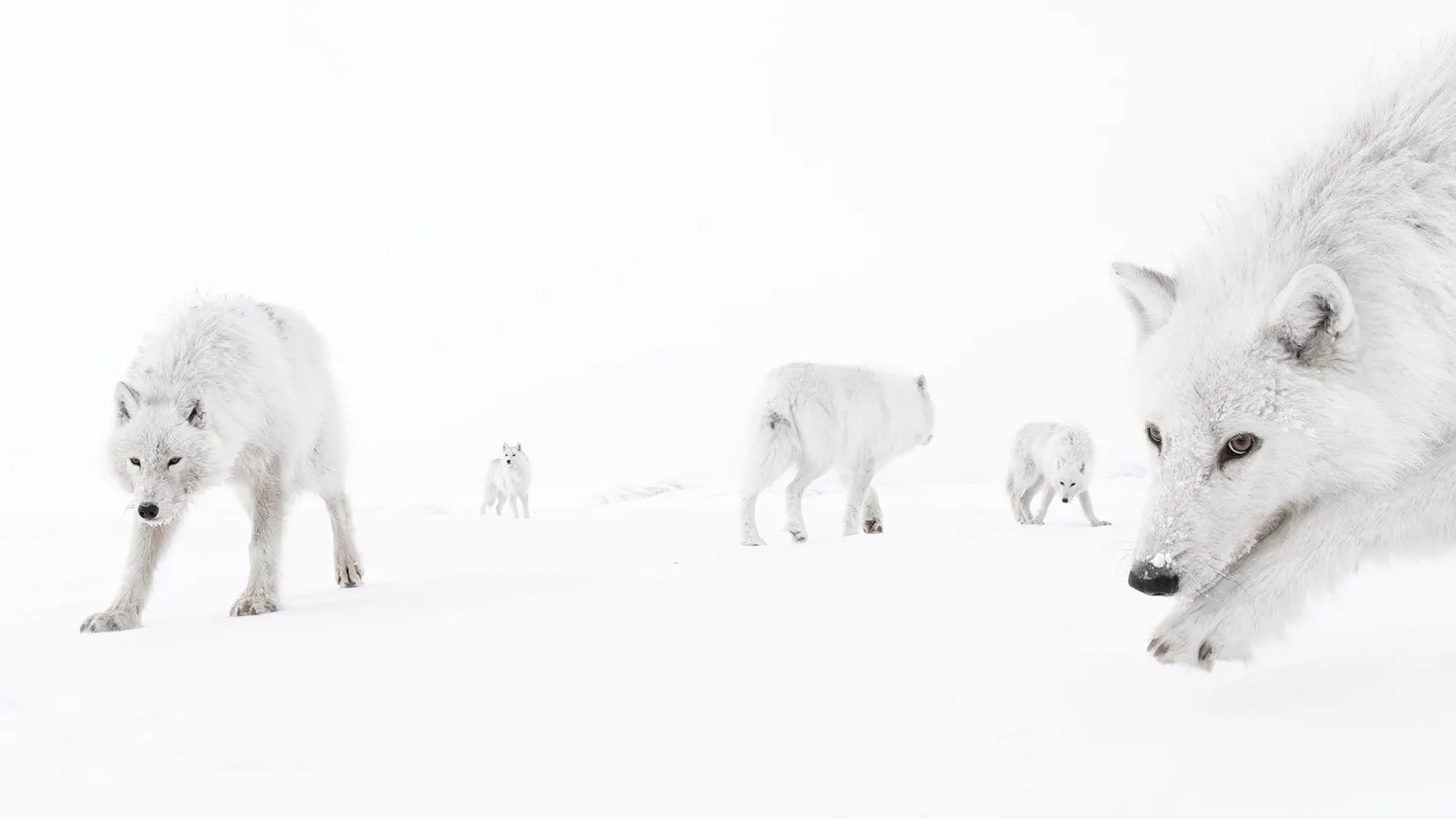
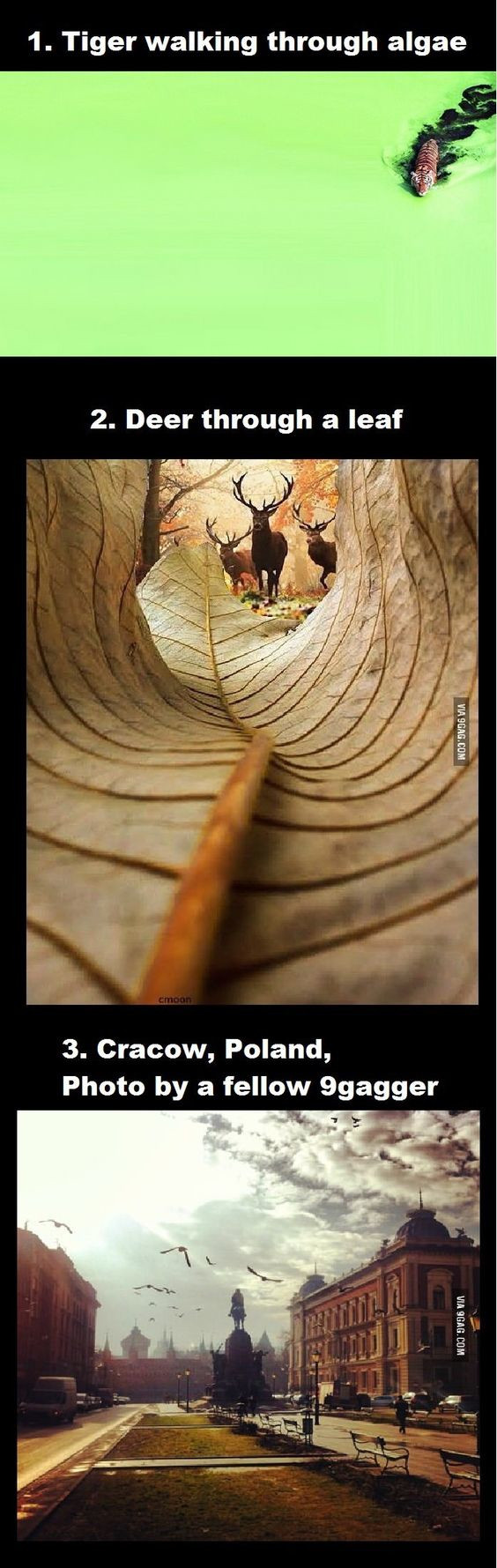
Where is our eye attracted first? Why?
Size. Focus. Lighting. Color.
Size. Mr. White (Harvey Keitel) on the right.
Focus. He’s one of the two objects in focus.
Lighting. Mr. White is large and in focus and Mr. Pink (Steve Buscemi) is highlighted by
a shaft of light.
Color. Both are black and white but the read on Mr. White’s shirt now really stands out.
(more…)
What type of lighting?
DESIGN
-
Kelly Boesch – Static and Toward The Light
Read more: Kelly Boesch – Static and Toward The Lighthttps://www.kellyboeschdesign.com
I was working an album cover last night and got these really cool images in midjourney so made a video out of it. Animated using Pika. Song made using Suno Full version on my bandcamp. It’s called Static.
https://www.linkedin.com/posts/kellyboesch_midjourney-keyframes-ai-activity-7359244714853736450-Wvcr(more…)
COLOR
-
No one could see the colour blue until modern times
Read more: No one could see the colour blue until modern timeshttps://www.businessinsider.com/what-is-blue-and-how-do-we-see-color-2015-2
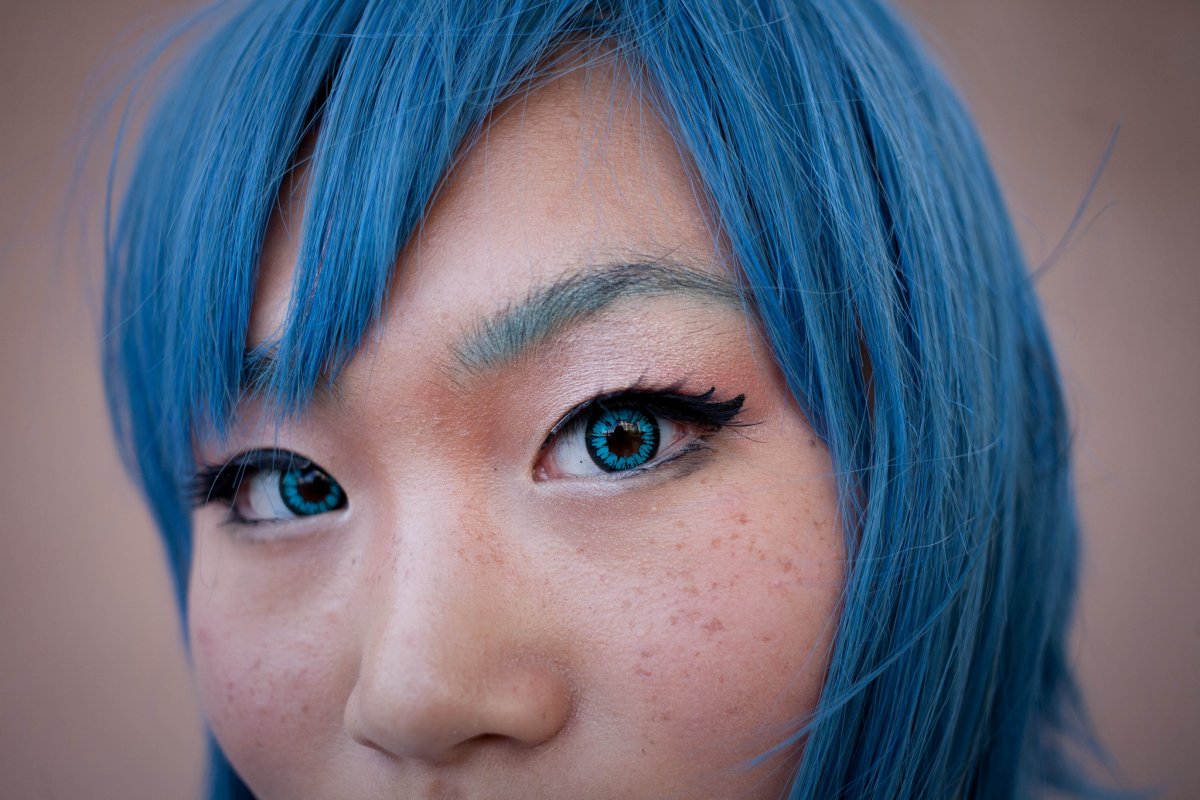

The way humans see the world… until we have a way to describe something, even something so fundamental as a colour, we may not even notice that something it’s there.
Ancient languages didn’t have a word for blue — not Greek, not Chinese, not Japanese, not Hebrew, not Icelandic cultures. And without a word for the colour, there’s evidence that they may not have seen it at all.
https://www.wnycstudios.org/story/211119-colorsEvery language first had a word for black and for white, or dark and light. The next word for a colour to come into existence — in every language studied around the world — was red, the colour of blood and wine.
After red, historically, yellow appears, and later, green (though in a couple of languages, yellow and green switch places). The last of these colours to appear in every language is blue.The only ancient culture to develop a word for blue was the Egyptians — and as it happens, they were also the only culture that had a way to produce a blue dye.
https://mymodernmet.com/shades-of-blue-color-history/True blue hues are rare in the natural world because synthesizing pigments that absorb longer-wavelength light (reds and yellows) while reflecting shorter-wavelength blue light requires exceptionally elaborate molecular structures—biochemical feats that most plants and animals simply don’t undertake.
When you gaze at a blueberry’s deep blue surface, you’re actually seeing structural coloration rather than a true blue pigment. A fine, waxy bloom on the berry’s skin contains nanostructures that preferentially scatter blue and violet light, giving the fruit its signature blue sheen even though its inherent pigment is reddish.
Similarly, many of nature’s most striking blues—like those of blue jays and morpho butterflies—arise not from blue pigments but from microscopic architectures in feathers or wing scales. These tiny ridges and air pockets manipulate incoming light so that blue wavelengths emerge most prominently, creating vivid, angle-dependent colors through scattering rather than pigment alone.
(more…) -
Photography basics: Why Use a (MacBeth) Color Chart?
Read more: Photography basics: Why Use a (MacBeth) Color Chart?Start here: https://www.pixelsham.com/2013/05/09/gretagmacbeth-color-checker-numeric-values/
https://www.studiobinder.com/blog/what-is-a-color-checker-tool/
In LightRoom
in Final Cut
in Nuke
Note: In Foundry’s Nuke, the software will map 18% gray to whatever your center f/stop is set to in the viewer settings (f/8 by default… change that to EV by following the instructions below).
You can experiment with this by attaching an Exposure node to a Constant set to 0.18, setting your viewer read-out to Spotmeter, and adjusting the stops in the node up and down. You will see that a full stop up or down will give you the respective next value on the aperture scale (f8, f11, f16 etc.).One stop doubles or halves the amount or light that hits the filmback/ccd, so everything works in powers of 2.
So starting with 0.18 in your constant, you will see that raising it by a stop will give you .36 as a floating point number (in linear space), while your f/stop will be f/11 and so on.If you set your center stop to 0 (see below) you will get a relative readout in EVs, where EV 0 again equals 18% constant gray.
In other words. Setting the center f-stop to 0 means that in a neutral plate, the middle gray in the macbeth chart will equal to exposure value 0. EV 0 corresponds to an exposure time of 1 sec and an aperture of f/1.0.
This will set the sun usually around EV12-17 and the sky EV1-4 , depending on cloud coverage.
To switch Foundry’s Nuke’s SpotMeter to return the EV of an image, click on the main viewport, and then press s, this opens the viewer’s properties. Now set the center f-stop to 0 in there. And the SpotMeter in the viewport will change from aperture and fstops to EV.
-
VES Cinematic Color – Motion-Picture Color Management
Read more: VES Cinematic Color – Motion-Picture Color ManagementThis paper presents an introduction to the color pipelines behind modern feature-film visual-effects and animation.
Authored by Jeremy Selan, and reviewed by the members of the VES Technology Committee including Rob Bredow, Dan Candela, Nick Cannon, Paul Debevec, Ray Feeney, Andy Hendrickson, Gautham Krishnamurti, Sam Richards, Jordan Soles, and Sebastian Sylwan.
-
Paul Debevec, Chloe LeGendre, Lukas Lepicovsky – Jointly Optimizing Color Rendition and In-Camera Backgrounds in an RGB Virtual Production Stage
Read more: Paul Debevec, Chloe LeGendre, Lukas Lepicovsky – Jointly Optimizing Color Rendition and In-Camera Backgrounds in an RGB Virtual Production Stagehttps://arxiv.org/pdf/2205.12403.pdf
RGB LEDs vs RGBWP (RGB + lime + phospor converted amber) LEDs
Local copy:
LIGHTING
-
Composition – These are the basic lighting techniques you need to know for photography and film
Read more: Composition – These are the basic lighting techniques you need to know for photography and filmhttp://www.diyphotography.net/basic-lighting-techniques-need-know-photography-film/
Amongst the basic techniques, there’s…
1- Side lighting – Literally how it sounds, lighting a subject from the side when they’re faced toward you
2- Rembrandt lighting – Here the light is at around 45 degrees over from the front of the subject, raised and pointing down at 45 degrees
3- Back lighting – Again, how it sounds, lighting a subject from behind. This can help to add drama with silouettes
4- Rim lighting – This produces a light glowing outline around your subject
5- Key light – The main light source, and it’s not necessarily always the brightest light source
6- Fill light – This is used to fill in the shadows and provide detail that would otherwise be blackness
7- Cross lighting – Using two lights placed opposite from each other to light two subjects
-
Capturing the world in HDR for real time projects – Call of Duty: Advanced Warfare
Read more: Capturing the world in HDR for real time projects – Call of Duty: Advanced WarfareReal-World Measurements for Call of Duty: Advanced Warfare
www.activision.com/cdn/research/Real_World_Measurements_for_Call_of_Duty_Advanced_Warfare.pdf
Local version
Real_World_Measurements_for_Call_of_Duty_Advanced_Warfare.pdf
-
3D Lighting Tutorial by Amaan Kram
Read more: 3D Lighting Tutorial by Amaan Kramhttp://www.amaanakram.com/lightingT/part1.htm
The goals of lighting in 3D computer graphics are more or less the same as those of real world lighting.
Lighting serves a basic function of bringing out, or pushing back the shapes of objects visible from the camera’s view.
It gives a two-dimensional image on the monitor an illusion of the third dimension-depth.But it does not just stop there. It gives an image its personality, its character. A scene lit in different ways can give a feeling of happiness, of sorrow, of fear etc., and it can do so in dramatic or subtle ways. Along with personality and character, lighting fills a scene with emotion that is directly transmitted to the viewer.
Trying to simulate a real environment in an artificial one can be a daunting task. But even if you make your 3D rendering look absolutely photo-realistic, it doesn’t guarantee that the image carries enough emotion to elicit a “wow” from the people viewing it.
Making 3D renderings photo-realistic can be hard. Putting deep emotions in them can be even harder. However, if you plan out your lighting strategy for the mood and emotion that you want your rendering to express, you make the process easier for yourself.
Each light source can be broken down in to 4 distinct components and analyzed accordingly.
· Intensity
· Direction
· Color
· SizeThe overall thrust of this writing is to produce photo-realistic images by applying good lighting techniques.
COLLECTIONS
| Featured AI
| Design And Composition
| Explore posts
POPULAR SEARCHES
unreal | pipeline | virtual production | free | learn | photoshop | 360 | macro | google | nvidia | resolution | open source | hdri | real-time | photography basics | nuke
FEATURED POSTS
-
ComfyUI FLOAT – A container for FLOAT Generative Motion Latent Flow Matching for Audio-driven Talking Portrait – lip sync
-
Gamma correction
-
Photography basics: Color Temperature and White Balance
-
Zibra.AI – Real-Time Volumetric Effects in Virtual Production. Now free for Indies!
-
Python and TCL: Tips and Tricks for Foundry Nuke
-
JavaScript how-to free resources
-
Types of AI Explained in a few Minutes – AI Glossary
-
Most common ways to smooth 3D prints
Social Links
DISCLAIMER – Links and images on this website may be protected by the respective owners’ copyright. All data submitted by users through this site shall be treated as freely available to share.